AT 505 Ch.6 pt1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
main site of transport of water, gases,electrolytes, substrates, and waste products between the bloodstream and the extracellular fluid
capillaries
Hypoperfusion
At times, the system fails to provide sufficient circulation for every body part to perform its function, which can lead to death.
Blood is a specialized connective tissue that contains these formed elements
red cells, white cells, and platelets
liquid portion of the blood
plasma
Plasma contains
key electrolytes and dissolved nutrients, namely, glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids.
The average adult has about 5.3 quarts (5L) of whole blood
true
how many liters of blood do men have
5.0-6.0 L
how many liters of blood do women have?
4.5-5.5 L
Perfusion
The circulation of blood within an organ or tissue with adequate amounts to meet the cell's current needs for oxygen, nutrients, and waste removal
The microcirculation regulates blood flow to the following
-Individual organs
• The distribution of blood flow within organs
• Diffusion distances between an organ's blood supply and tissues
-The capillary surface area available for exchange or materials between the plasma and tissues
Reduced perfusion of vital tissues leads to declines in
oxygen delivery to cells and is inadequate for aerobic metabolism
hemorrhage
Bleeding that leads to an acute loss of circulating blood volume.
Complications with hemorrhage that the AT may encounter in the prehospital setting include disorders associated with clotting.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and Other hypercoagulable conditions
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Clotting of blood in a deep vein of an extremity (usually calf or thigh) or the pelvis, it isthe primary cause of pulmonary embolism.
Hypercoagulable conditions
Excessive blood clotting, or failure to break down and remove clots, limiting or blocking blood flow
Major orthopedic injuries, in particular fractures of large bones(pelvis, femur), that often require surgery carry a high risk for
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), Pulmonary embolism (PE)
Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
A blood clot that starts in a vein
Pulmonary embolism (PE)
Sudden blockage of a major artery in the lung by a blood clot
Upper-extremity DVT
occurs as a result of a hypercoagulable state or subclavian vein compression at the thoracic outlet. (less common in sports medicine)
Factors that contribute to severity of hemorrhage include the following
-Patient's age
• Severity of injury, with special attention to type and anatomic location of injury
