Cardiopoulm Test 2 Part 1: Chest X rays
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
air shows up as what color on x rays
black
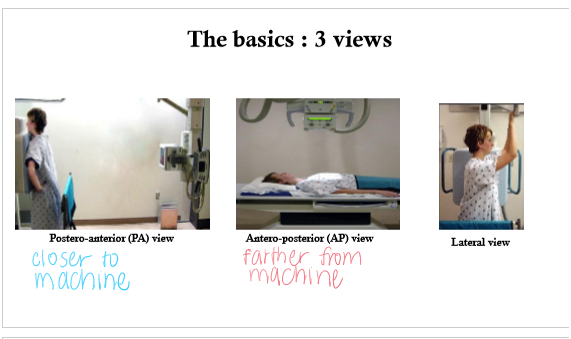
what are the 3 basic views for chest xrays
PA
AP
Lateral
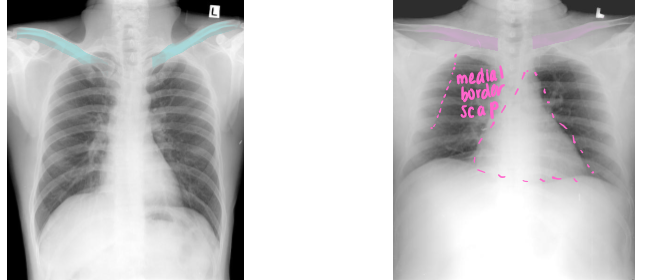
Differentiate which is PA vs AP view. Why
Left PA:
clavicles ELEVATED
medial border of scap NOT in center of lung fields
heart NOT magnified and enlarged
Right: AP
clavicles HORIZONTAL
scapulae in lung fields
heart appears magnified/elarged
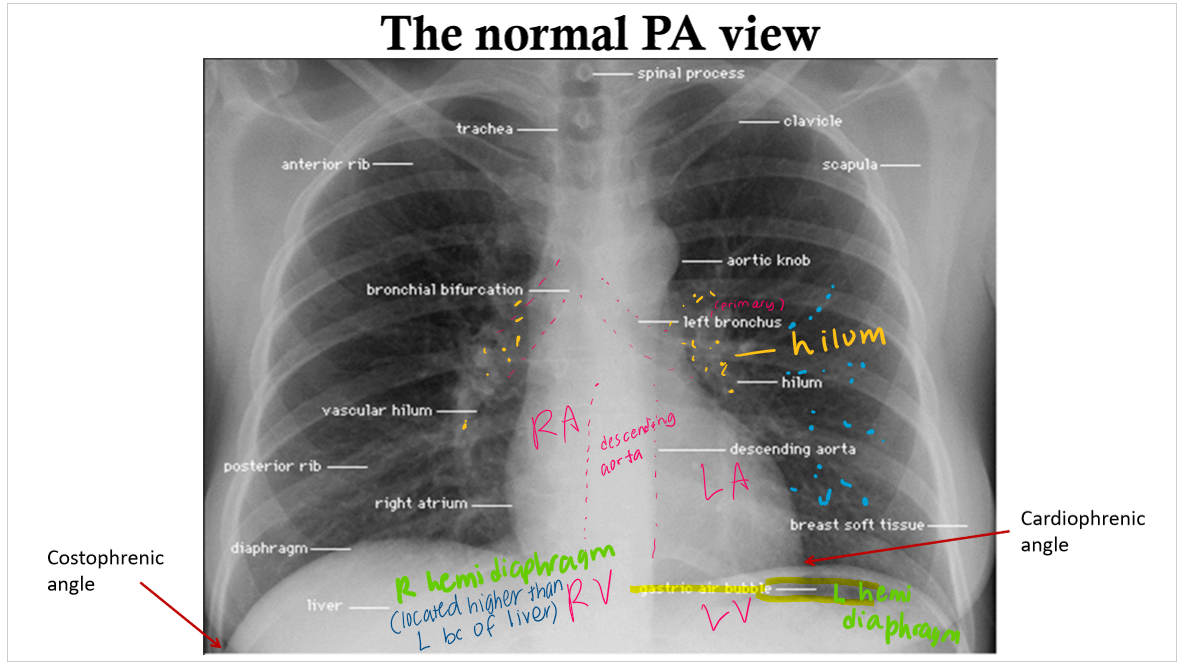
labeled PA view
first rib attaches to
T1
3 ways x rays can be unreliable
rotation
exposure
inspiration vs. expiration
look at the distance btwn ___ and ___ to tell if pt was rotated during x ray
spinous process and medial clavicles

which was was this pt rotated when getting imaging?
