3.2.4 - Properties of Period 3 elements and their oxides and chlorides
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
List the metalic period 3 elements.
Na,Mg,Al
Which one has a higher melting point magnesium or Sodium?
magnesium has a higher melting point as it has stronger metallic bonding.
Describe the reaction between sodium and cold water
This is a very vigorous reaction, sodium floats on the surface of the water and and melts to form a ball. There is a lot of fizzing (due to the hydrogen released) and heat produced in this reaction.
The colourless sodium hydroxide formed will have a pH of around 13-14 forming a very alkaline solution.
Describe the reaction between magnesium and cold water
This is a slow reaction, not many bubbles are formed. The solution will have a pH of about 10 which is less alkaline than NaOH as magnesium hydroxide is only partially soluble.
Describe the reaction between magnesium and steam
The reaction is faster when reacted with steam. Magnesium burns with a bright, white flame. In this reaction. Magnesium oxide is produced instead of magnesium hydroxide.
Describe the reaction between sodium and oxygen
Sodium is heated with oxygen and reacts vigorously with a bright yellow flame. A white solid is produced (sodium oxide.) Sodium oxide is ionic and basic, it has an ionic lattice structure. Some sodium peroxide can also be formed from the reaction.
Describe the reaction between magnesium and oxygen
Magnesium is heated with oxygen and also reacts vigorously with a bright white flame to produce a white solid (magnesium oxide.) Magnesium oxide is also an ionic lattice with high melting points.
Describe the reaction between aluminum and oxygen?
Aluminium has to be powdered when it is reacted with oxygen as if you just add the a piece of aluminium, a protective oxide layer covers it and prevents further reaction. The reaction with oxygen is fast and it burns with a bright white flame to produce a white powder (Aluminium oxide.) Aluminium oxide is an ionic and amphoteric oxide. The formula of this oxide is Al2O3. It has a slightly lower melting point than magnesium oxide.
Describe the reaction between silicon and oxygen
Silicon has to be powdered and heated strongly for it to react with oxygen. The reaction is quire slow and emits bright white sparkles. A white power (silicon dioxide.) Silicon dioxide is a covalent, acidic oxide. It has a macromolecular (giant covalent) structure. Silicon dioxide has a lower melting point compared to aluminium oxide. Silicon dioxide is used to make sand and glass.
Describe the reaction between phosphorous and oxygen
Phosphorus is heated with oxygen in a vigorous reaction. Yellow or white flames are seen and the product is a white solid (phosphorus oxide). Phosphoric oxide is a covalent acidic oxide. It has a simple covalent structure. It has a significantly lower melting point as less energy is needed to break the weak intermolecular forces of attraction.
Describe the reaction between sulfur and oxygen
Sulfur has to be powdered and heated to react with oxygen. The reaction is gentle and a blue flame is seen. The product is toxic flames. The reaction with sulfur can produce two different oxides, sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide. Both of these oxides are covalent acidic oxides. Sulfur dioxide is a colourless gas and sulfur trioxide is a colourless liquid. For sulfur trioxide to be formed, a catalyst must be present and the reaction must take place at a high temperature. The melting points of sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide is lower than phosphorus oxide.
What is the overall trend of period 3 with oxygen?
Overall, The reaction becomes less vigorous as you go down the group with the exception of phosphorus which is a very vigorous reaction.
What happens to the melting point of the period 3 chlorides as you move across the period?
As you go across the period the melting point of the period 3 chlorides decrease with the exception of phosphorus chloride which increases.
Describe the reaction between sodium and chlorine
Sodium is heated with chlorine and emits a bright orange flame to form white solid sodium chloride. Sodium chloride has a giant ionic structure (lattice).
Describe the reaction between chlorine and magnesium
Magnesium is heated with chlorine and emits a bright white flame. White solid magnesium chloride is formed which also has a giant ionic structure (lattice).
Describe the reaction between aluminum and chlorine
Aluminium is heated with a stream of chlorine to produce very pale yellow aluminium chloride. Aluminium chloride also forms a dimer(a molecule consisting of two identical molecules (monomers) together ) Al2Cl6 which is formed from covalent bonds. Which chloride forms depends on the conditions. AlCl3 exists at room temperature and is a giant ionic structure while Al2Cl6 exists at higher temperatures and is a dimer with covalent compounds. Bonding in the solid aluminium chloride is largely ionic with a good deal of covalent character. Both AlCl3 and Al2Cl6 form in the gas phase.
Describe the reaction between silicon and chlorine
When chlorine is passed over silicon powder heated in a tube, silicon tetrachloride is formed. Silicon tetrachloride is a molecular covalent compound that is a colourless liquid and volatile.