• Time lapse between injury and initiation of treatment• Prehospital treatment available
• Medications used for chronic conditions
• The degree of blood volume loss is related to the magnitude of the tissue injury.
Cardiac output is the determinant of
tissue perfusion
In most cases, ________ is the earliest measurable circulatory sign of shock.
tachycardia
External hemorrhage (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
• Bleeding is visible
• Controlled via direct pressure or pressure bandage
Internal hemorrhage (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
• Not typically visible
• Often identified later in the assessment
• Usually controlled by surgeon
Ecchymosis (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
bruise
Epistaxis (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
nose bleed
Hematemesis (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
vomiting blood
Hemoptysis (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
coughing up blood - lungs
Menorrhagia (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
menstrual blood flow - excessive or prolonged
Petechiae (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
intradermal or mucosal hemorrhage - small
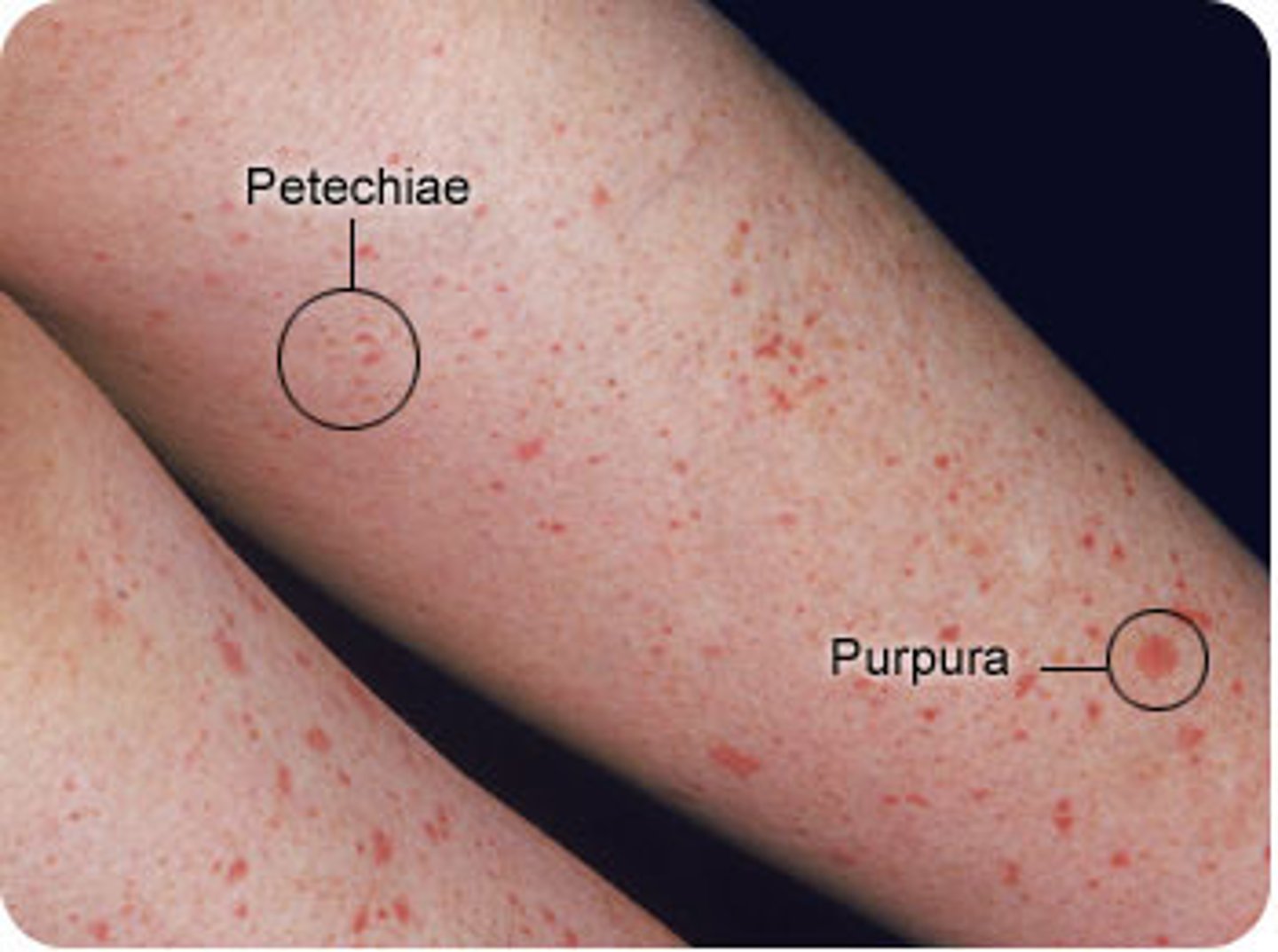
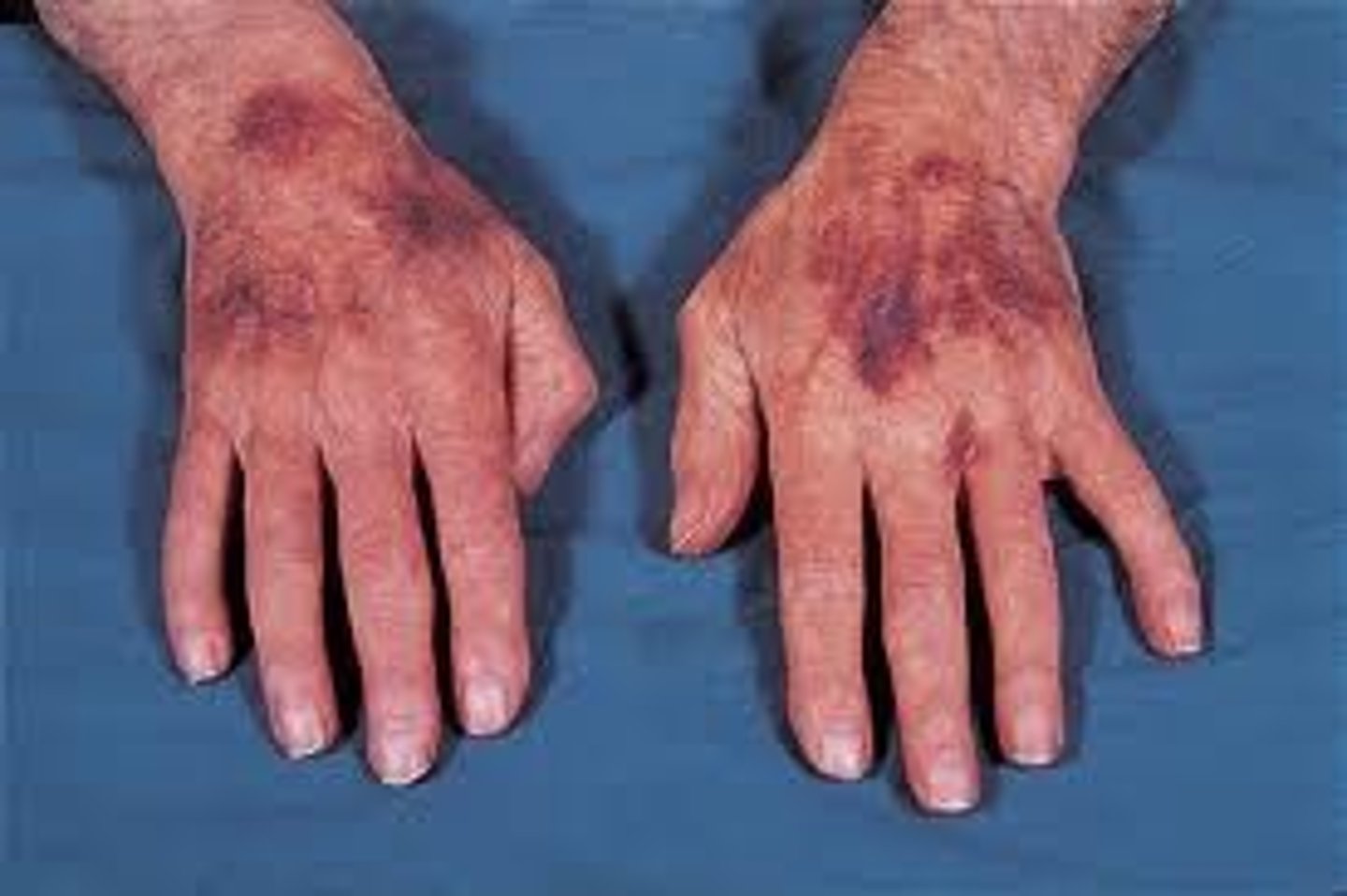
Purpura (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
