Chapter 11 - Monopoly
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is a monopoly?
Only seller of a good or service that does not have a close substitute.
What prevents other firms from entering a monopoly market?
Barriers to entry prevent other firms from entering (near impossible)
How does the demand curve for a monopoly firm relate to the market demand curve?
The firm's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve.
What are some barriers to entry in a monopoly?
Economies of scale, government regulations, and ownership of a resource.
What is a natural monopoly?
When the minimum efficient scale is larger than the quantity demanded by consumers.
Example of a natural monopoly
A small town may only support one coffee shop due to low demand.
What role do government regulations play in monopolies?
Include licenses, patents, copyrights
May grant a public franchise or crown corporation
What is a public enterprise?
A business/organization fully or partially owned and controlled by the government
Established to provide essential goods/services (like utilities, transport, postal) at fair prices
Focus on public welfare and economic development rather than profit
What is a crown corporation in Canada?
An enterprise owned by the government to provide services that businesses do not, such as Canada Post or GO Transit.
(its a form of a public enterprise)
Ownership of a resource
Natural, human and knowledge resources
Very common source of market power
How can ownership of a resource create a monopoly?
Ownership of essential resources can prevent other firms from entering the market.
Local monopoly
A business that is the only seller of a product or service in a specific area, so customers have no nearby alternatives.
Example of a local monopoly
Once you enter the gates / walk into a theatre of an amusement park, you've entered a local monopoly
These are the only sellers you can buy from when you're on their premises
What is the relationship between a monopoly's quantity and market quantity?
The monopoly's quantity (q) is the same as the total market quantity (Q).
What happens to profits when: MR > MC
Profits will increase as revenues grow faster than costs.
What is the universal relationship for profit maximization across all market structures?
Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
In a monopoly, how does the price compare to marginal cost?
The price consumers pay is higher than the marginal cost (P > MC).
What is a price markup in a monopoly?
Price markup is the difference between the price and marginal cost (Markup = P - MC).
How is total profit calculated for a monopoly?
Total Profit = (P - ATC) x q, where P is price and ATC is average total cost.
What occurs when price is greater than average total cost (P > ATC) for a monopoly?
The firm earns a profit per unit.
What does it mean when P < ATC in a monopoly?
The firm incurs a loss per unit.
How do you determine the profit-maximizing quantity in a monopoly?
Set MR equal to MC and solve for quantity.
Given the demand curve P = 700 - 2q, what is the formula for marginal revenue (MR)?
MR = 700 - 4q.
If the marginal cost function is MC = 6q, what is the profit-maximizing quantity when MR = MC?
The profit-maximizing quantity is 70.
What price corresponds to the profit-maximizing quantity of 70 in the demand equation?
The price is $560.
How do you calculate total profit at the profit-maximizing quantity?
Total Profit = (P - ATC) x q.
What is the average total cost (ATC) function given in the example?
ATC = 8,000 + 3q.
What is deadweight loss in the context of monopolies?
Deadweight loss refers to the loss of economic efficiency when the equilibrium outcome is not achievable or not achieved in a monopoly.
How does a monopoly affect price elasticity of demand?
In a monopoly, demand becomes less elastic due to the lack of competition, leading consumers to pay higher prices.
What is monopoly rent?
Monopoly rent is the economic profit earned by monopolists simply due to their market position, without needing to work for it.
Why do monopolies not achieve productive efficiency?
Monopolies do not achieve productive efficiency because they typically do not produce at the minimum efficient scale.
What is the profit-maximizing quantity for a monopoly?
The profit-maximizing quantity is where marginal cost (MC) equals marginal revenue (MR), but it is usually not at the minimum efficient scale.
What happens to consumer prices in a monopoly?
Monopolies tend to raise prices above marginal cost, leading to higher prices for consumers.
What is the role of antitrust laws?
Designed to prevent mergers that would create monopolies and maintain competition in the market.
How can governments regulate monopolies?
Governments can impose licensing fees, price ceilings, or create state-owned enterprises to regulate monopolies and reduce their economic profit.
What is a price ceiling and how does it affect monopolies?
A price ceiling is a government-imposed limit on how high a price can be charged, which can increase consumer surplus and reduce deadweight loss in monopolies.
What is allocative efficiency?
Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are distributed in a way that maximizes consumer satisfaction, which monopolies fail to achieve.
What is the impact of monopolies on market entry?
Monopolies prevent other firms from entering the market, maintaining their market power and economic profits.
What is horizontal integration?
Occurs when two competing firms in the same industry merge, potentially leading to a monopoly.
What is the relationship between price and marginal cost in a monopoly?
In a monopoly, the price charged (P) is greater than the marginal cost (MC), indicating inefficiency.
