chapter 5 review cog
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Memory
the process of retaining, retrieving, and using information about stimuli, images, events, ideas, and skills after the original information is no longer present
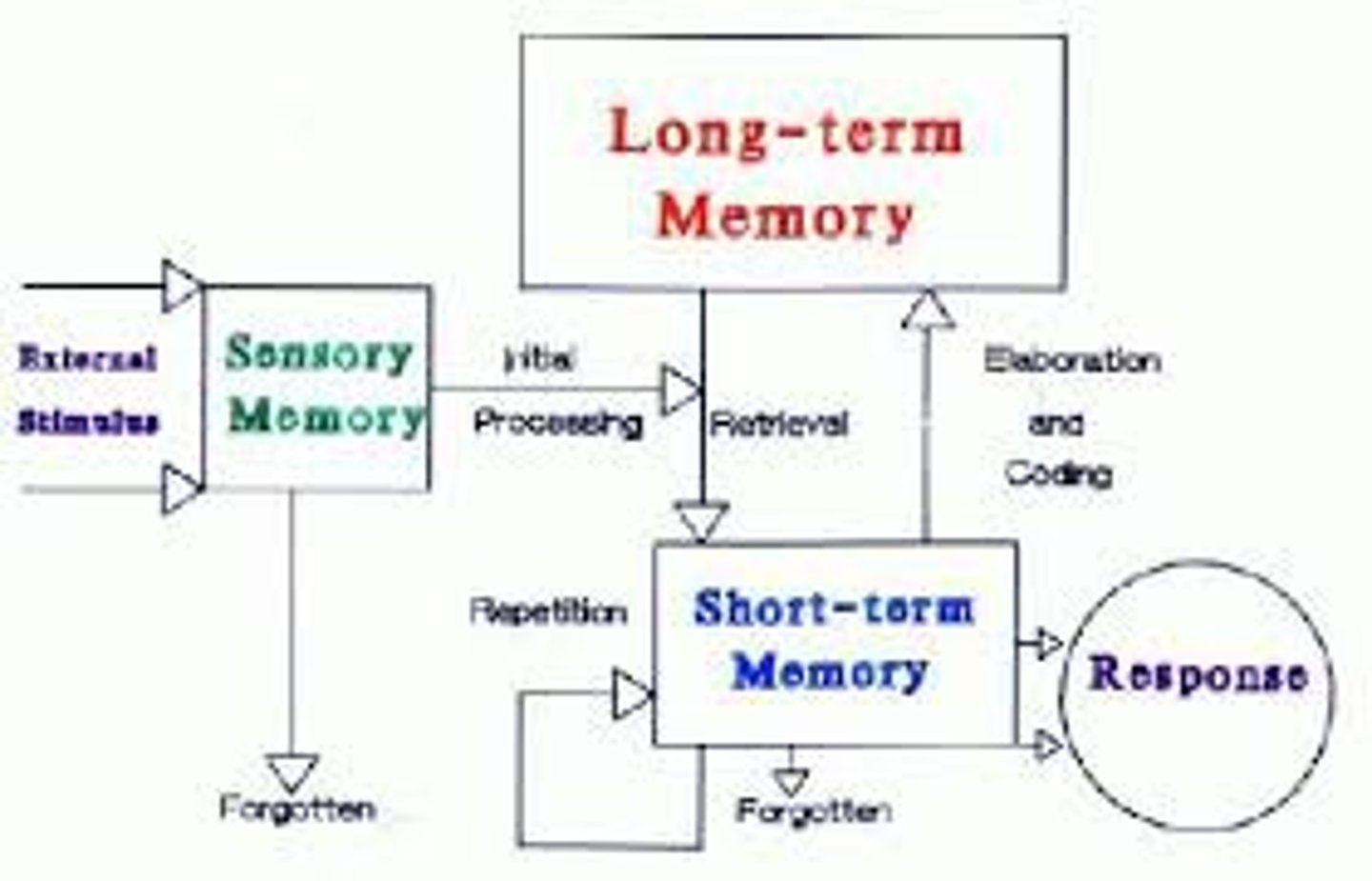
Modal model of memory
