Wk Six - STEMIs and Ventricular Rhythms
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
STEMI management steps sheet
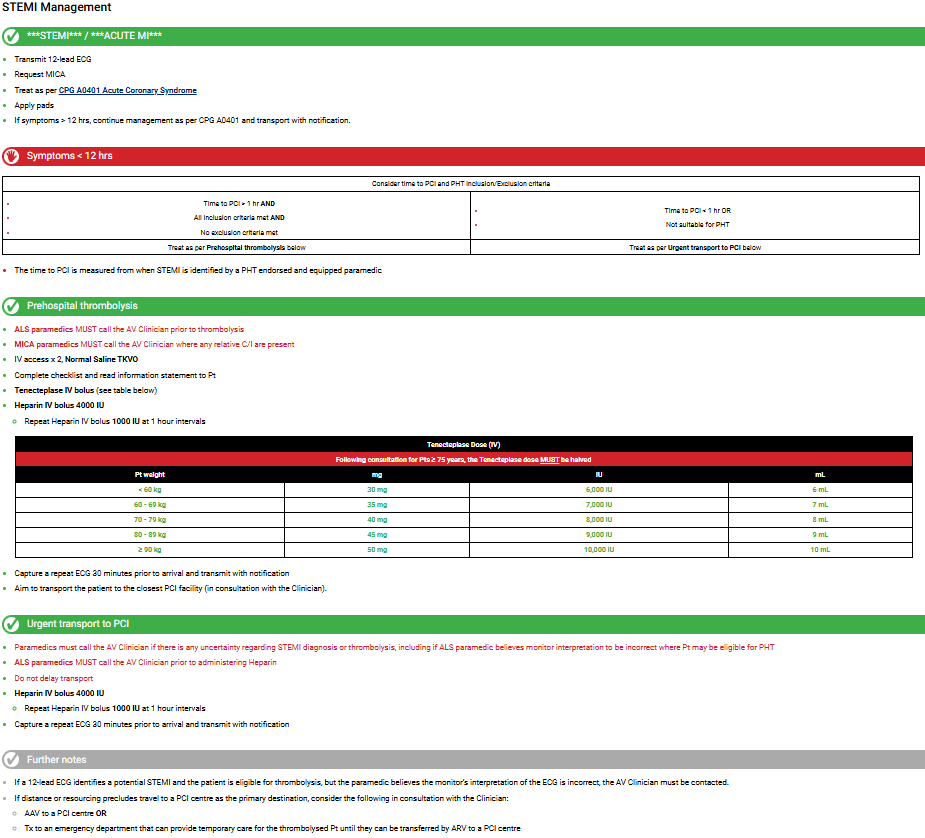
Heparin Indis/Contras Etc.. Sheet
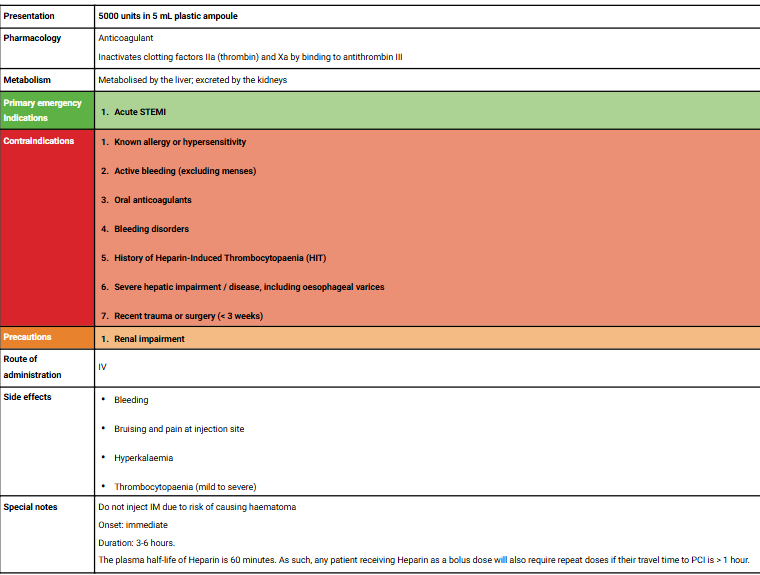
Tenectaplase Indis/Contras Etc.. Sheet

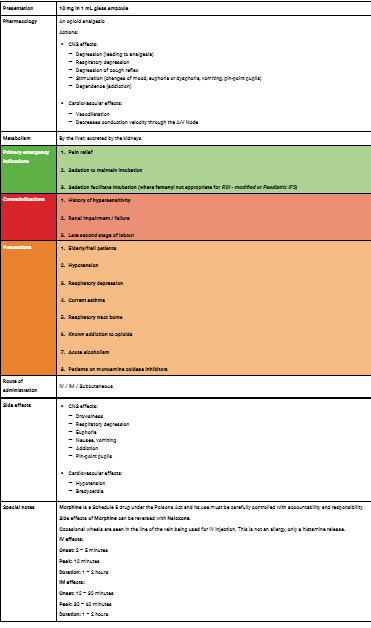
Morphine Indis/Contras Etc.. Sheet
What happens when you bleed? (Steps)
Injury (Bleeding, release of signalling molecules)
Vasoconstriction (local immeadiate control)
Platelet formation
Coagulation (Fibrinogen forms fibrin mesh)
Fibrinolysis (Plasminogen forms plasmin)
Clotting Cascade
The complex series of events in your body when bleeding is stopped by forming a clot. The three main pathways are Intrinisc, Extrinisic & Common
CC Intrinisc Pathway
Activated within the blood vessel often by damage to the endothelium or expose to collagen. Factor XII (Hageman) is activated > XIIa. This activates XI > XIa, which activates IX > IXa, and IXa + factor VIIa + calcium & phospholipids activates factor X which forms a blood clot.