R line is larger so it means R side was farther away. meaning pt was rotated R. whichever line is longer means pt was rotated that way (this info might be wrong. check w ahmed!!!)
if you cannot see the thoracic vertebrae behind the heart in a a CXR, the xray is _____________
underexposed
if u can clearly see the thoracic vertebrae behind the heart, your x ray might be ______
overexposed
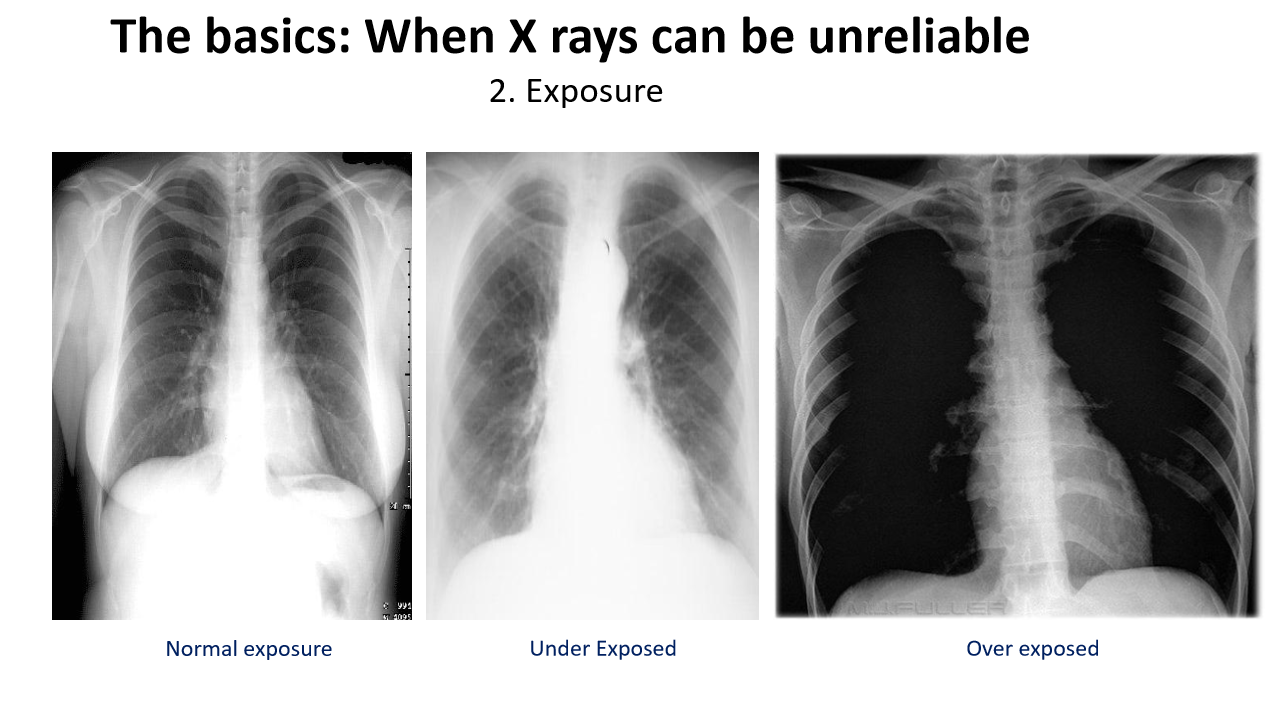
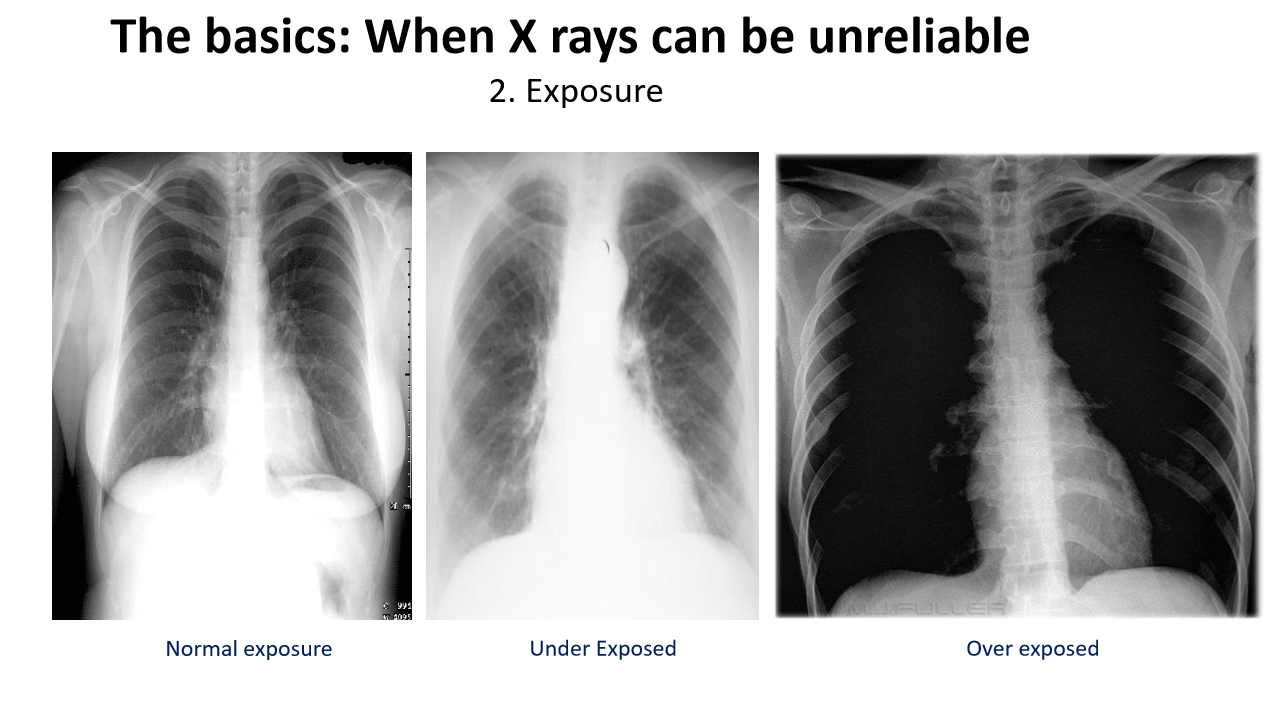
in an (over/under)exposed x ray, people might think that there is too much air and pt has pneumothorax
overexposed
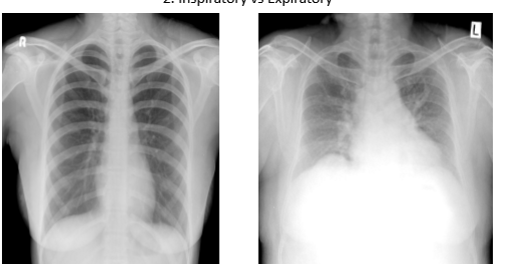
which is inspiration vs expiration. how do u know?