a model of how different types of memory operate and interact
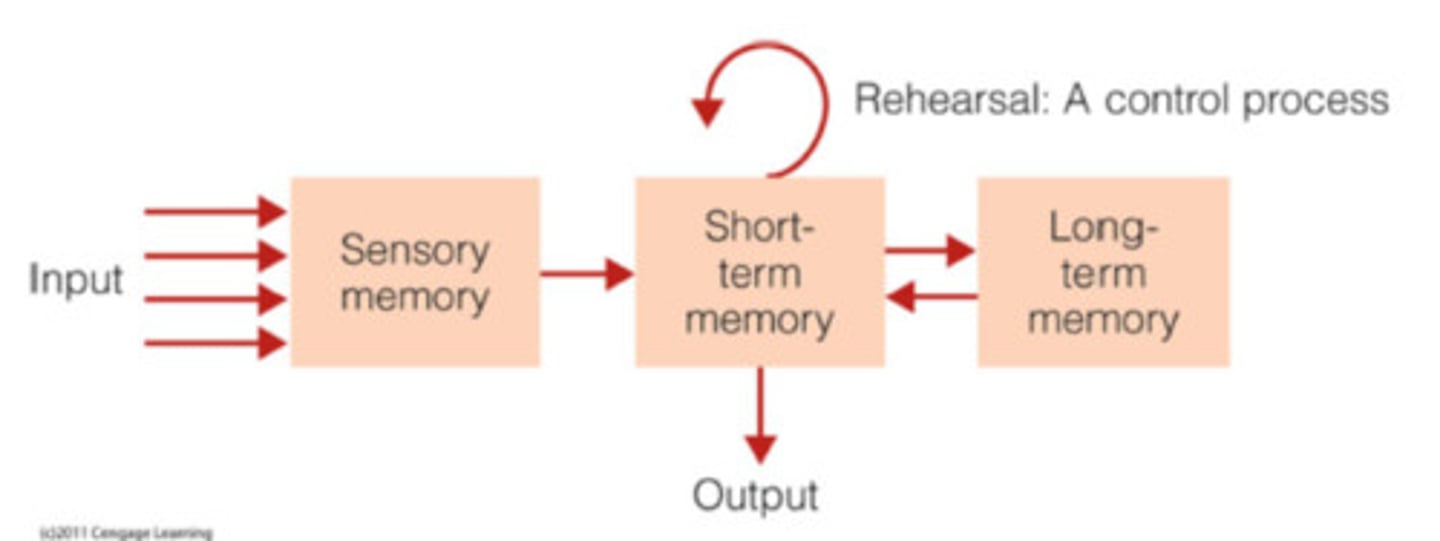
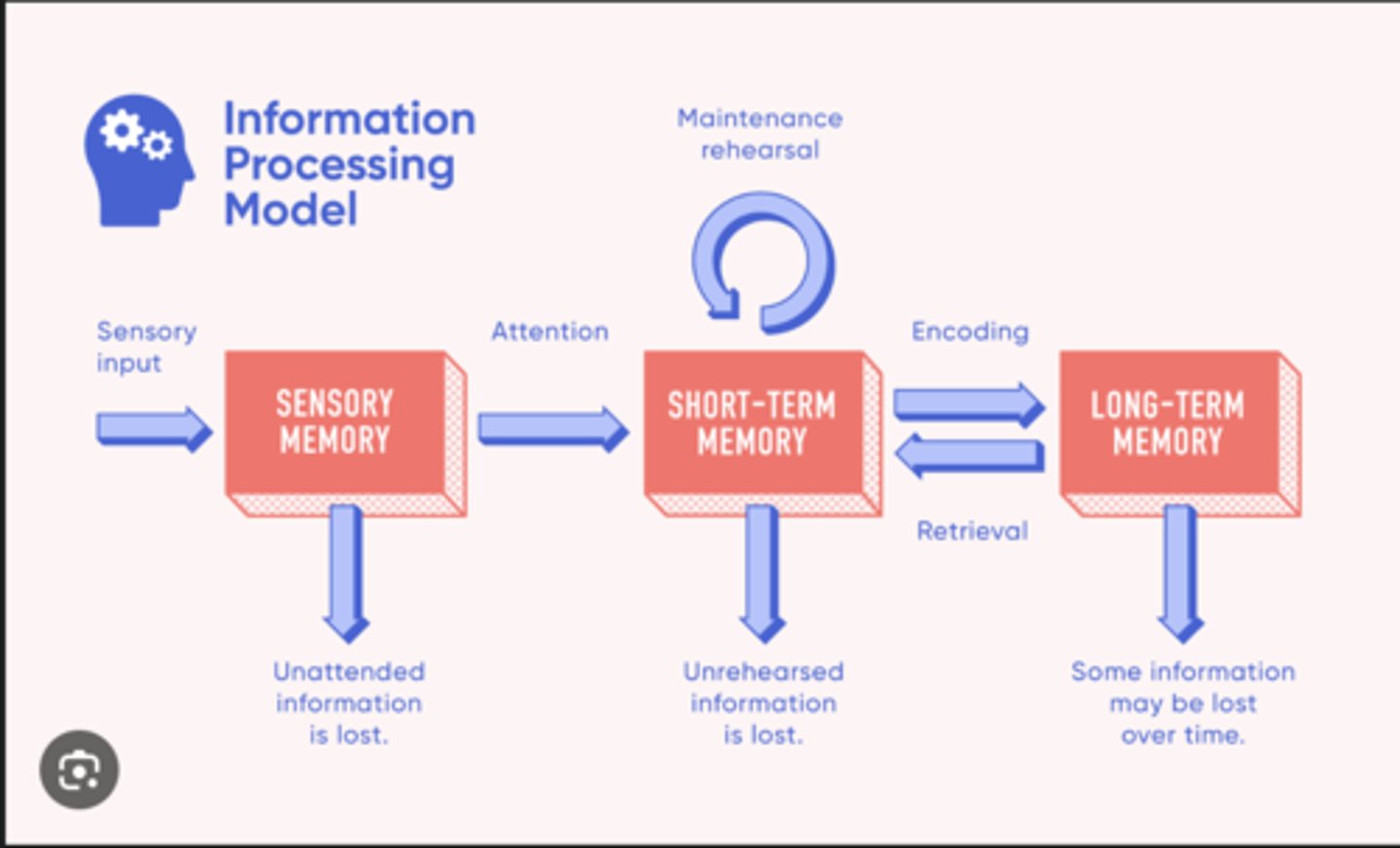
Information processing modal
that describes memory in terms of information flowing through a system
Structural features
three types ( or stages) of memory
