PT 714 OMPT Lecture 2025
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
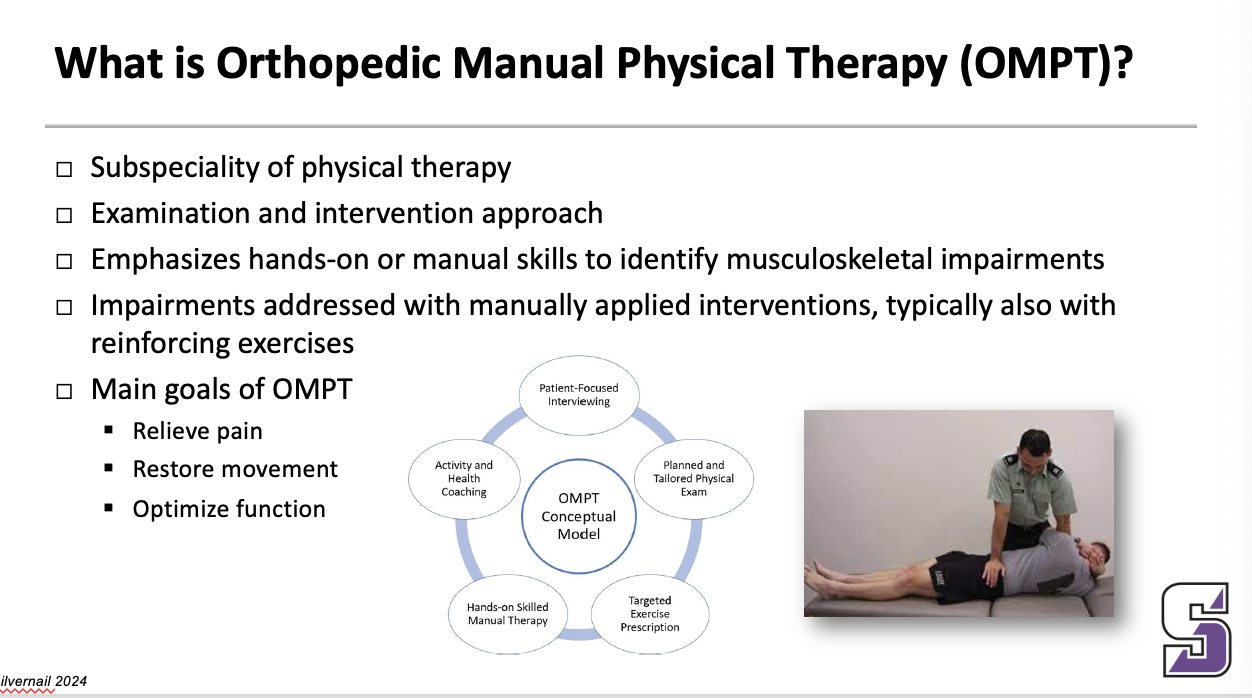
What is Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy (OMPT)?
Subspeciality of physical therapy
Examination and intervention approach
Emphasizes hands-on or manual skills to identify musculoskeletal impairments
Impairments addressed with manually applied interventions, typically also with reinforcing exercises
Main goals of OMPT
Relieve pain
Restore movement
Optimize function
______
“Orthopedic manual physical therapy is a subspecialty of physical therapy featuring a systematic active approach to the management of a broad spectrum of physical disorders. Based on a patient-centered advanced clinical reasoning model taught in fellowship training, OMPT has key distinguishing characteristics that include expertise in hands-on iterative examination and treatment strategies inclusive of thrust and nonthrustmanipulation. Essential to OMPT is a focus on continuous reassessment, through all aspects of care, synergistic application of carefully designed and dosed exercise, and a patient-centered long-term mindset driven by the available scientific and clinical evidence, and the biopsychosocial framework of each individual patient.
Army-Baylor Doctoral Fellowship in OMPT
One of the first AAOMPT-recognized residencies in 1996
Approved as a Doctor of Science degree program in 2001 by Baylor University
Re-credentialed as a clinical fellowship in 2004
Australian approach with exposure to MDT and Mulligan Concept
_____
Different from most fellowship programs … dual purpose … clinical fellowship and terminal doctoral degree program
