MIDTERM: Chinese Architecture
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
China
The most populous state in the world with over 1.3 billion people
Beijing
Capital city of China
Shanghai
Largest City in China
Shih Huang di
China's First Emperor
known as the builder of Great wall of China (Great Wall)
Great Wall of China
to protect the settled Chinese people from the raids of barbarian nomads lived beyond it
Sun Yat-Sen
Founder and first president of the republic of China
Dragon
National Symbol
- are legendary creatures in Chinese mythology and folklore
- the emperor of China often used this symbol to represent his imperial power and strength
- traditionally symbolize potent and auspicious powers, particularly control over water, rainfall, hurricane, and floods
9, 596, 961 sqkm.
China's total area
Mount Everest
Highest point at 8, 850m
Turpan Pendi
Lowest point at 154m
East
along the shores of the Yellow Sea and the _____ China Sea, there are extensive and densely populated alluvial plains
North
While on the edges of the Inner Mongolian plateau in the ______ grasslands can be seen
South
dominated by hill country and low mountain ranges. In the central-east are the deltas of China's two major rivers, the Yellow River and the Yangtze River (Chang Jiang). Other Major rivers include the, Mekong, Brahmaputra, and Amur
West
Major mountain ranges, notably the Himalayas, with the China's highest point at the eastern half of Mount Everest at 8, 848m, and high plateaus feature among the more arid landscapes such as the Taklamakan and the Gobi Desert.
2010
What year did china became the world's largest exporter
open-door-policy
open to foreign investor
Copper, Tin, Zinc, Antimony, Tungsten, Manganese, Mercury
Geological in south
7 materials
CTZATMM
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Soil, Alluvium
Geological in north
SA
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Timber
Principal material in China
Bamboo, Pine, Persia Nanmu
The tallest and straightest of all the trees in China
BPPN
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Bricks, Limestone, Sandstone
_____were also used, as well as _____ and _____
Glazed Tiles or Majolica
Walls are also faced with ________
Format:
Answer or Answer
Clay Tiles, Black, Red, Azure, White, Yellow
colored and glazed with symbolic colors
BRAWY
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism
What are the dominant faiths (religions)
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Christianity
was first introduced during the Tang period in the 7th century with the arrival of the _____
Islam
eighteen yeas after Muhammad's death.
Hinduism, Dongbaism, Bon
Minority religions
HDB
Confucianism
new code of social conduct and philosophy of life; it was not a religion
Taoism
founded by Lao Tzu; doctrine of universal love as his solution to social disorder
Buddhism
introduced to China under the Han Dynasty
Calligraphy and Painting
Higher forms of art than dancing or drama
Confucianism and Conservatism
China's traditional values were derived form various versions of ___________
