Ecosystems - Role of Organisms & Symbiosis (2023)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
predator
An organism that hunts and eats other organisms to live.

prey
The organism that is hunted and eaten by a predator.

habitat
the place where an organism lives

producers
organisms that use sunlight directly to make food through a process called photosynthesis.

consumers
organisms that cannot make their own food and must eat other organisms for energy

decomposers
organisms that get energy by breaking down the remains of dead organisms and animal wastes.

scavengers
animals that feed on the bodies of dead organisms.

herbivore
eats producers (plant eater) - primary consumer

carnivore
meat eater - consumer

omnivore
eats both plants and meat - consumer

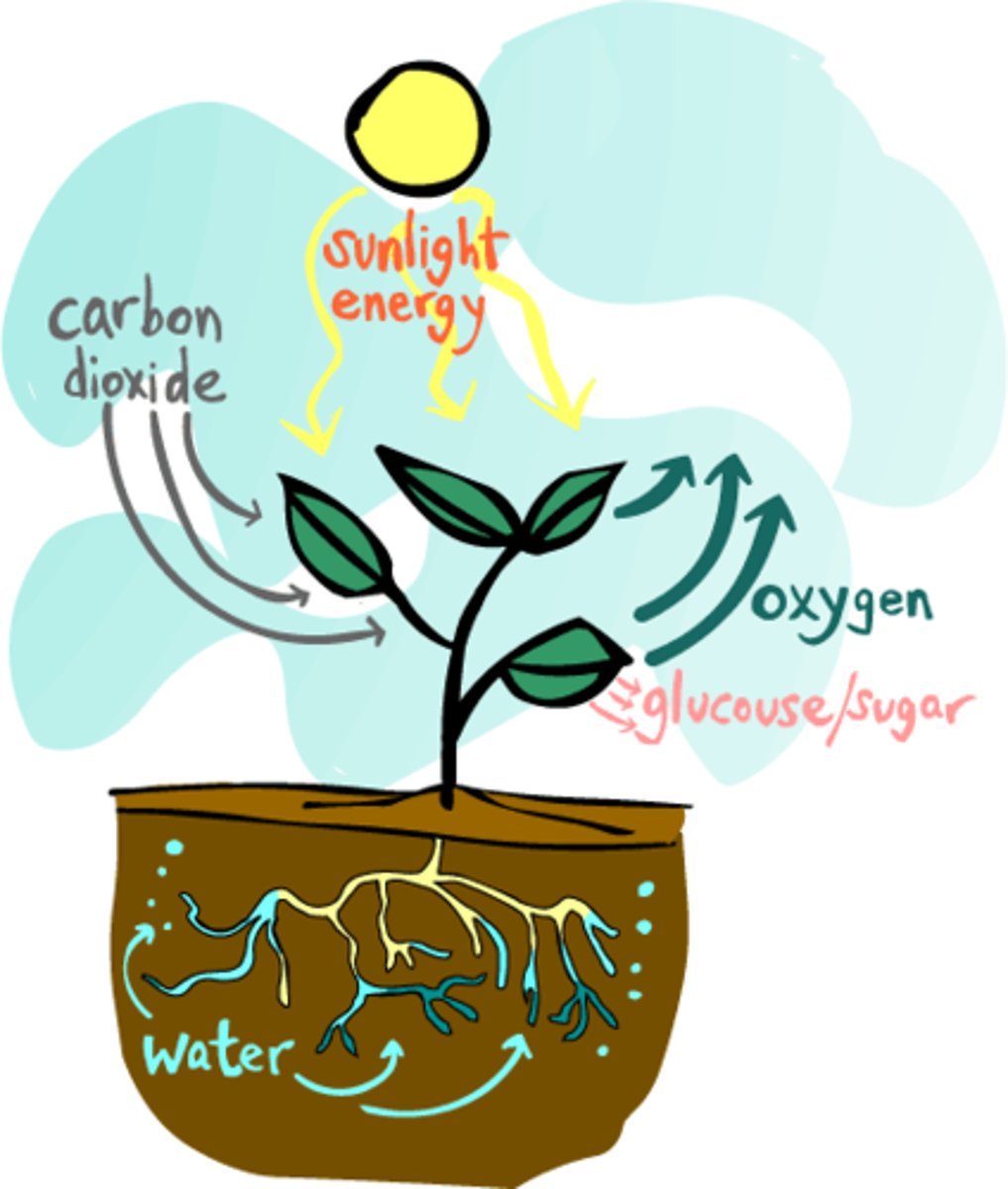
photosynthesis
plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
chlorophyll
green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis

oxygen
a gas released by plants during photosynthesis
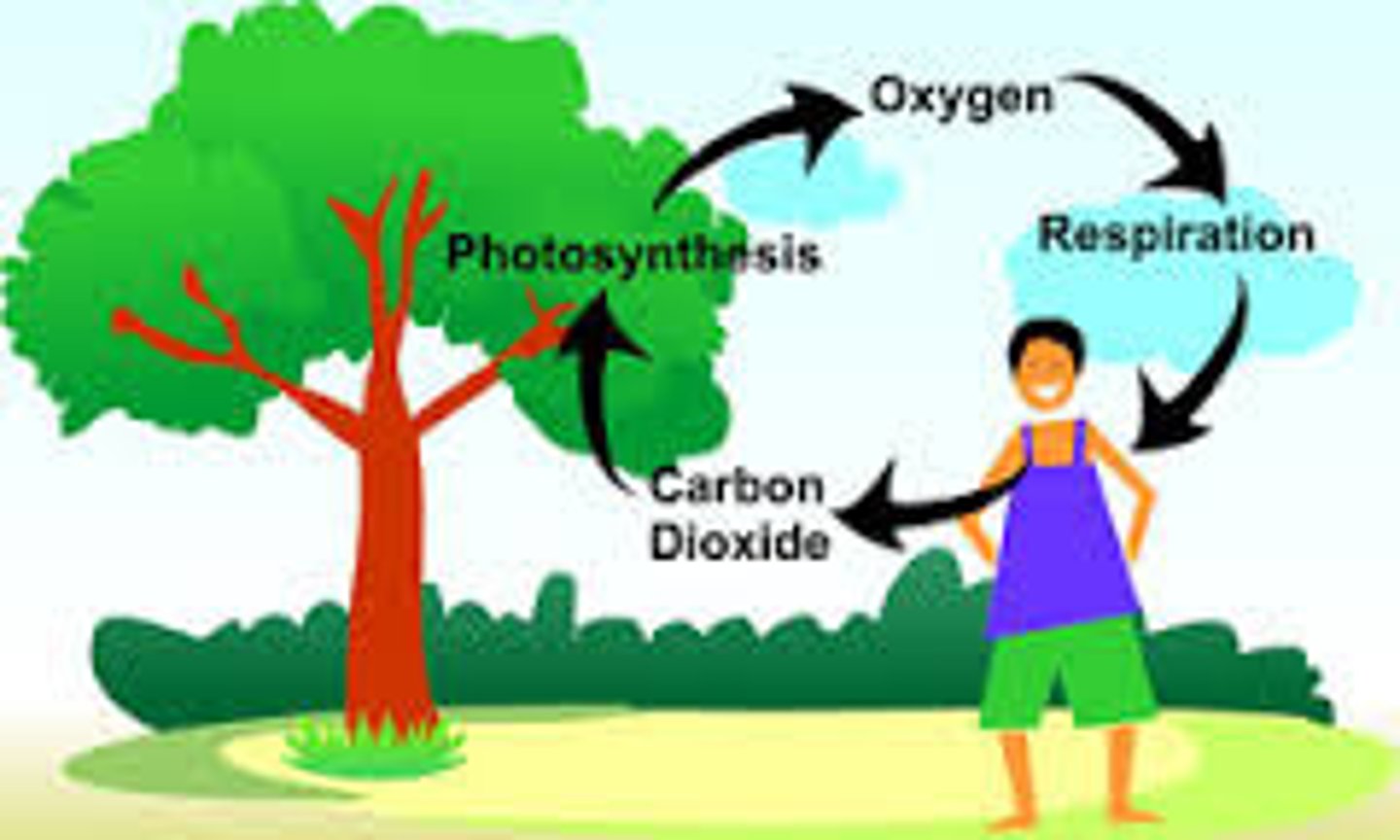
carbon dioxide
a gas taken in by plants during photosynthesis