mucosal or skin hemorrhage - large
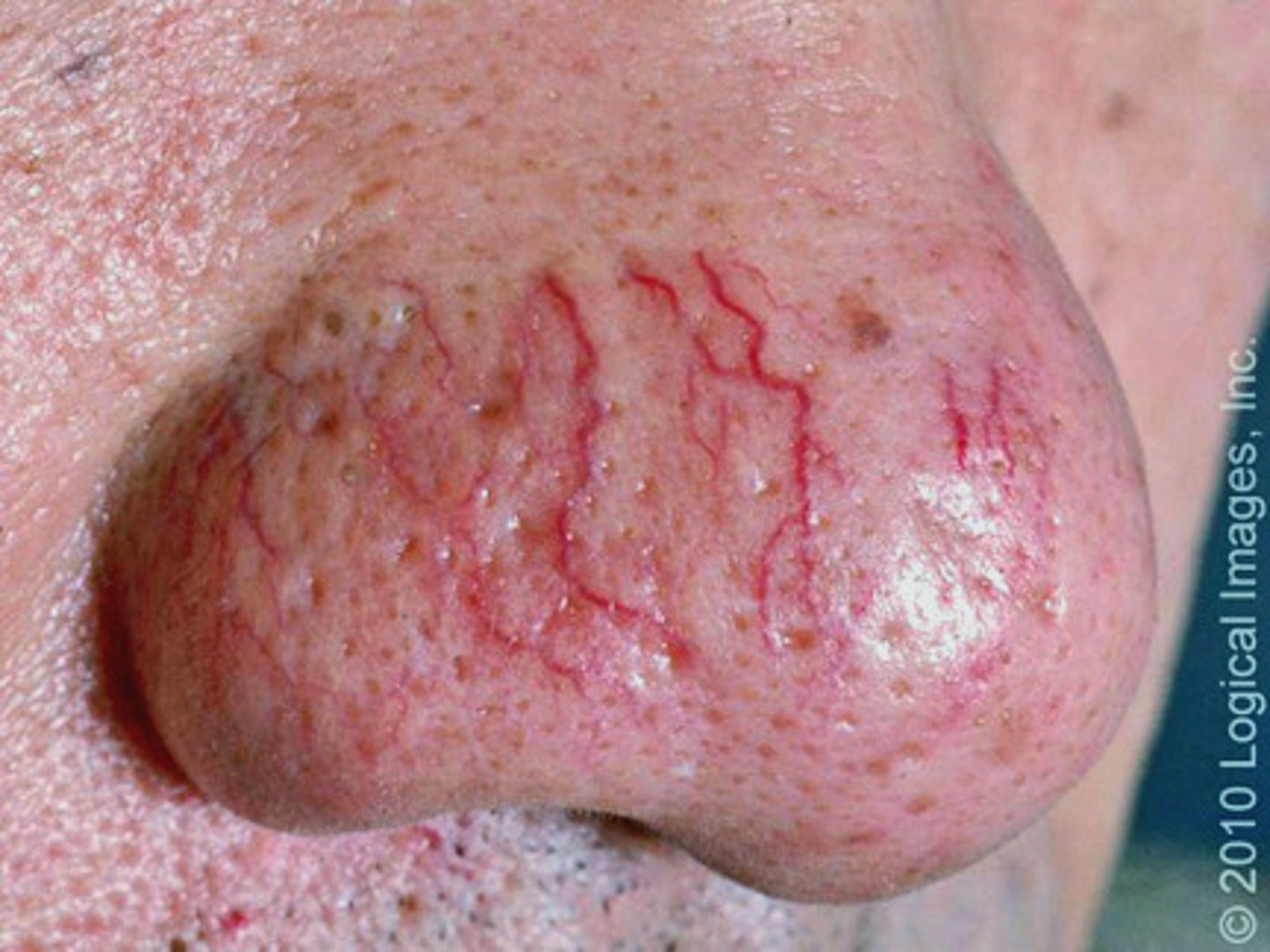
Telangiectasias (Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhage)
spider veins
Class 1 hemorrage
-Nonshock state, such as occurs when donating a unit of blood.
-Typically no change occurs in vital signs, and fluid resuscitation is notusually necessary
class 2 hemorrage
-When 15% to 30% of total blood volume is lost
• Often patient is tachycardic with a narrowing of the difference between the systolic and diastolic blood pressures.
• The body attempts to compensate with peripheral vasoconstriction such that the skin may start to appear pale and be cool to the touch.
• The patient may exhibit slight changes in behavior.• Volume resuscitation with crystalloid is typically required, but blood transfusion is not required.
-Saline solution or lactated Ringer's (LR) solution
class 3 hemorrage
-When 30% to 40% of circulating blood volume is lost
.• Patient has decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate
• Peripheral hypoperfusion (shock) is indicated by slow capillary refill and anxious mental status
.• Fluid resuscitation with crystalloid and blood transfusion are usually necessary.
class 4 hemorrage
-When more than 40% of circulating blood volume is lost
-Reaches the limit of the body's compensation and aggressive resuscitation is required to prevent death.
