Platform Technology module 2
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
midterm preparation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
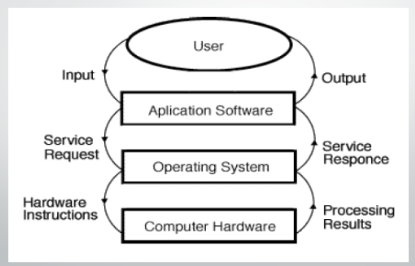
Operating System
A collection of programs that manage and coordinate the activities taking place within a computer.
It acts as an intermediary between the user and the computer and between the application programs and system hardware.
Dynamic View of System Components
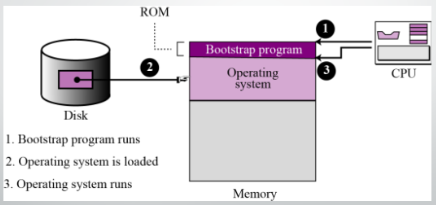
Bootstrap Process
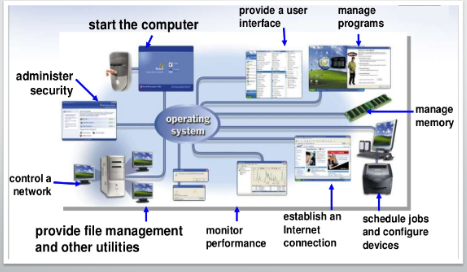
Operating System Tasks
Single-User, Single Task
Types of Operating Systems
This operating system is designed to manage the computer so that one user can effectively do one thing at a time.
Example: The Palm OS for Palm handheld computers.
Multi-User, Multi-Task
It is a system that allows many different users to take advantage of the computer's resources simultaneously.
Example: Unix, VMS and mainframe operating systems, such as MVS,
Mainframe Operating System
Under Multi-User, Multi-Task
It is networking software infrastructure that allows a mainframe computer to run programs, connect linked machines, and process complex numerical and data-driven tasks.

Real Time Operating Systems
Types of Operating Systems
These are used to control machinery, scientific instruments, and industrial systems.
Example: Air Traffic Control System, Network Multimedia Systems, Command Control Systems
Single-User, Multi-Tasking
Types of Operating Systems
OS allows a single user to work on two or more programs that reside in memory at the same time
Foreground
Under Single-User, Multi-Tasking
refers to the active program currently in use
Background
Under Single-User, Multi-Tasking.
refers to the other programs running but not in use.
Multiprocessing Operating System
Types of Operating Systems
One in which two or more central processing units (CPUs) control the functions of the computer. Each CPU contains a copy of the OS, and these copies communicate with one another to coordinate operations.
Multiprocessing
It is a processing technique in which multiple processors or multiple processing cores in a single computer each work on a different job.
Parallel processing
is a processing technique in which multiple processors or multiple processing cores in a single computer work together to complete one job more quickly.
Embedded Operating Systems
Is a specialized operating system designed to perform a specific task for a device that is not a computer. An embedded operating system's main job is to run the code that allows the device to do its job. They are specific to a device and are less resource intensive.
First Generation
History of OS
Vacuum tubes and plugboards. (1945 - 1955)
Second Generation
History of OS
Transistor and Batch System. Each program to be executed was called a job. A programmer who wished to execute a job sends a request to the operating system.(1955 – 1965)
Third Generation
History of OS
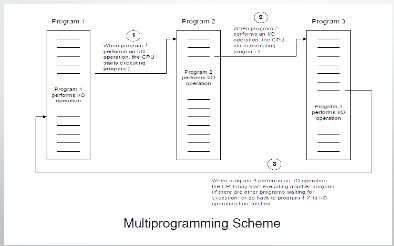
IC and Multiprogramming. Uses multiprogramming, spooling, and time sharing.(1965 – 1980)
Fourth Generation
Personal Computer, LSI.
Fifth Generation
Networked Computing and GUIs. brought about the integration of networked computing and graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Operating systems like Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, and Linux gained prominence. Networking capabilities became central, facilitating communication and resource sharing across connected computers. (1980-2000)
Server Operating System
Also called Network operating systems which allow the sharing of resources among computers connected in a network.
Distributed Operating System
is a system software over a
collection of independent, networked, communicating, and
physically separate computational nodes. They handle jobs which
are serviced by multiple CPUs.
Sixth Generation
History of OS
Mobile and Cloud Computing.
Operating systems like Android and iOS revolutionized mobile devices, while cloud-based systems such as Linux-based servers and Microsoft Azure redefined how computing resources are accessed and utilized. (2000 – present)
Seventh Generation
History of OS.
IoT and Edge Computing.
Operating systems are adapting to handle the unique challenges of interconnected devices and the need for real-time processing at the edge of networks.
Unix
First operating systems to be written in 1971.
MS-DOS
A disk operating system for IBM PC–compatible computers. single-user, single-task operating system.
Windows
The Big 3
The predominant personal operating system developed by Microsoft Corporation.
Billy Gates and Paul Allen
Form a partnership called Microsoft (1975-1981)
Linus Torvalds
Developed Linux in 1991 by a university student in Finland.
Mac OS
Proprietary operating System for computers made by Apple Corporation
Chrome OS
The first cloud operating system
file
a collection of related information or data that is stored together in secondary storage for future use