sun
source of all energy on earth
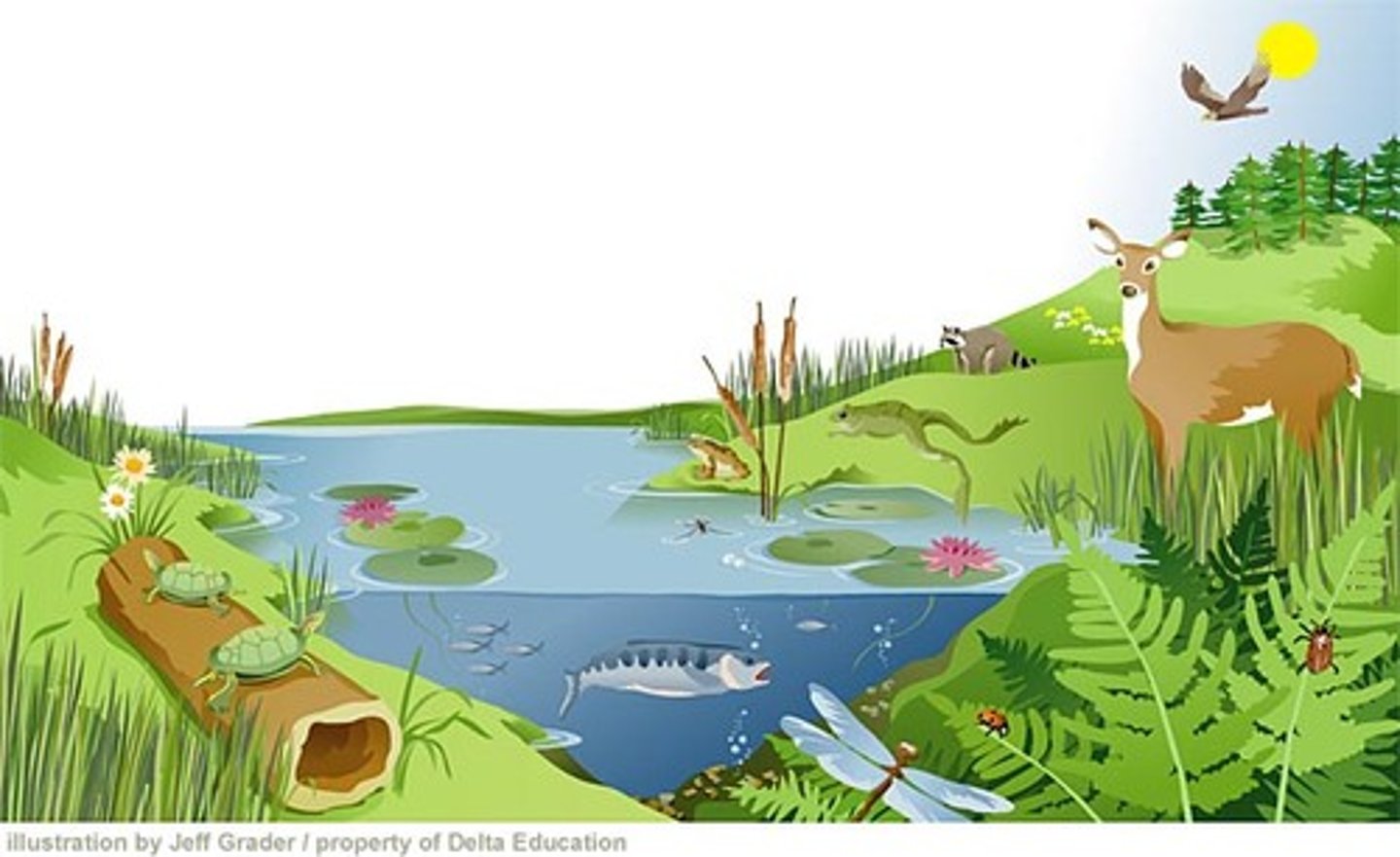
ecosystem
all the organisms that live in a place, together with their nonliving environment