150 hours of clinical mentorship
OMPT Interventions
Joint manipulation (thrust manipulation)
Joint mobilization (non-thrust manipulation)
Physiologic movement
Accessory movement
Muscle energy techniques
Mobilization with movement
Soft tissue mobilization
Manual
Instrument-assisted
Dry needling
Well tolerated strategies for managing knee OA: article
Reassessment: within & between sessions
Exercise “dose” … FITT factors
Prescribe minimal effective dose
Compliance decreases with complexity
Compliance increases with perceived value
Attempt to prescribe exercises that have multiple effects
Reduces overall time to perform program
Improves compliance
Home exercise timing
Perform active movement early in the day for reduced symptoms and reinforcement of improved movement through day
Perform strengthening later in day so patient isn’t fatigued by daily activity
_________
With the person sitting next to you, what are the key 1-2 take-aways from this article?
1. Doing the minimal but effective dosing – not doing more than we have to (minimleffective dose)
2. Tailoring the activity to the individual –
3. Choosing exercises with multiple effects (making sure that their HEP exercise can accomplish multiple goals so they are more compliant)
- what Dr. Crowell picked: paying it forward type stuff: concept of the reassessment – use it to know the overall treatment is working but it also shows what is giving the most benefit so you can do more of that than the useless stuff
Important concepts of the article
- reassessment
- minimally effevctive dose
- exercise with musciple effect
