Developmental Reflexes and Postural Control
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
rcolo
infants prefer faces and patterns with _____ contrast (black and white)
3
infants can track slow moving objects by ____ months
5 months
at what age does color vision develop?
spontaneous movement
movements not caused by known external stimuli
reflexive movement
stereotypical responses elicited by specific external stimuli
similar
the current theory is that spontaneous movement is the building blocks and _____ to some voluntary movements
4; 6
primitive/neonatal reflexes typically integrate between ____ and ____ months of age
righting reactions
maintain or restore the normal position of the head in space (eyes parallel to the horizon) and its normal relationship with the trunk and limbs
equilibrium reactions
maintain balance when COG is disturbed
protective reactions
prevent injury when unable to restore balance
sucking reflex
touch roof of mouth and baby will suck
- develops 28-34 weeks gestation
- integrates at 5 months
rooting reflex
stroke the corner of the mouth, baby turns towards stimulus and opens mouth
- develops at 28 weeks gestation
- integrates at 3 months
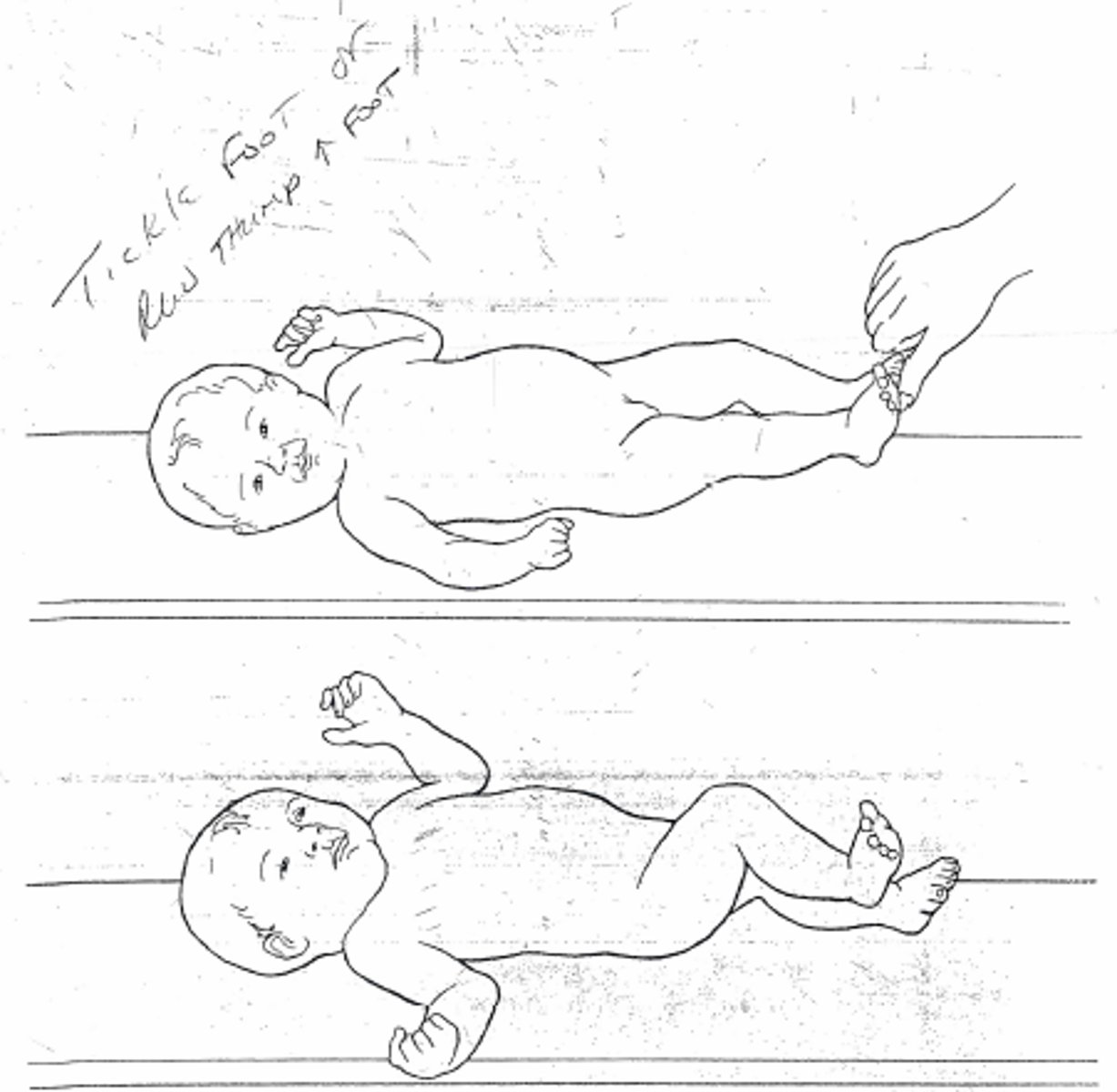
flexor withdrawal
pain to sole of foot, baby will pull LE into flexion to get away
- develops at 28 weeks gestation
- integrates 1-2 months
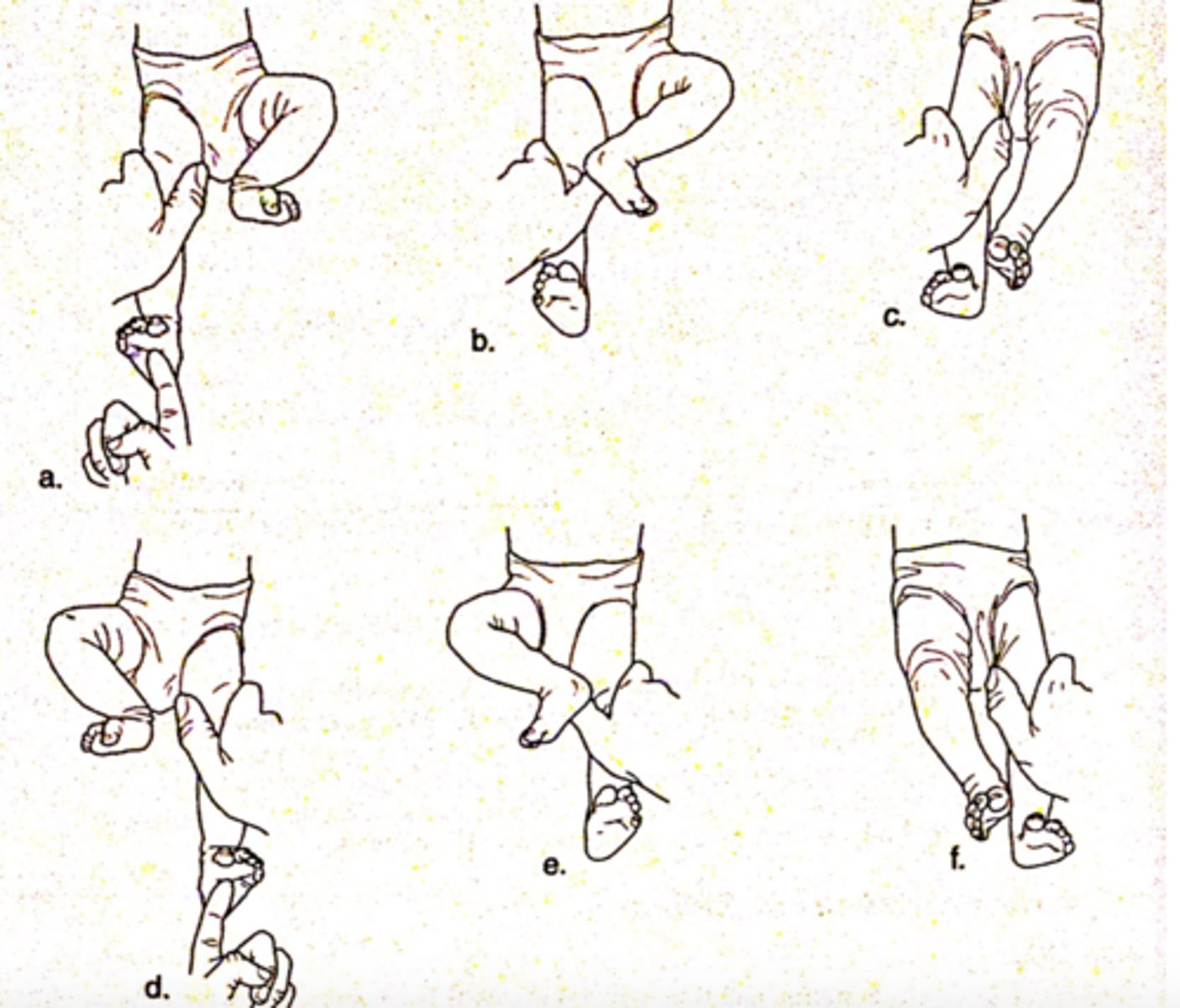
crossed extension
pain to foot while holding LE into position, baby will pull opposite leg into flexion and add and try to push you away
- develops at 28 weeks gestation
- integrates at 1-2 months
positive support
balls of feet contact support surface, baby's legs will extend to bear weight
- develops at 35 weeks gestation