Hemostasis
This instinctive response stops bleeding and reduces the loss of blood at the site of vascular injury through the formation of an impermeable platelet and fibrin plug
Process of hemostasis occurs within ______of the initial insult
60 seconds
Vascular spasm (hemostasis)
Vasoconstriction that reduces blood flow through the area and limits blood loss

Formation of platelet plug (hemostasis)
Circulating platelets are activated to become sticky and adhere to exposed collagen,forming a loose, temporary platelet plug that limits blood loss.
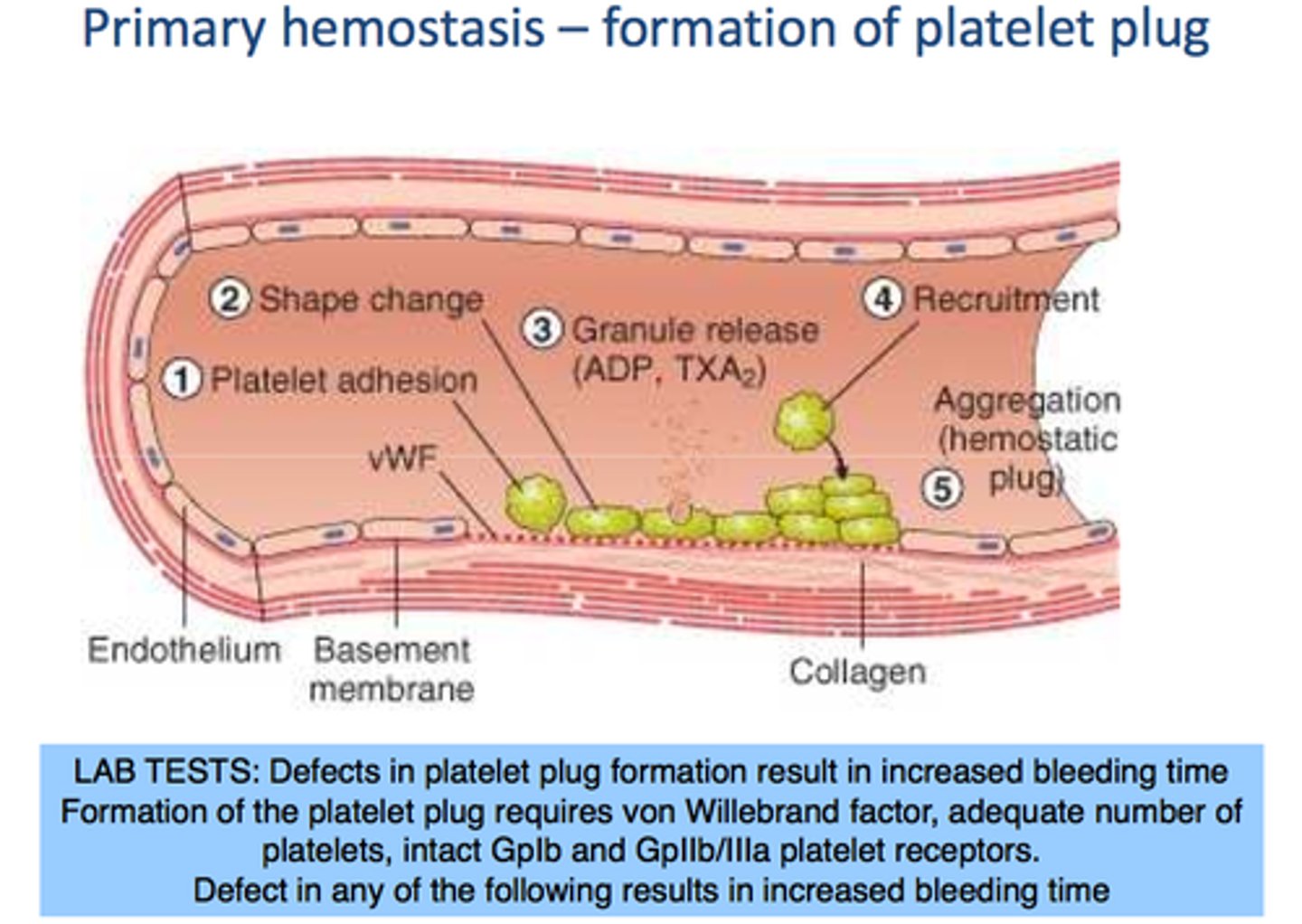
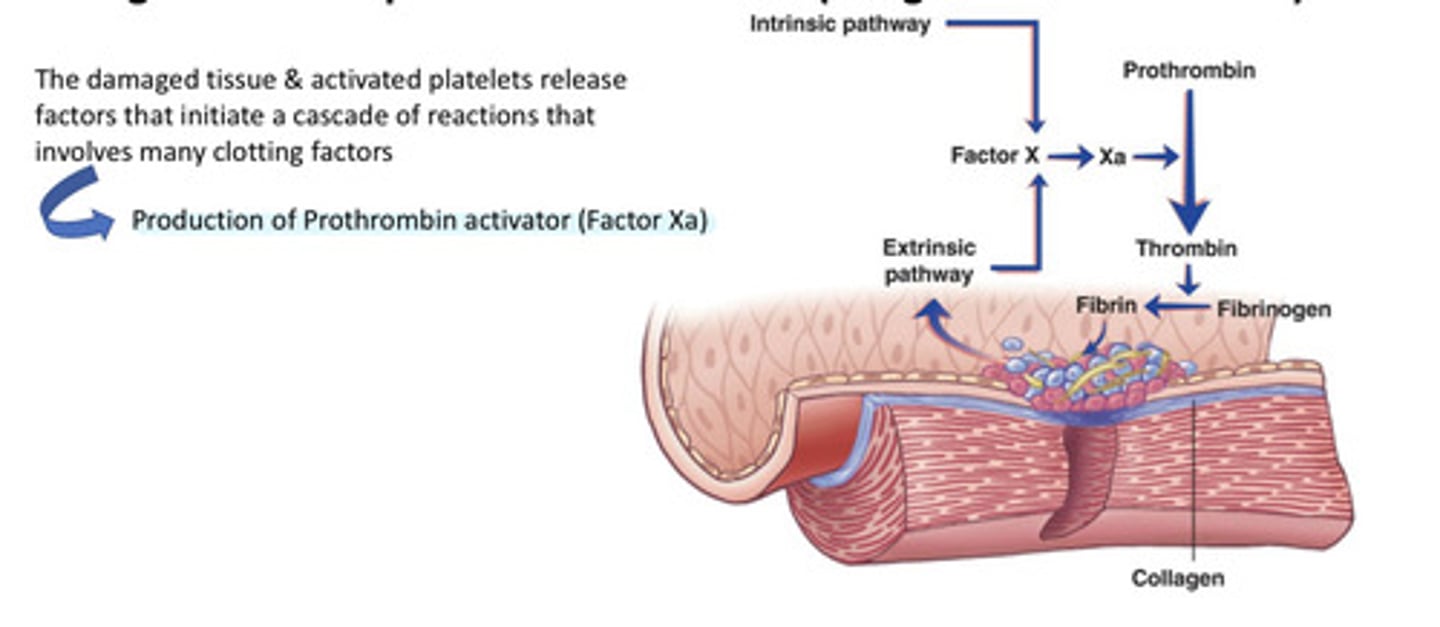
Development of clot (hemostasis)
Clotting factors are proteins carried in blood plasma in an inactive state that become activated (coagulation cascade) leading to thrombin, which converts fibrinogen intofibrin.
Inadequate production of platelets (Complications with Hemorrhage)
leukemia, some anemias
Drug-induced platelet destruction (Complications with Hemorrhage)
by heparin, some sulfa antibiotics
Inadequate platelet function (Complications with Hemorrhage)
Drug-induced dysfunction, e.g., by aspirin or NSAIDs
Acquired platelet disorders (Complications with Hemorrhage)
Vitamin K deficiency, vitamin C deficiency, vasculitis, liver disease, anticoagulation with warfarin,heparin, or direct inhibitors of thrombin or other clotting factors
Other Complications with Hemorrhage include
-Coagulation disorders
-Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
-vascular disorders
hereditary disorders Complications with Hemorrhage
hemophilia, connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome