Module 3: Endocrine System (Adrenal Gland, Pineal Gland, Pancreas)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
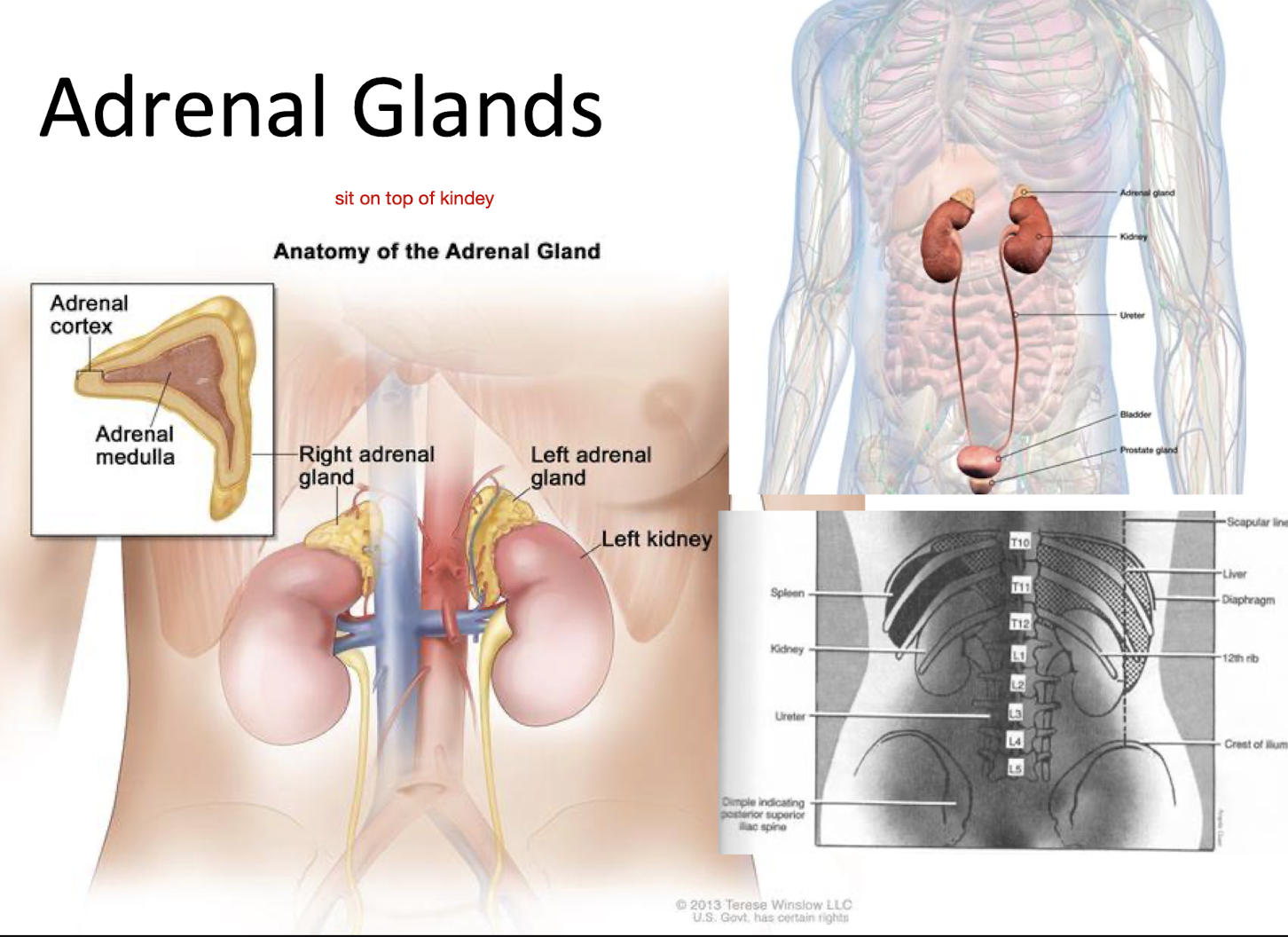
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Glands
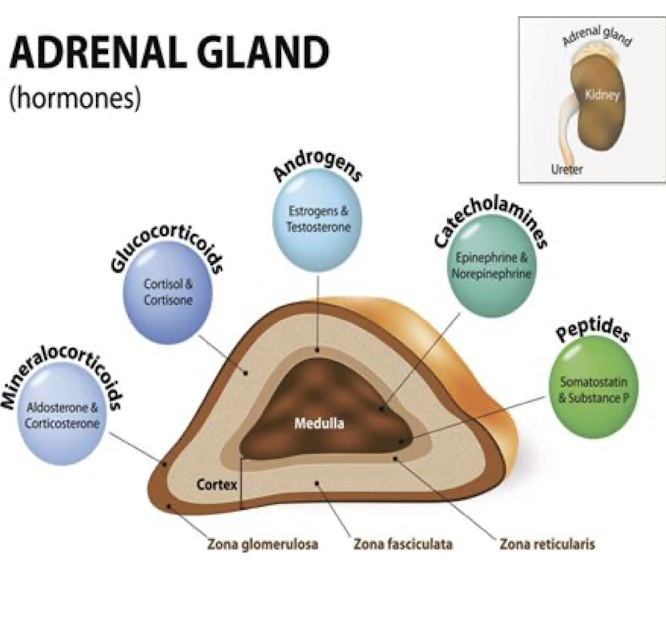
Adrenal Medulla
What are the 2 main hormones produced by the Adrenal Medulla?