niche
A role or "job" a plant or animal plays in its habitat

adaptation
a trait or characteristic that helps an organism survive
carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle
the process by which carbon dioxide and oxygen cycle among plants, animals, and the environment
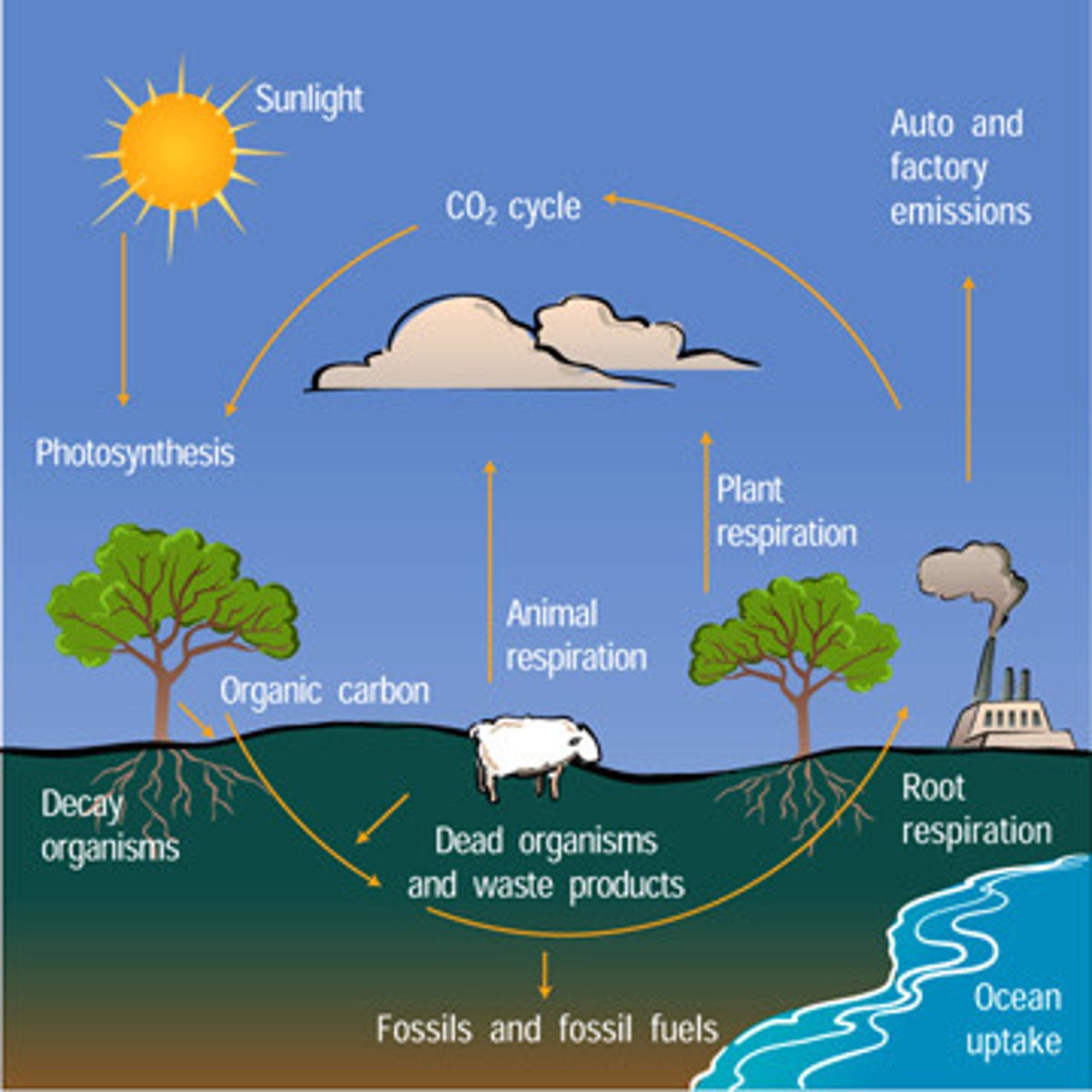
enzymes
chemical used to break down the remains of plants, animals, and wastes.
equilibrium
A state of balance
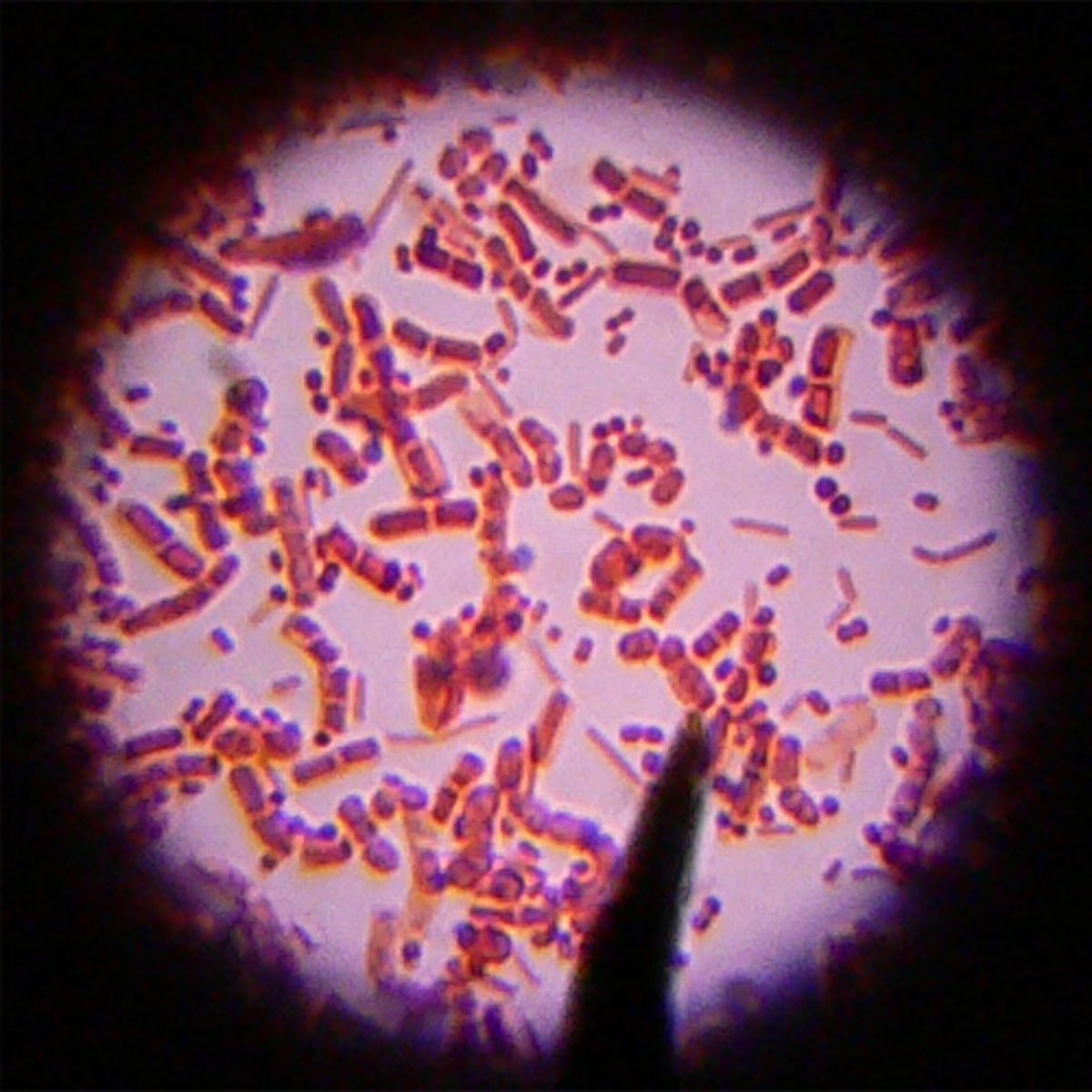
bacteria
a microscopic decomposer
symbiosis
a close relationship between two or more organisms
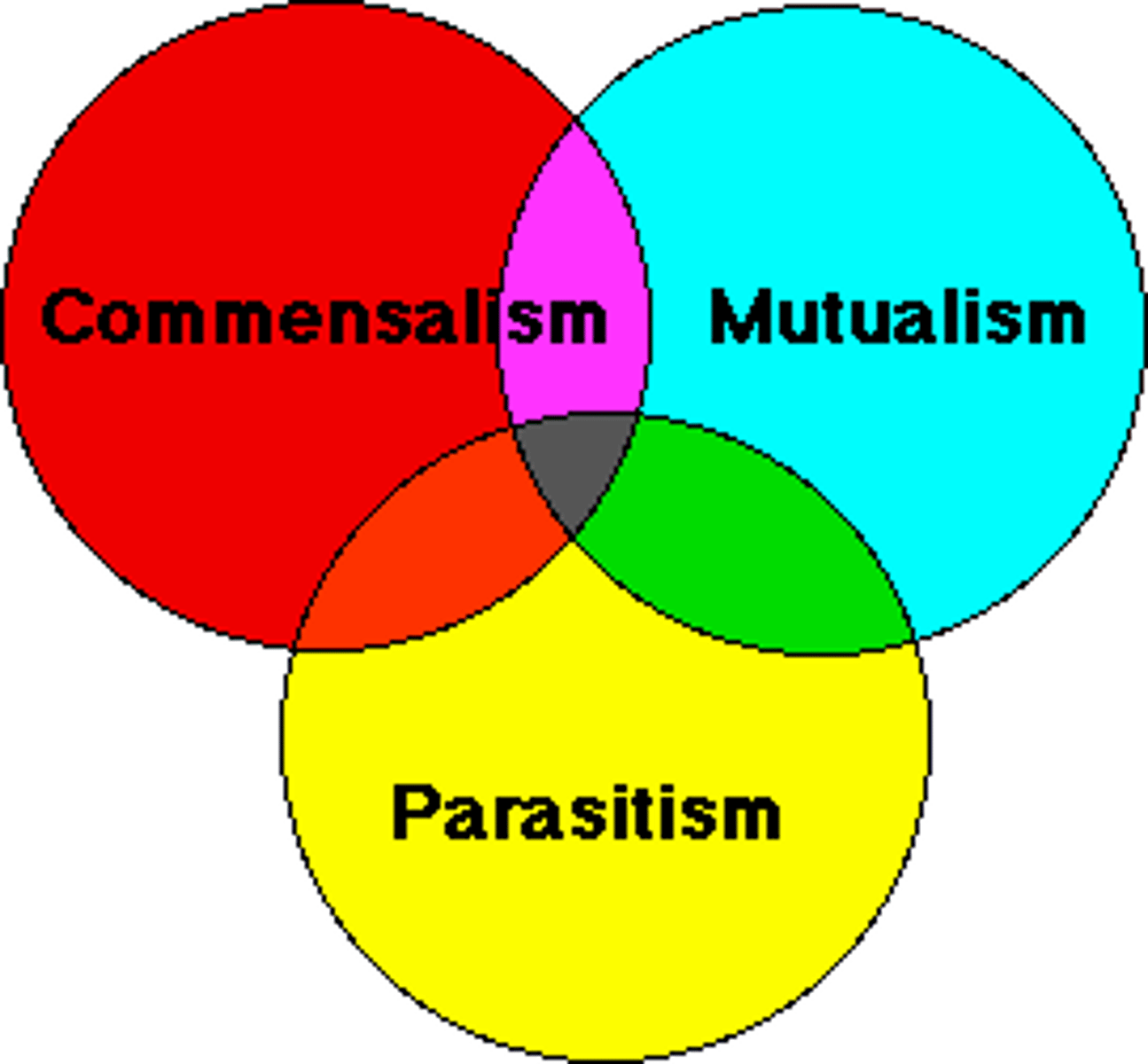
commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
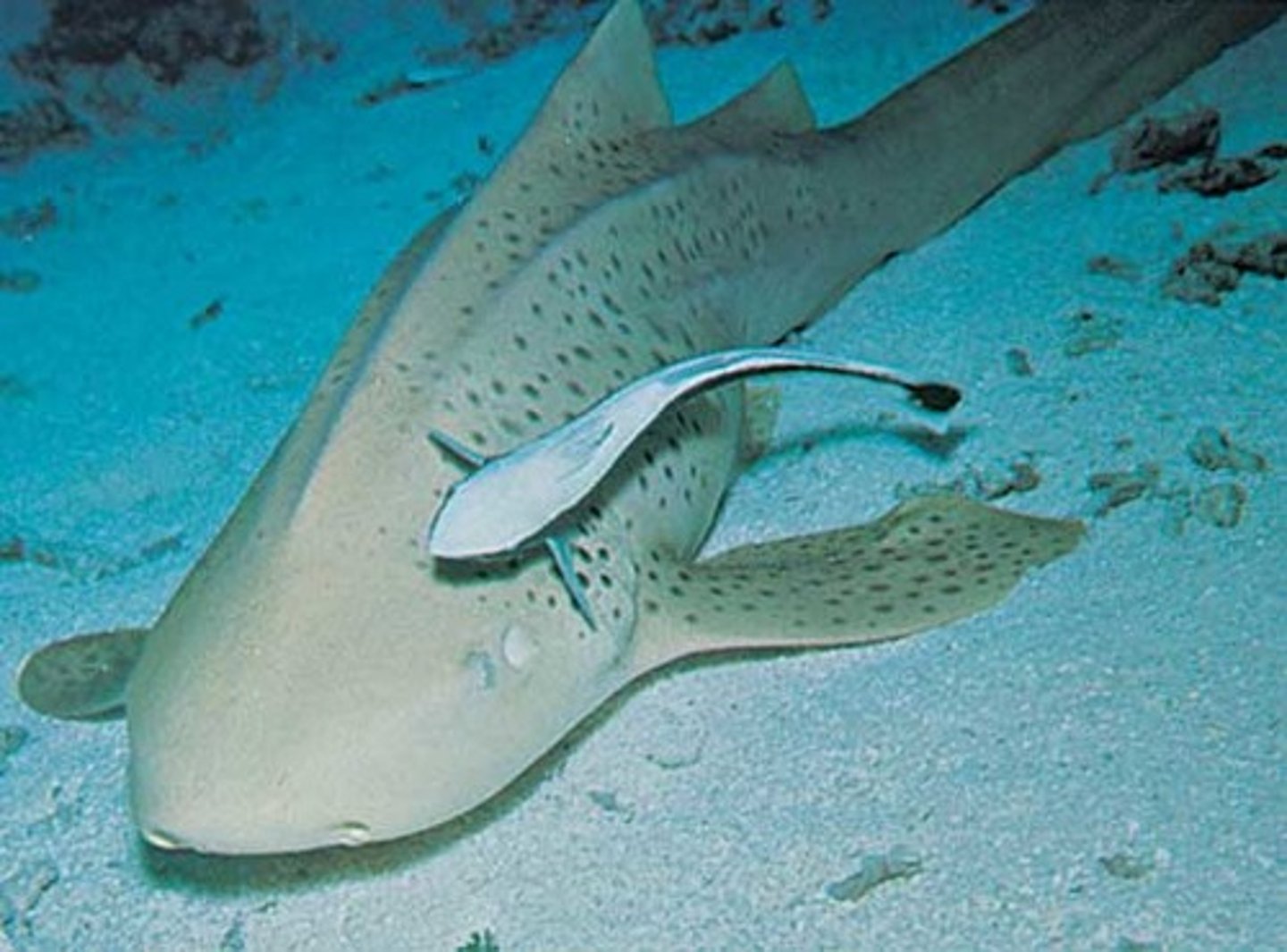

parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed

mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit

host
An organism on which a parasite lives.

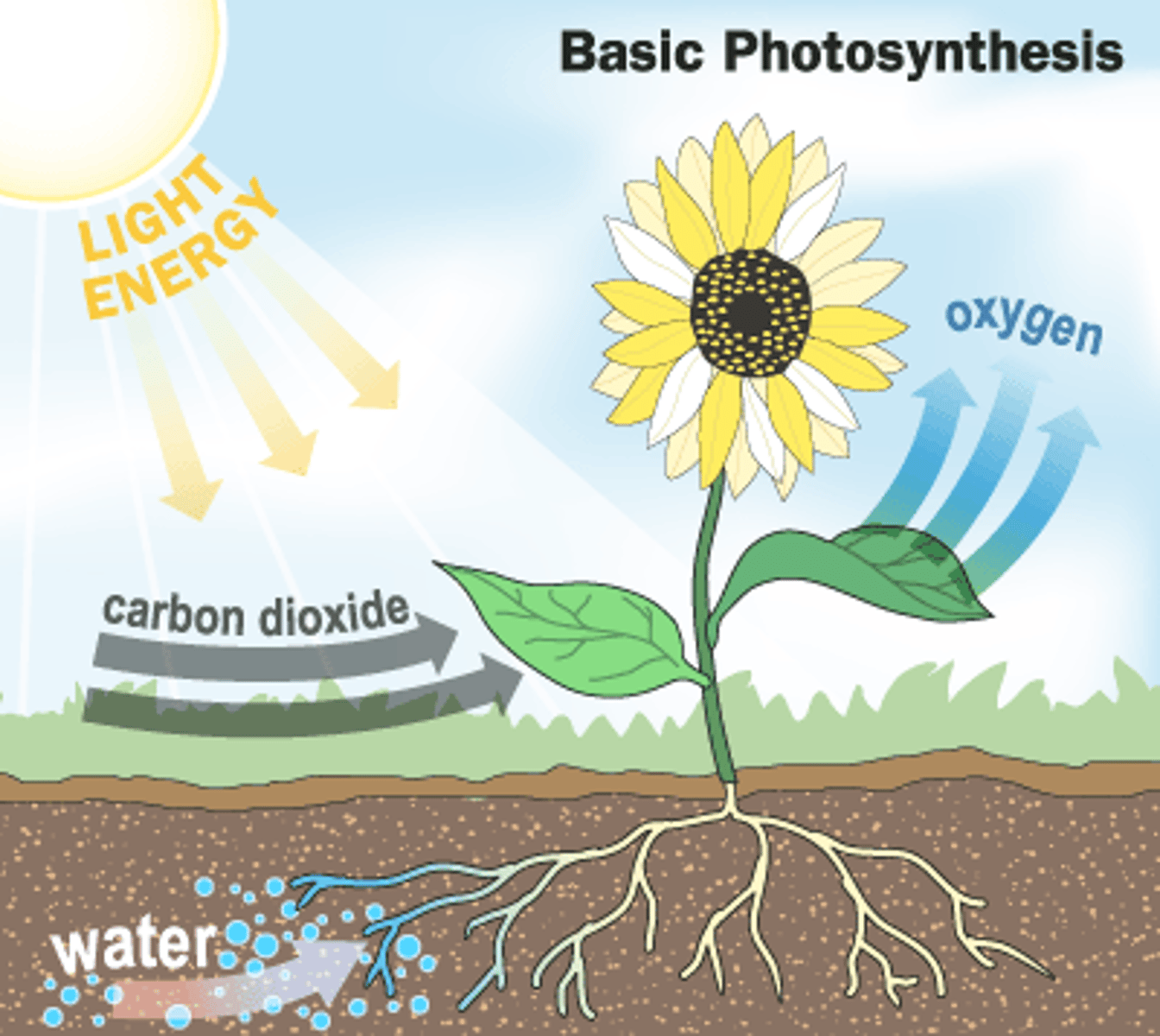
The three main substances needed for plants to perform photosynthesis.
carbon dioxide, water, sunlight
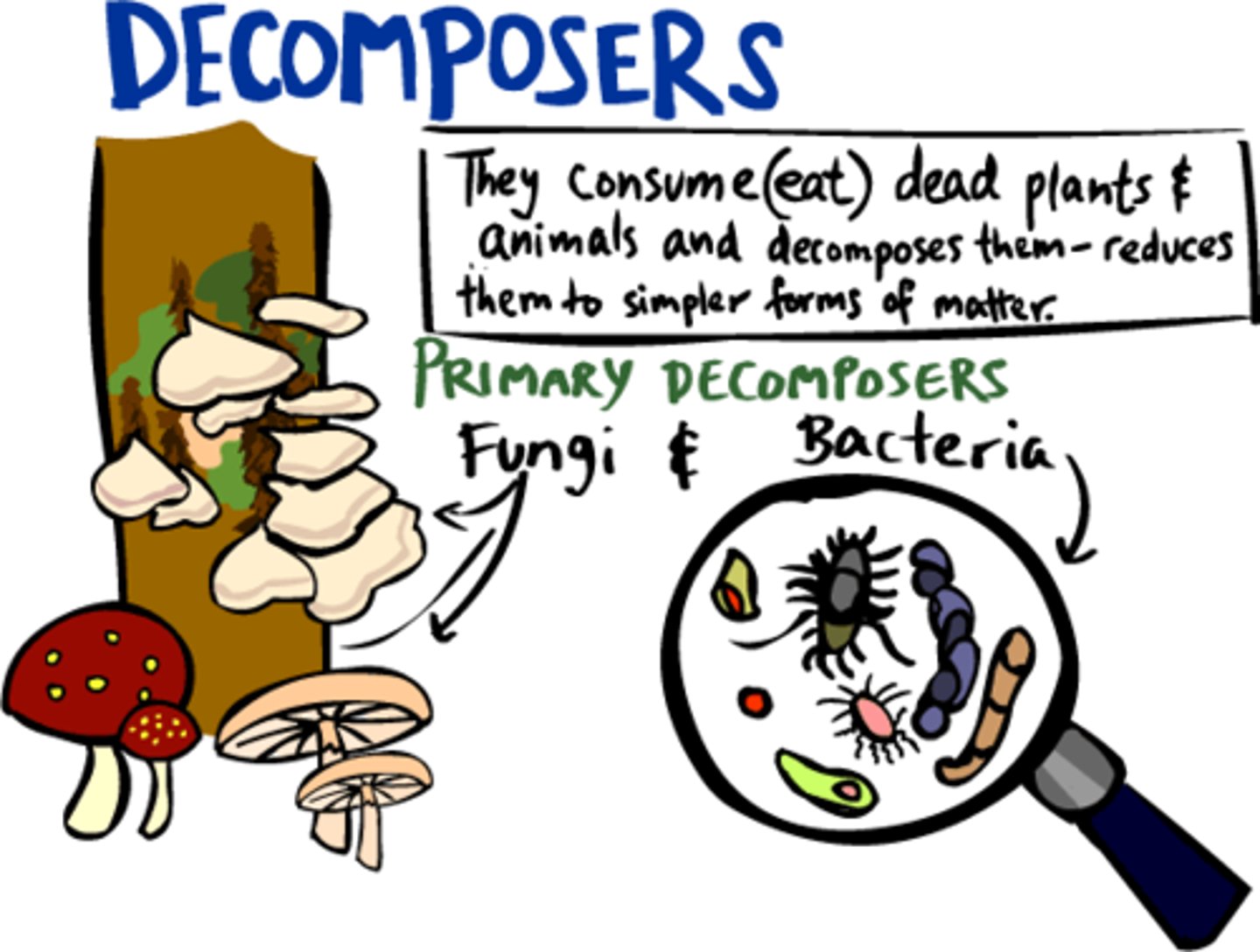
How decomposers help an ecosystem?
Put nutrients back in the soil for plants to grow.

