microbial cell structure
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
5 major groups of microorganisms
bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae, viruses
3 kingdoms of life
bacteria, archea, eukaryota
bacteria have a larger…
surface area to vol ratio
can viruses be viewed using light microscope ?
no - electron
diameter range of eukaryotic cells
10 - 200um
1mm = ?µm
1000
protozoa
single celled eukaryotes
diameter of Saccharomycetes (fungi)
5um
diameter range of prokaryotic cells
0.2 - 700µm
viruses can only replicate within
cytoplasm of host
2 types of bacterial cell wall
gram pos or neg
gram pos
one thick cell wall multiple layers of peptidoglycan
teichoic and lipoteichoic acids
gram neg
2 layers with single peptidoglycan layer
LPS and porins
bacterial cell walls composed mainly of
peptidoglycan (murein)
peptidoglycan is composed of…
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG)
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM)
amino acids
what % of gram pos is peptidoglycan
60 - 90
how thick are gram pos cell walls ?
30-60nm
role of teichoic acid in gram pos mem
bound to NAM of PG
helps cross-link PG chains and adhere to surface
what
porins
transmembrane proteins
channels for movement of hydrophilic low-molecular weight substances
1nm diameter hole
porins are composed of how many identical polypeptides
3
periplasm
space between cytoplasmic and outer membranes
15nm wide
contains digestive enzymes, transport proteins and chemoreceptors
cytoplasmic/plasma mem
found in both gram pos and neg
8-10nm wide
phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
highly selective permeable barrier
what stains are used to differentiate between gram pos and neg
crystal violet and safranin
gram pos stains
purple - retain crystal violet
gram neg stains
pink/red - lose crystal violet, retain safranin counterstain
inclusion bodies
particles of aggregated proteins
nucleoid
chromosome region
single circular closed loop of double stranded supercoiled and highly condensed DNA
no membrane
ribosomes absent
ribosomes
granular appearance
small and large subunits
some antibiotics work by preventing protein synthesis at ribosome eg. tetracycline
plasmids
nonessential DNA molecules
loop of 5-100 genes
replicate independently of host chromosome
transfer genetic traits between bacteria - conjugation
antibiotic resistant genes
bacterial DNA replication is
bi-directional
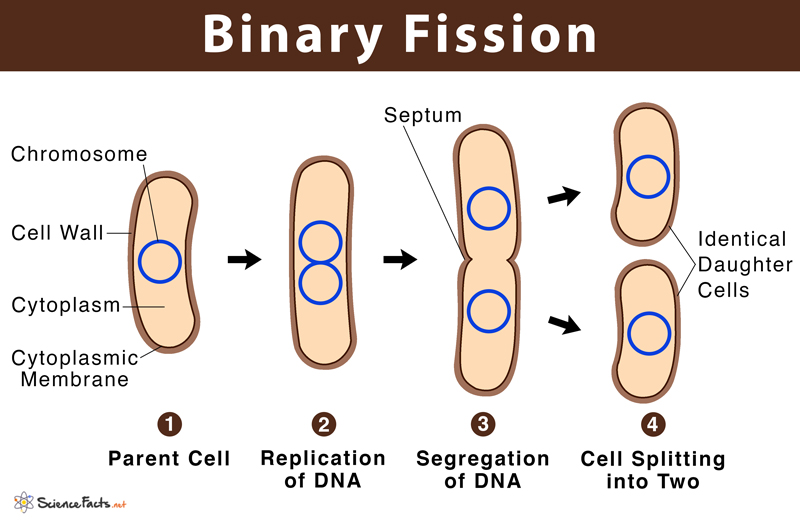
binary fission
form of asexual reproduction where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells
what major microorganism groups are eukaryotic
fungi, algae, protozoa
nucleus can be viewed
under light microscope without staining
nucleolus
site of ribosome and protein synthesis
fungi reproduce via
spores - asexual or sexual
saprotrophic
dead or decaying organic matter
symbiotic
mutually beneficial relationship
commensal
one organism benefits, and the other is neither helped nor harmed
cell wall of fungi is composed of
chitin and glucan
in cell mem of fungi cholesterol is substituted with
ergosterol
protozoa
simple microorganisms
live in/on organism of another species - heterotrophic
can cause direct/indirect harm to host