Chapter 3: Market Research
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
marketing research
= focused study of a specific problem or opportunity
Suppliers of marketing research
Marketing research firms
Company owned research department
Universities, students, professors
Marketing information system
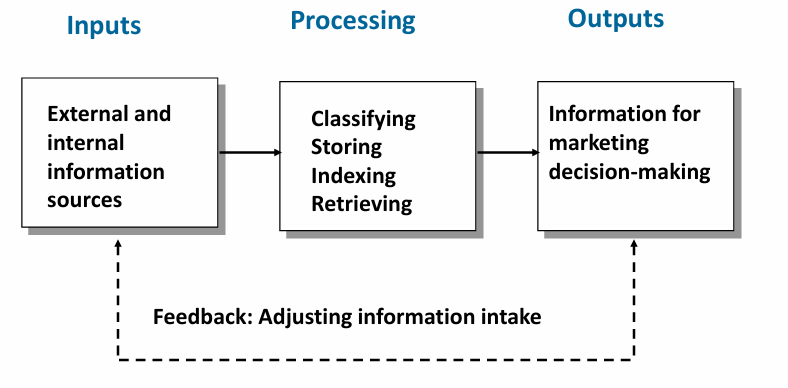
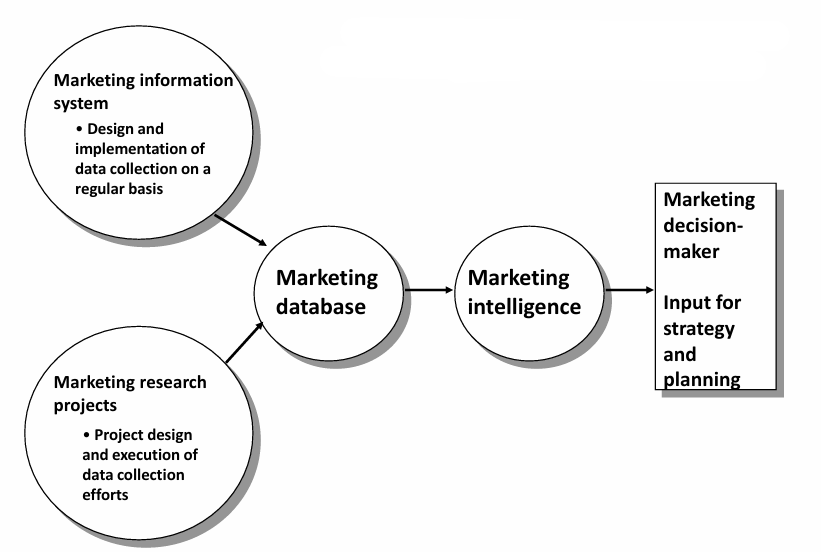
Combining marketing research and marketing information system
Marketing research process: 5 steps
1) Problem and objectives
2) Develop research plan
Data sources
Research approach
Research instruments
Sampling plan
Contact methods
3) Collect the information
4) Analysis
5) Presentation
Marketing research process: Step 1: Problem & Objectives
Too broadly ←> too narrowly
Influences the cost of the research
3 types of research projects
Exploratory = preliminary data, explain the problem (Qualitative)
Descriptive = describe magnitutes (Quantitative)
Causal = test cause - effect
Marketing research process: Step 2: Develop the research plan: Data sources
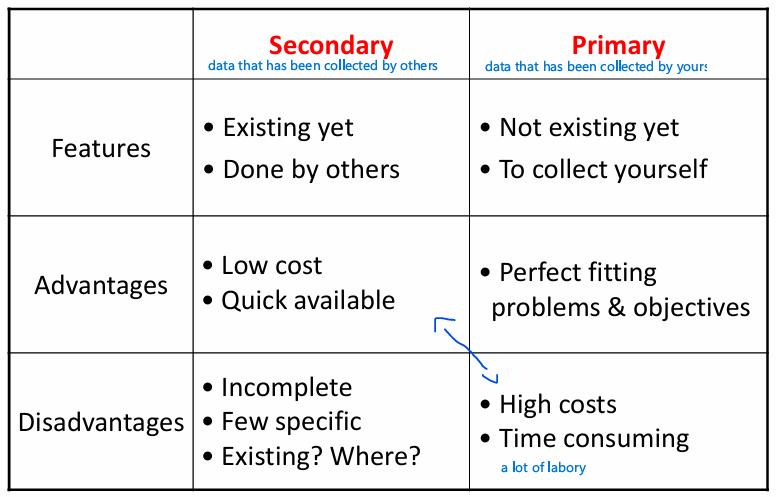
Marketing research process: Step 2: Develop the research plan: Research approach
Structured ←> not structured
direct < - > indirect
Approaches
1) Observation
Observe people / consumers
Human or mechanical observers
2) Focus groups / Depth interviews
Face to face, personal
Moderated by trained interviewer
Exploratory research
3) Survey research
Quantitative research
Descriptive research
4) Experimental research
Cause and effect relationships
Groups subjected to different treatments / conditions
Marketing research process: Step 2: Develop the research plan: Research instruments
Questionnaire
people must understand the question
must be willing to answer
must be able to answer
know the answer
remember the answer
able to express it in words
Mechanical instruments
virtual environment
eye camera / eye tracking
psychogalvanometer → around peoples wrist and measures the tension on your skin