Short term memory
holds a limited amount of information for up to 20 seconds
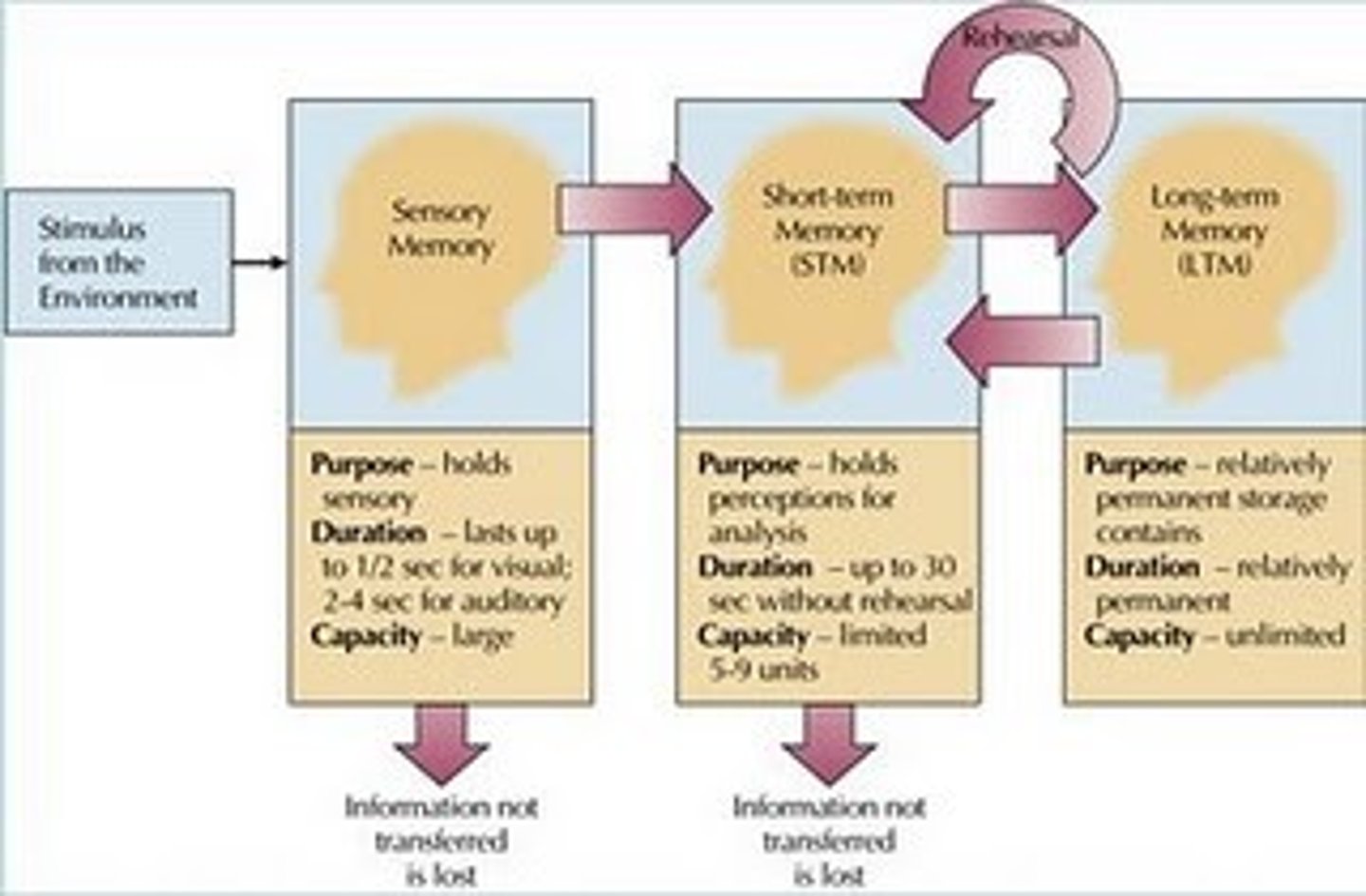
Long term memory:
holds a large amount of information for many years
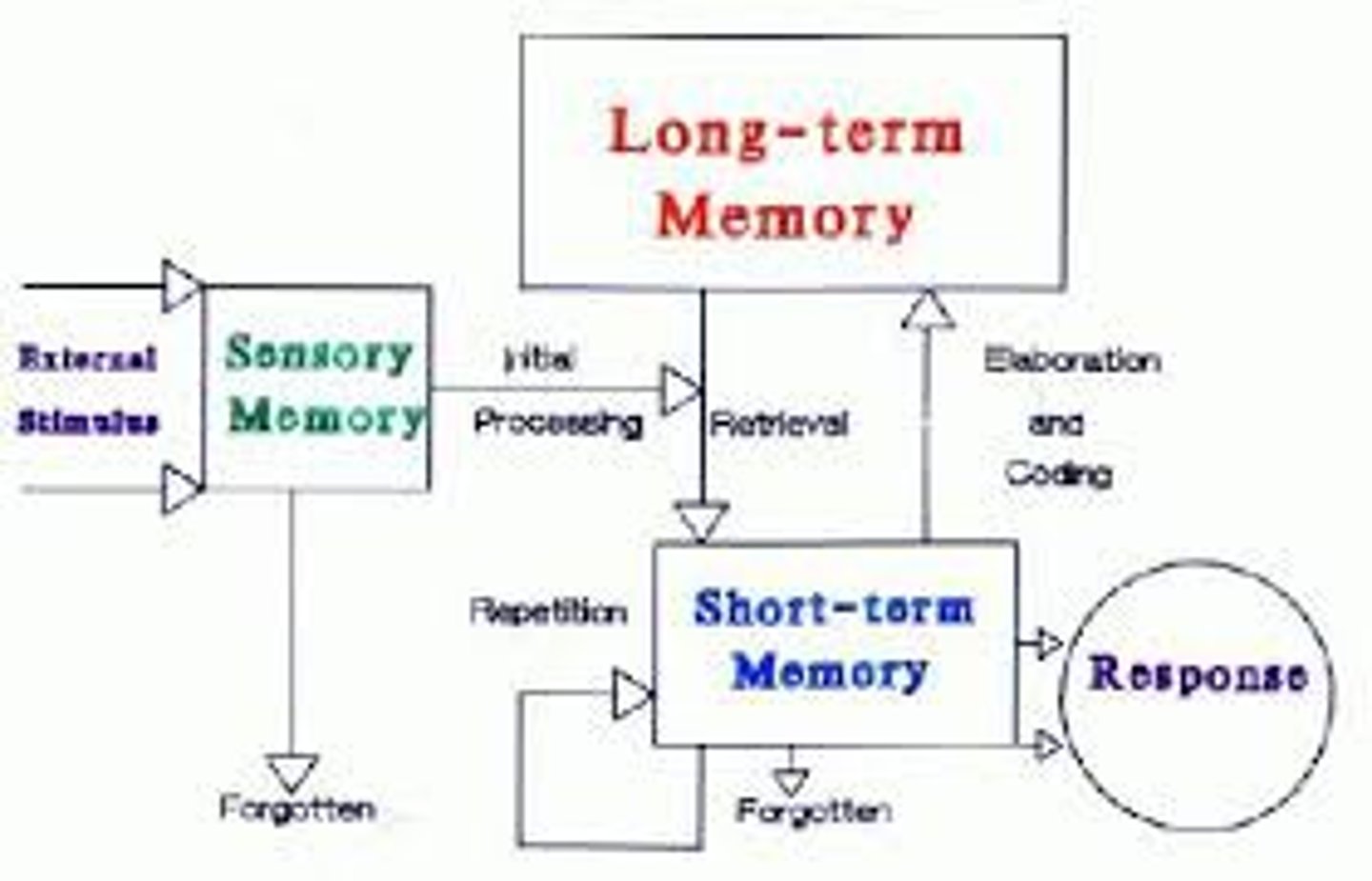
Control processes
three dynamic processes that can be controlled by the person
