Unit 1 Terms
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Confederation
form of gov. where power is shared between a weak central government and strong states
Realignment
when a group of voters change parties
Dealignment
when a group of voters move to a independent party
Pluralism
different factions that are together in a society
EX: rich v. poor, North v. South
Hyperpluralism
multiple factions become powerful enough to take over society, gov can’t function
Direct Democracy
people in households would vote and propose ideas, (no representatives)
New Jersey Plan
each state is equally represented (one vote in congress)
unicameral
power to tax
Virginia Plan
-bicameral:
each states representation based on population share (1 house)
one by taxes (1 house)
-three branches
Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise)
Bicameral:
one house by population ( house of representatives)
one house by Equal representation (senate, each state gets 2 senators)
-three branches
Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation
-no executive branch
-no judicial branch
- no power to tax
-no power to regulate commers (business)
-only one rep. from each state
-9/13 states had to agree to pass laws
Marbury v. Madison
Supreme Court asserted its right to determine the meaning of the Constitution, creates judicial review
McCulloch v. Maryland
case involved a dispute over the Second Bank of the United States, Maryland tried to tax the bank
court ruled that Congress had implied powers under the Necessary and Proper Clause to create the bank, establishes the Supremacy Clause
Supremacy Clause
makes the Constitution, national laws, and treaties supreme over state laws as long as the national government is acting within its constitutional limits
Gibbons v. Ogden
Supreme Court interpreted Constitution very broadly giving Congress the power to regulate interstate commerce as encompassing virtually every form of commercial activity, establishes Commerce Clause
Social Contract Th.
“life, liberty, and the pursuit of property”, if gov. neglects natural rights, citizens can dissolve the gov.
Unitary
gov. where all the power resides in the central government
Elite Th.
theory that republic isnt by the will of the ppl, but by a small elite class who makes all the important decisions
3/5 Compromise
allowed southern states to count a slave as 3/5 of a person for seats in the House
Slave Trade Compromise
No regulation in slave trade for 20 years
Article 1 of the Constitution
Legislative Branch
Article 2 of the Constitution
Executive Branch
Article 3 of Constituion
Judicial Branch
Article 4 of the Constitution
Relations among the States
Article 5 of the Constitution
Provisions for the Amendments
Article 6 of the Constitution
National Debts, Supremacy of national law, Oath
Article 7 of the Constitution
Ratification of the Constitution
Commerce Clause
giving Congress the power to regulate interstate commerce as encompassing virtually every form of commercial activity
delegated, enumerated, expressed powers
powers the Constitution specifically gives the federal government
inherent powers
the government is the sovereign power, so they have all the powers a government should have
reserved powers
no power given to the government, nor prohibited by the states, are reserved for the states/people
prohibited powers
any power not directly given or implied to the federal government or states
extradition
return fleeing criminals in another state back to their home
Necessary and Proper Clause (Elastic)
authorizes Congress to pass all laws “necessary and proper” to carry out the enumerated powers
Nullification
states disregard a rule a federal government placed cus they believe it is unconstitutional
Privileges and Immunities
according citizens of each state the privileges of citizens of other states (no discrimination)
interstate compacts
contract between two states on a problem, policy, etc.
preemption
allows federal gov. to stop or limit a state who created laws conflicting other laws.
Full Faith and Credit Clause
each state needs to recognize the public, acts, and records of all other states
federal grants-in aid
national government gives funds to state and local governments
Categorical grants
grants to state and local governments for very specific programs
EX: fed gov gives states a grant to fix 3rd graders reading in a lower class with less than 55,00+ population in their town
Block grants
grants to state and local government for broad, general purposes
EX: fed gov gives states a grant to fix 3rd graders overall reading
Mandate
requirements that states or local government get from the local government, in return w a condition or receipt of a grant
unfunded mandate
mandate, but the government doesnt give a grant, u just gotta do it
Dual Federalism
federal and state governments are separate in their work (layer cake)
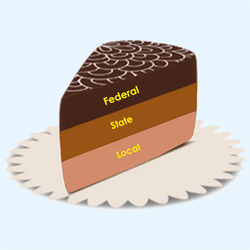
Cooperative Federalism
federal and state government cooperate together in complex problems
New Federalism
give states some power back, and the power of devolution
devolution
Transferring responsibility for policies from the federal government to state and local governments.
Fiscal Federalism
The pattern of spending, taxing, and providing grants in the federal system: how states and fed government carry relations w each other
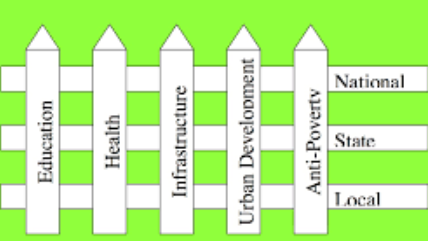
Picket Fence Federalism
different levels of the government work together to promote a develop each policy.