traffic counter
Marketing research process: Step 2: Develop the research plan: Sampling
Population = anyone who is a potentially valid participants to the study
Sample = actual participants
Non-probability sampling
Convenience sampling
Judgement sampling
Probability sampling
Random sampling = complete frame and equal probability of being selected
Cluster sampling = heterogenous groups; random selection of clusters
Eg. random sample in a certain UGent home
Stratified sampling = homogenous groups = strata; random selection within each stratum
do a survey of only Indian people
Practice
Lack of sampling frame = no list of population
Probability sampling impossible
Sample size = f(time, budget, rules of thumb)
Measurement scales
Nominal / Dichotomous
Yes/No - Female/Male
Ordinal / Ranking
Rank five attributes in order of importance
Interval
equal intervals between scale points
What is your monthly spending on food (0-100, 101-200…)
Ordinal by nature
How important is taste? 1-2-3-4-5
Ratio
From the 10 L of soft drink, how many litres are brand X?
Specific attitude measurement scales
Semantic differential
bipolar
poles with opposite meaning
Eg. bad quality ————————— good quality
Likers = interval scale assessing the degree of agreement with statements
1 (totally not agree), 2 (not agree), 3 (neutral), 4 (agree), 5 (strongly agree)
Marketing research process: Step 2: Develop the research plan: Contact methods
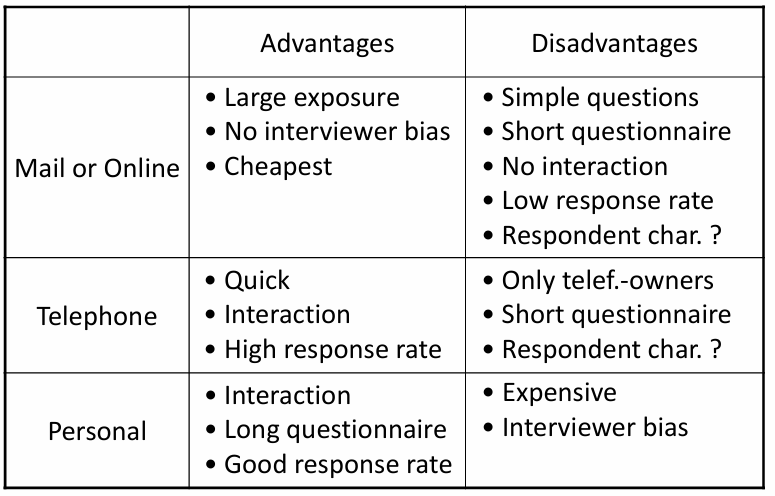
Marketing research process: Step 3: Collect information
field work
Marketing research process: Step 4: Analyse the information
prepare the data
prepare data sheet
data input
data processing
interprete the results
Marketing research process: Step 5: Present the findings
written report
oral presentation
What is a good marketing research
uses scientific and valid methods
follows a creative approach
uses multiple methods
uses models and data that are interdependent
provides a good value to cost ratio