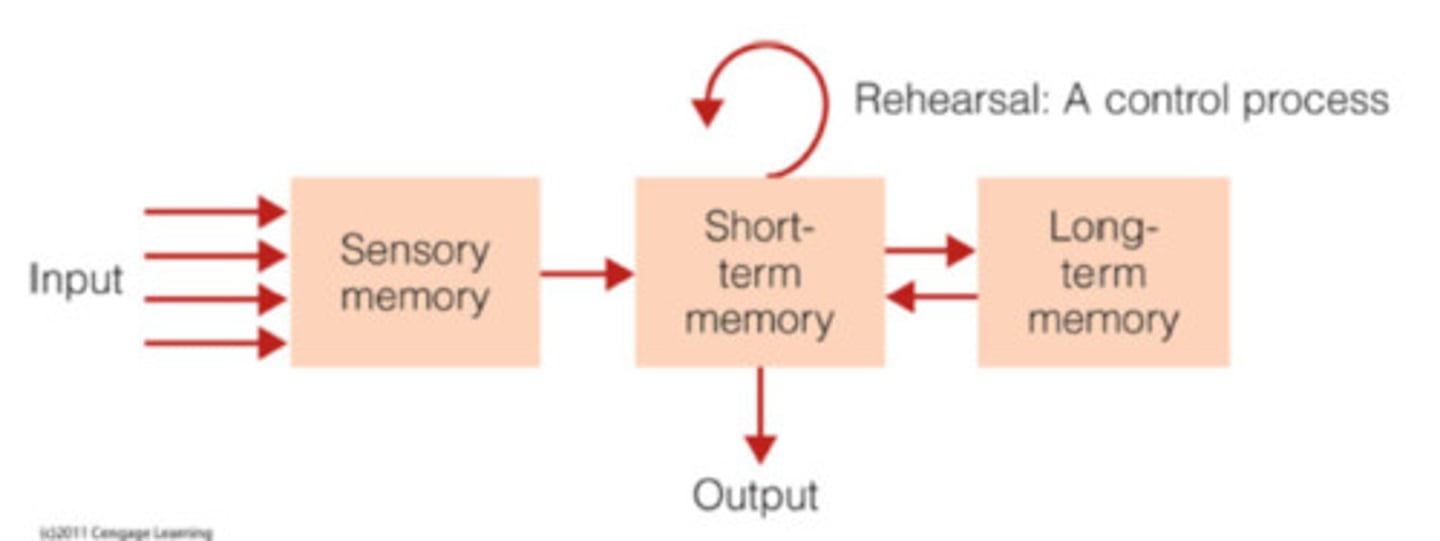
Rehearsal
control processes used to keep information in short term memory
Memorizing
control processes used to get information from short-term memory into long term memory

Retrieval
control processes used to get information from long term memory into short term memory