CC Extrinisc Pathway
Triggered by external trauma that causes the blood to escape from the vessel. Damaged tissue releases Tissue Factor (III) which binds wih factor VII > VIIa, and the TF-VIIa complex activates Factor X.
CC Common Pathway
Where both pathways meet and lead to clot formation. Factor X is activated to become Xa, combined with factor V makes the prothrombin complex. This converts Prothrombin to Thrombin, which converts Fibrinogen to Fibrin, which activates Factor XIII which cross links fibrin into a stable clot.
Haemostasis
the psyiological process that stops bleeding after a vessel is injured
Haemostasis steps
Vasoconstriction (vessel is damaged, surrounding muscle constricts to reduce blood flow)
Platelet Plug Formation (Platelets attracted to site, adhere to exposed collagen to form a temporary plug)
Coagulation Cascade
Fibrin Clot Formation (fibrin clot, dissolves as the tissue heals & vessel is repaired
How is a blood clot broken down
Fibrinolysis - Plasmin inside the clot is triggered, which degrades the fibrin until the clot disintergrates
How does tenecteplase work?
A clot has a fibrin mesh, Plasmin breaks up that clot, Plasminogen is activated by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to make that plasmin.
What AMPLE factors increase suspcision of NSTEACS
DM, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Previous cardiac Hx, hormone replacement for menopause
Inferior Stemi Signs
ST elevation in 2 or more inferioir leads, may see hyperacute T waves, reciprocal depression in aVL, progressive development of Q waves in II III and AVF.
Complications of inferior stemis
Bradycardia, 2nd/3rd degree heart block
Anterior/Anteroseptal Stemi Signs
ST elevation in 2 or more leads. V1&2 = septal, V3&4 = anterior, V1-4 = anteroseptal
May also see hyperacute t waves, reciprocal ST depression in I leads, progressive development of Q waves in V1-4
Complications of anterior/anteroseptal stemis
Poorest prognosis (most amount of myocardium under attack), irritable myocardium (PCS & risk of VFib)
Lateral Stemi Signs
St elevation in 2 or more lateral leads, may see hyperacute T waves & reciprocal depression in inferior leads
Complications of lateral stemis
Rarely isolated infacrtions, usually part of a larger occlusion.
Kinds of Lateral Stemis
anterolateral - STEMI due to LAD occlusion
Inferior-positerior-lateral - STEMI due to LCx
Isolated lateral - due to occlusion of smaller branch arteries like the ramus intermedius
Posterior Stemi Signs
ECG shows 0.5mm ST elevation in 2 or more leads V7-9
May see horizontal ST depression, tall broad R waves ?30ms and upright T waves in V1-3.
Complications of posterior stemis
Rarely isolated, usually occurs with inferior or lateral infarction. Much larger area damages, and theyre often missed!
Right Ventricle Stemi Signs
Confirmed by ST elevation in 2 or more of V3R-V6R. May see ST elevation in V1 & St dep in V2. Isoelectric ST segment in V1 with marked ST depression in V2, ST elevation in III > II
Complications of RV stemis
40% of inferior stemis. PRELOAD sensitive due to poor contractility, can develop severe hypotension in response to nitrates. Treated with fluid loading
Automati
property of cardiac cells that allows them to reach threshold potential by themselves, and depolarize spontaneously
What does rate of firing depend on?