Format:
Answer and Answer
Feng Shui
widely used to orient buildings
often spiritually significant structures such as tombs, but also dwellings and other structures in an auspicious manner
Peking Man
Paleolithic - the most famous specimen of Homo Erectus found in China is the so-called ______
Xihoudu, Shanxi
the earliest recorded use of fire, archaeological site
Xiaochangliang
Stone tools found in ______
Yellow River
began to establish itself as a cultural center, where the first villages were founded
Xia Dynasty
the first dynasty to be described in ancient historical records
from this period found on pottery and shells are thought to be ancestral to modern Chinese characters
Shang Dynasty
discovered inscriptions of divination records in ancient Chinese writing on the bones or shells of animals
Oracle bones
the first system of writing of China
writings in the bones or shells of animals
foretell future events - prophecy
used as a form of divination in ancient China, mainly during the late Shang dynasty. _____ provides us with one of the earliest examples of writing in Ancient China
Anyang
Where was oracle bones first fully excavated
Han Dynasty
emerged in 206 BC
the first dynasty to embrace the philosophy of Confucianism
China made advanced in many areas of the arts and sciences
commonly used structural techniques included "bean in tiers" and "column and tie beam" methods
Northern and Southern Dynasty
China's architecture first developed noticeably
Pagodas and Grottoes
As a result of Buddhism
Tang and Song Dynasty
China's building methods maturing rapidly
The architectural use of color and decoration became more and more exquisite
Ming and Qing Dynasty
High levels of skill were developed in the arrangement and layout of groups of buildings
Examples:
Forbidden City of Beijing
Summer Place
Tian Tan Shrine
Yiheyuan
The Summer Place known as _______
Forbidden Palace
Chinese imperial palace from the Ming Dynasty to the end of Qing dynasty
Commoner
Architectural Type:
the houses of _________, be they bureaucrats, merchants or farmers
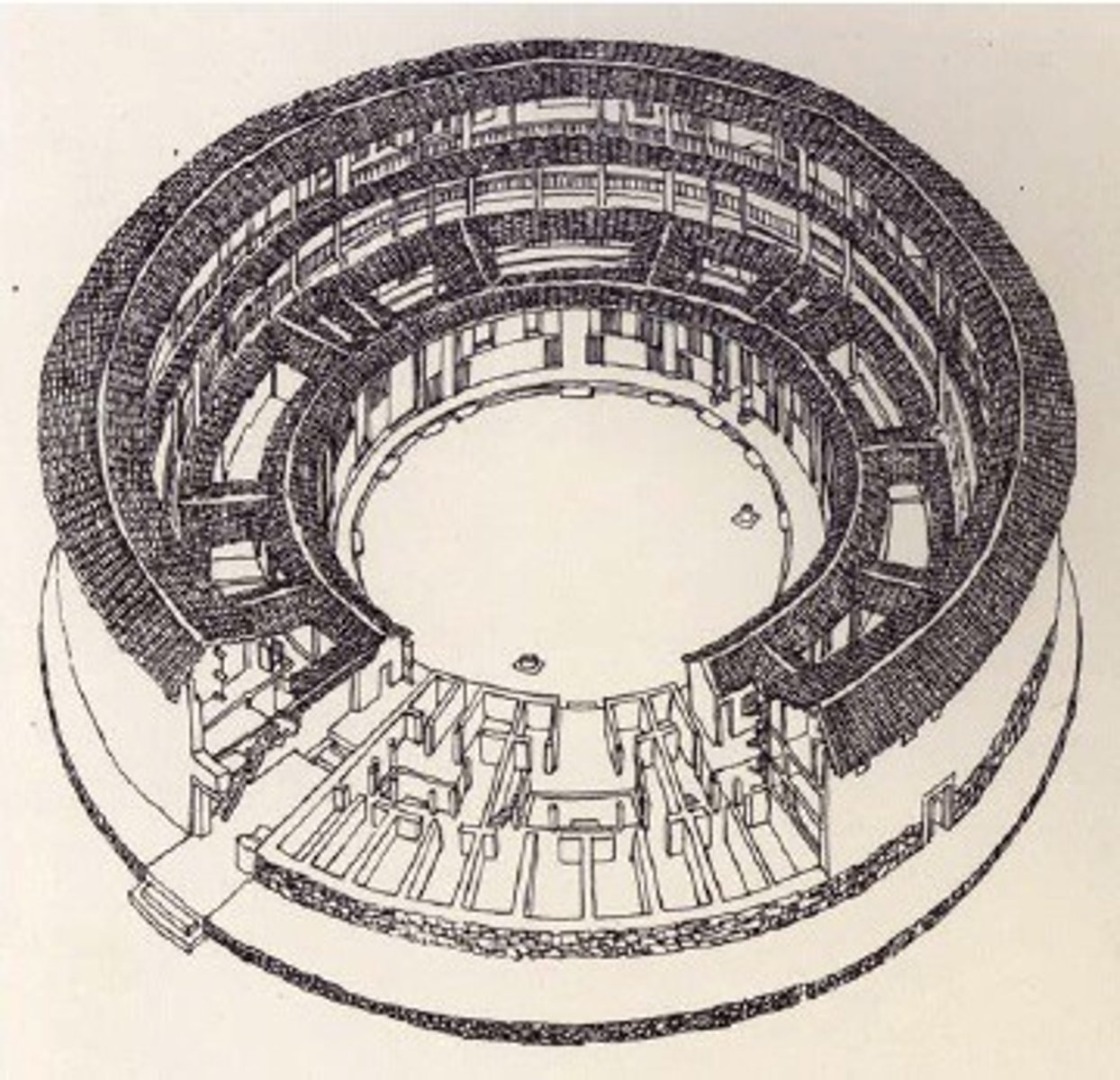
Tulou
Communal fortress for protection
Center
where the shrine for the deities and ancestors are located
also used during festivities
Two Sides
bedroom for elders
Two Wings
________ of the building known as "guardian dragons" by the Chinese for:
Junior members of the family
living room
dining room
the kitchen
Sometimes the living room could be close to the center
Imperial
Architectural Type:
reserved solely for buildings built for the Emperor of China
Yellow
Imperial Color
________ roof tiles
Blue
______ roof tiles
symbolize sky
Dougong
brackets that supports the roof
a feature shared only with the largest of religious buildings
Red
Color of the wooden columns as well as surfaces of the walls
Black
famous color often used in Pagodas
It is believed that the gods are inspired by the black color to descend to earth
South
The buildings are faced _________ because the ________ had cold winds
Religious
Architectural Type:
Buddhist architecture follows the imperial style