Sensory memory
memory system for holding sensory stimulation for very brief periods of time
- Typically lasts under a seconds to a few seconds
- So short that sometimes considered part of perception
Echoic memory (hearing)
memory for auditory stimulation that lasts a few seconds

Iconic memory (visual)
memory for visual stimulation that lasts longer than a second
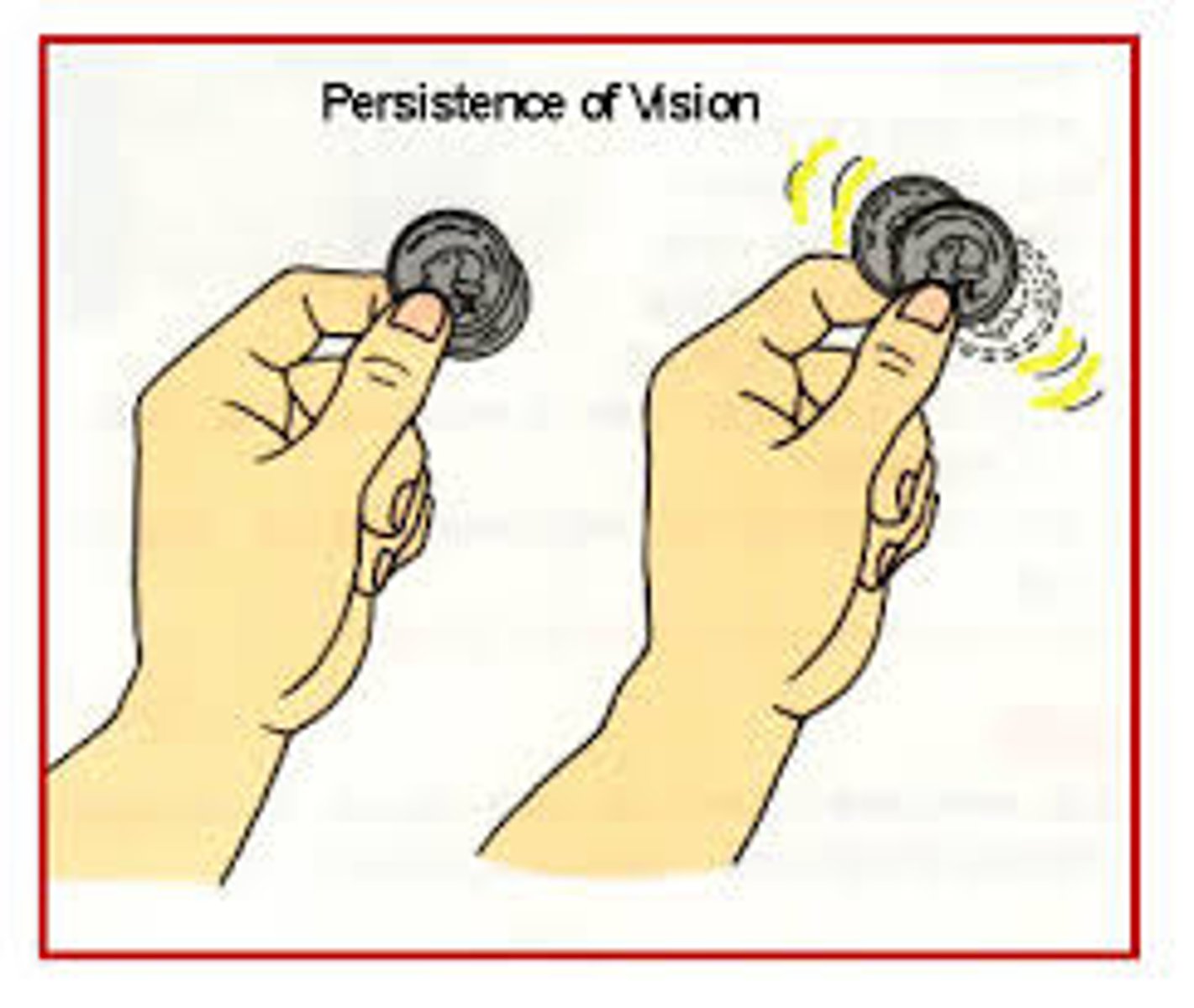
Persistence of vision
continued perception of a visual stimulus after it is no longer present
whole report method
briefly view a 12 letter array and try to recall all of the letters in