Describe the reaction between phosphorous and chlorine
White phosphorus burns spontaneously ( unexpectedly bursts into flames ) in chlorine to produce phosphorus(V) chloride. Phosphorus(V) chloride is a white solid which sublimes at its melting point. It is a covalent molecule. PCl3 is also formed in this reaction. Phosphorus oxide has a higher melting point than silicon tetrachloride as it has one more Cl molecule so it has more electrons and more van der wall forces.
Describe the reaction of sulfur with chlorine
When chlorine is passed over heated sulfur it reacts to form an orange liquid (sulfur chloride). There are many sulfur chlorides formed. Sulfur chloride is a covalent molecule.
Describe the reaction of sodium oxide with water
Sodium oxide reacts with water to produce a colourless solution of sodium hydroxide. This solution is alkaline. When sodium oxide dissolves in water, the oxide ion acts as a base and accepts the H+ ion. NaOH- ionic
Describe the reaction between magnesium oxide and water
Magnesium oxide is partially soluble in water. Some magnesium oxide reacts with water to form magnesium hydroxide. The pH of a solution of magnesium oxide is slightly alkaline, a solution of around pH9. The oxide ion accepts protons from the acid to form water. MgOH- ionic
Describe the reaction between aluminum oxide and water
Aluminium oxide is insoluble in water because of the strength of the ionic bonds between the oppositely charged, small ions.
Describe the reaction between silicon dioxide and water
Silicon dioxide does not dissolve or react with water as water can't supply enough energy to break the strong covalent bonds in the macromolecular structure. The pH of a mixture of silicon dioxide and water is 7, silicon dioxide is still referred to as an acidic oxide as it reacts with bases.
Describe the reaction between sulfur dioxide and trioxide with water
Sulfur dioxide reacts with water to produce sulfurous acid (H2SO3) (covalent). This solution is weakly acidic and this reaction is also reversible.Sulfur trioxide reacts very vigorously with water to produce sulfuric acid (H2SO4)(ionic).Both sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide are acidic oxides which react with bases. Sulfur dioxide in water forms a solution with pH 3.
Describe how sodium and magnesium chloride react with water
Sodium and magnesium chloride do not react with water as the polar water molecules are attracted to the ions which dissolve the chlorides and break down the giant ionic structures. The metal and chloride ions become hydrated ions.
Describe how aluminum chloride reacts with water
When water is added to aluminium chloride, the dimers are broken down and Al3+ and Cl- ions enter the solution. The Al3+ ion becomes hydrated and causes a water molecule which is bonded to the Al3+ to lose an H+ ion. This causes the solution to turn acidic. The H+ and Cl- form hydrogen chloride gas which is given odd as white fumes.
Describe what happens when silicon chloride reacts with water
When silicon chloride is hydrolysed in water, it releases white fumes of hydrogen chloride gas in a rapid reaction. The silicon dioxide is seen as a white precipitate and some of the HCl has produced dissolves in water to form an acidic solution.
Describe what happens when phosphorous chloride reacts with water
Phosphorus chloride also gets hydrolysed in water, both H3PO4 and the dissolved HCL are highly acidic.
Describe the reaction between sulfur dichloride/disulfurdichloride with water?
When sulfur dichloride and disulfur dichloride reacts with water, it produces sulfur dioxide and hydrochloric acid. Sometimes a yellow sulfur precipitate is formed. This reaction is exothermic.
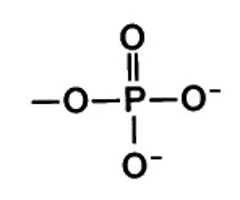
Describe the structure of the PO4(3-) ion
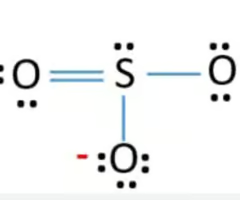
Describe the structure of the SO3(2-) ion
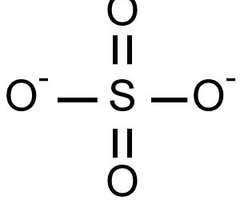
Describe the structure of the SO4(2-) ion
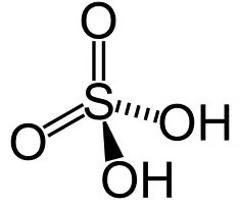
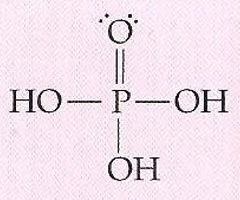
Describe the structure of phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid - Tetrahedral structure (109.5 bond angle)
Describe the structure of sulfuric acid
Pyramidal (bond angle 107.5)