What type of response do these hormones facilitate?
Blood Sugar: Adrenaline signals ___ to release ___ into the bloodstream to provide ___ ___.
2 Hormones: Epinephrine and Norepinephrine (Catecholamines)
Fight or Flight
Blood Sugar:
Liver, Glucose, Quick Energy
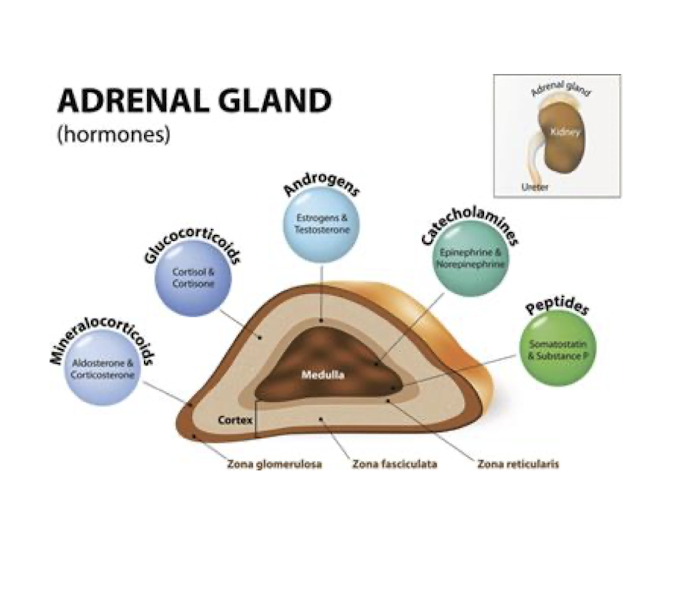
Adrenal Cortex:
What are the 3 main hormone Adrenal Cortex releases?
Cortisol
Antidiuretic Hormone (Aldosterone)
DHEA and Androgenic Steroids
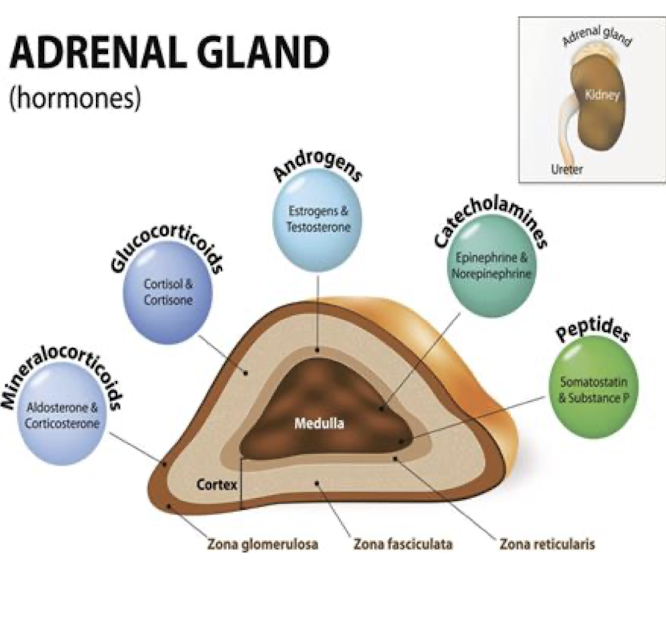
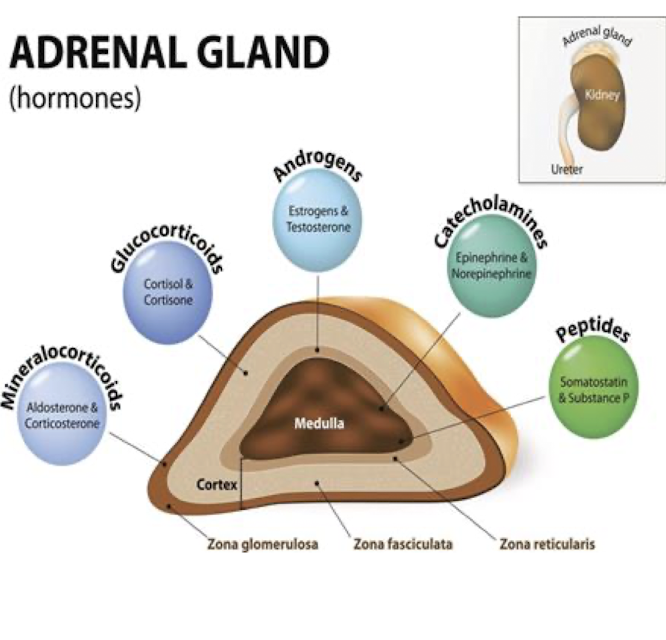