Examples of decomposers
bacteria, mushrooms, Fungi (earhworms)
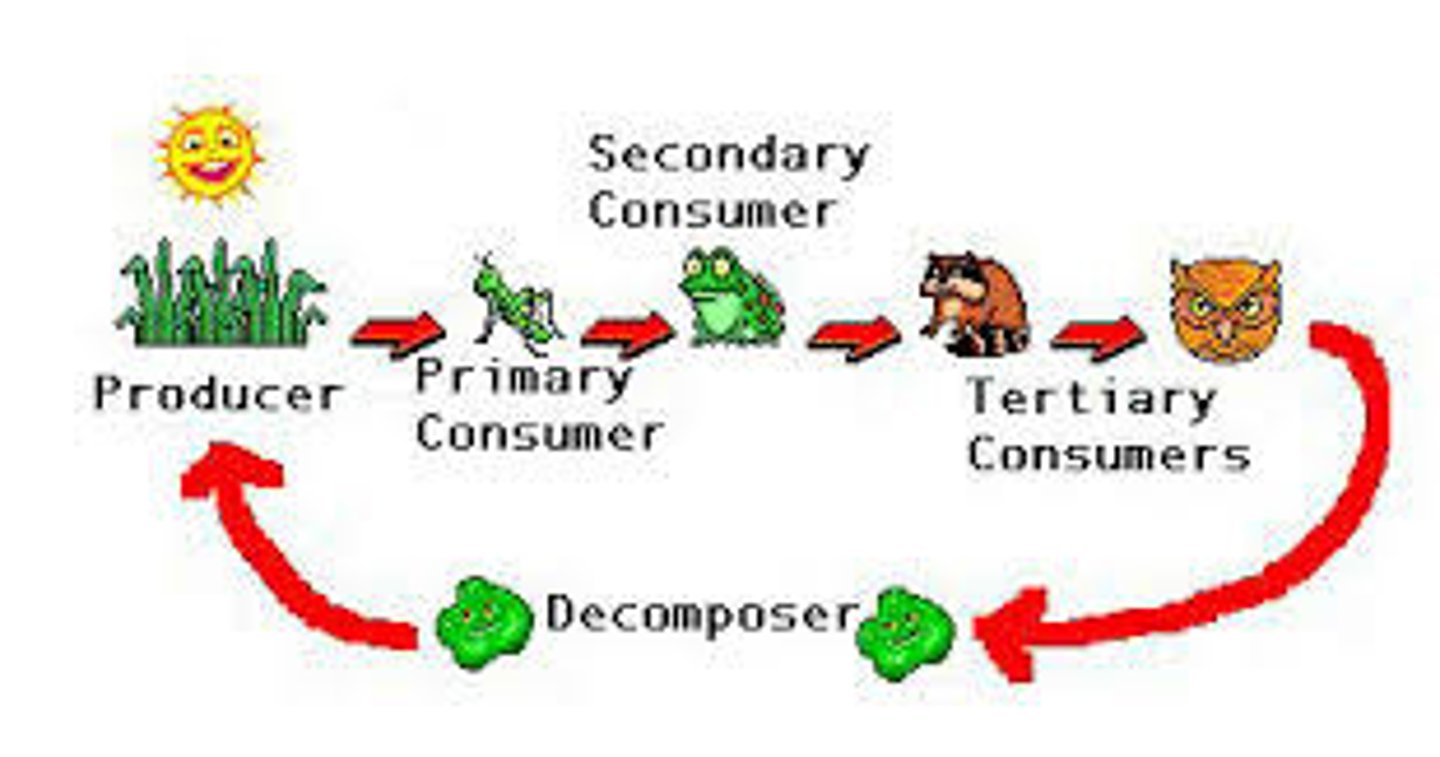
food chain
the transfer of food energy between organisms in an ecosystem
food web
a group of overlapping food chains in an ecosystem
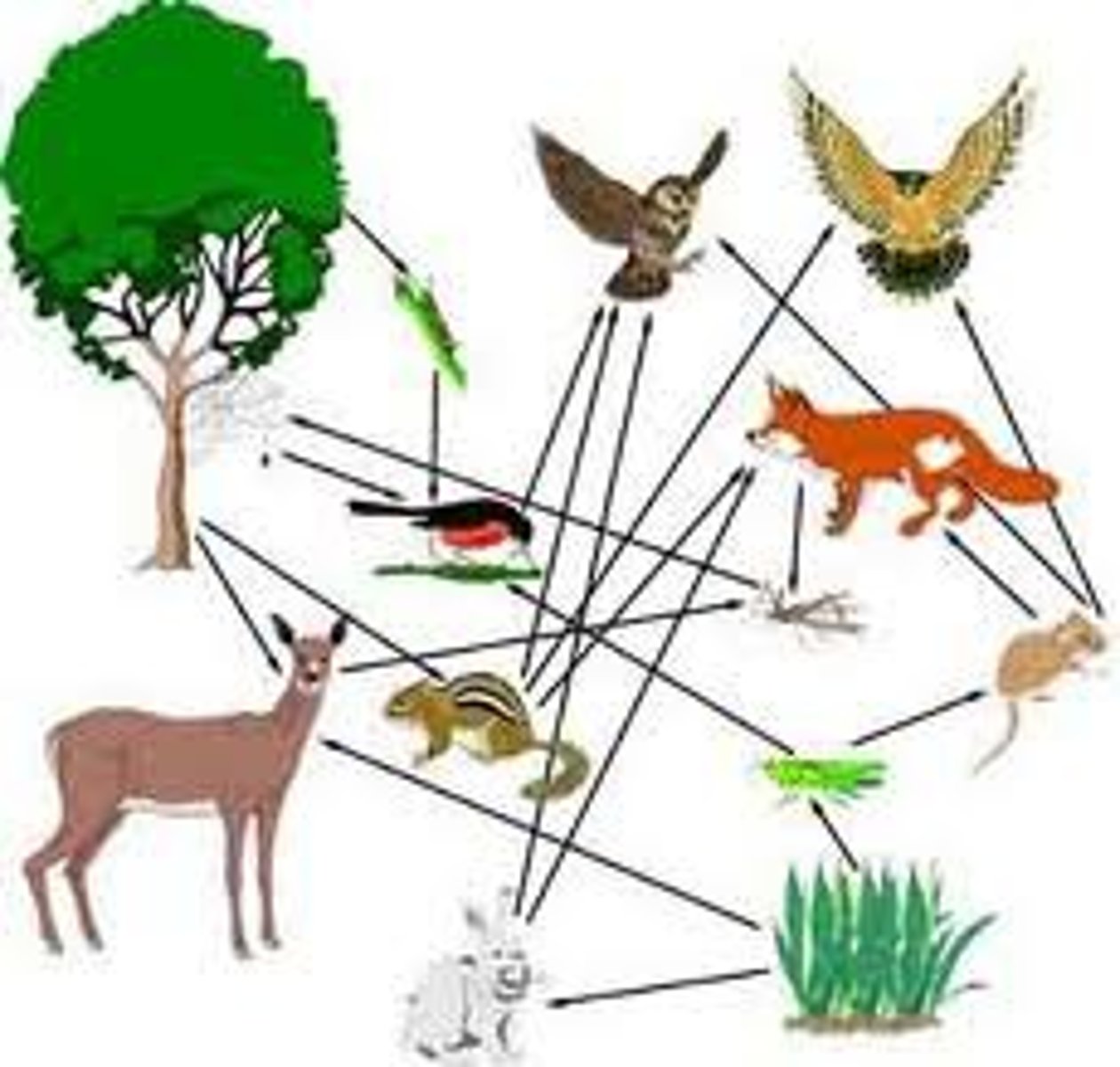