array. People usually only report 4.5 letters out of the 12
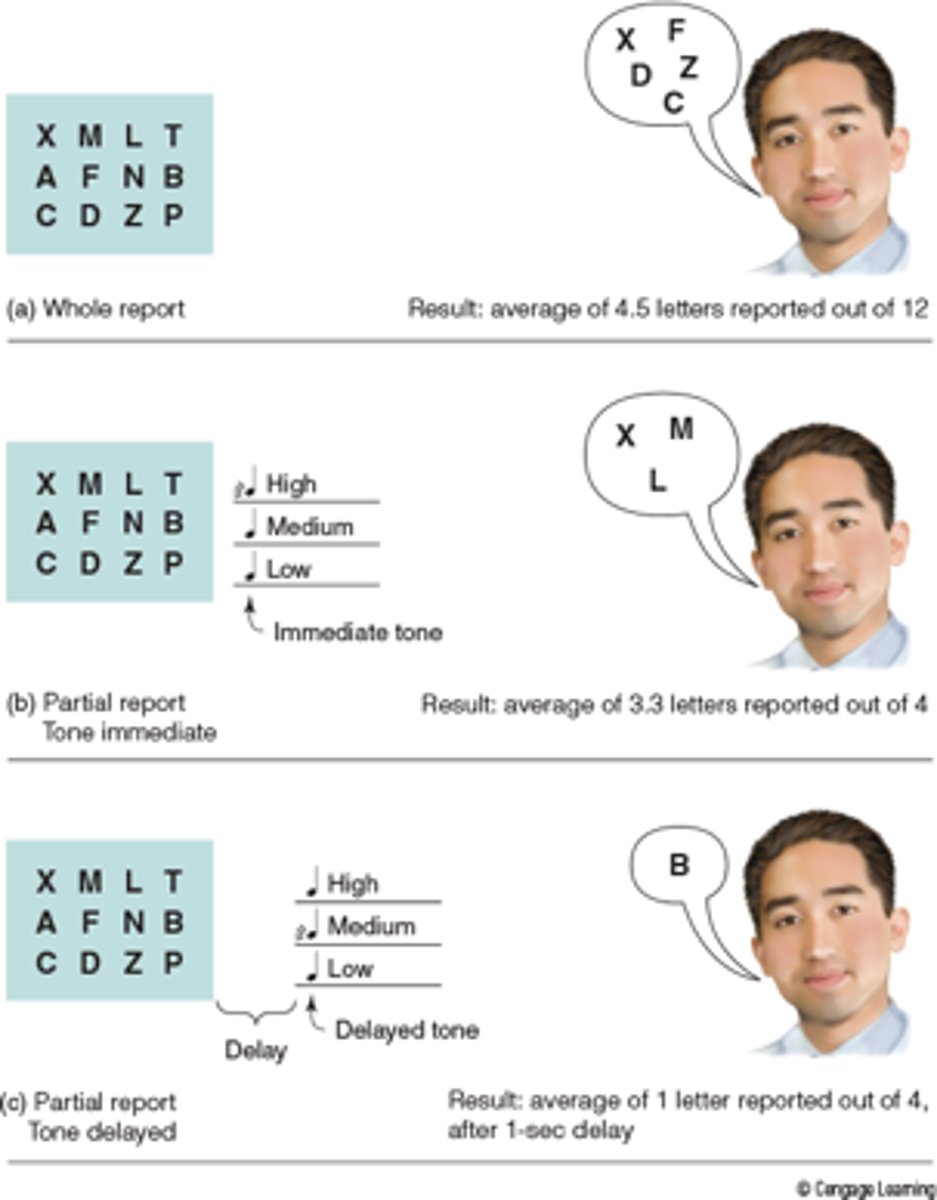
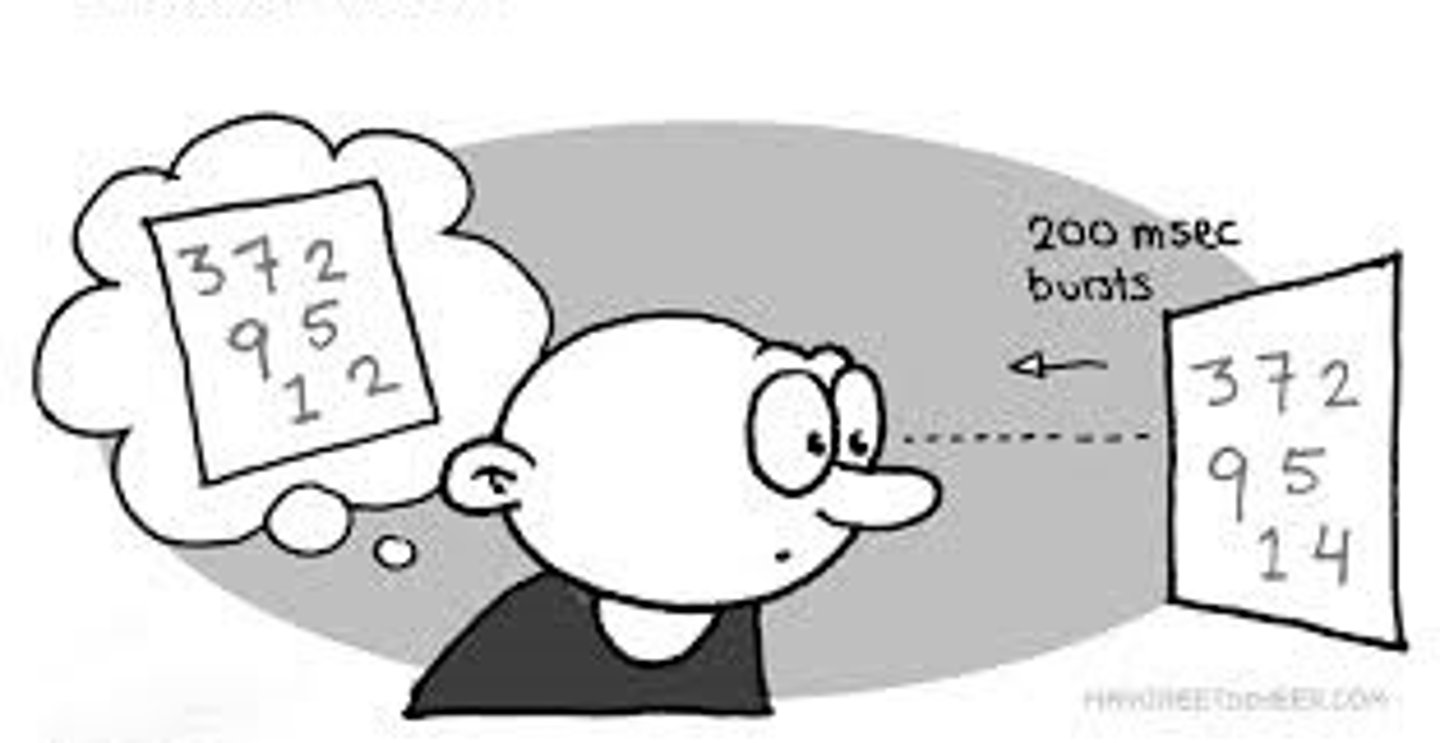
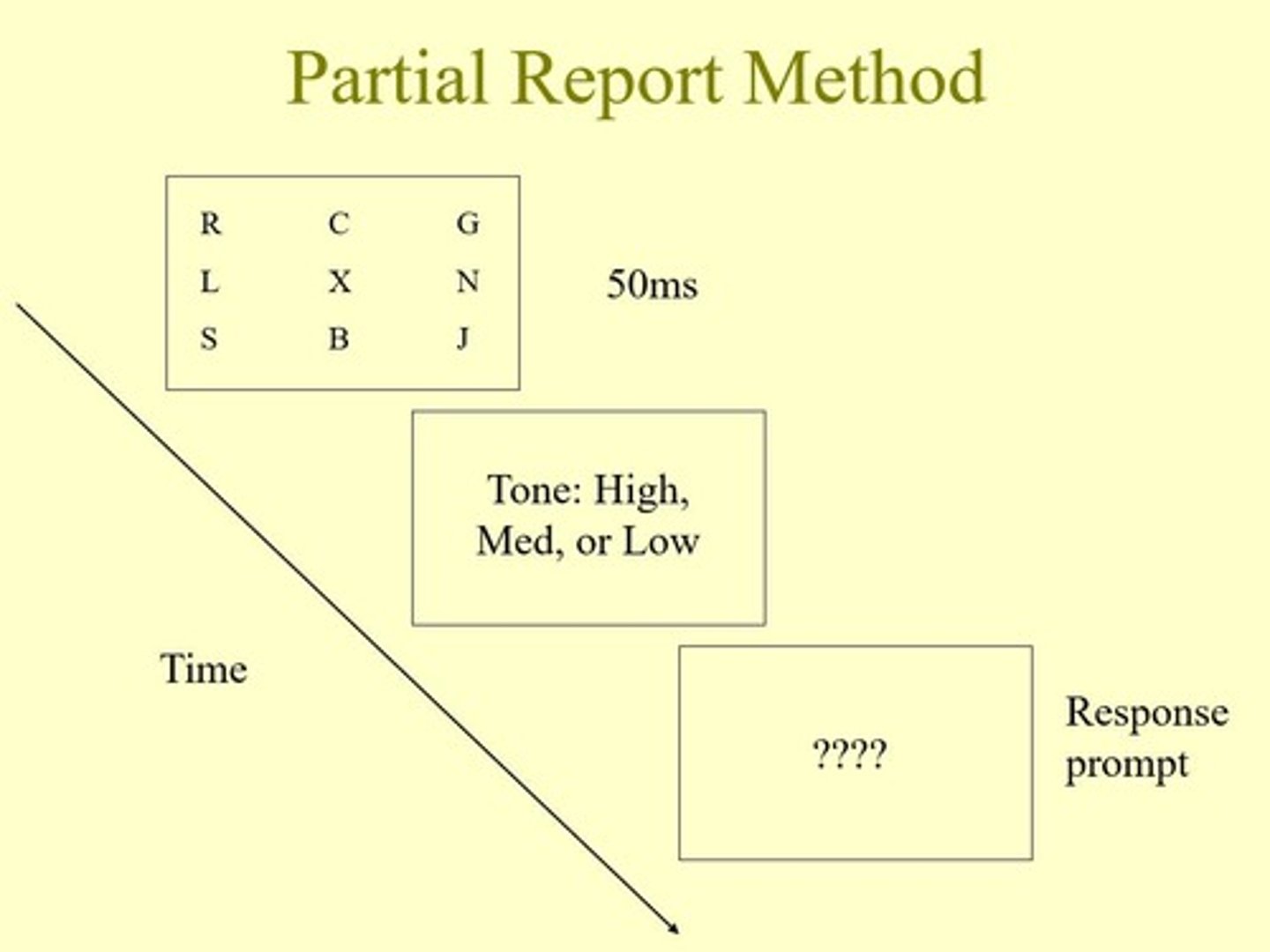
partial report method
briefly view a 12 letter array and try to recall letters in the row that corresponds to a tone pitch.