Adrenal Cortex: Cortisol
What does Cortisol influence in:
Liver:
Muscle
Short Term Effects:
Long Term Effects:
Infuence:
Liver: Glucose Production
Muscle: Protein Breakdown
Short Term:
Suppresses inflammation and other parts of the Immune System
Long Term:
Weakens immune response and increases Systemic Inflammation
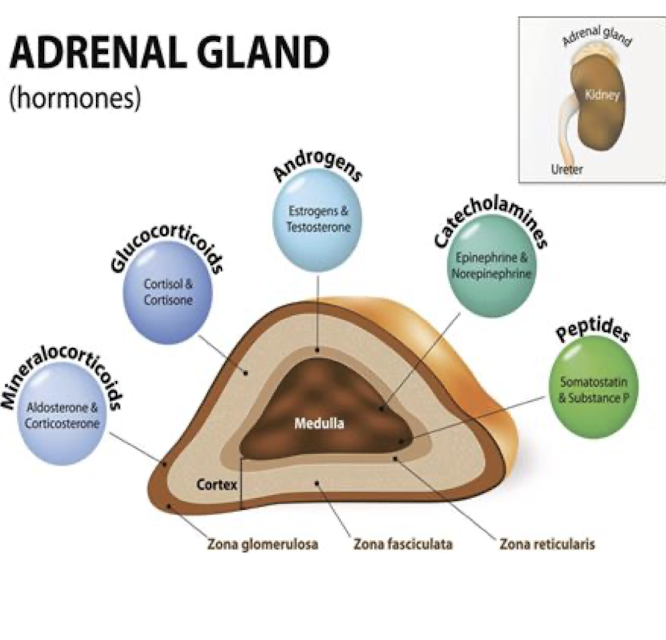
Adrenal Cortex: Antidiuretic Hormone (Aldosterone)
What does Aldosterone cause the Kidney?
This increases what?
What does this regulate?
