Chemistry Unit 10 Mr McMullen
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Properties of Acids
Looks like water
Tastes sour
At first feels like water, then it burns
Acids reacts to produce H2 gas when reacting with metal
Conducts electricity
Turns lithiums red
Turns menthol orange to red
Phenolphtaline turns colorless
pH<7
Properties of bases
looks like water
Has a bitter taste (medicine)
Feel slippery then start to burn
Only reacts with Al & Zn
Conducts electricity
Turns litmus blue
Keeps methyl orange orange
Turns phenolphtaline pink
pH > 7
Which acids are found in acid rain
Carbonic acid
Sulfuric acid
Nitric acid
Sulfurous acid
Nitrous acid
Which gases are responsible for producing acid rain
Carbon Dioxide - CO2
Carbon Oxide - CO
Sulfur Dioxide - SO2
Nitrogen Dioxide - NO2
Nitrogen Oxide - NO
What is a Neutralization reaction
Acid + Base —> Water + Salt
HCl + NaOH —> H2O + NaCl
Arrhenius acid definition
A substance that dissociates in water to produce hydrogen ions
Ex. Substances HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, H2CO3
Ex. Image
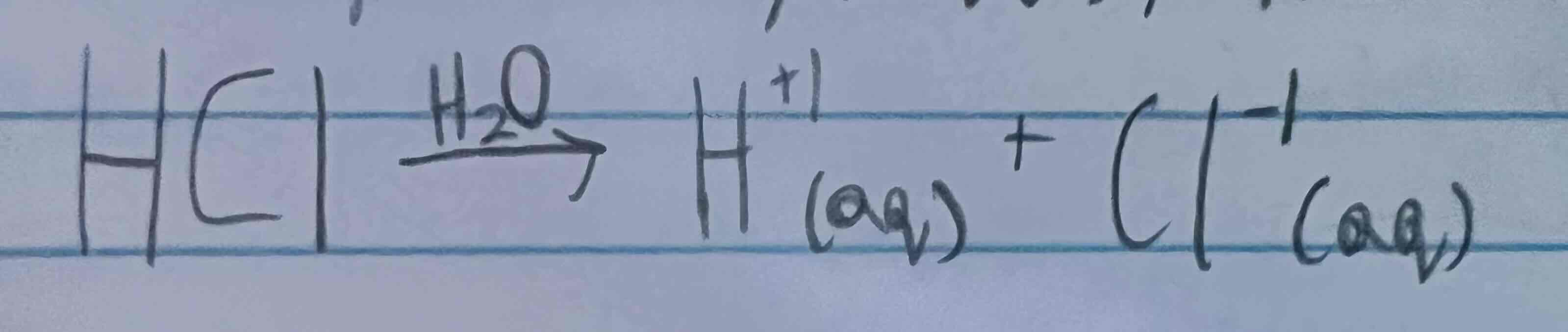
Arrhenius Base definition
A substance that dissociates in water to produce hydroxide Ions
Ex substances. KOH, LiOH, Ca(OH)2
Arrhenius three limitations
Oversimplified what happens between acids and water ex. Image