Pic 1: inspiration (inhale —> diaphragm goes down. you can see 9-10 ribs in full inspiration)
u want pt in full inspiration to see how much air lungs can hold. u want to see if there are issues w lung getting air
Pic 2 expiration: u see less than 9 ribs
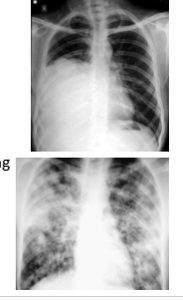
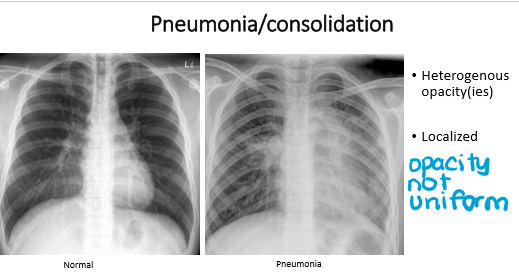
What do u term each of these pics in terms of opacity?
Pic 1: homogenous opacity - area of opacity with UNIFORM DENSITY throughout, appearing evenly white or grey
Pic 2: heterogenous opacity: area of opacity with NON-uniform density, appearing as a mix of lighter and darker regions
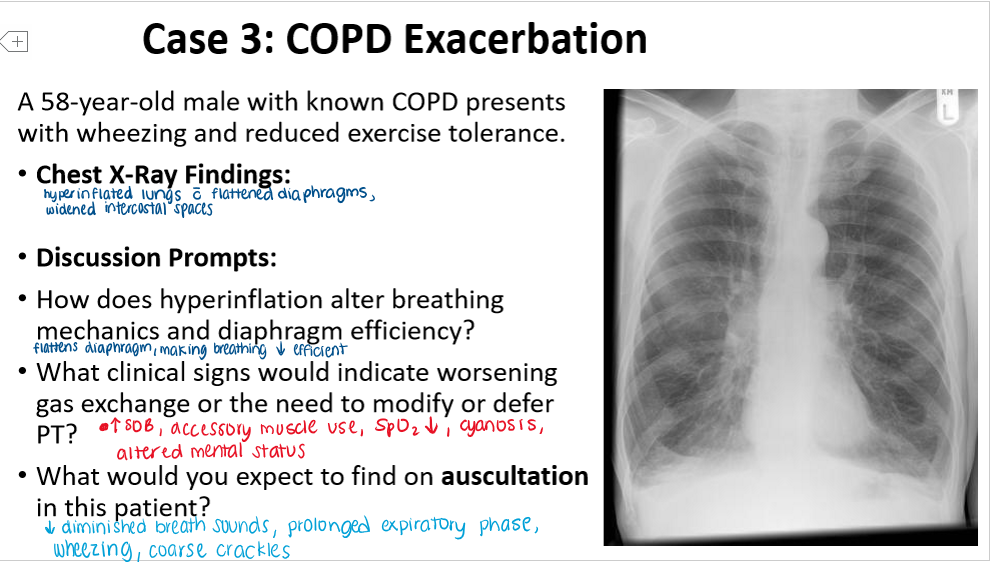
How will a pt with COPD present in a radiograph?
(Hypo/hyper)inflation
(increased/decreased) bronchovascular markings
(Inflated/flat) diaphragms
________ heart shape
hyperinflation
decreased bronchovascular markings
flat diaphragms
tubular heart shape
What is the hallmark pathophysiologic finding in COPD? How will this show up on an xray?
air trapped in lungs, resulting in HYPERinflation
reflects as more BLACK on xray
more air = decreased bronchiovascular markings
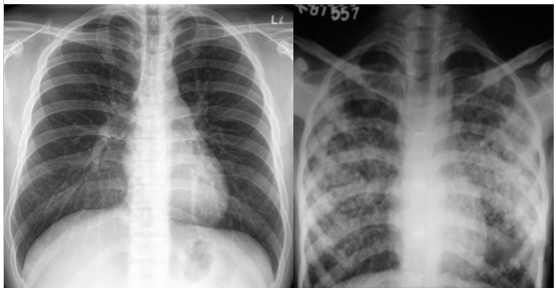
What is going on in these pictures. Whats the dx?
Left pic: normal
Right pic: COPD
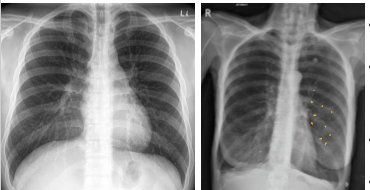
whats the dx for these pics?
Left: normal
Right: pneumonia
pneumonia has ________ opacity
It is (localized/general)
pneumonia
heterogenous
localized
whats the dx?
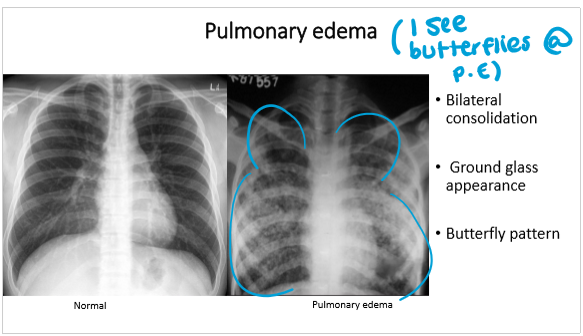
pulmonary edemap
pulmonary edema has
________ consolidation
_______ pattern
pulmonary edema:
bilateral consolidation
butterfly pattern
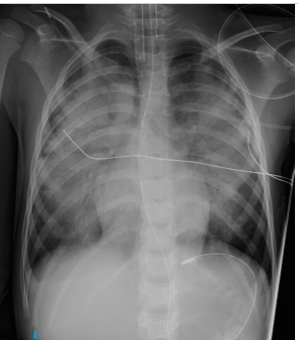
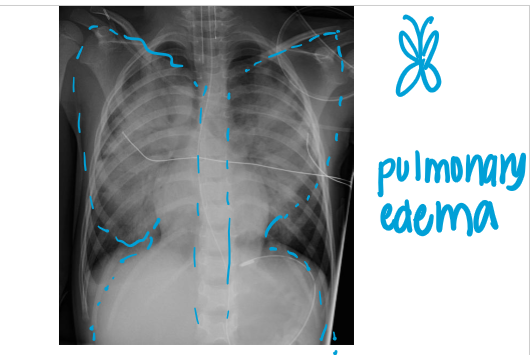
whats the dx
pulmonary edema
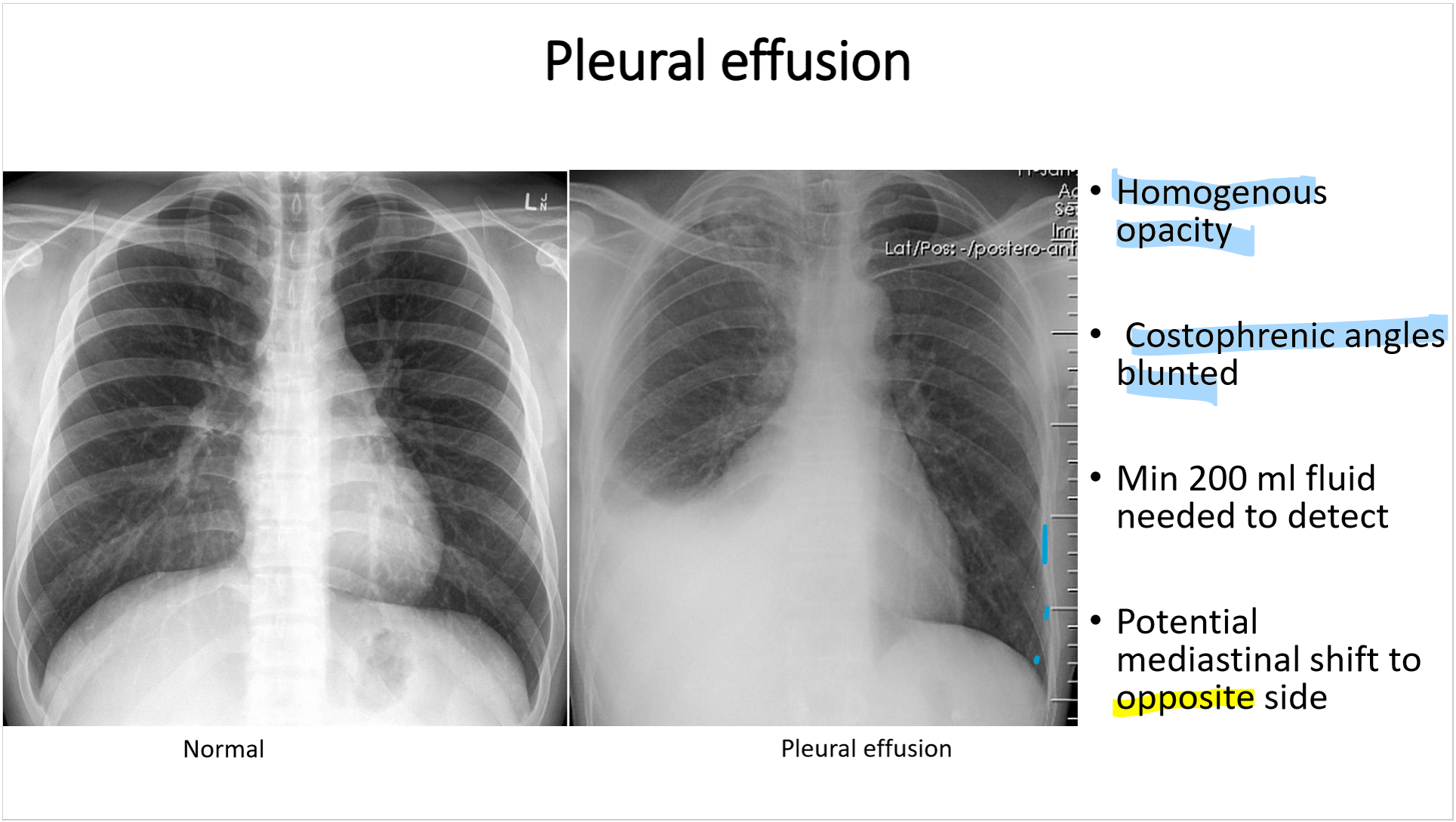
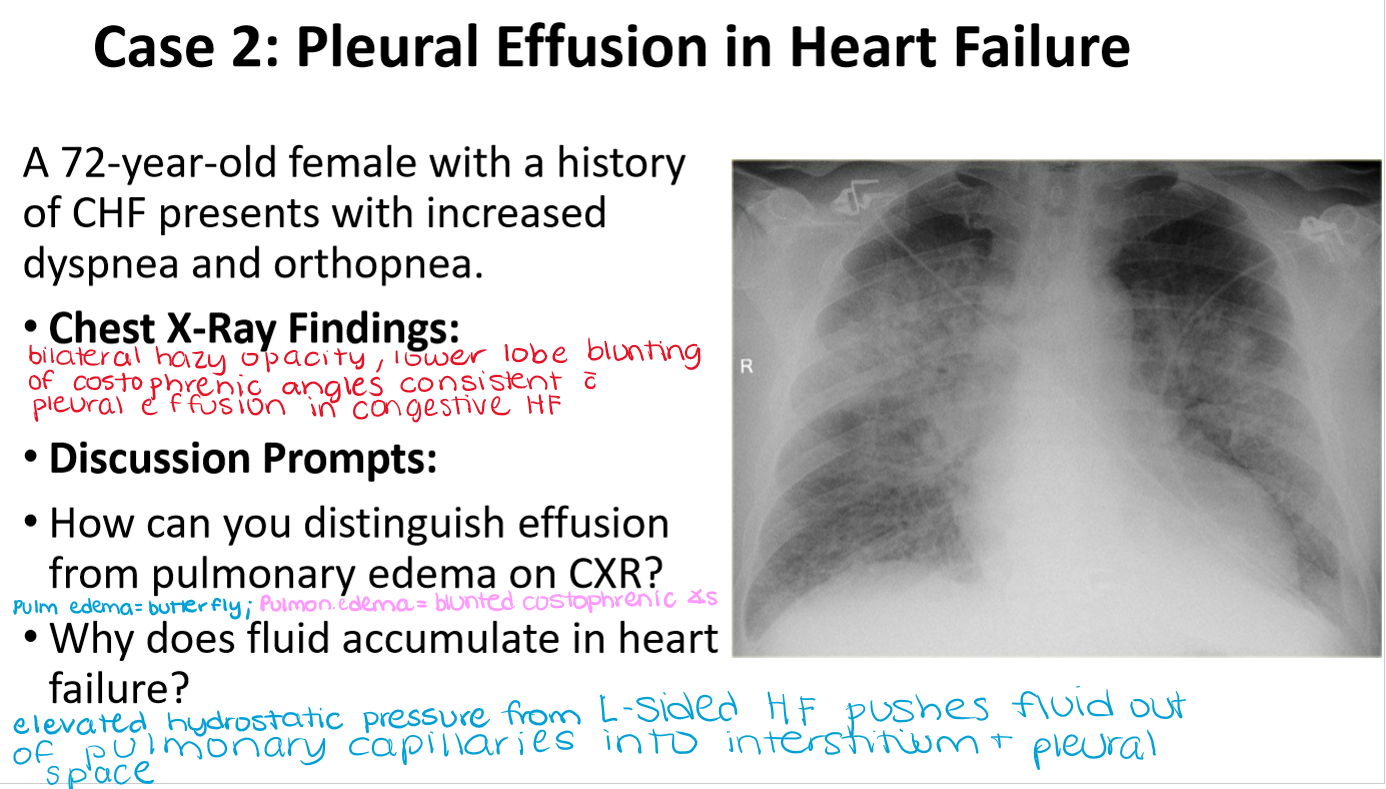
pleural effusion has
_______ opacity
blunted _____________
min _____ mL fluid needed to detect
potential mediastinal shift to (same/opposite) side
pleural effusion:
homogenous opacity
blunted costophrenic angles (bc
min of 200 ml fluid needed detect
potential mediastinal shift to OPPOSITE side
why does the mediastinum get shifted to the OPPOSITE side in pleural effusion?
