Glucose Metabolism Flashcards
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Glucose Metabolism, Obesity, and Insulin Resistance.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Glucose Homeostasis Goal
Regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Hyperglycemia
A condition characterized by abnormally high levels of glucose in the blood.
Hypoglycemia Symptoms
Dizziness, unconsciousness.
Short term Hyperglycemia Symptoms
Frequent urination (polyuria).
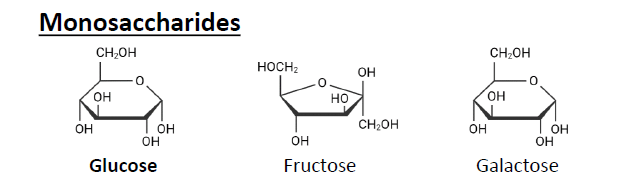
Monosaccharides
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose.
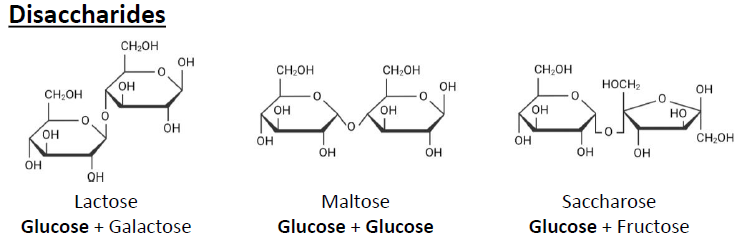
Disaccharides
Lactose, Maltose, Saccharose.
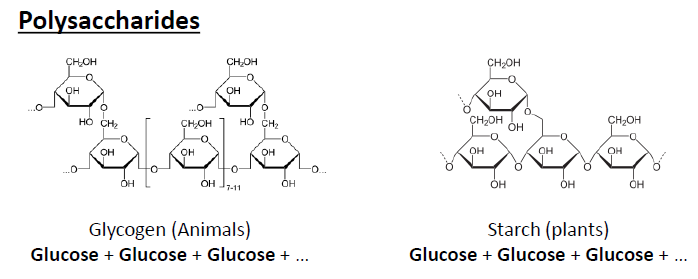
Polysaccharides
Starch (plants), Glycogen (Animals).
α-Amylase
Breaks down starch and glycogen in the mouth and stomach..
α-Glukosidase, Saccharase, Lactase
Breaks down disaccharides into monosaccharides.
SGLT1
Sodium-Glucose Transporter 1, active transport.
Transports glucose across cell membranes.
Uses active transport
Moves glucose into cells
GLUT2
Type: Facilitated diffusion (passive transport)
Function: Glucose uptake, release, and sensing, Can move glucose in or out
Location & Cells:
Liver (Hepatocytes
Kindey
Intestine (Enterocytes)
Pancreatic β-cells
Function of GLUT1/3
Basal glucose uptake.
Affinity:
1-2 mM
Function of GLUT2
Glucose «sensing» und uptake.
Affinity:
15-20 mM
Function of GLUT4
Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake.
Affinity:
5mM (physiological avg. ~4.8mM)
Function of White Adipose Tissue (WAT)
Mechanical protection, energy storage, isolation.
Endocrine Function Factors of White Adipose Tissue (WAT)
Leptin, Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα).
BMI formula
Body weight [kg] / (Height [m])2
AgRP
Agouti-Related Protein.
POMC
Proopiomelanocortin.
Treatment Options for Common Obesity
Lifestyle intervention, Pharmacotherapy, Bariatric surgery.
Insulin Resistance
A decreased ability of insulin to promote the uptake of glucose in peripheral tissues and to inhibit hepatic glucose output.
Hypoglycemia
A condition characterized by abnormally low levels of glucose in the blood.