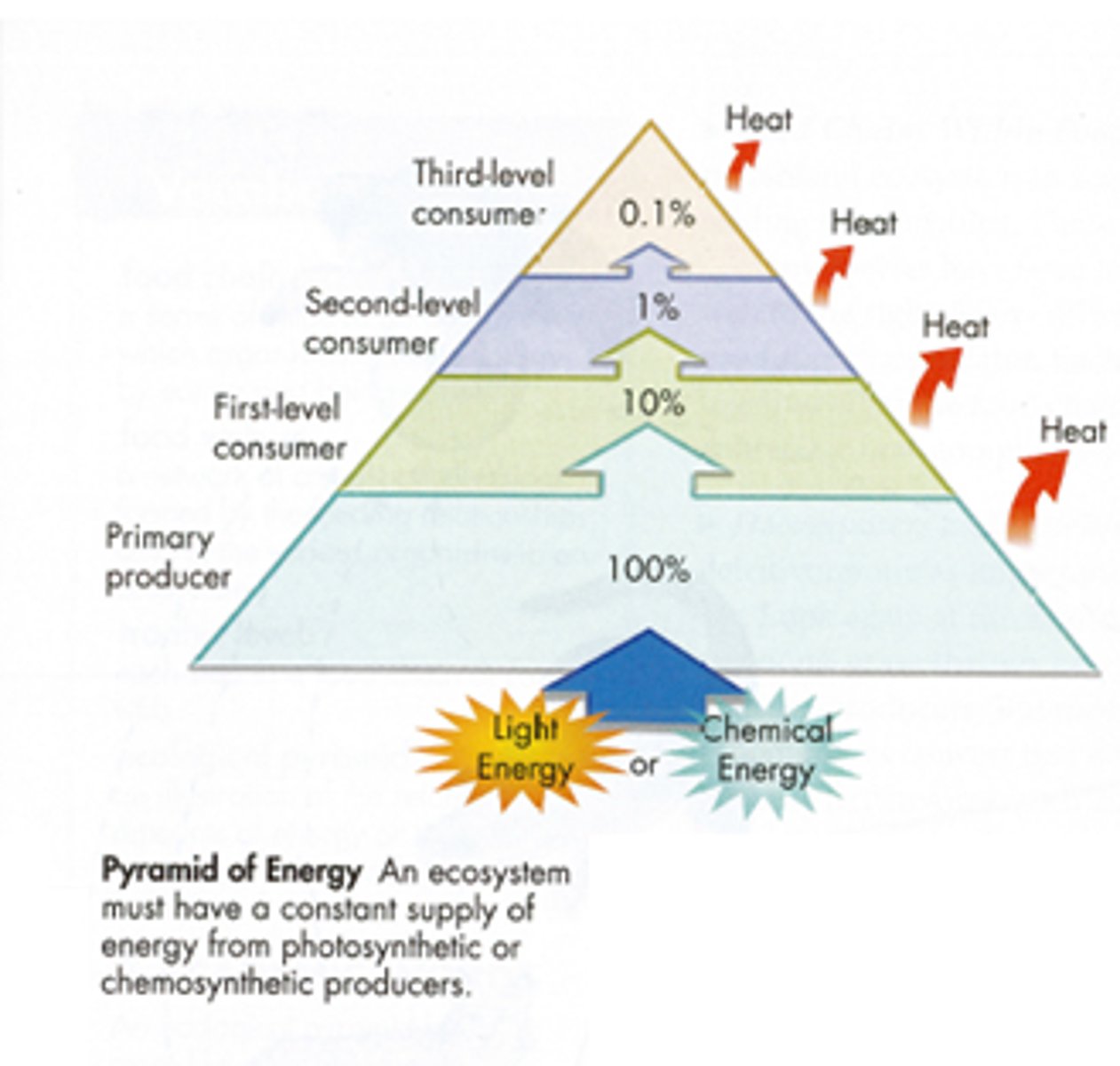
energy pyramid
A diagram that shows how much food energy is passed from one organism to the next at each level in a food chain
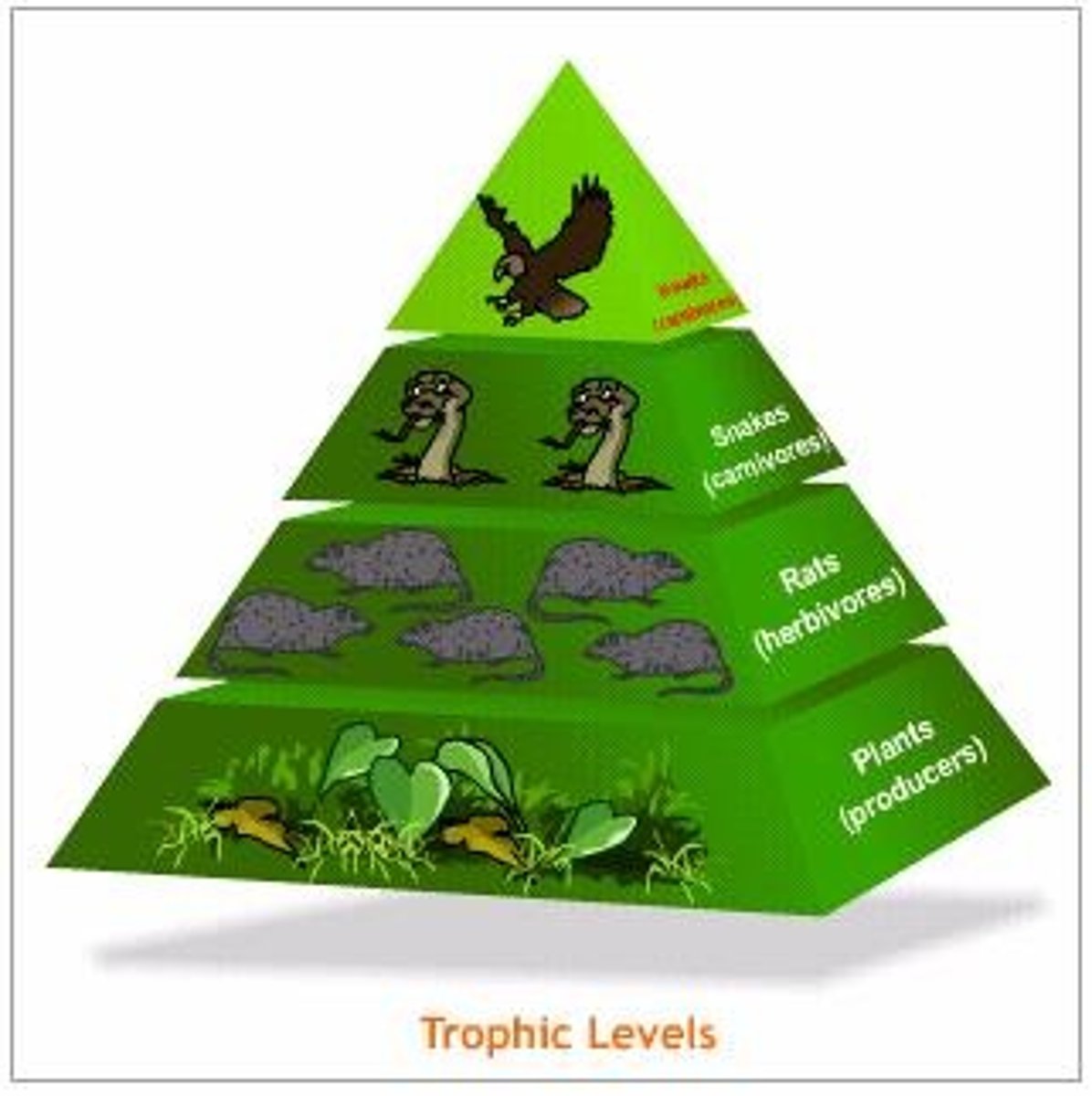
primary consumer
organisms that eat producers; also called first-level consumer

