BBH 143 Exam 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Cell body
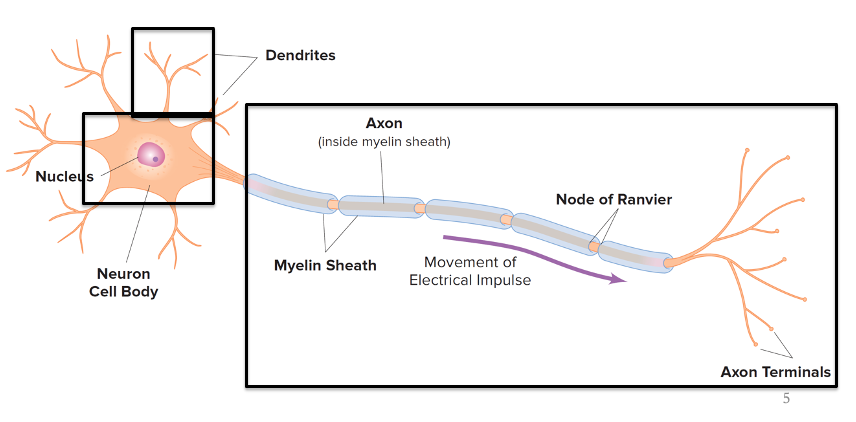
Dendrite
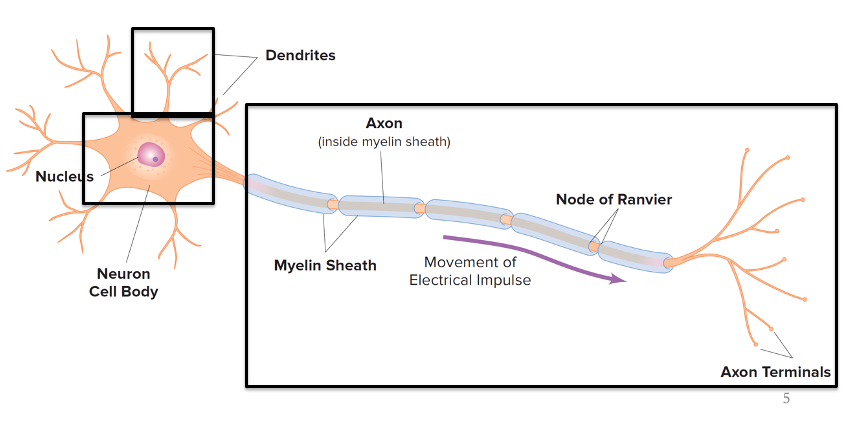
Axon
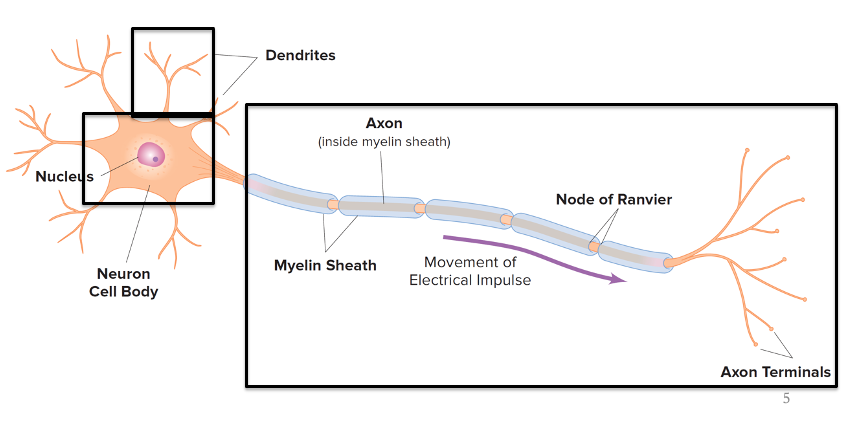
Glia
Support cells (glue) of the nervous system
Neurons
Cells that allow for rapid signaling throughout the body
Blood-Brain Barrier
Blocks big bundles (only certain small molecules, like those comprising psychoactive drugs, can cross into the brain)
Microscopic structure between blood vessels and the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord
Neurotransmission
Communication between neurons (In brain, spinal cord, nerves of the body)
Action Potentials
Electrochemical events that trigger neurotransmission
Synapse
A junction between two neurons where those neurons are communicating
Synaptic Cleft
Space between the presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron
Presynaptic Neuron
Sending the signal
Postsynaptic Neuron
Receiving the signal
Neurotransmitters
Molecules that are performing the signaling
GABA
Glutamate and Acetylcholine
Some hallucinogens block receptors
Serotonin
A factor in hallucinations, mimicked by psychedelic drugs
Monoamines
Dopamine
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
At the heart of the brain’s reward system
Reuptake
Presynaptic neuron reabsorbing NTs via transporters
Degradation
NTs are chemically metabolized (broken down) by enzymes
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves and ganglia
Includes autonomic nervous system
Prefrontal Cortex (Frontal lobe)
Higher-order cognitive functions
Reduced and dysregulated activity in addiction
Brainstem
Involved in many autonomic/homeostatic functions
Cerebellum
Involved in sequencing/coordination of movement, balance
Can be damaged by chronic alcohol use
Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway
The brain’s major reward system
Dopamine is synthesized in…
ventral tegmental area
Pharmacology
The interaction between drugs and living organisms
Or the biomedical field that studies these interactions
Neuropharmacology
The interaction between drugs and the nervous system
Psychopharmacology
The interaction between drug and cognitive processes
Specific Drug Effects
The effects of a drug depending on its presence at specific concentrations in the target tissue (direct pharmacological effects)
Non-Specific Drug Effects
The effects of a drug relating to anything except its direct pharmacological effects
Set
User’s psychological state, personality, expectations
Setting
Physical and social environments of use
Placebos
Inherit drug that doesn’t do anything
Side Effects
Unintended (usually undesired) secondary drug effects
Drug Interactions
Chemical reactions between drugs affecting physiology and/or psychology
Pharmacokinetics
The factors that affect the movement of a drug into, through, and out of the body
Time Course
The timing of the onset, duration, and termination of a drug’s effect
First-Pass Metabolism
The phenomenon in which the bioavailability of drugs is reduced
Most significant in oral administration via liver metabolism
Bioavailability
Percentage of drug that is administered that enters your bloodstrem
Metabolite
The intermediate or end product(s) of metabolism
Half-Life
The amount of time it takes for a drug’s blood concentration to be reduced by 50%
ADME
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Absorption
How does the drug get in?