- develop a clear plan – ask them how they exercise then incorporate that into the program; if they don’t exercise add daily activities like getting up out of their chair at work
- you don’t need the complicated exercises to get extra benefit – simple is good
Evidence for Joint Mobilization/Manipulation (CPGs): lower quarter strong recommendation
acute low back pain
chronic low back pain
hip OA
acute ankle sprain
chronic ankle instability
Plantar heel pain
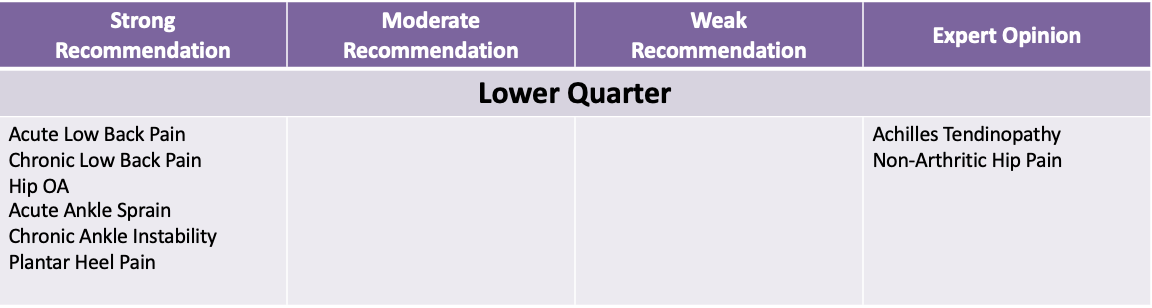
Evidence for Joint Mobilization/Manipulation (CPGs): lower quarter expert opinion
achilles tendinopathy
non-arthritic hip pain
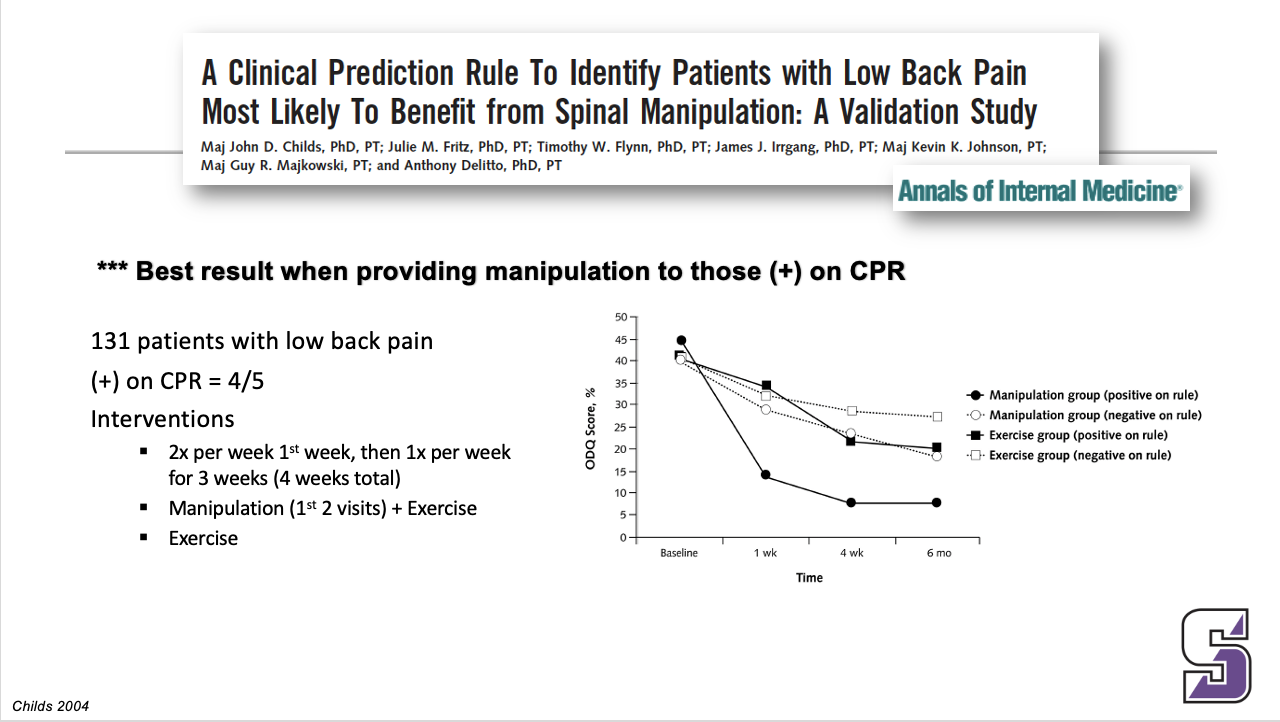
Clinical Prediction Rule for classifying patients with low back pain who demonstrate short-term, improvement with spinal manipulation
_____
3 treatments … initial, 2-4 days later, 2-4 days after 2nd
*** Probability of success with 4 and 3 predictor variables present
This is a clinical prediction rule which shows the characteristics of the people that get better in a study. The found these 5 things (predictor variables)
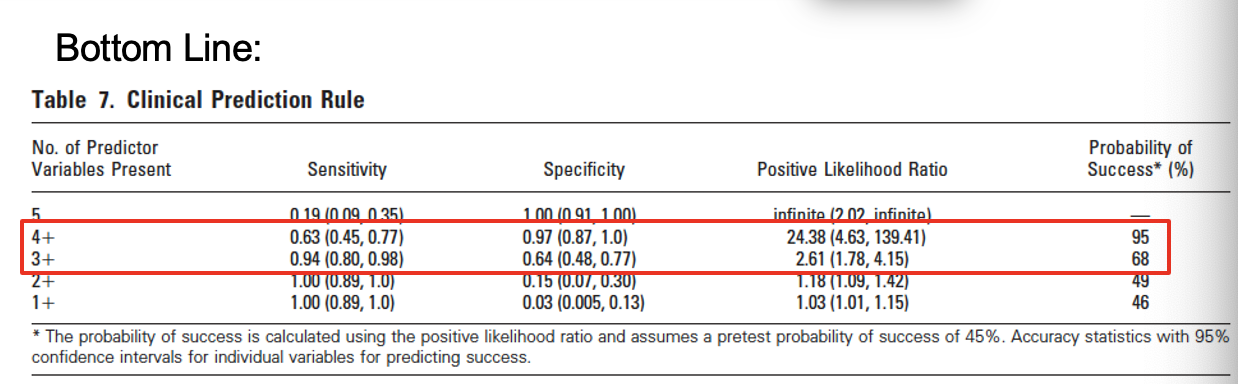
Clinical Prediction Rule for classifying patients with low back pain who demonstrate short-term, improvement with spinal manipulation: predictor variables
Duration of symptoms < 16 days
FABQ work subscale score < 19
At least one hip with > 35° of IR ROM
Hypomobility in the lumbar spine
No symptoms distal to the knee
Success = 50% reduction in ODI
______
3 treatments … initial, 2-4 days later, 2-4 days after 2nd
*** Probability of success with 4 and 3 predictor variables present
This is a clinical prediction rule which shows the characteristics of the people that get better in a study. The found these 5 things (predictor variables)