Fluid buildup in the pleura increases pressure and pushes the heart to the other side
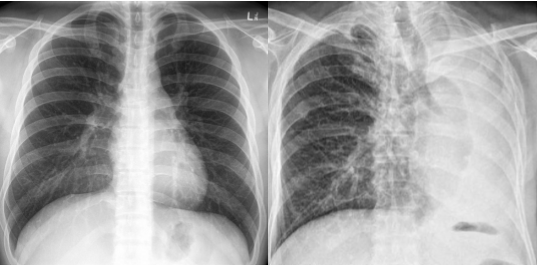
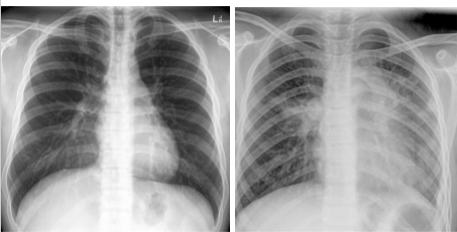
whats the dx
left: normal
right: atelectasis
atelactasis has
_______ opacity
costophrenic angles _____
________ of ribs
potential mediastinal shift to ____ side
atelactasis:
homogenous opacity
costrophrenic angles blunted
crowding of ribs
potential mediastinal shift to SAME side
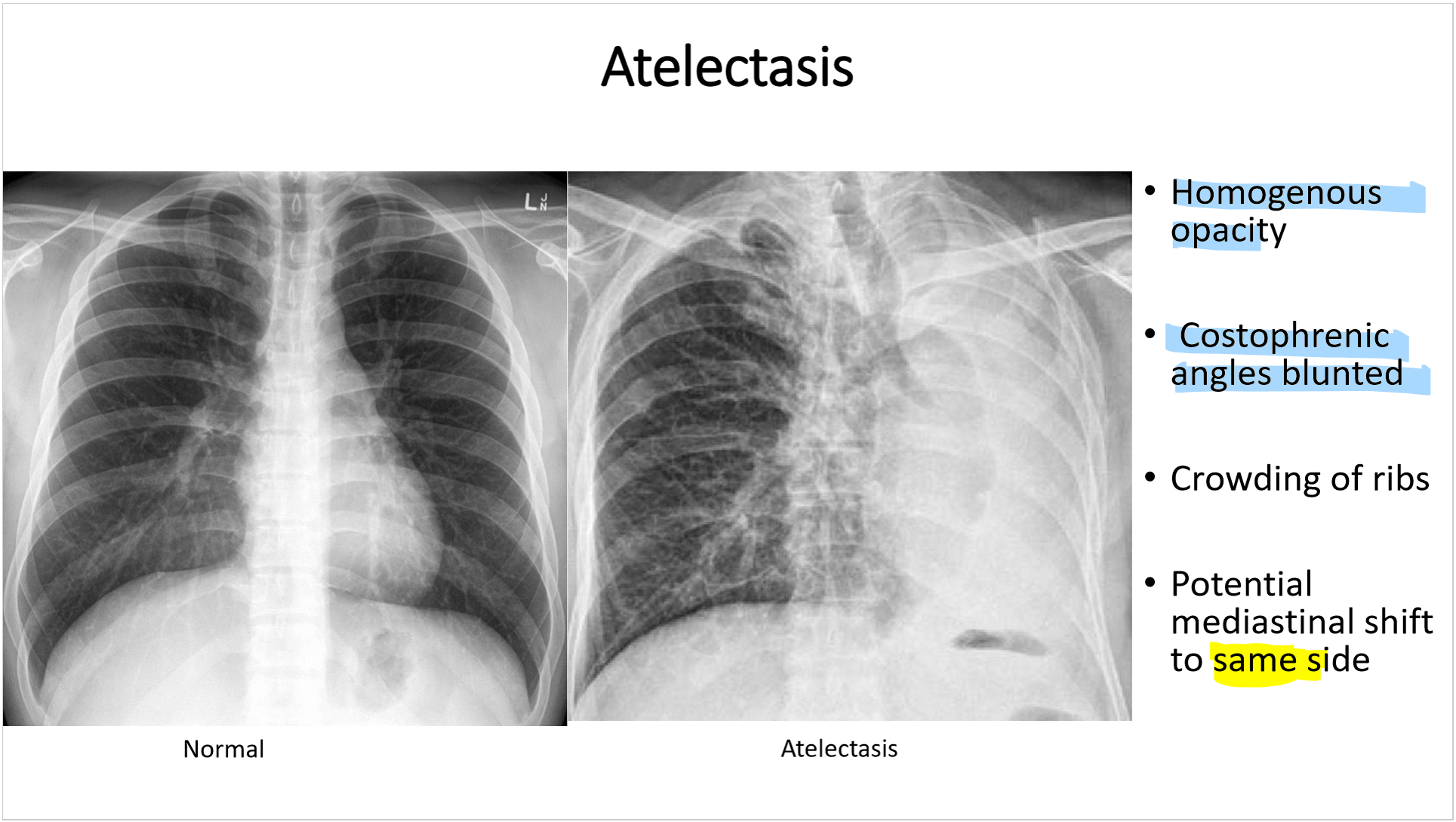
the mediastinum shifts to the (same/opposite) side in atelectasis. why?
same; when the lung collapses, it acts as a vacuum and sucks everything to the same side
whats the dx
pneumothorax
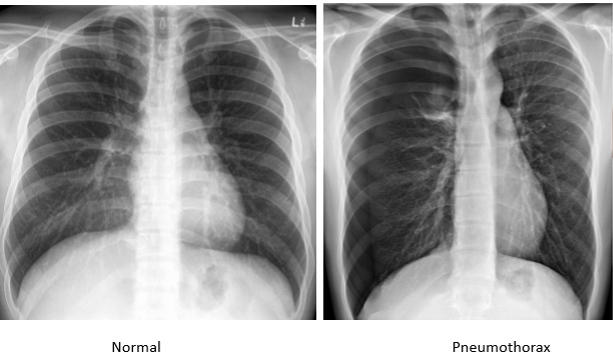
what is pneumothroax?
air in the pleural cavity (thorax)
there should not be air in the pleural cavity. There should be fluid there
pneumothorax has
__________ bronchovascular markings
affected side appears what color?