How does a licensing fee affect a monopoly's pricing?
A licensing fee increases average total cost (ATC) but does not affect marginal cost (MC), reducing the monopoly's profit.
What industries are typically federally regulated?
Industries such as rail, air travel, telecommunications, and banking are often federally regulated to prevent monopolistic practices.
What is the effect of a price ceiling on consumer surplus?
A price ceiling can increase consumer surplus by lowering prices and making the market more efficient.
What is the significance of the minimum efficient scale?
The minimum efficient scale is the lowest point at which a firm can produce its goods at the lowest average total cost.
What is the impact of monopolies on investment capital allocation?
Monopolies can lead to inefficient allocation of investment capital since they do not operate at the point where price equals average total cost (ATC).
Which utility is considered a natural monopoly?
Natural gas and water services.
How are public transportation services typically managed?
They are run by local municipal governments as not-for-profit services.
What determines the maximum tuition price for public colleges/universities in Canada?
The provincial government sets the maximum tuition price each year.
What is price discrimination?
The practice of charging different prices to different customers for the same good or service.
What conditions must be met for price discrimination to work?
The firm must have market power, identify customers willing to pay more, and prevent resale.
What are the three types of price discrimination?
Multi-market (3rd Degree)
Quantity-based (2nd Degree)
Perfect (1st Degree).
What is multi-market price discrimination?
Charging different prices to different market segments based on characteristics like geography or age.
Give an example of multi-market price discrimination.
Offering age-related discounts to seniors and students.
What is quantity-based price discrimination?
Offering bulk discounts where larger purchases have a lower price per unit.
Those that want a smaller quanity pay a higher price (overcharging)
What is perfect price discrimination?
Charging each consumer their exact willingness to pay, eliminating consumer surplus.
What is a two-part tariff?
A pricing strategy where a firm charges a membership fee plus a fee for usage.
What is a junk fee?
An additional charge, such as processing or administrative fees, added to the stated price.
What is the purpose of price matching (Low Price Guarantee)?
To enhance firm reputation and profits by matching competitors' prices.
What is a loss leader?
An item sold below cost to attract customers, with the hope they will buy additional items.
Why might rivals be unwilling to match a loss leader price?
Because it guarantees a loss for them.
What challenge does price matching present for firms?
They must verify claims of lower prices from rivals.
How can price matching facilitate price discrimination?
By allowing firms to charge higher prices to customers unaware of cheaper alternatives.
What is the effect of perfect price discrimination on consumer surplus?
It eliminates consumer surplus, allowing the firm to capture all surplus.
What is the relationship between price discrimination and producer surplus?
Price discrimination can increase overall output and producer surplus.
What role do individual consumer preferences play in pricing strategies?
They influence the optimal pricing for two-part tariffs and junk fees.
What is a common example of a two-part tariff?
Country clubs with annual membership fees and charges for golf or meal
Example of how monopolies are not efficient (real-life scenario)
When you go the movies it's obvious that the $12 bag of popcorn is very overpriced
If the movie theatres charged lower prices, more people would buy the popcorn
However they wouldn't do that since they'd make less profit
When does federal government's competition bureau typically prevents mergers?
When the new firm would have more than 35% market share
The 4 biggest firms in the industry have more than 65% of market share
What is an example of a junk fee
If you sign up for a cell phone plan, there's often an activation fee
Buying concert tickets online instead of the venue's box office, there's usually a transaction fee
How long do patents last?
20 years
The monopolist produces an output that is __________ the perfectly competitive industry would produce.
Less than
for a perf comp
MR = MC = P
Many buyers and many sellers
Which of the following rights is given to the holder of a patent?
The exclusive right to a new product
In Canada, which of the following laws prohibited charging buyers different prices if the result would reduce competition?
The compeition Act
The monopolist charges a price that is __________ the perfectly competitive industry.
higher than
When network externalities are present, the usefulness of:
The product increases as more consumers use it
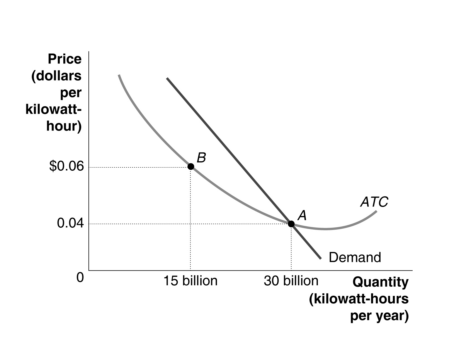
Which point on this graph corresponds to a natural monopoly serving this market and breaking even?
Point A
What is the definition of market power?
The ability of a firm to charge a price greater than marginal cost
The only legal restriction concerning price discrimination is that firms cannot use it to:
drive rivals out of business