Retain Sodium
Increases Total Body Fluid/Fluid Retention
BP, pH
Adrenal Cortex: DHEA and Androgenic Steroids
DHEA and Androgenic Steroids are precursors to what? (2)
Estrogen
Androgens
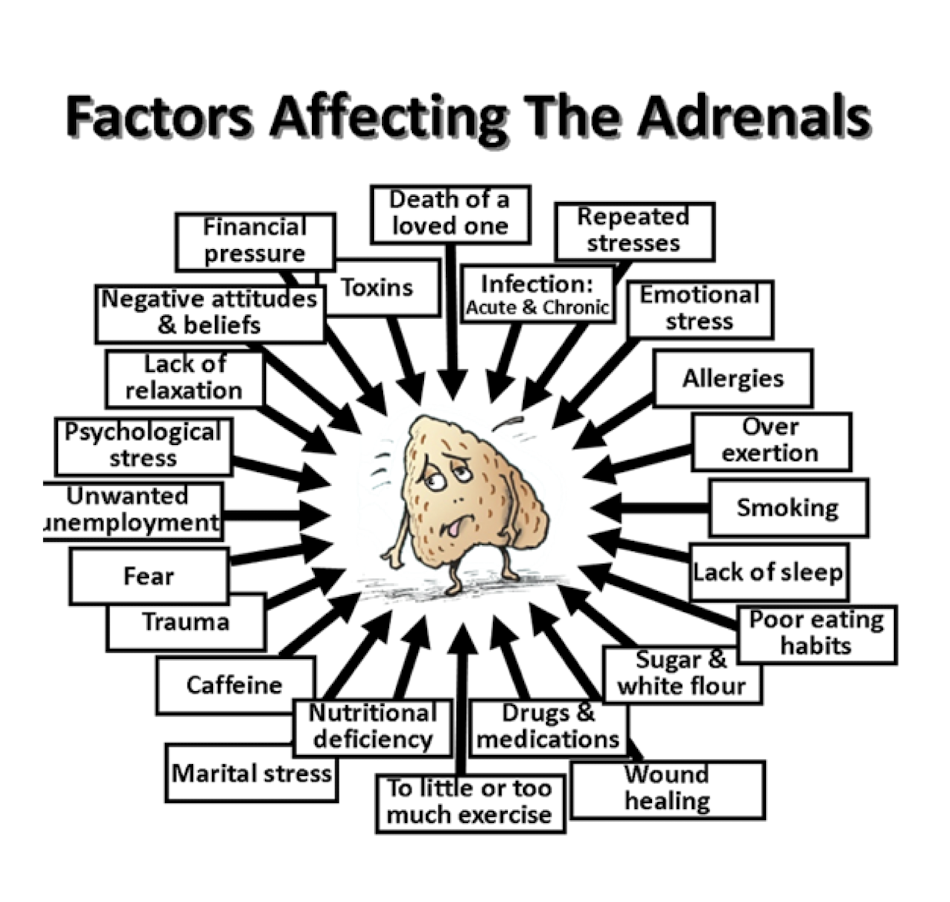
What is ONE main factor that can affect the Adrenal Gland?
Stress
Adrenal Gland Malfunction:
Diseases of the Adrenal Gland are usually caused by either what?
What are the 3 main Adrenal Gland Malfunctions?
Too Much or Too Little of an hormone
3 Main Malfunctions:
Addison’s Disease
Cushing’s Disease
Primary Hyperaldosterone
Adrenal Gland Malfunction:
What is Addison’s Disease?
Potentially ___
Requires ___ hormone supplementation
What is:
Primary Adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal Gland is NOT producing enough cortisol/aldosterone
Potentially FATAL
Requires EXOGENOUS
Addison’s Disease:
Main S/S (Pt 1 - 3)
Fatigue, Body Aches, Muscle Weakness
Unexplained Weight Loss, GI distress, increased thirst, decreased appetite
Low BP
Addison’s Disease:
Main S/S (Pt 2 - 3)
Lightheadedness, Dizziness
Loss of Body Hair
Hyperpigmentation of skin, lips, gums
Adrenal Fatigue:
What is Adrenal Fatigue?
T/F NOT currently an accepted medical dx.
Often confused w what disease?