Clinical Prediction Rule for classifying patients with low back pain who demonstrate short-term, improvement with spinal manipulation: BEST RESULT
*** Best result when providing manipulation to those (+) on CPR
Exercise group = low stress aerobic and lumbar spine strengthening program.
Explain table …
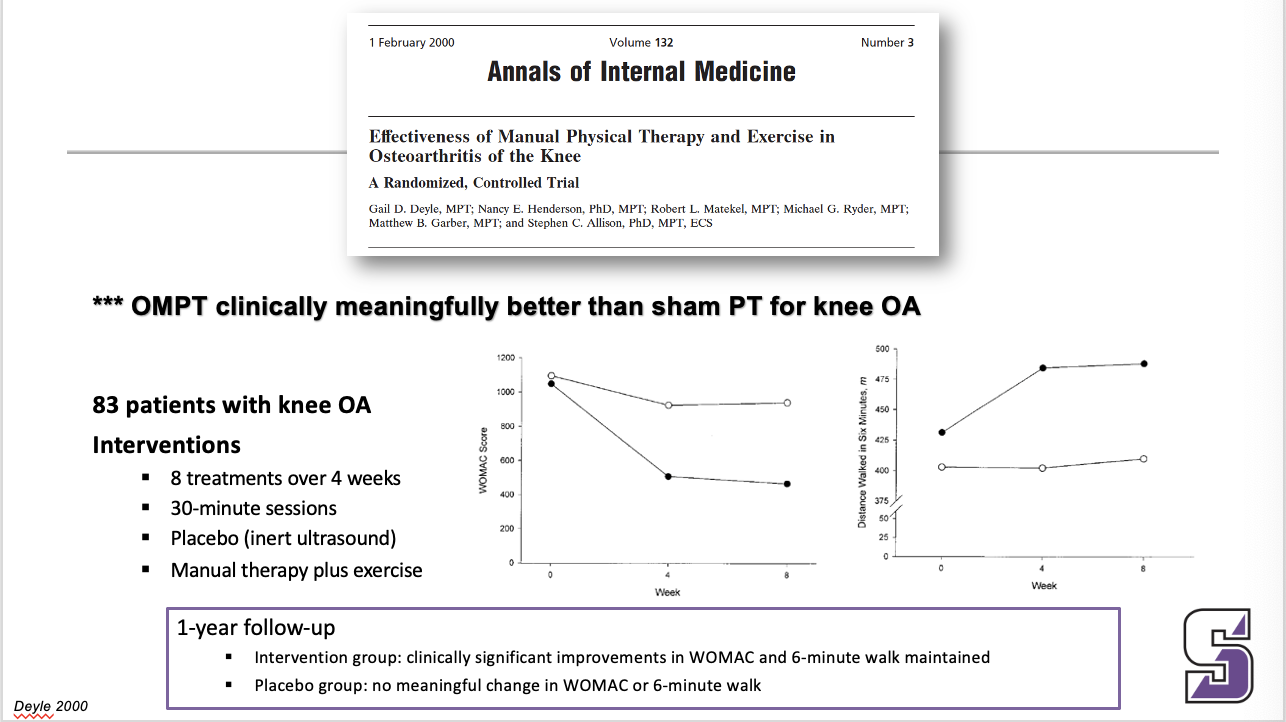
What is clinically meaningful for knee OA
*** OMPT clinically meaningfully better than sham PT for knee OA
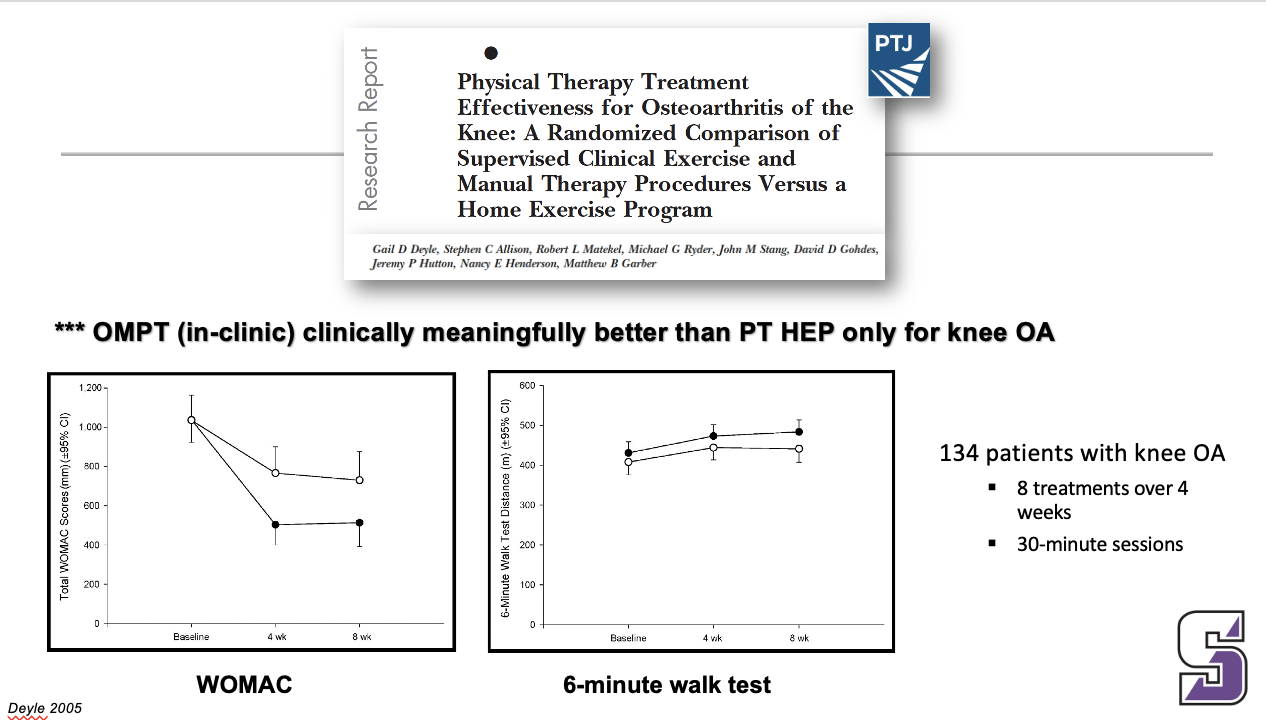
What is clinically meaningful for knee OA
*** OMPT (in-clinic) clinically meaningfully better than PT HEP only for knee OA
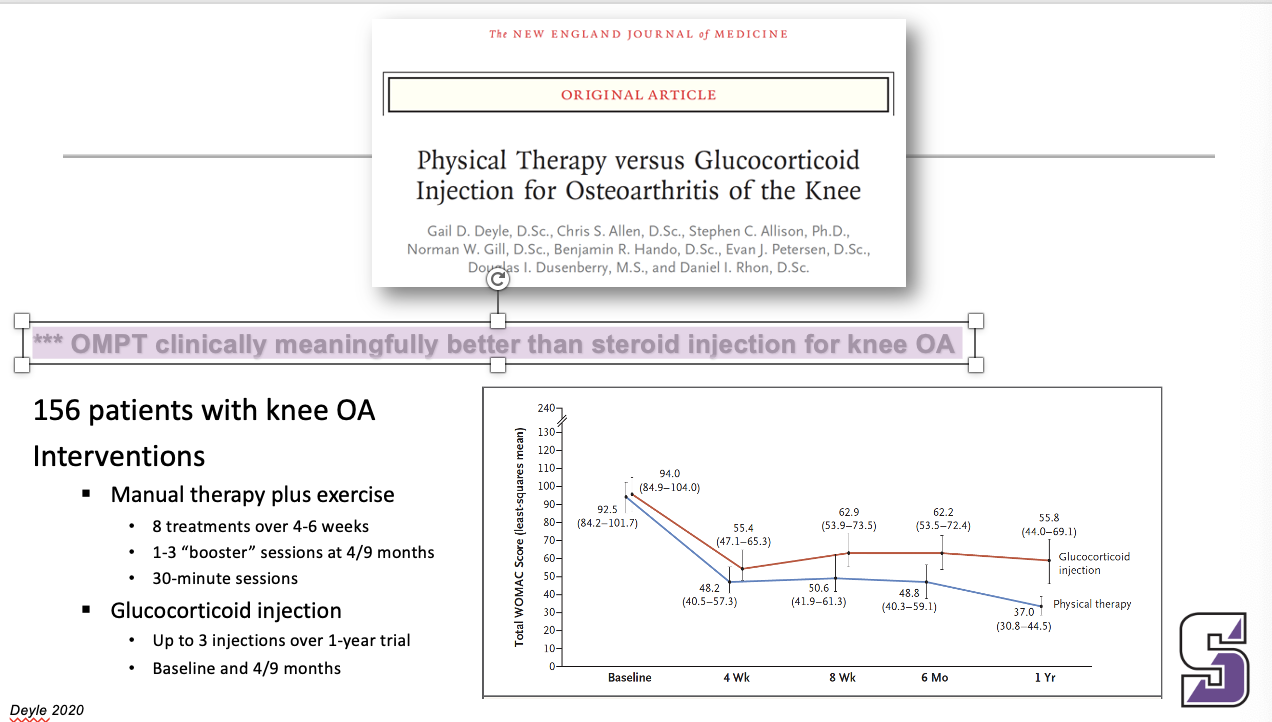
What is clinically meaningful for knee OA
*** OMPT clinically meaningfully better than steroid injection for knee OA
Detailed interview and physical examination to determine impairments and functional limitations + manual therapy techniques and reinforcing exercises
Impaired movement
Reduced strength
Reduced flexibility
Impaired motor control
Manual therapy techniques and reinforcing exercises
Primary: knee region
Secondary: L-S, hip, foot/ankle
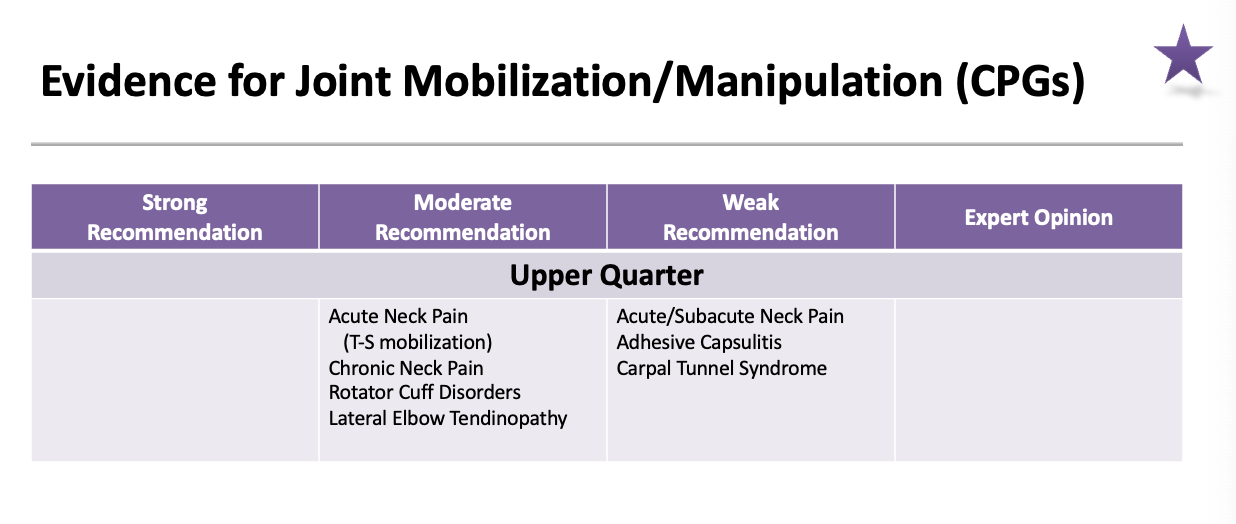
Evidence for Joint Mobilization/manipulation (CPGs): Upper Quarter moderate recommendation
Acute Neck Pain (T-S mobilization)
Chronic Neck Pain
Rotator Cuff Disorders
Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy
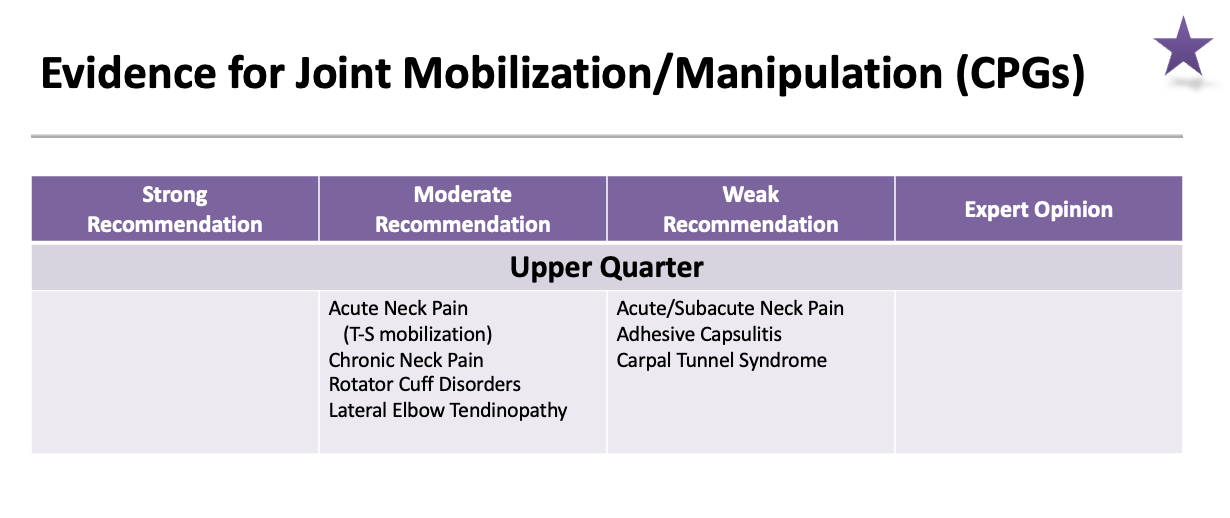
Evidence for Joint Mobilization/manipulation (CPGs): Upper Quarter weak recommendation
Acute/Subacute Neck Pain
Adhesive Capsulitis