A large Buddhist monastery normally has a greater hall, housing statues of Buddhas
Accommodations for the monks and the nuns are located at two sides
Roof
Architectural Character:
the chief feature
ridges were laden with elaborate ornamental cresting
adorned with fantastic dragons and grotesque ornaments
Man Riding Bird, Nine Beasts, Immortal Figure, Dragon
Kinds of roof decoration
MRB
NB
IF
D
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
S-Shape (Pan Tiles)
Roofs covered with enameled tiles of _______
- Up-turned corner eaves
- Heavy ornaments
- Superposition of roofing
The most pronounced features composed of:
Pai-Lou
A Chinese ceremonial gateway erected in memory of an eminent person
Towers
square like those in the great wall, shows, influence of Mesopotamia in the use of arch and vault
Pagoda
Most typical Chinese building, usually octagonal in plan, odd number o stories usually 9 or 13 storeys and repeated roofs, highly colored and with upturned eaves, slopes to each storey.
Walls
are often constructed hollow; Bricks sometimes have a glazed coloured surface and walls are also faced with Glazed tiles or Majolica
Bricks
what material is pagoda made of
South
Houses, like temples are oriented at this place
Columns
special feature of dwelling houses
Doorways
squared header but varied in outline by fretted pendants
Pai-Lou
May be used as entrances to temples and tombs
Polygonal, Candle, Moon-gate
Types of doorway
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Windows
_____ are also rectangular in form
Rice Paper
was also used instead of glass in windows
Dougong
a system of brackets inserted between the top of a column and a crossbeam, a unique structural element of interlocking wooden brackets used to join pillars and columns to the frame of the roof
Tou-kung
cluster of brackets
Dou
Block of wood
Gong
bracket formed of a double bow-shaped arm
Yellow tiles
color of palace tiles
Red tiles
color of mandarin houses
Pagoda
Chinese style buildings
also known as common oriental traditional buildings
Ting
Pavillions
Tai
Terraces
Lou
Multistory
Curved roof
to ward of evil spirits
Palatial
Religions
Funerary
Residential
Main purposes/functions of Chinese architecture
PRFR
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Imperial buildings
Traditional residences/cave dwellings,
Religious buildings
Three building types in China
IB
TR/CD
RB
Format:
Answer, Answer, Answer
Shenyang Imperial Temple
the oldest palace in China
Forbidden City Complex
World's largest palace
Siheyuan
Chinese houses generally of one storey like temples, are constructed with timber supports filled in with brick work
Nine
Bays for Emperor
Seven
Bays for Prince
Five
Bays for a Mandarin
Three
Bays for ordinary citizen
Tombs
not of great architectural value
a) vestibule or porter's lodge on the street;
b) audience chamber and family rooms;
c) kitchen and servant's room
Windows open inside there are three principal divisions:
Bridges
the most surviving ancient bridges are made of stone and demonstrate a high level of bridge-building skill