_____ state.
What is:
Collection of NONSPECIFIC Symptoms
True
Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison’s)
Hypersympathetic State
Always flight mode
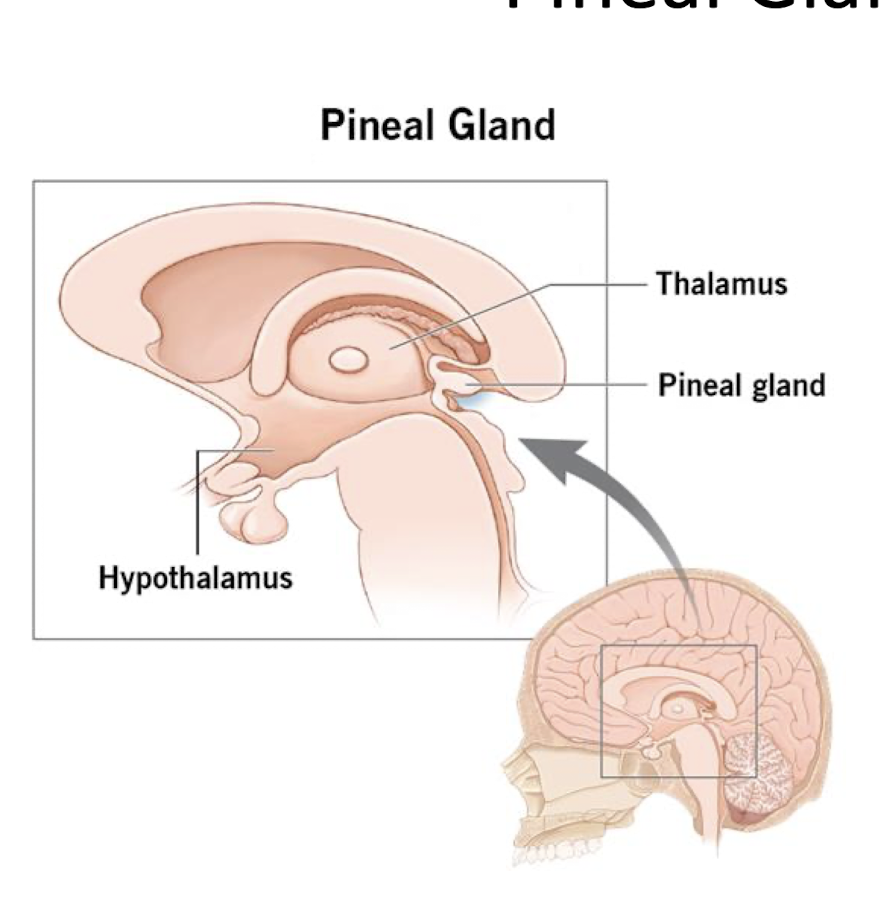
Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland
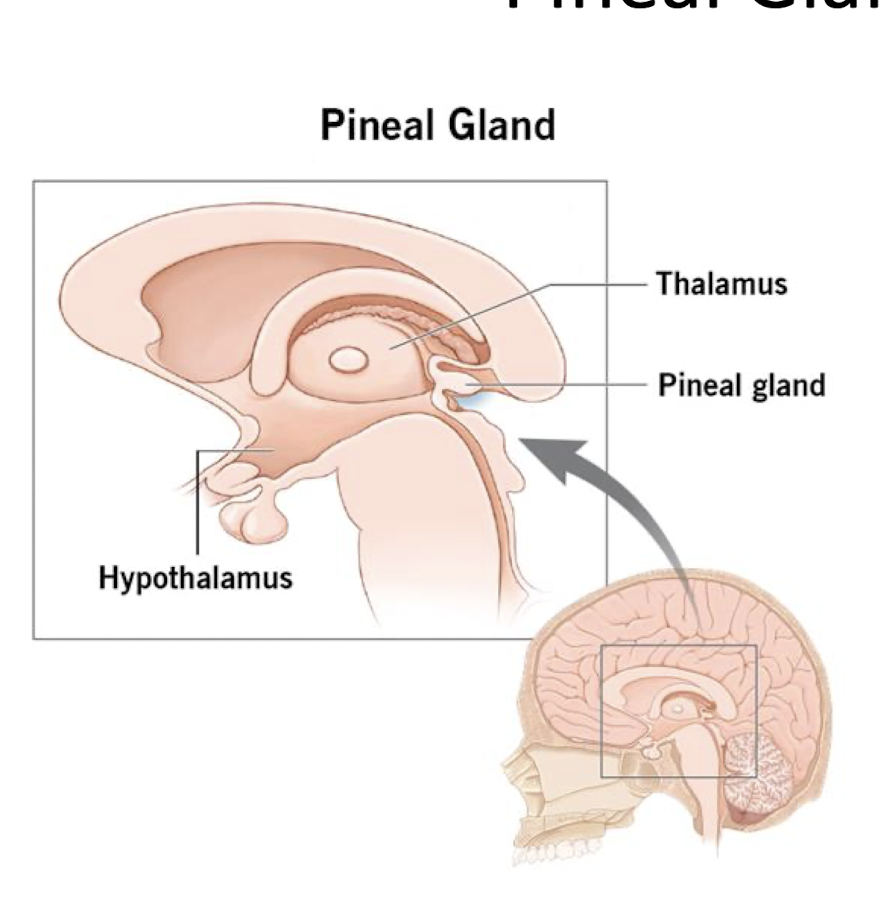
Pineal Gland:
What does the Pineal Gland secrete?
What does the Pineal Gland regulate?