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome

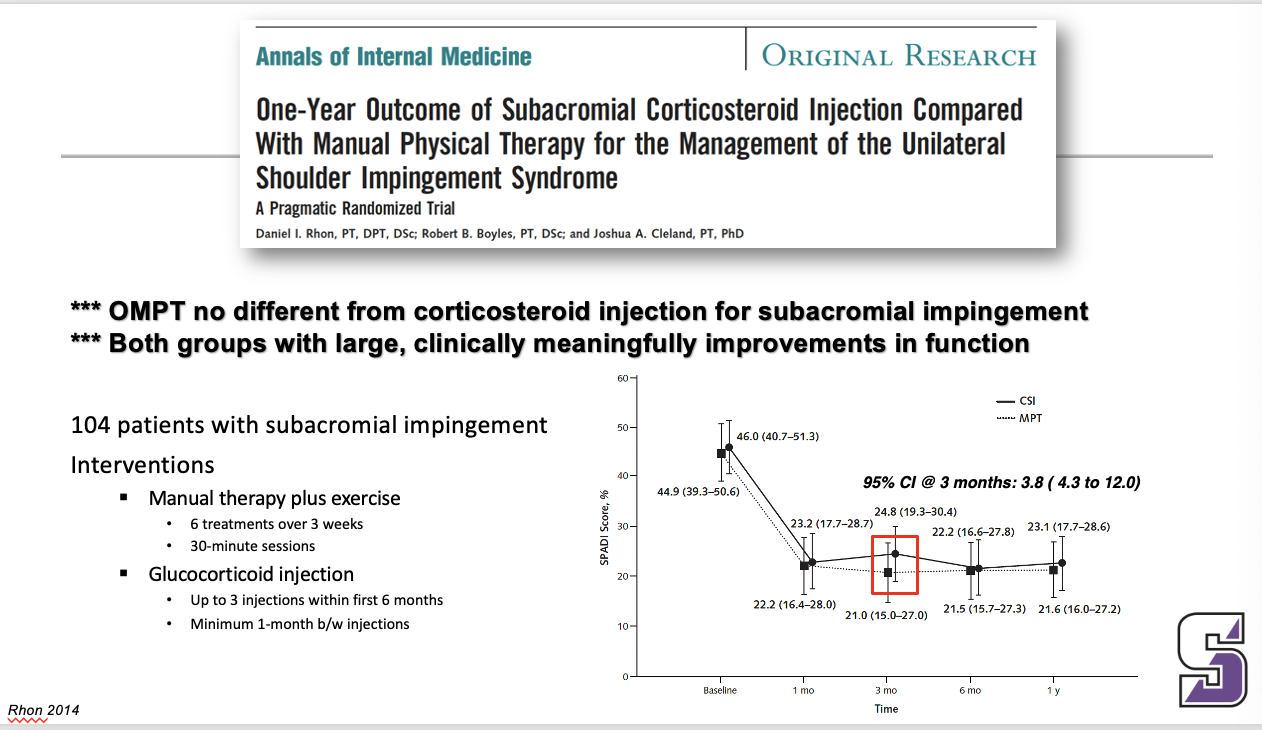
*** OMPT no different from corticosteroid injection for subacromial impingement
*** Both groups with large, clinically meaningfully improvements in function
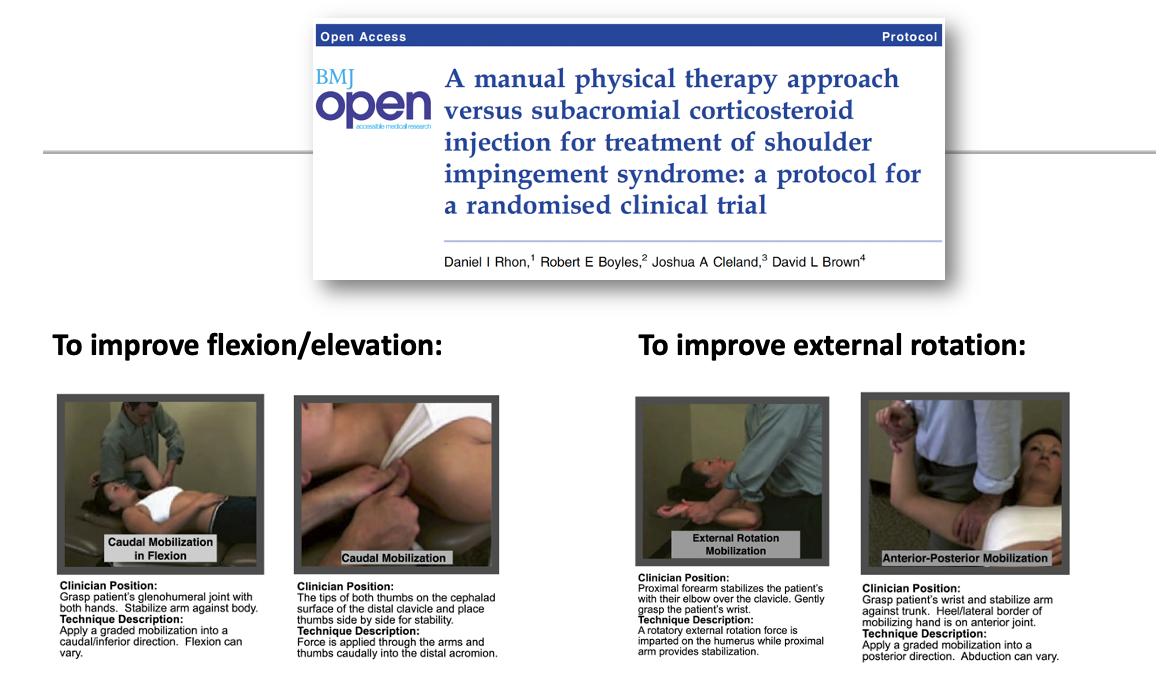
manual therapy to improve flexion/elevation or to improve external rotation

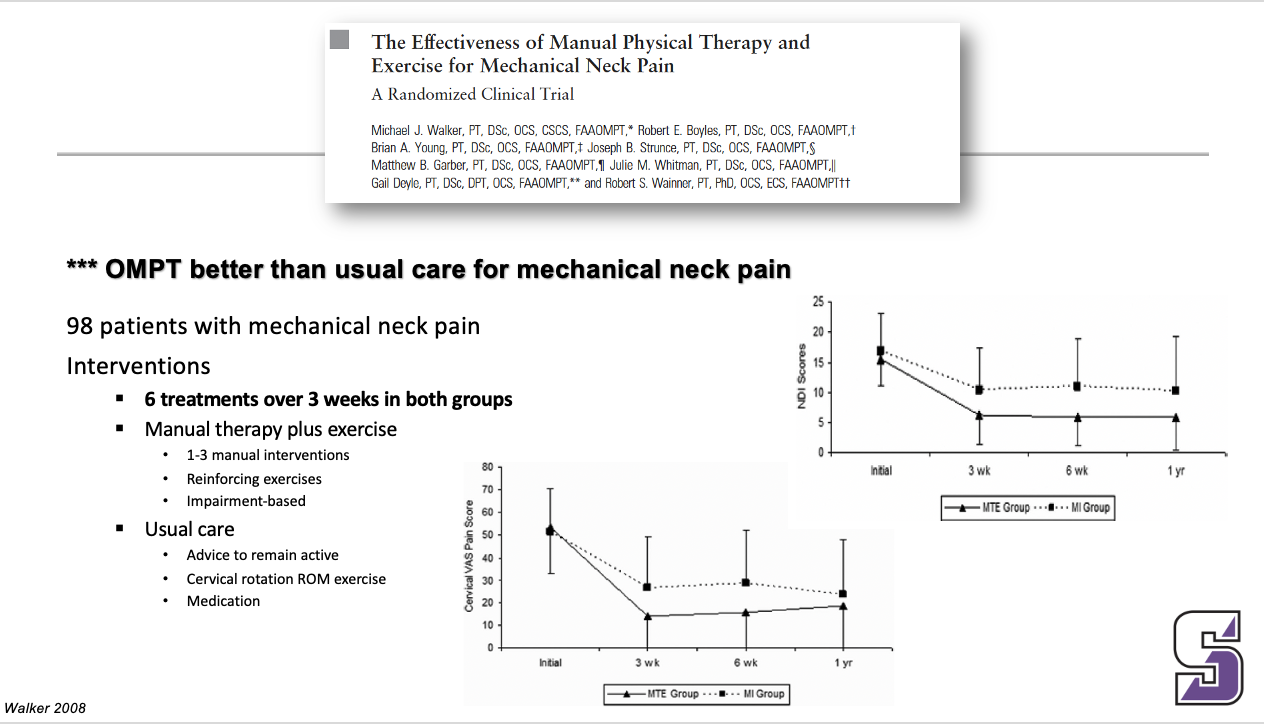
*** OMPT better than usual care for mechanical neck pain
__
Manual therapy was better than usual care for mechanical neck pain
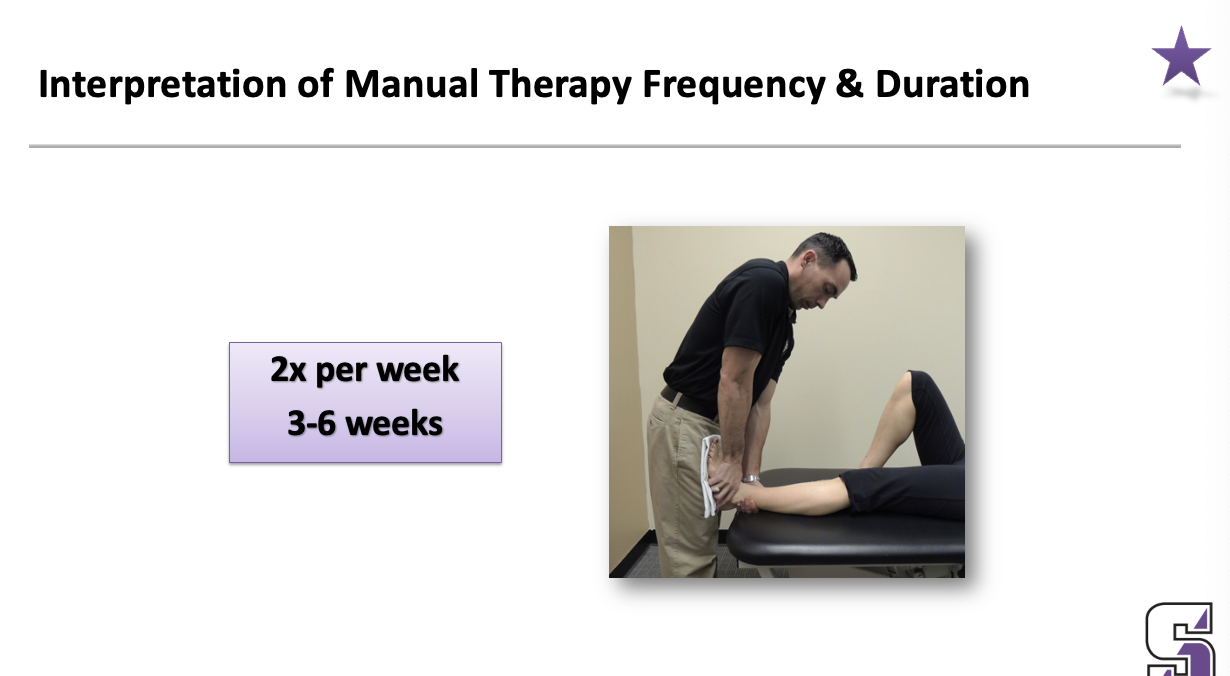
Interpretation of Manual Therapy Frequency & Duration
2x per week
3-6 weeks
______
This is the actual answer for the past slide. This is for MANUAL THERAPY ONLY
Only need about 10-12 visits of manual therapy
Review of Manual Handling Basics (3 things)
Expose areas to be examined
Use your hands to feel throughout the examination and treatment
Use your eyes for additional information
Use appropriately slow and confident movements
Use soft but as firm as required hand contact pressure
Use large skin contact areas and padding as required
Avoid pulling skin or hair, folding of skin, or putting pressure through your or the patient’s jewelry
Do not put manual pressure over or through clothing
Keep your fingernails trimmed short and filed

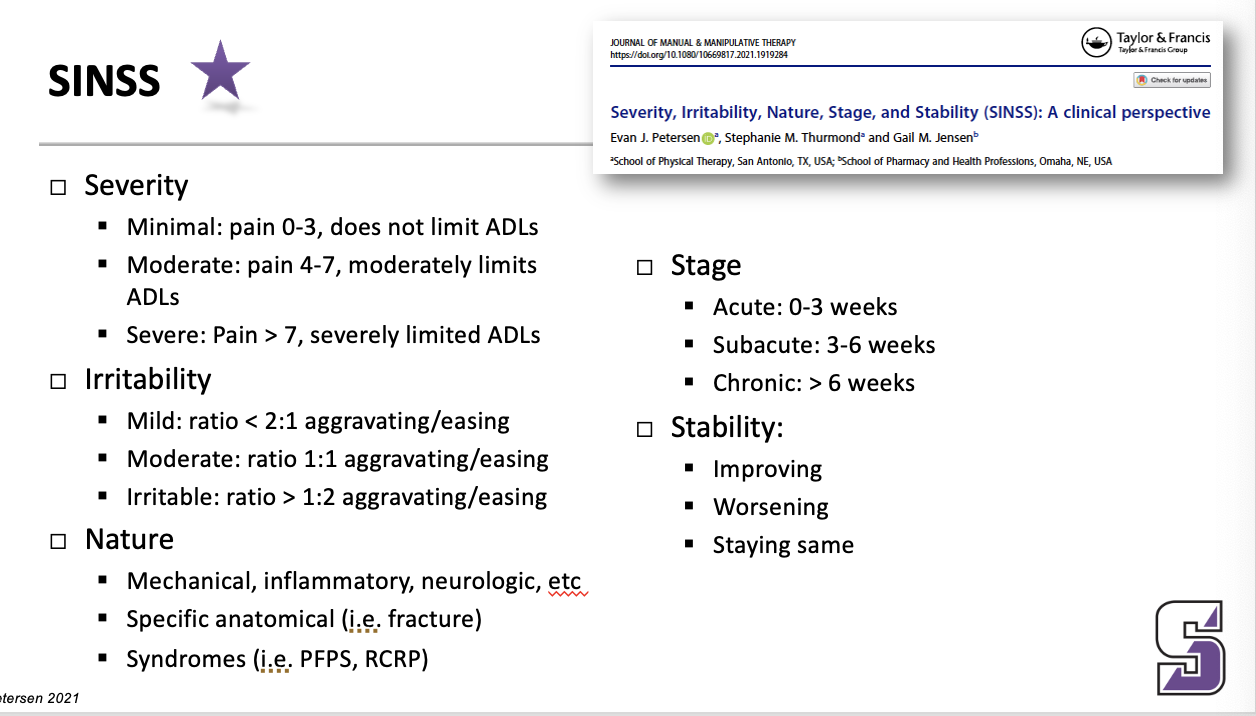
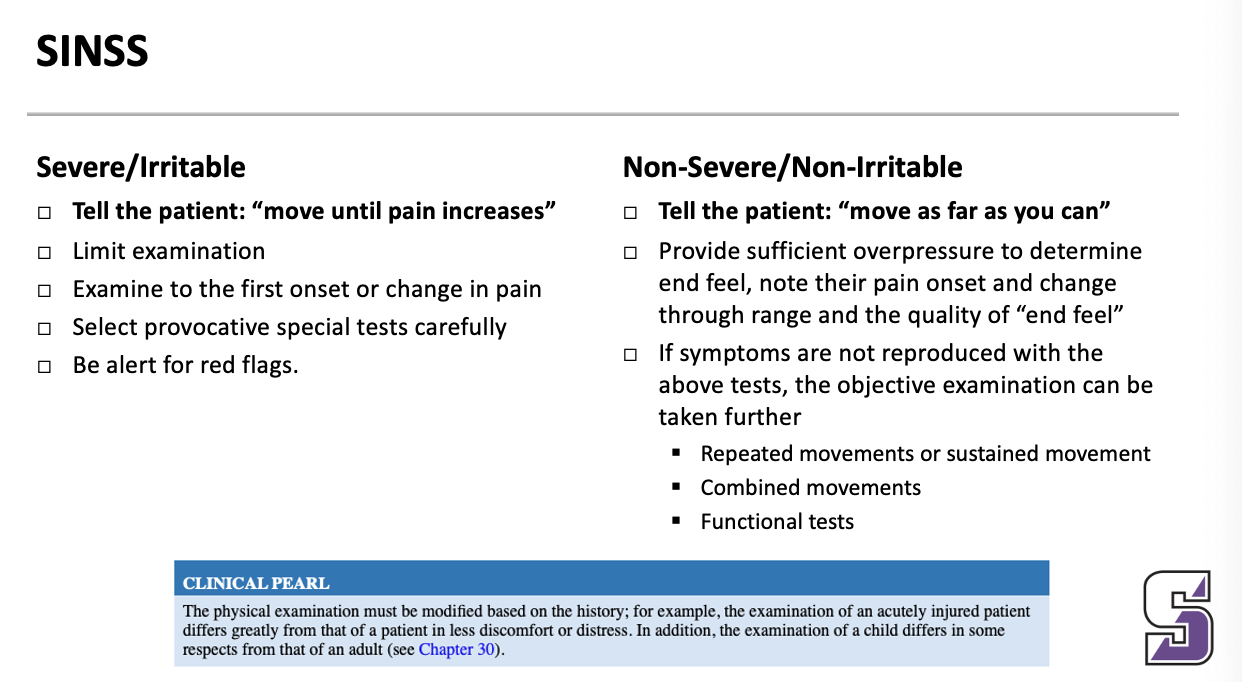
SINSS
SINSS: Severe/irritable what do you tell the patient
Severe/Irritable
Tell the patient: “move until pain increases”
Limit examination
Examine to the first onset or change in pain
Select provocative special tests carefully
Be alert for red flags.