- evidence that sensory memory has a relatively large capacity (>80% of the inout)
- but's it hard to estimate the overall capacity because the memory trace decays rapidly
Brown Peterson Task
vary the duration of a distractor task to estimate how long information stays in STM
- Fewer letters are recalled as the length of the distracting task (the delay) gets longer
- Suggest that information stays in STM for 15-20 seconds

Digit Span task
increase the number of digits to repeat to estimate how much information is in STM
- People recall 5-9 digits, indicating that digit span is approximately 7+/- 2 digits

Digit span task with chunking
combine smaller units of digits into larger units
- More digits can be recalled with chunking and extensive training
Chunking
convert meaningless digits into more manageable bits
- Notably, STM capacity for other information (e.g letters) did not improve
- I.e., chunking does not change capacity limits, but you can get in more "items" when the information is chunked

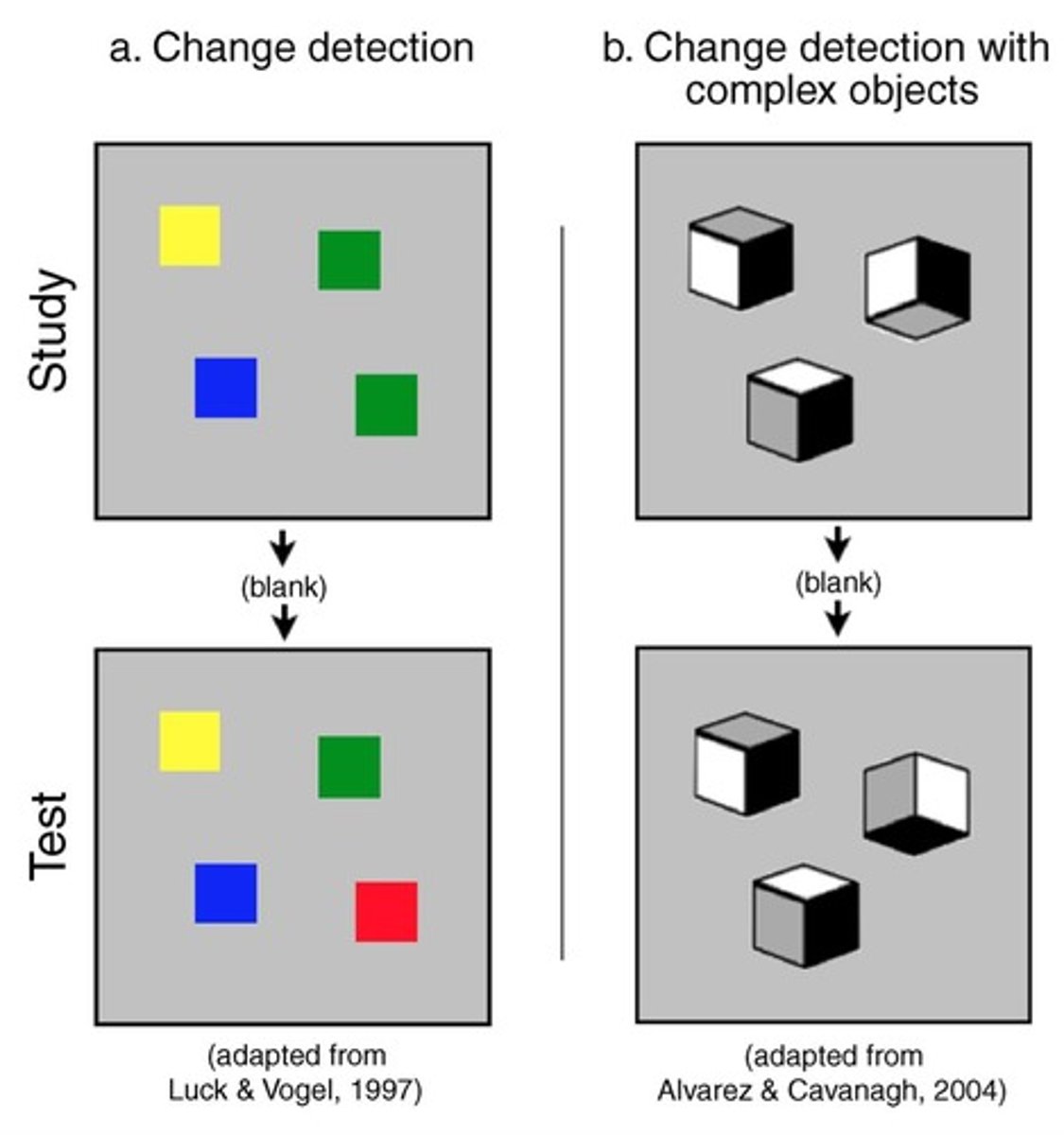
change detection task
Increase the number and complexity of items in an array
- Less accurate to arrays with more than 4 squares (simple items), but just 1 cube (complex item)
- Suggests we may need to think of capacity as amount of information, not just number of items