3 main Malfunctions:
Secrete Melatonin
Regulate Circadian Rhythm
3 Main
Tumor (rare)
Post TBI/Concussion
Calcification
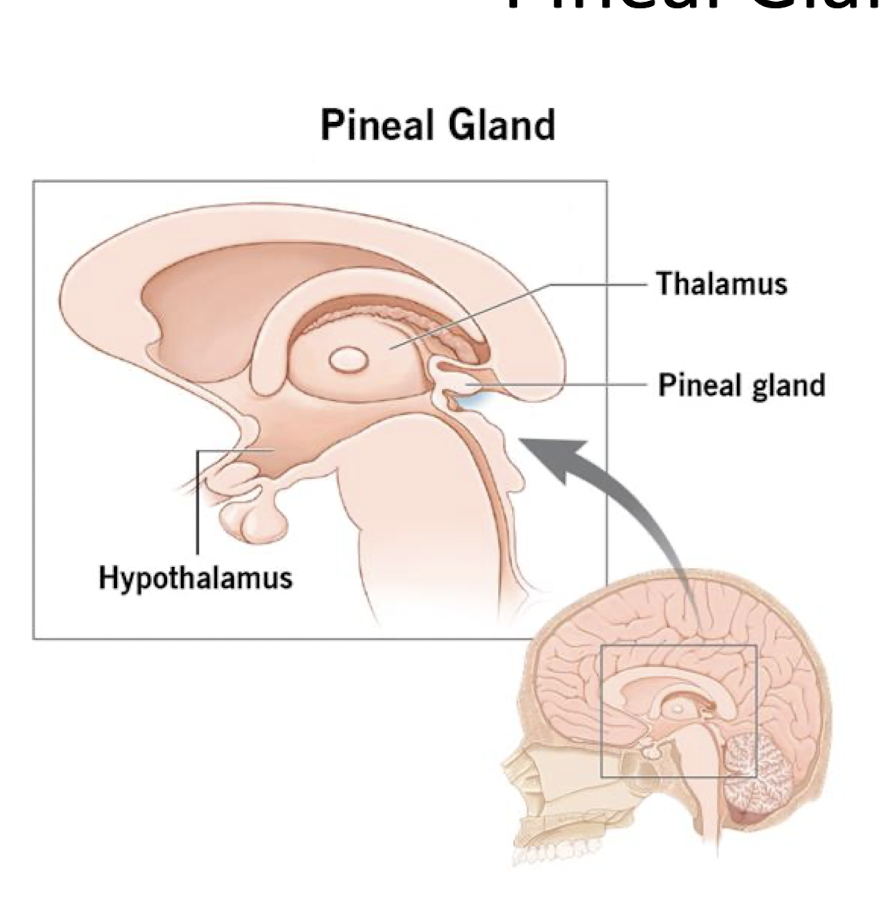
Pineal Gland:
Calcification:
T/F: Common and Age Related
Excessive Calcification may lead to consider what 2 conditions?
True
Excess:
Alzheimer’s
Migraines HA
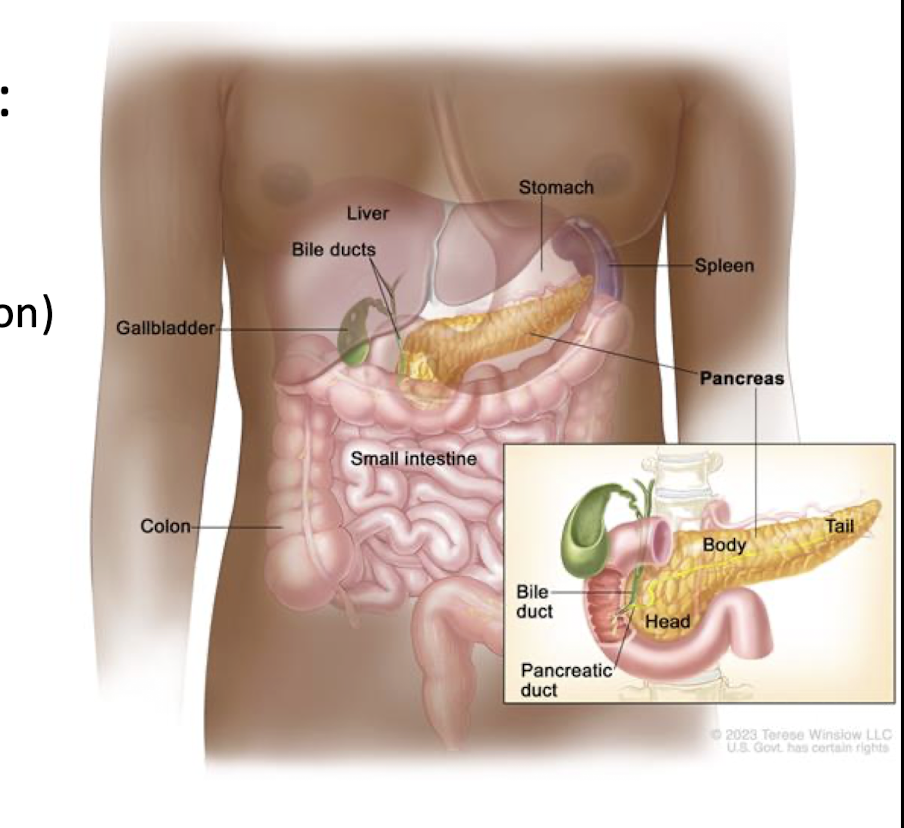
Pancreas
Pancreas
Pancreas:
What are the 2 main Functions of the Pancreas?