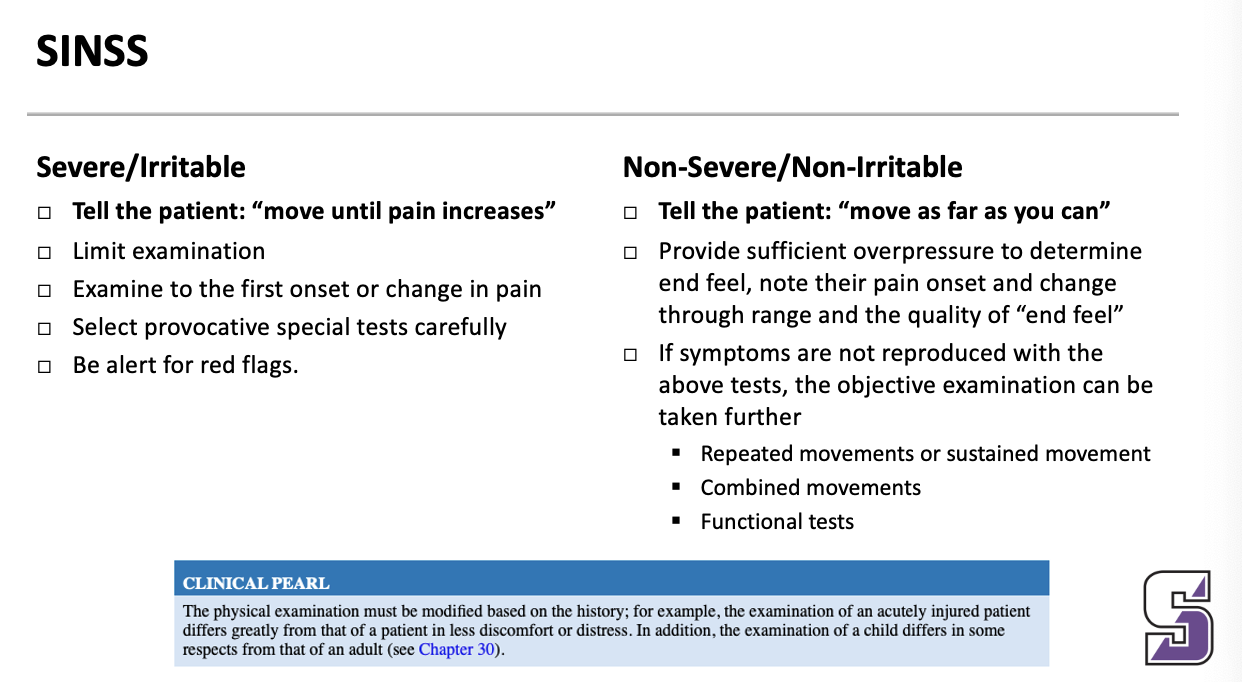
SINSS: Non-Severe/Non-irritable what do you tell the patient
Tell the patient: “move as far as you can”
Provide sufficient overpressure to determine end feel, note their pain onset and change through range and the quality of “end feel”
If symptoms are not reproduced with the above tests, the objective examination can be taken further
Repeated movements or sustained movement
Combined movements
Functional tests
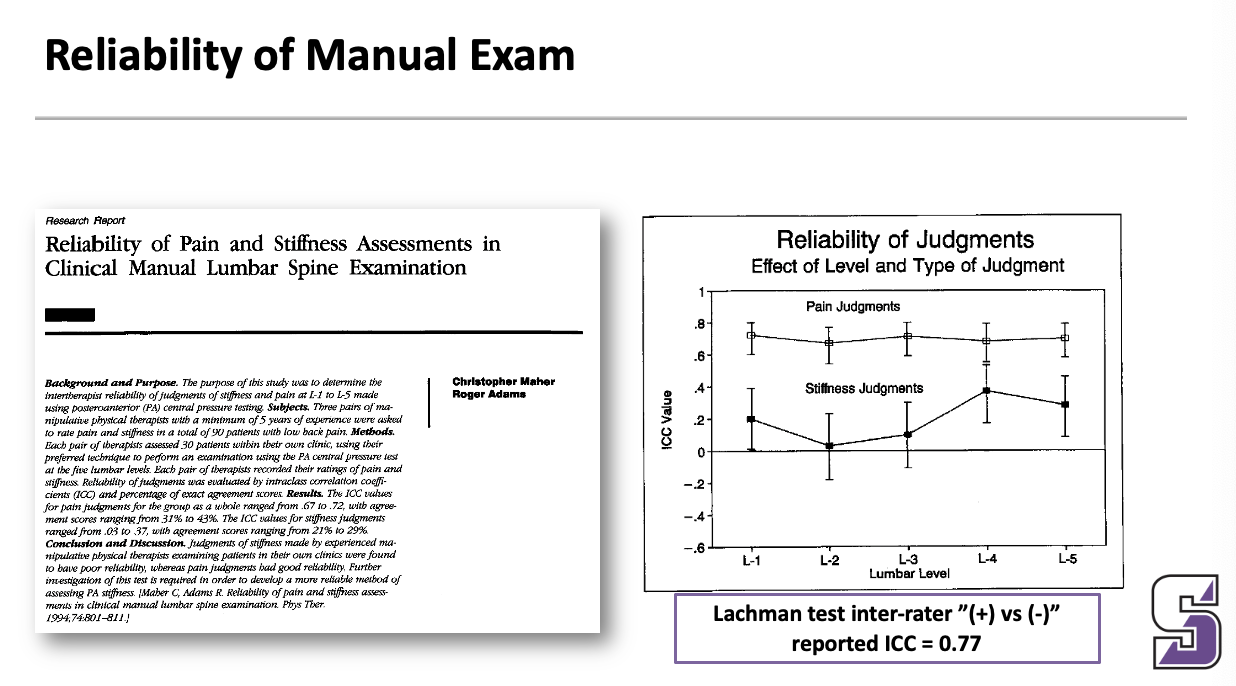
Reliability of manual exam
Pain is more reliable than stiffness
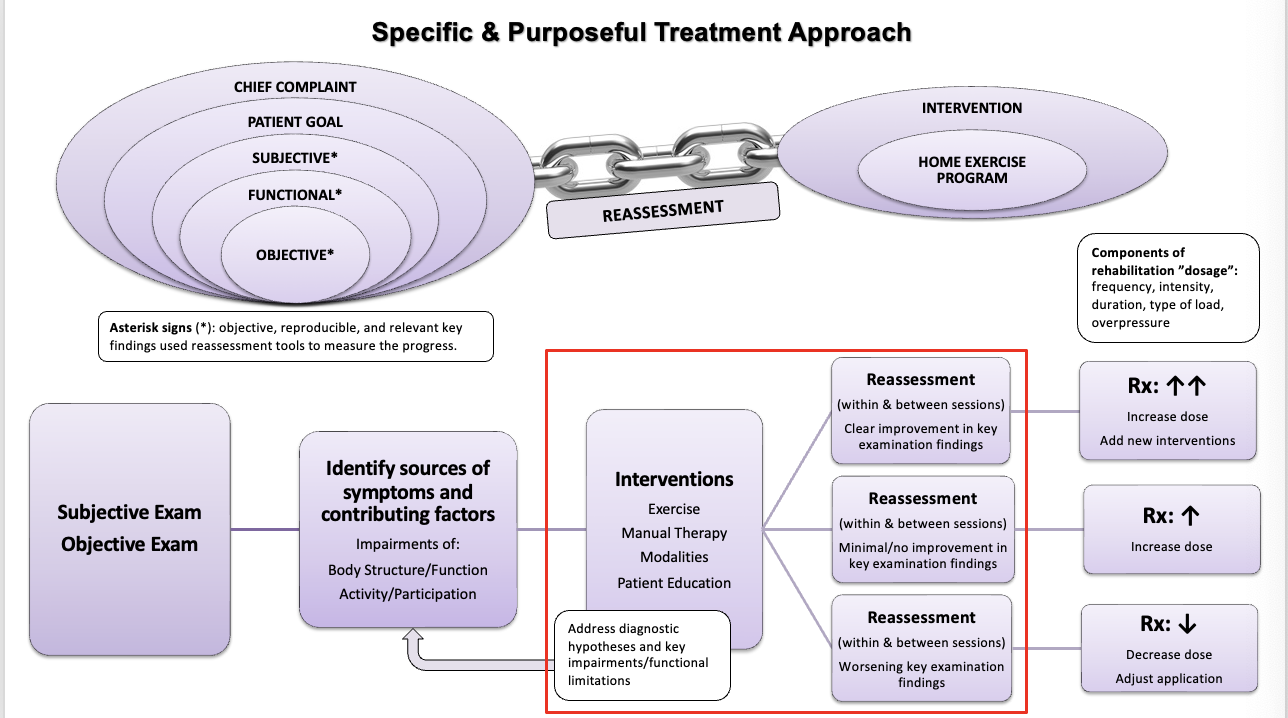
Specific and purposeful treatment approach
ignore the red
Treatment decisions: my typical treatment sequence for most patients:
My typical treatment sequence for most patients:
Initial evaluation: treat primary source of symptoms & reassess
Manual therapy
Reinforcing exercises (become home exercise program)
Quickly address contributing factors
Therapeutic exercises (may add to initial home exercise program)
Quickly address secondary problems
At subsequent visits

HEP
Home exercise program:
Should directly compliment/reinforce your initial in-clinic treatment.
Consists of 2-3 exercises that will maximize benefit.
Reassessment: what is reassessed? when are they reassessed?
What is reassessed? à ASTERISKS
When are asterisks reassessed?