Second level consumer
organisms that eat primary consumers

How much energy is passed from one level to the next in an energy pyramid?
10%
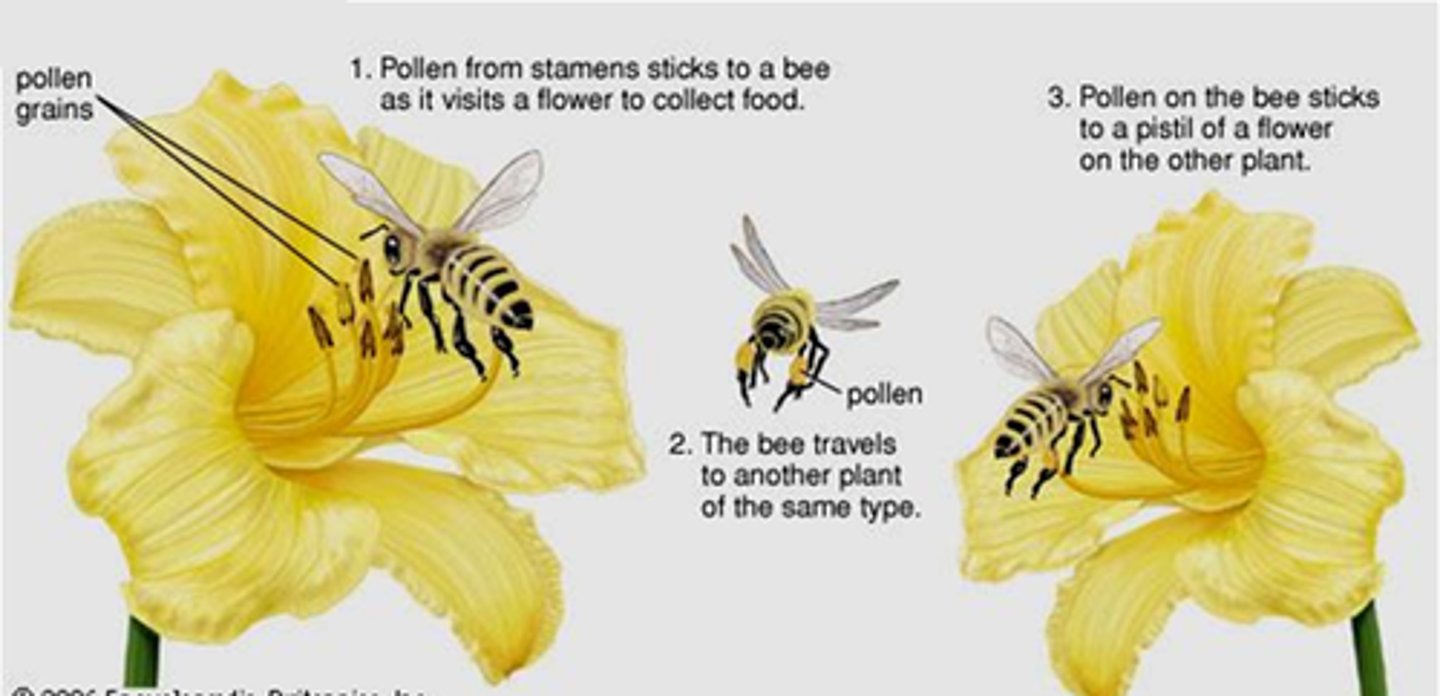
Pollination
transfer of pollen from one flower to another in order to produce seeds and have more flowers.

phytoplankton
Microscopic organisms that are producers in the ocean and supply at least 50% of oxygen on Earth
decay
to break down or decompose

In Ohio, producers make the most food during which time of the year?
Summer because it has the most daylight hours (sun)