Exocrine:
Endocrine:
Exo:
Digestive Enzymes (95% of function)
Endo:
Regulates Blood Sugar w Insulin and Glucagon (5% of Function)
Pancreatic Issues:
What are 2 main Pancreatic Issues?
Pancreatitis
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic Issues: Pancreatitis
What is it?
Excess…
Digests…
What is:
Inflammation of Pancreas
Excess Pancreatic Enzyme Secretion
Digests organ itself
Pancreatic Issues: Pancreatic Cancer
What is MC type of Pancreatic Cancer?
What type of tumor is it?
____ tumors account for < 5% of Pancreatic Tumors
Common S/S (3)
MC: Pancreatic Adenocarsinoma
Exocrine Tumor arising from cells lining pancreatic duct
Endocrine
Common S/S:
Weight Loss
Gall Bladder and Liver Enlargement
N/V
Pancreatitis:
Causes/Risk Factors (Pt 1 - 4)
Alcohol/Smoking (25% of acute pancreatitis cases)
Gall bladdder Stones (40 % of acute pancreatitis cases)
Abdominal injury, sx, trauma
Hereditary conditions
Pancreatitis:
Causes/Risk Factors (Pt 2 - 4)
Hormonal Irregularity
Recurring Pancreatitis (Acute » Chronic)
Cystic Fibrosis
Affects digestive and resp symptoms
Obesity, High Triglycerides
Pancreatitis:
S/S of ACUTE Pancreatitis (7)
LUQ Abdominal Pain/TTP
Pain radiates to back
Pain feels worse after eating
Pain intensifies laying down
Fever
Rapid pulse
N/V
Pancreatitis:
Chronic Pancreatitis S/S: (3)
LUQ Abdominal Pain
Unintended Weight Loss
Oily, Smelly Stool (Steatorrhea)
Diabetes Mellitus:
It is a Complex Disorder of what?
Results in what?
Complex disorder of carbs, fat, protein metabolism
Results in High Blood Glucose Levels
DM 1:
What is DM 1 AKA?
Decreases … in pancreas
____ Onset
Insulin ____
AKA: Insuline Dependent OR Juvenile Onset
Decrease in Size/Number of Islet Cells
Sudden
Insulin Dependent
DM 2:
When does it occur?
Progressive…
____ Onset
T/F: Modifiable
Insulin ____
Adult Onset
Progressive beta cell dysfunction
Gradual
True
Resistant
DM:
Main S/S (8)
Hyperglycemia
Glycosuria
Polyuria
Polydipsia
Excessive thirst/dry mouth
Excessive hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue
Blurred Vision/HA
DM:
Complications (Pt 1 - 4)
Micro and Macrovascular Disease
Impaired Wound Healing
Polyneuropathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
Fatty Liver
DM:
Complications (Pt 2 - 3)
Exercise increases insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance
Circadian Rhythm
Stress Management
Metabolic X Syndrome:
Refers to what?
How to treat?
Refers:
Group of risk factors that increase risk for:
Heart Disease
DM 2
Stroke
Tx:
Lifestyle changes
Pharm management
Metabolic X Syndrome:
Diagnosis requires presence of 3 of the following: (5)
Abdominal Obesity (Men 40”, Women 30”)
High Triglyceride Levels (of it already on meds)
Poor LDL:HDL ratio
Hypertension
High Blood Glucose Levels