WITHIN SESSION: immediately following application of the intervention and/or immediately following the treatment session
BETWEEN SESSIONS: prior to starting the next treatment session
____
Example … low back pain … pain with running & pain with sitting
Special tests … straight leg raise

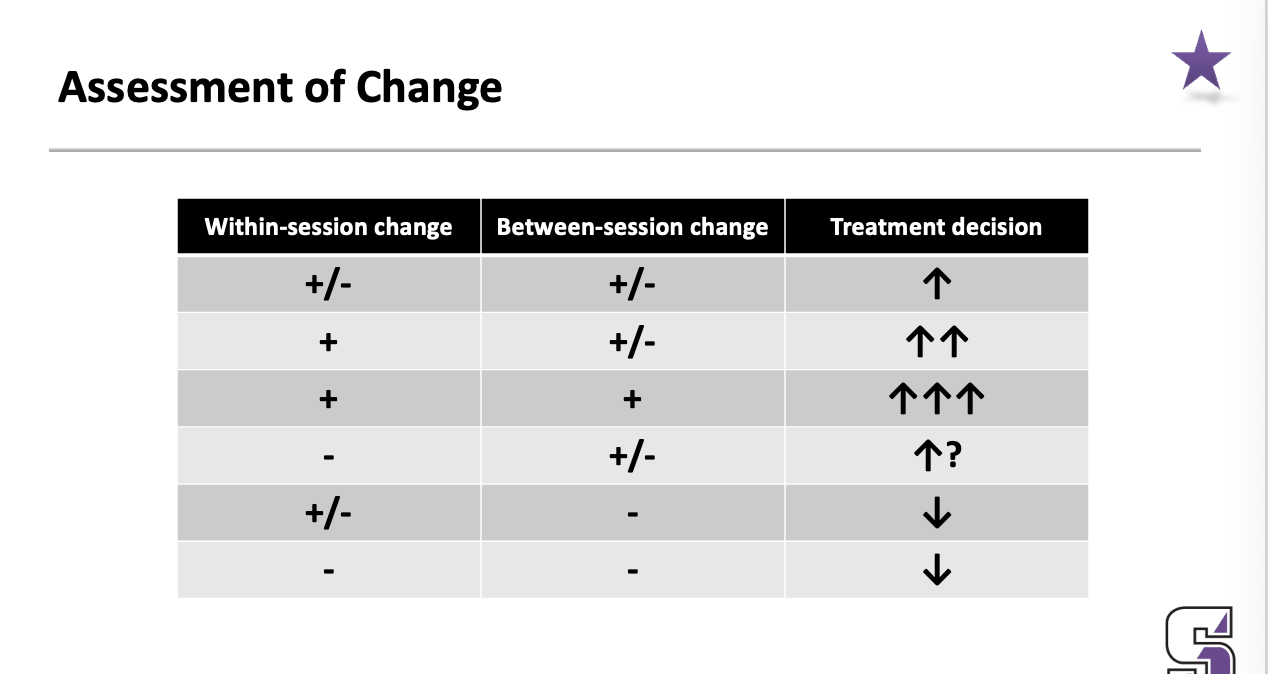
Assessment of change
within-session change
between-session change
treatment decision
“Dosage” in physical therapy: exercise variables: to improve mobility
To improve mobility
Sets & repetitions
More is better
Load/resistance
Low-moderate
Frequency per day
Frequently
Total volume
High
# of exercises
More is better
“Dosage” in physical therapy: exercise variables: to improve muscle force production
To improve muscle force production
*** Depends on the goal
Endurance vs strength vs hypertrophy vs power
Tissue loading
Sets & repetitions
Load/resistance
Frequency per day
Total volume
Speed
# of exercises
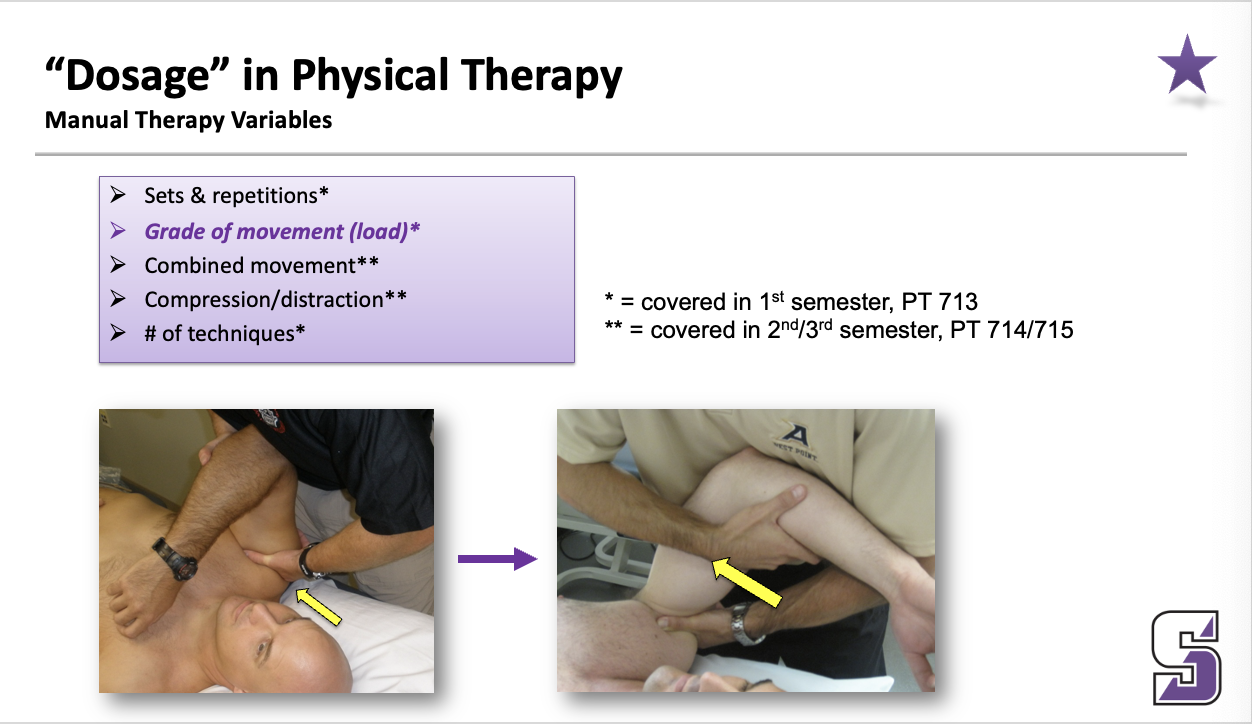
“Dosage” in physical therapy: manual therapy variables
Sets & repetitions
Grade of movement (load)
Combined movement
Compression/distraction
# of techniques
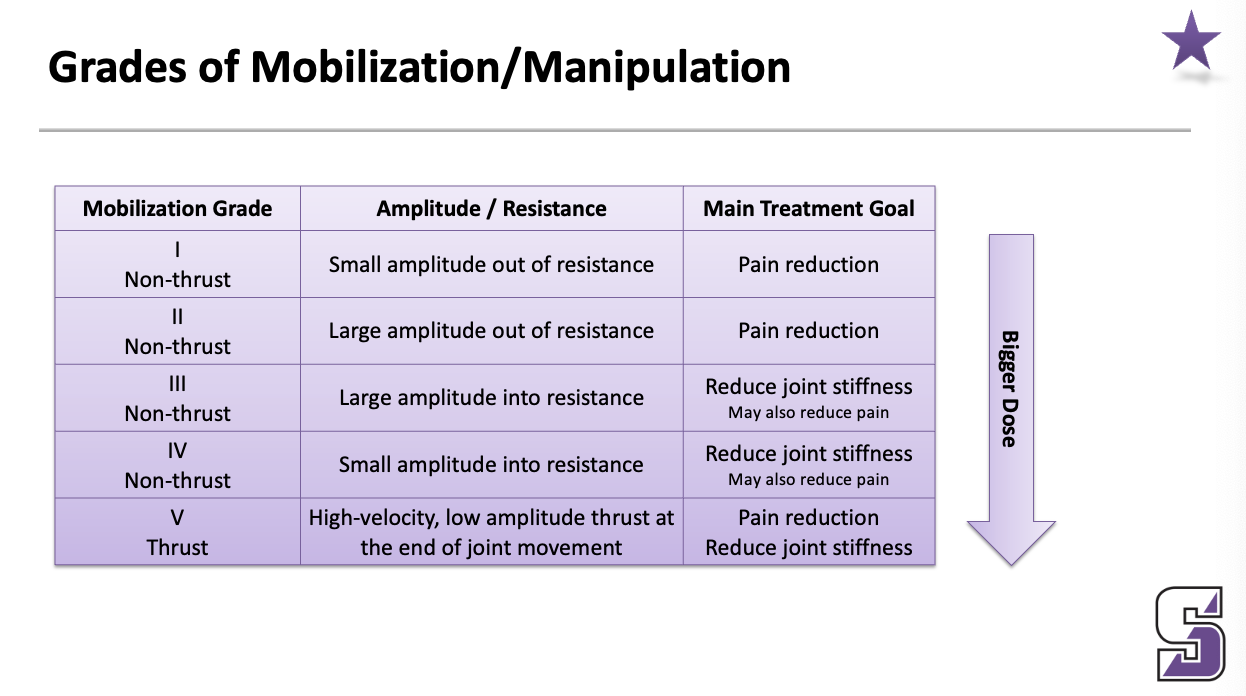
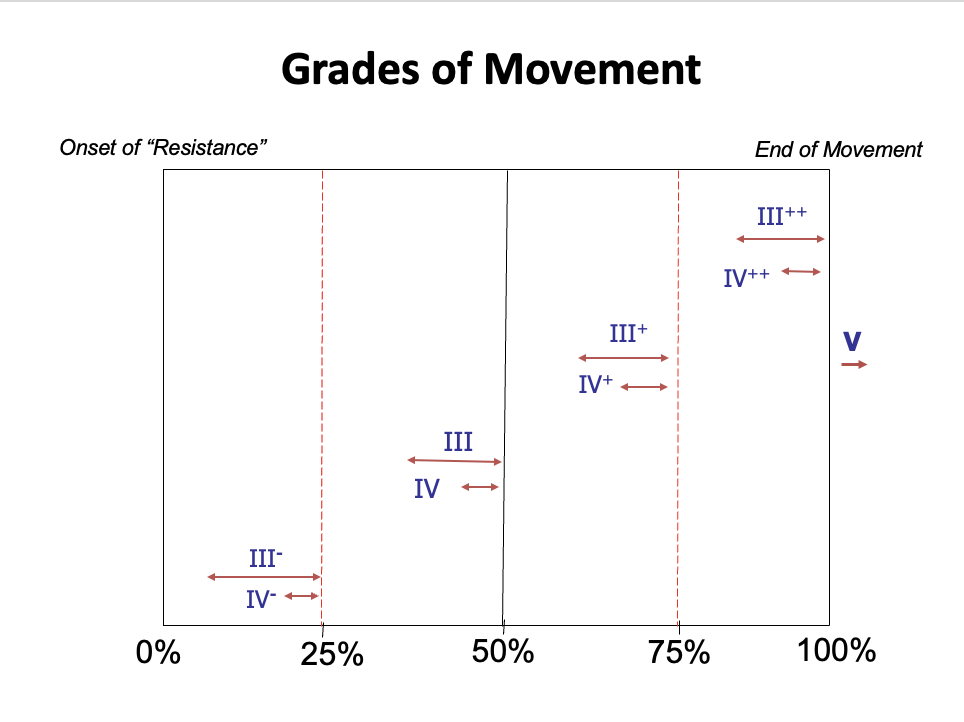
Grades of Mobilization/Manipulation
Grades of Movement: other photo
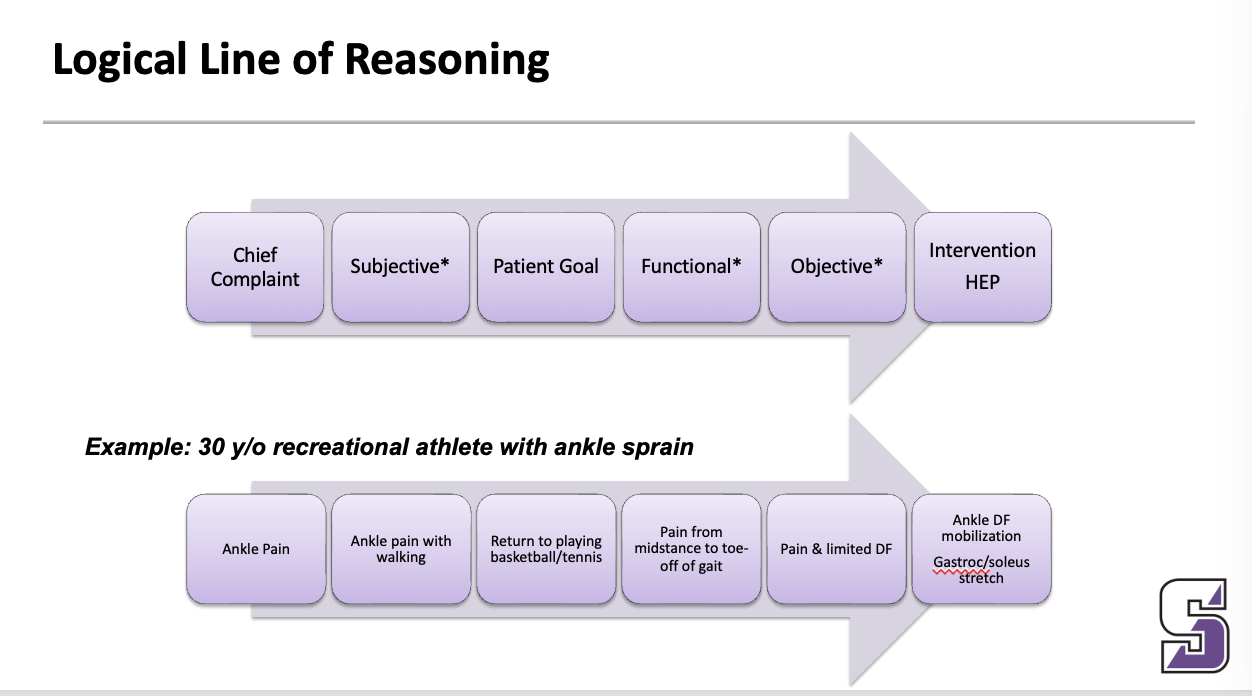
Logical Line of Reasoning
____
May have more than 1 logical line of reasoning for a patient … different components of the same disorder …
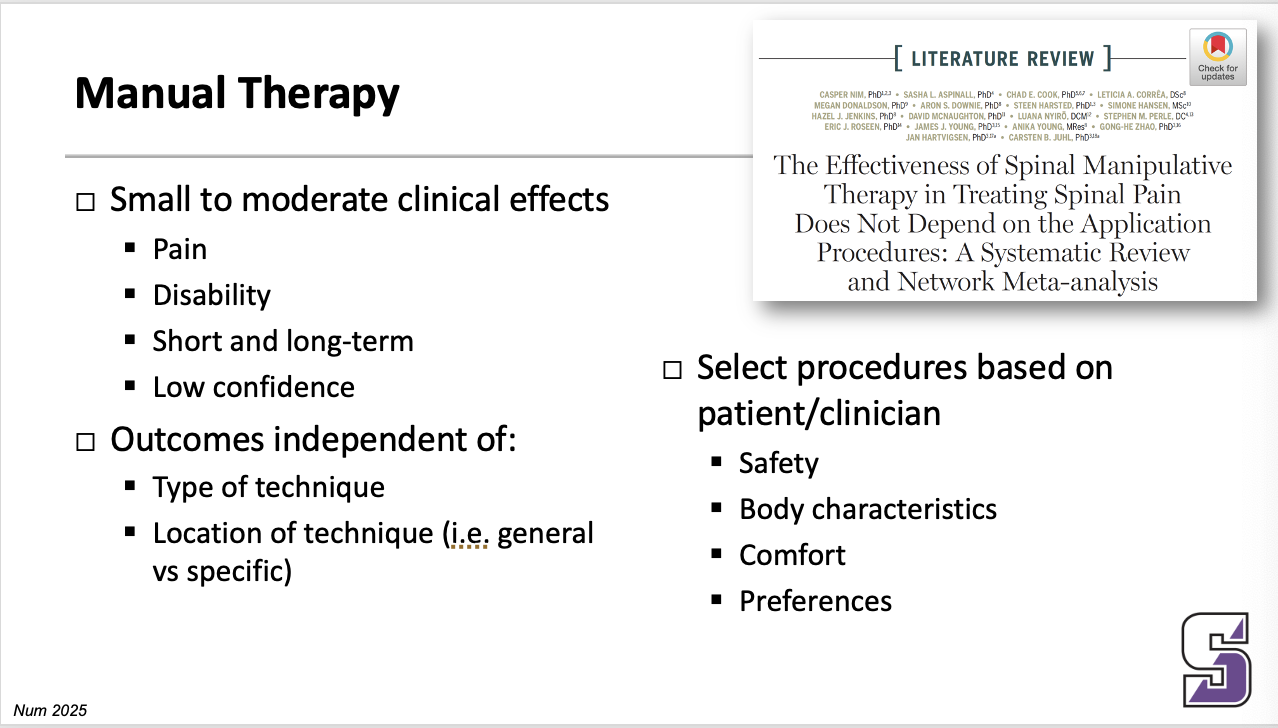