Restricted acids and bases to water solutions
Excludes based without hydroxide ex. NaHCO3, NH3, CaCO3
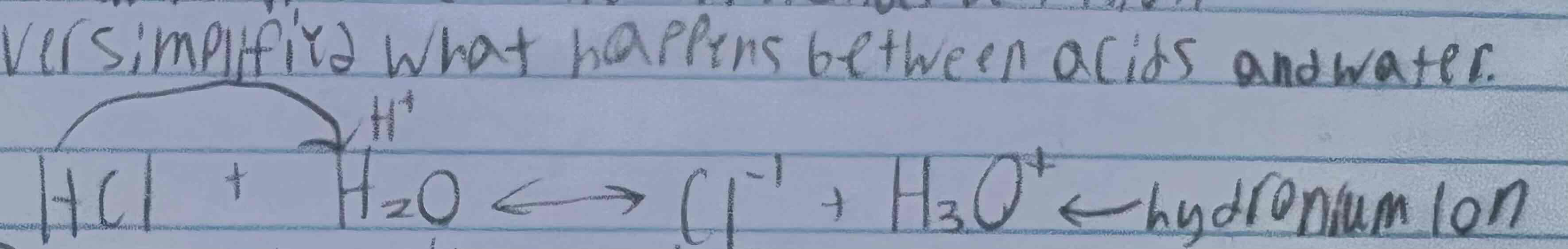
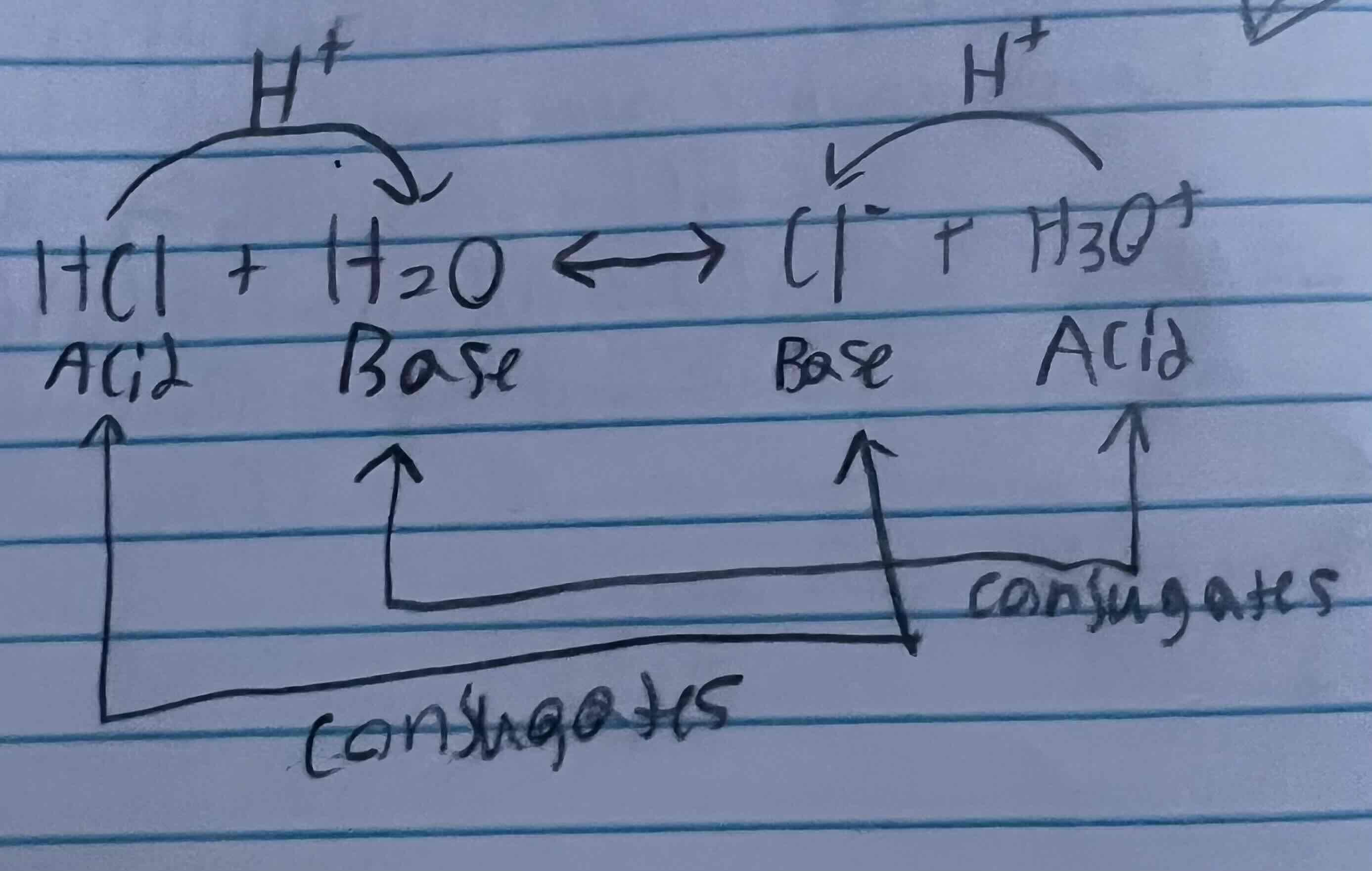
Bronstead-Lowrery Acid definition
A substance that donates H+ ions (proton donator)
Bronstead-Lowery Base definition
A substance that accepts H+ ions (Proton acceptor)
Amphoteric
A substance that can react as either an acid or a base ex. H2O
Conjugate acid/base pairs and definition
Acids and baseS that differ by 1 H+ ion
H2SO4 | HSO4-1
H3O+1 | H2O
HCO3-1 | CO3-2
Strong acid definition and examples
An acid that completely ionizes to form many H3O+1 ions in water
Ex. HCl, HNO3, H2SO4

Weak acid definitions and examples
An acid that partially ionizes to form few H3O+1 ions in water
Ex. HC2H3O2, H2CO3
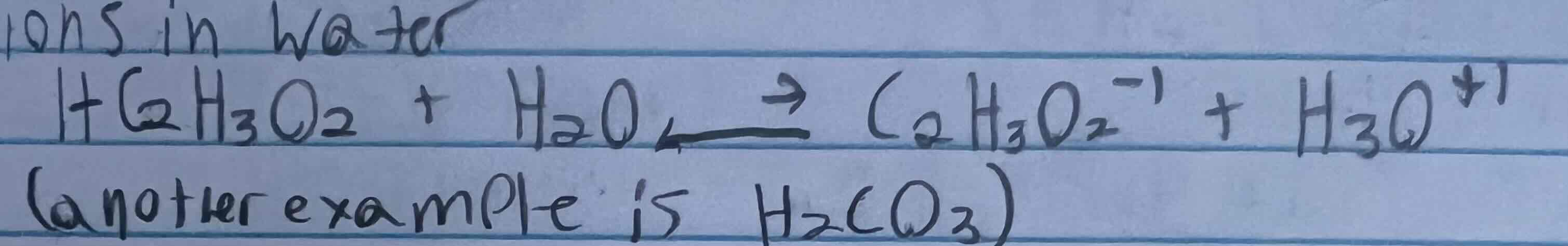
Titration
A lab procedure where a standard solution is used to determine the unknown concentration of an acid or base
Standard Solution
The acid or base of known concentration
Equivalence point
The neutralization point at which the concentration of the H3O+ ions are equal to the OH- ions
End point
The point at which the indicator changes color
Monoprotic
Acid with one ionizable hydrogen (HCl)
Diprotic
Acid with two ionizable hydrogen (H2SO4)
Triprotic
Acid with three ionizable hydrogens (H3PO4)