Distribution
Where does the drug go?
Metabolism
How is the drug broken down?
Excretion
How does the drug leave?
Corelates
General health status
Age
Gender/Sex
Ethnicity
Pharmacodynamics
The factors that affect the relationship between a drug and its target receptors
Agonist
A drug that binds to and activates a neuronal receptor, mimics the action of that receptor’s NT
Antagonist
A drug that binds to and blocks the NT from binding to its receptor
Cross-Tolerance
Tolerance of one drug generalizing to other chemically related drugs
Behavioral tolerance
Tolerance caused by learned behavioral adaptation to a drug
Threshold
The lowest dose of a drug that has an effect
Effective dose (ED)
The amount of drug required to produce a specific response
The potency of one drug relative to another is measured by comparing EDs relative to the same specific response
High potency = Lower relative ED
ED50
The effective dose for 50% of the tested population
Lethal dose (LD)
The amount of drug required to result in death
LD50
The lethal dose for 50% of the population
Therapeutic Index (TI)
LD50/ED50
Lower = More lethal
Cocaine
A psychoactive alkaloid produced by the coca plant
Native to South America
Cocaine Hydrochloride (HCI)
Powdered Cocaine
Typically snorting or intravenously injected (dissolved)
Crack Cocaine
Mode of administration: Smoking
Coca Plant
Native to South America
Stimulant
“Upper”
A drug that generally increases activity in the CNS and/or body
Crack Baby
Children doomed to life of addiction, physical, and psychological suffering, intellectual disability
Fair Sentencing Act of 2010
Reduced crack-to-cocaine HCL sentencing disparity from 100:1 to 18:1
Cocaine Pharmacodynamics
Blocks reuptake by suppressing presynaptic transporters for monoamine neurotransmitters
Speedballs
A stimulant and depressant (usually opioid) co-administered
Carry higher risk of dependence and overdose than cocaine alone
Possible Chronic Effects of Cocaine
Insomnia
Cardiomyopathy
Septal Necrosis
Formication
Insomnia
Chronic effect of cocaine
Inability to fall or stay asleep
Cardiomyopathy
Chronic effect of cocaine
Disorder of the muscles in the heart
Septal Necrosis
Chronic effect of cocaine
Damaging the nasal septum overtime due to snorting cocaine
Formication
Chronic effect of cocaine
Break from reality; Hallucination that there re bugs crawling on your skin
Amphetamine (Proper)
Powder and pills
Benzendrine
Inhaler
Replacement for ephedrine in treating asthma
Methamphetamine
Substituted amphetamine
Powder, pills, base, crystal
Crystal Meth
“Ice”
Most common in the US
Cathinone
“Bath Salts”
Bath Salts
Cathinone
Flakka
Type of bath salt
Ephedrine
Used for ~5000 years in Chinese medicine
Replaced by Benzedrine
Summer of Love
“Speed Scene” Culminates in 1967
Pharmacodynamics of Amphetamines
Mimic monoamine neurons
Enhanced release of monoamines into synaptic cleft
Enhanced signaling at dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine synpases
Meth is more effective than Amphetamine proper
Stroke
Death of tissue in the brain due to extended deprivation of oxygenated blood
Hyperthermia
Abnormal inability to cool oneself down
Meth Mouth
Severe tooth decay/loss
Meth Sores
Open wounds on skin
Caused by formication or injection
Therapeutic Uses of Amphetamines
Depression
Weight loss
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder marked by extreme fatigue during the day and involuntary lapses into sleep
ADHD
Neurodevelopmental disorder variably marked by excessive inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and/or emotional dysregulation
Explain the relationship between the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, and dopamine in the context of the mesolimbic reward pathway
The mesolimbic reward pathway is the brain’s major reward system. Dopamine is synthesized in the ventral tegmental area, also the brainstem, which signals the nucleus accumbens, also the deep forebrain structure. This activates both during and anticipating pleasurable activities.
Explain why drugs with a lower therapeutic index (TI) are more likely to kill you, using the terms LD50 and ED50
Drugs with a lower TI are more likely to kill you because you calculate TI by dividing LD50 by ED50. If a drugs LD50 is 10 grams and ED is 5, that means the TI is 2. But a drug that has a LD50 of 20 and a ED of 2, then the TI is only 10. So the lower the TI, the lower the gap between an effective dose and a lethal dose.
Explain why there has been a rise in reported cocaine-related fatal overdoses since 2015
Cocaine is being laced with potent opioids, like fentanyl. Speedballing
Provide two reasons why amphetamines were preferred as stimulants over cocaine during combat in WWII
Cocaine has a very short half-life
Amphetamines are easier to swallow
Identify and explain one potential cause of meth sores
Formication; Hallucination that there are bugs crawling all over your skin → Scratching and itching at skin until cuts/wounds form.