Manual therapy: small to moderate clinical effects, outcomes independent of, select procedures based on patient/clinician
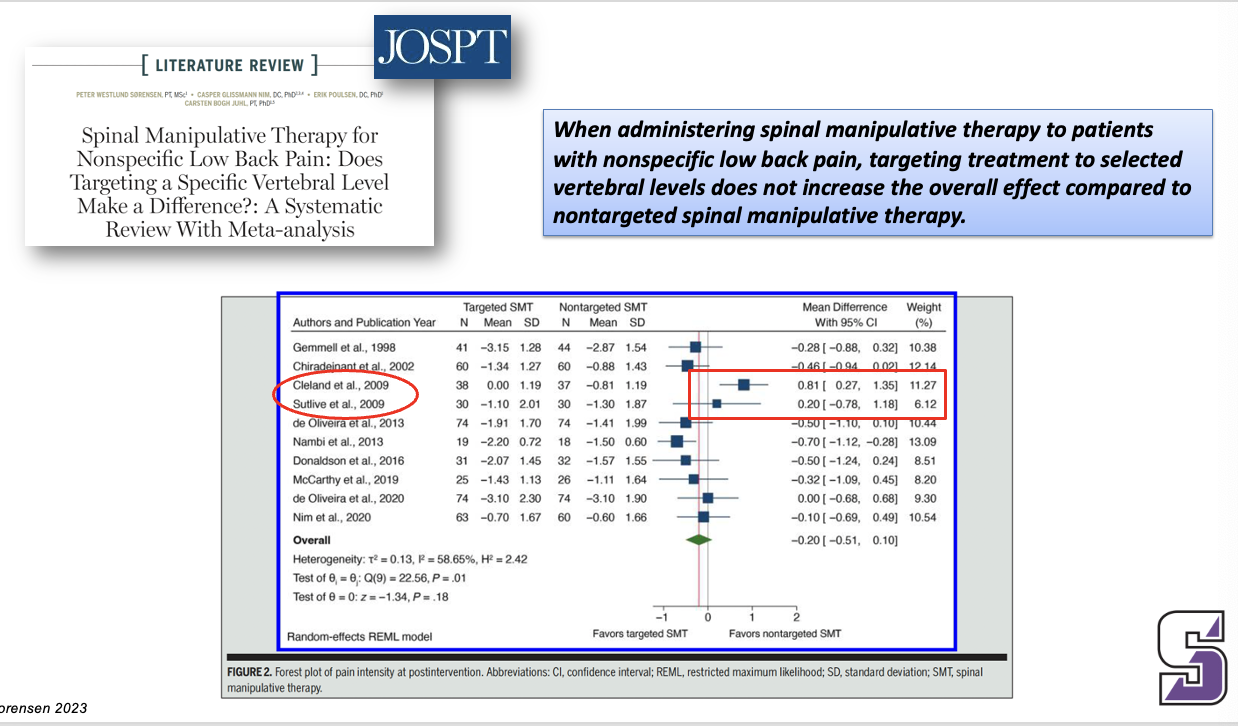
When administering spinal manipulative therapy to patients with nonspecific low back pain, targeting treatment to selected vertebral levels does not increase the overall effect compared to nontargeted spinal manipulative therapy.
Absolute Contraindications to Manual Therapy
Systemic or localized infection (e.g., osteomyelitis)
Acute circulatory condition
Malignancy
Open wound or sutures at the treatment site
Recent fracture
Hematoma
Hypersensitivity of the skin
Inappropriate end-feel (spasm, empty, and bony), or evidence of joint ankylosis, or joint hypermobility
Advanced diabetes
Rheumatoid arthritis (in a state of an exacerbation)
Cellulitis
Constant, severe, or extensive radiating pain, including pain at rest or that disturbs sleep, indicating that the condition is likely to be very irritable
Any condition that has not been fully evaluated

Relative Contraindications to Manual Therapy
Joint effusion or inflammation
Rheumatoid arthritis (not in a state of an exacerbation)
Presence of neurologic signs
Osteoporosis
Pregnancy, if a technique is to be applied to the spine
Dizziness
Steroid or anticoagulant therapy
Multiple effects
-Central nervous system
-Peripheral nervous system
-Musculoskeletal tissue
-Neural tissue

continue the current manual treatment, but reinforce need to perform HEP

increase dose of current dose