Week 5 - soil bio properties (organisms)
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
animals, fungi, bacteria
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Role of soil organisms
mix + aerate soil
fix atmos nitrogen
decompose org substances
not all creatures decompose substances, some promote soil aggregation and change structure
What are the 4 groups of soil organisms +1? sub groups?
plant, animal, fungi (& mycorrhizae), bacteria
+ protista
mseo + macro
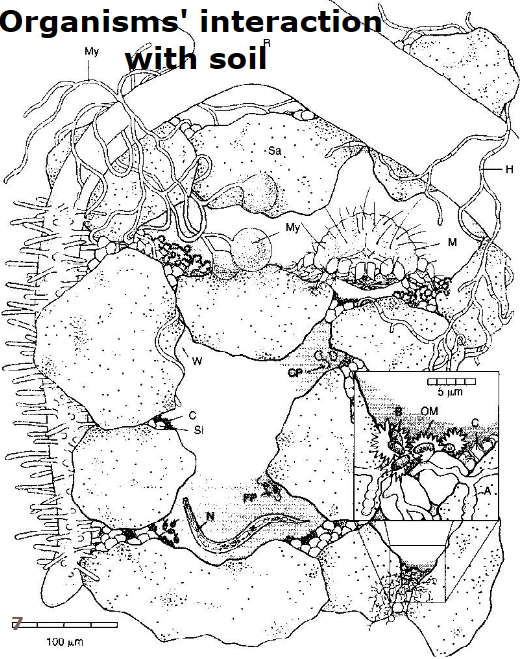
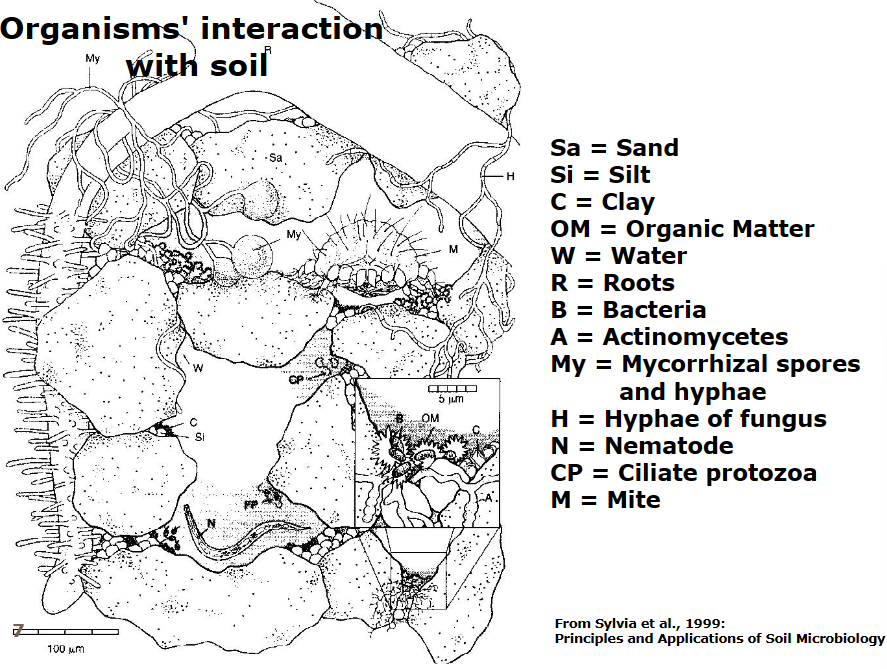
name the different components
what % of species live in the soil?
59%
What soil animals are there? (4) name their functions
mice, rabbits, moles - aerate soil + change soil structure, fertility
earthworms - poop waste = nutrients, aerate + mix soil
anthropods + gastropods - feed on decaying veg, aerates
termites - breaks down plant fibre and builds mounds (high OM)
soil nematodes - microscopic (<2mm long)
name the different types of soil nematodes
classified according to diff feeding habits
omnivores – feed ono decaying OM
predacious – feed on bacteria, fungi, algae
parasitic – infest plant roots
what are the functions of soil fungi?
the greatest biomass of all soil organisms
the GOAT of decomposition
eats dead/living OM
first visual sign of decomp → speeds up OM decomp
directly attack cellulose + complex compounds
fungi excrete org substances that aid in soil aggregation
types of soil fungi (3+)
yeast = unicellular
molds, mildew, mushrooms = multicellular
soil mycorrhizae = mutualistic association between fungi + plant roots
roots → transmits energy to fungi
fungi → transmits nutrients and water back
good protection of plant root
what are soil protistias? what do they do?
algae, protoza, slime molds
dont play a role in decomp
produce nutrients
improve soil aggregation
abundant in water and surface soil
what are soil bacterias? classified?
unicellular organisms
most imp to biologicall process in soil
classified by:
nutritional pattern
oxygen demand
symbiotic relationships
autotrophic vs heterotrophic (produce their own energy vs consuming)
autotrophs = very important → can nitrify bacteria
what role does bactiera play in nitrogen fixation?
causes formation of root nodule → bacteria enter → transforms N2 from atmos into amino acids
symbiotic bacteria infect plant root hairs
leguminous plants, pod bearing plants, some trees (alders)
what is the optimal environment for soil microbial activity?
temperature
warm temperatures for good activity (15-20C)
microbes are dormant at freezing (except arctic soil)
water
near or at field capacity
some good in saturated. anaerobic conditions
pH
bac less tolerant of acidic cond vs fungi
some bac good at low pH (6)
nutrient needs of bacteria, how does the amount affect the processes?
N, P to decompose
C for energy
low nutrients = hard to decomp material, immobilization (not available for plants)
high nutrients = mineralization
2 categorizations of soil flora
macroflora
sources of OM (carbon) - crops, litter
plants roots = 50% of plant biomass
microflora
some are N2 fixing
help in nutrient acquisition
decomposition of OM
What are 5 drivers of soil biodiversity loss?
land use change
invasive species
unsustainable soil mgmt practices
pollution
soil sealing + urbanization
What is soil organic matter (SOM)?
fraction of soil composed of material that was once alive
plant + animal remains = OM
diff stages of decomp (cells + tissues + roots + microbes)
all org matter has carbon
org c undergoes combustion → transformed into other types of C → released as CO2
what are the major sources of SOM? (5)
manure + crop residues in agriculture
above ground plant inputs leaves, needles, wood
below ground roots
microfauna
macrofauna
Where can you find areas with a lot of SOM in canada?
peatlands, grasslands, praries
places with a lot of soil carbon