Physics Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCQ questions and three definitions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
A uniform force of (2i^ + j^) N acts on a particle of mass 1 kg. The particle displaces from position (3j^ + k^ )m to (5i^ + 3j^) m. The work done by the force on the particle is _______.
c) 10 J
A ball of mass 1 kg and another of mass 2 kg are dropped from a tall building whose height is 80 m. After, a fall of 40 m each towards Earth, their respective kinetic energies will be in the ratio of _______.
d) 1 : 2
A body of mass 1 kg is thrown upwards with a velocity 20 m s-1. It momentarily comes to rest after attaining a height of 18 m. How much energy is lost due to air friction?
a) 20 J
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water of the jet. What is the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water?
a) 1/2 mv3
What is the minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter a vertical loop of radius R so that it can complete the loop?
c) √5gR
A body of mass 4 m is lying in xy-plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into three pieces. Two pieces each of mass m move perpendicular to each other with equal speed v. The total kinetic energy generated due to explosion is
b) 3/2mv²
The potential energy of a system increases, if work is done
a) by the system against a conservative force
The work done by the conservative force for a closed path is
b) zero
If the linear momentum of the object is increased by 0.1%, then the kinetic energy is increased by
b) 0.2%
If the potential energy of the particle is α – β/2x², then force experienced by the particle is _______.
b) F = βx
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electric energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional to
c) v3
Two equal masses m1 and m2 are moving along the same straight line with velocities 5ms-1 and -9ms-1 respectively. If the collision is elastic, then calculate the velocities after the collision of m1 and m2, respectively _______.
c) -9ms^-1 and 5 ms^-1
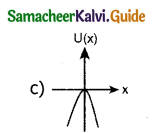
A particle is placed at the origin and a force F= kx is acting on it (where k is a positive constant). If U(0)=0, the graph of U(x) versus x will be (where U is the potential energy function
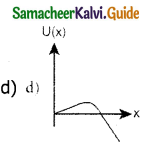
A particle which is constrained to move along x-axis, is subjected to a force in the same direction which varies with the distance x of the particle from the origin as F(x) = – kx + ax3. Here, k and a are positive constants. For x > 0, the functional form of the potential energy U(x) of the particle is
A spring of force constant k is cut into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other. Then, the long piece will have a force constant of
b) 3/2 k
Coefficient of Restitution
It is defined as the ratio of velocity of separation (relative velocity) after collision to the velocity of approach (relative velocity) before collision, i.e.,

Power
a measure of how fast or slow a work is done. Power is defined as the rate of work done or energy delivered.
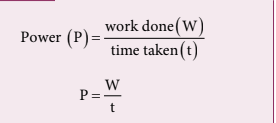
The law of conservation of energy
energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It may be transformed from one form to another but the total energy of an isolated system remains constant.