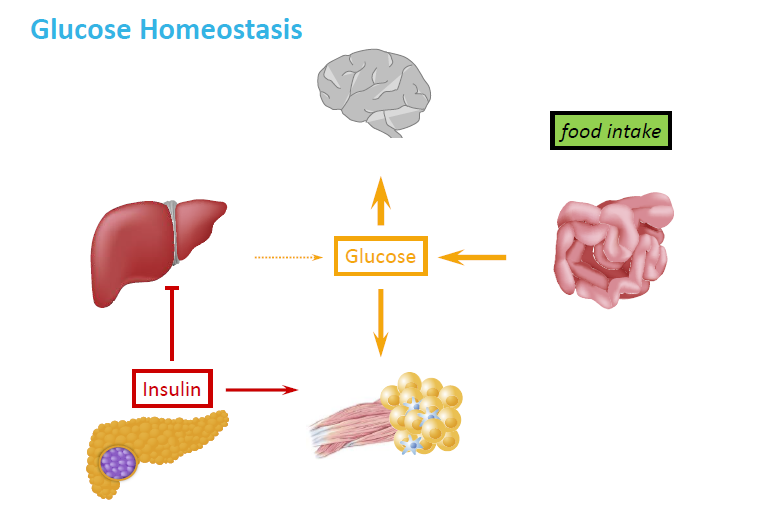
How does the body maintain glucose homeostasis after eating?
Food intake increases glucose absorption from the intestine.
Blood glucose rises → sensed by the pancreas.
The pancreas releases insulin.
Insulin signals:The liver to store glucose as glycogen
Muscle and fat tissue to take up glucose
Brain uses glucose as fuel.
This helps lower blood glucose back to normal.
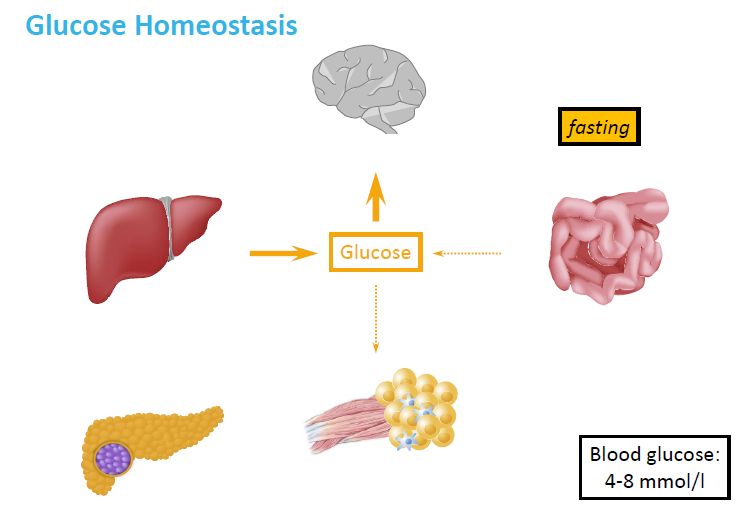
How does the body maintain glucose levels during fasting?
No food intake → glucose from digestion is unavailable
Liver releases glucose via:
Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis)
New glucose production (gluconeogenesis)
Insulin levels are low
Glucose is supplied to essential organs like the brain and muscles
Blood glucose is kept stable at ~4–8 mmol/L
What does insulin do in skeletal muscle, and why?
↑ Glucose uptake
→ Insulin signals muscle cells to pull glucose in from the blood using GLUT4 transporters.↑ Glycogen synthesis
→ The extra glucose is stored as glycogen, a fast energy source for muscles.
✅ Why?
After eating, muscles take up glucose to store energy for later movement or exercise.
How does insulin affect adipose tissue (fat), and why?
↑ Glucose uptake
→ Insulin helps fat cells absorb glucose from the blood.↑ Lipogenesis (fat creation)
→ Extra glucose is converted into fat for long-term energy storage.↓ Lipolysis (fat breakdown)
→ Insulin blocks the breakdown of stored fat.
✅ Why?
Insulin tells the body that energy is available, so it stores it instead of breaking down fat.
What are insulin’s effects on the liver, and why?
↓ Glucose release
→ Insulin stops the liver from making new glucose (gluconeogenesis).↑ Glycogen synthesis
→ The liver stores glucose as glycogen.↑ Lipogenesis
→ Extra glucose is turned into fat (for storage or transport as lipoproteins).
✅ Why?
After a meal, insulin tells the liver to store nutrients and stop adding more glucose to the blood.
What is Insulin?
Anabolic hormone = “building up”
→ Insulin promotes storage and synthesis of nutrients:
Stores glucose as glycogen
Converts glucose to fat (lipogenesis)
Helps cells take up amino acids and build proteins
Why is Glucagon a catabolic hormone?
Catabolic = promotes the breakdown of stored energy to release fuel when the body needs it (especially during fasting or low blood sugar).