The steepness of Phase 4
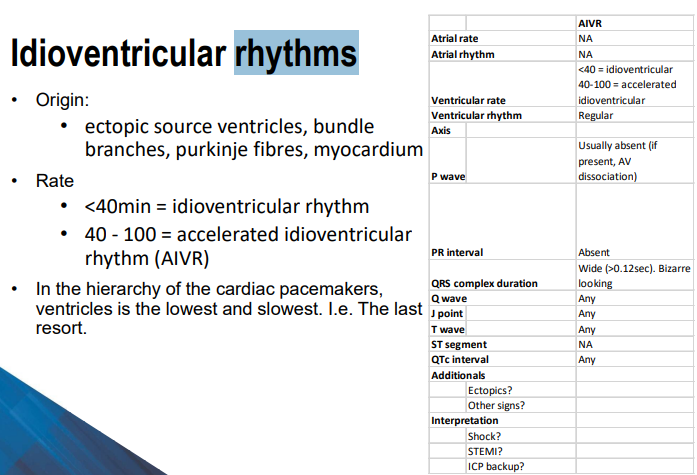
Hierarchy of pacemakers
SA Node > AV Node > Bundle Branches/Purkinje Network
Pacemakers & Their rates
SA - 60-100, sinus rhythm
AV - 40-60 junctional escape rhythm
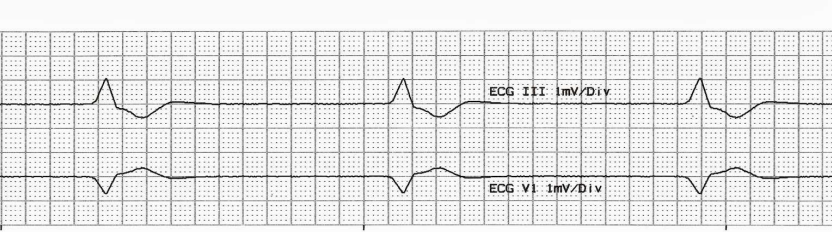
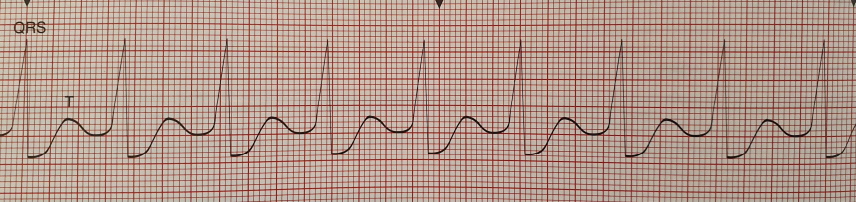
BB/PN - <40 idioventricular rhythm
Enhanced Automaticity
cells firing at a rate beyond its inherent rate because cell membrane has become more permeable to sodium during phase four
Causes of enhanced automaticity
increased catechloamine levels
myocardial ischemia/infarction
digoxin toxicity
atropine
hypoxia, hypercapnia, hypocalcemia, temp changes
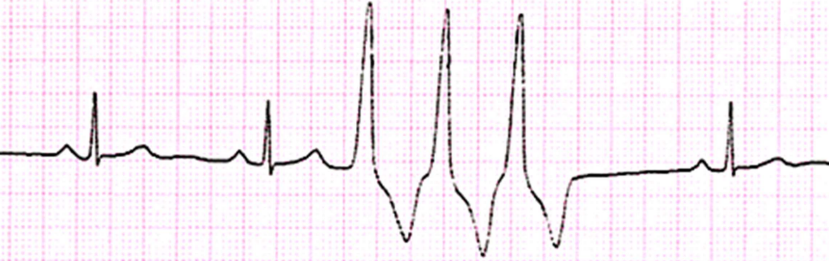
Premature Ventricular Contraction
an unexpected beat, that can be fe;t. wide and bizzare looking - originates from ectopic source ventricles, bundle branches, PF & myocardium. there is a compensatory beat due to SA node not being depolarised. only concerning if there is multiple.
Single PVC
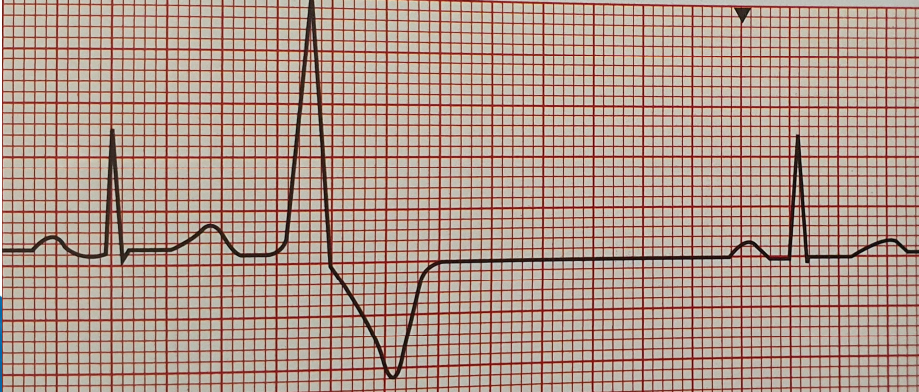
Multifocal PVC
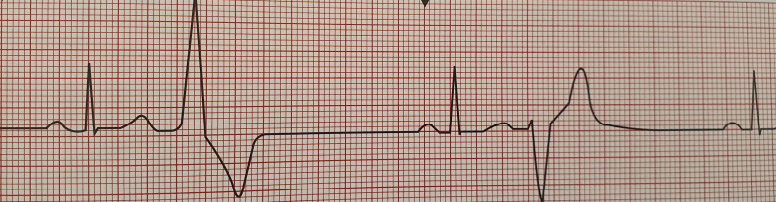
Ventricular Bigeminy
a heart rhythm disorder where every other heartbeat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
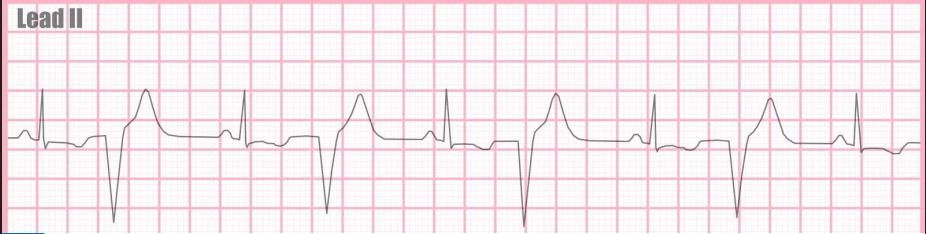
Ventricular Trigeminy
a heart rhythm disorder where after every two normal heartbeats is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
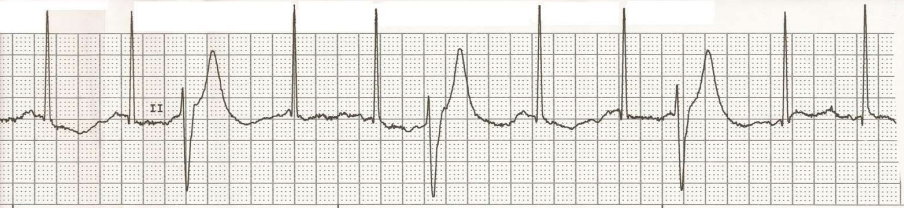
Couplet
Two consecutive premature beats
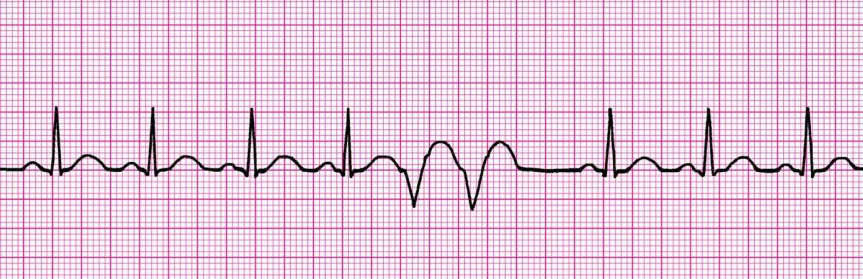
Triplet
Three consecutive premature beats
Idioventricular rhythms sheet
Idioventricular rhythm ECG
Accelerated Idioventricular rhythm ECG
Pathophys & Causes of Idioventricular rhythm
PATH:
rate of impulses from the SA and AV node is less than the rate of the escape rhythm of the ventricle pacemaker
electrical impulses from the atria fail to reach the ventricles due to blockage
enhances automaticity of ventricular pacemaker
CAUSES:
Reperfusion phase of an AMI
Beta-sympathomimetics (adrenaline)
Drug toxicity
Electrolyte imbalances
cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, athletic heart myocarditis
ROSC after CA
How to treat idioventricular R
Treat the underlying cause - electrolytes, perfusion…
VT
ventricular tachycardia. 120-300bpm, not coordinated
VF
ventricular fibrilation, irregular heart rhythm, chaotic and uncoordinated