can see borders of _________
potential mediastinal shift to _____ side
pneumothorax:
ABSENT bronchovascular markings
affected side appears black
can see borders of affected lung
potential mediastinal shift to OPPOSITE side
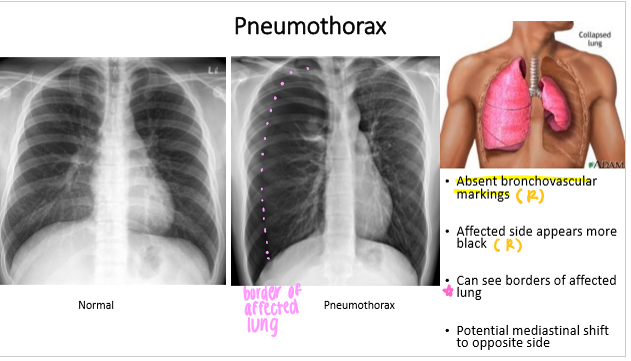
The mediastinum moves to (same/opposite) side in pneumothorax. Why
opposite; the excess air causes a buildup of pressure, pushing everything to the opposite side (like an inflating balloon crowding everything out)
what lung condition may occur if a PT accidentally dry needles too deep?
pneumothorax (air in the pleura)
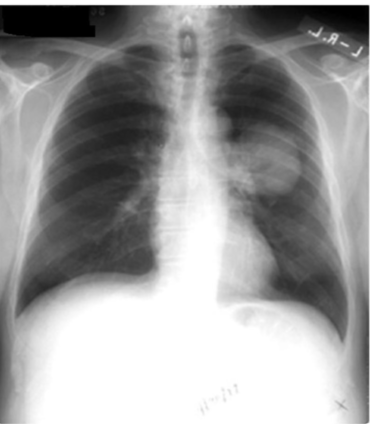
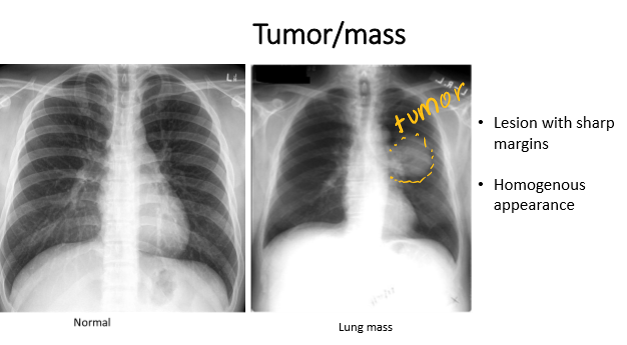
whats the dx
tumor
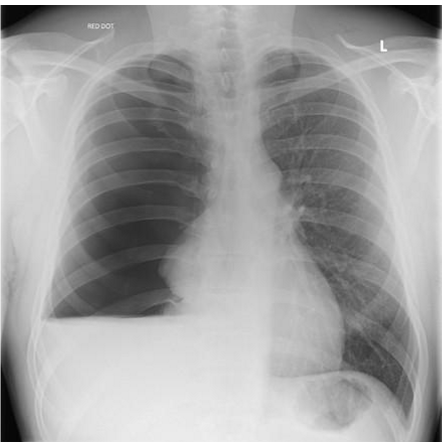
whats the dx
hydropneumothorax (air AND water in pleural space)
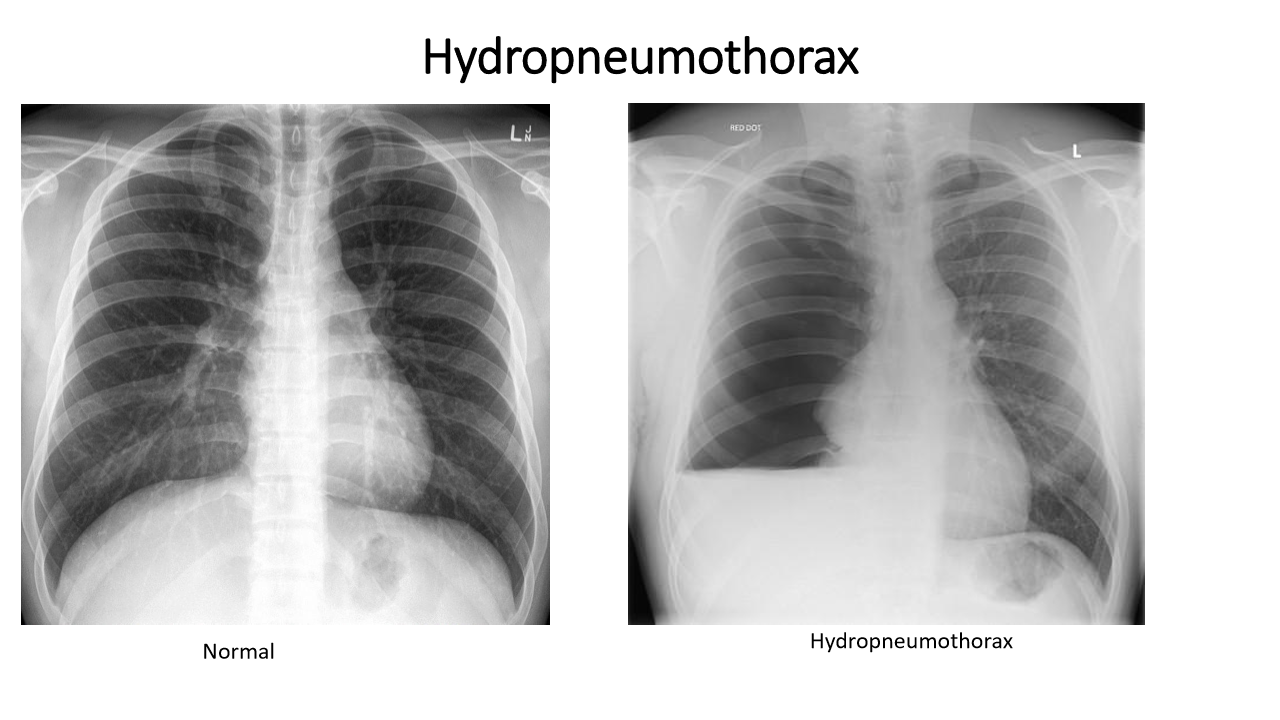
hydropneumothroax has:
_______ opacity on the same side
bronchovascular markings are ___
mediastinum pushed to (opp/same) side
hydropneumothorax:
homogenous opacity on same side
bronchovascular markings absent on same side
mediastinum goes to opp side
where is the endotracheal tube supposed to end and why
above the “carina” (bifurcation of the lungs)
If not, it tends to move when the pt flexes/extends neck and has a tendency to slip into the R mainstem bronchus. This leads to only ONE lung getting air and may lead to collapse of the other (u will not hear the other lung when u auscultate)
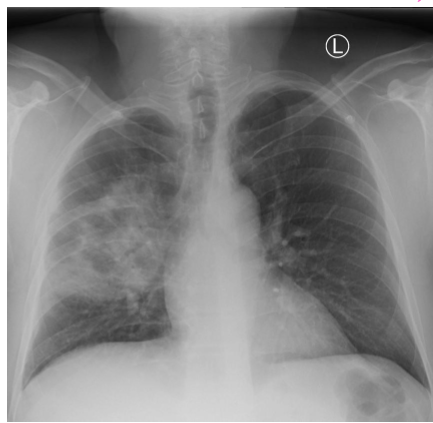
whats the dx
pneumonia (R side?)
consolidation, heterogenous opacity, localized
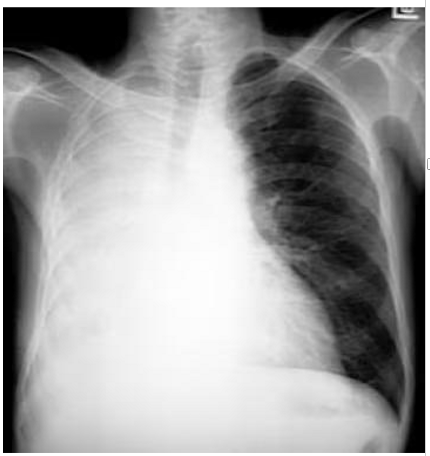
whats the dx
massive pneumothorax L side
(L side dark no bronchovascular markings)
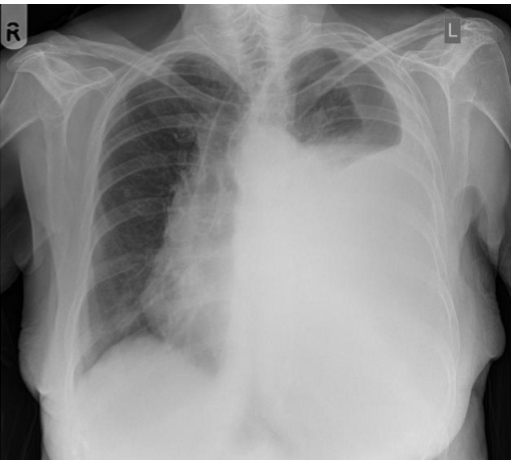
whats the dx?
pleural effusion
a 65 y/o male, 2 days post abdominal surgery reports SOB. He’s been lying supine most of the time and has shallow breathing due to pain. Whats your dx?
atelectasis

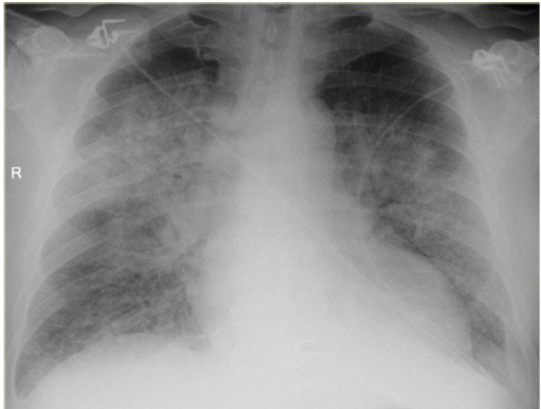
whats the dx?
pleural effusion
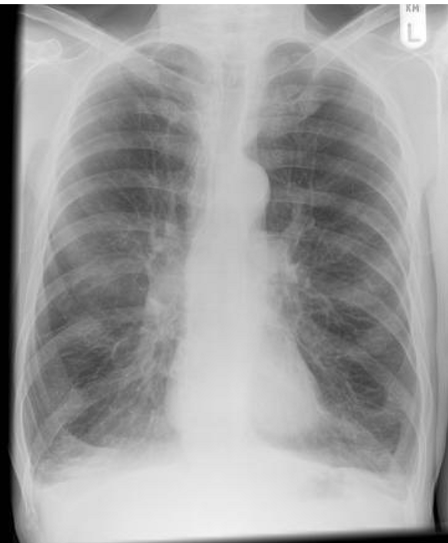
whats the dx?
COPD