- integrates at 1-2 months
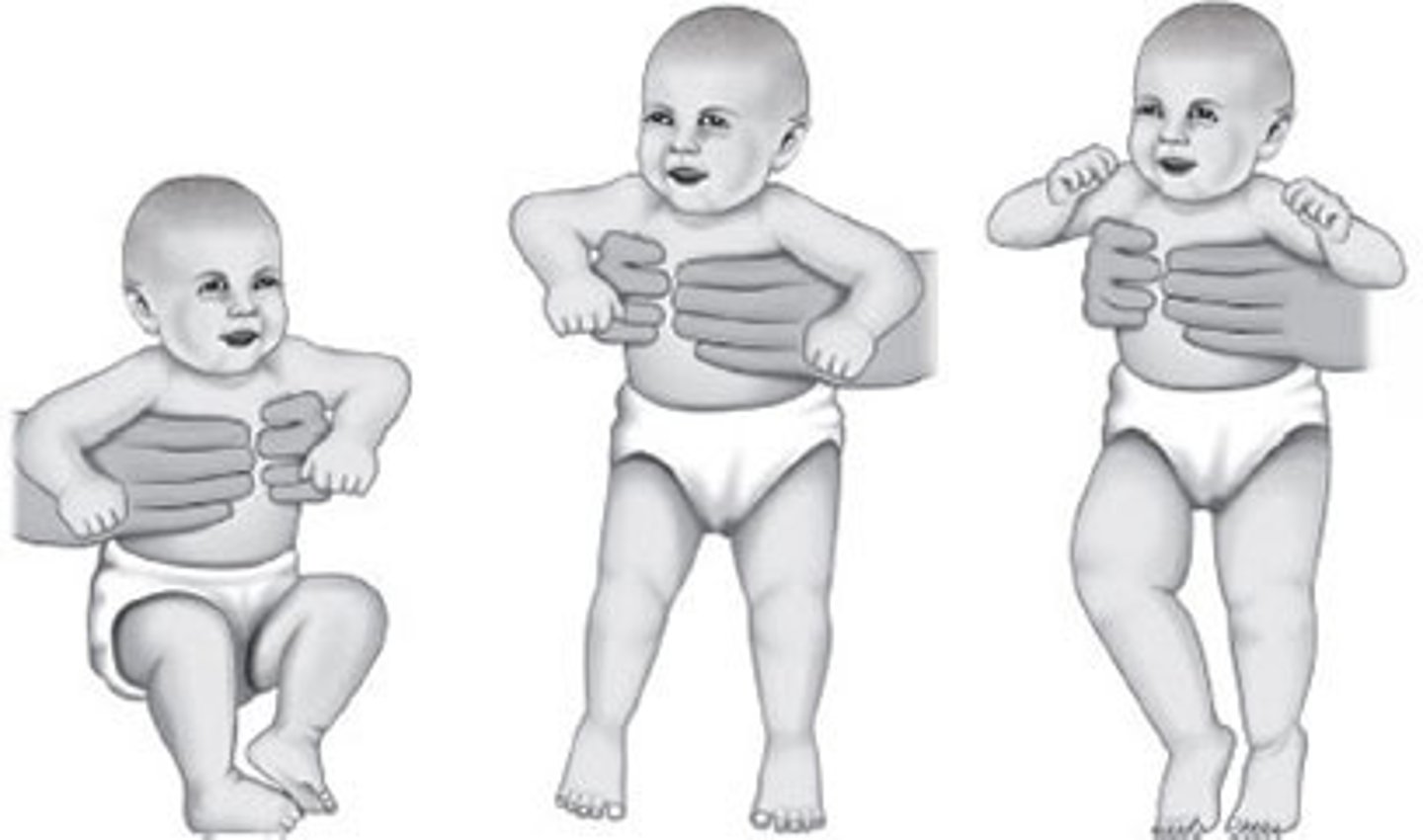
stepping
when held upright touch baby's feet to surface, rhythmic stepping will occur
- develops at 37 weeks gestation
- integrates at 3-4 months
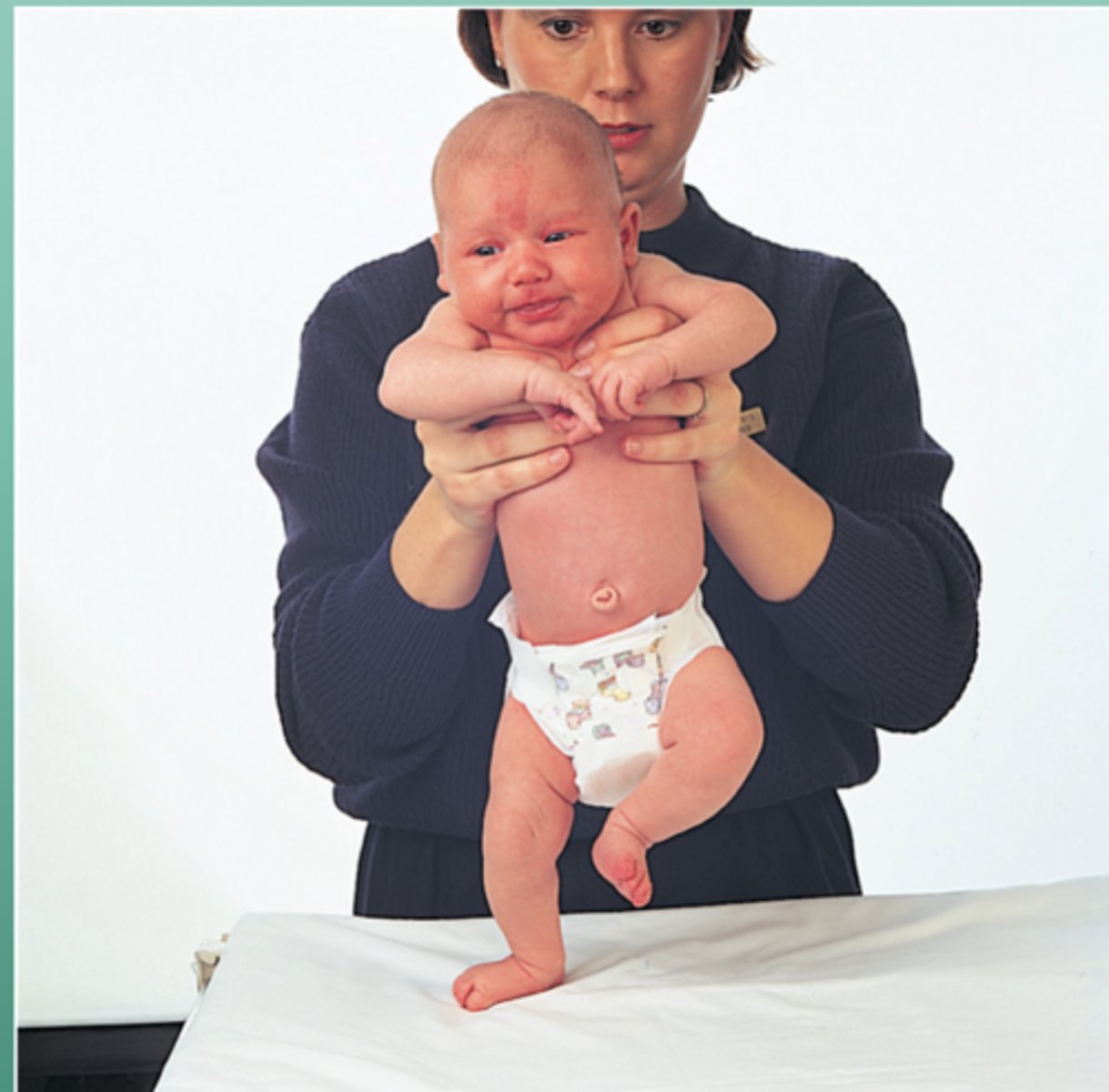
galant
in ventral suspension stroke paraspinals on one side, baby SBs toward stimulated side
- develops at 28 weeks gestation
- integrates at 3 months
moro
when startled or when head is allowed to drop backward, baby will abd/extend and then add/flex the extremities
- develops at 28 weeks gestation
- integrates 3-6 months
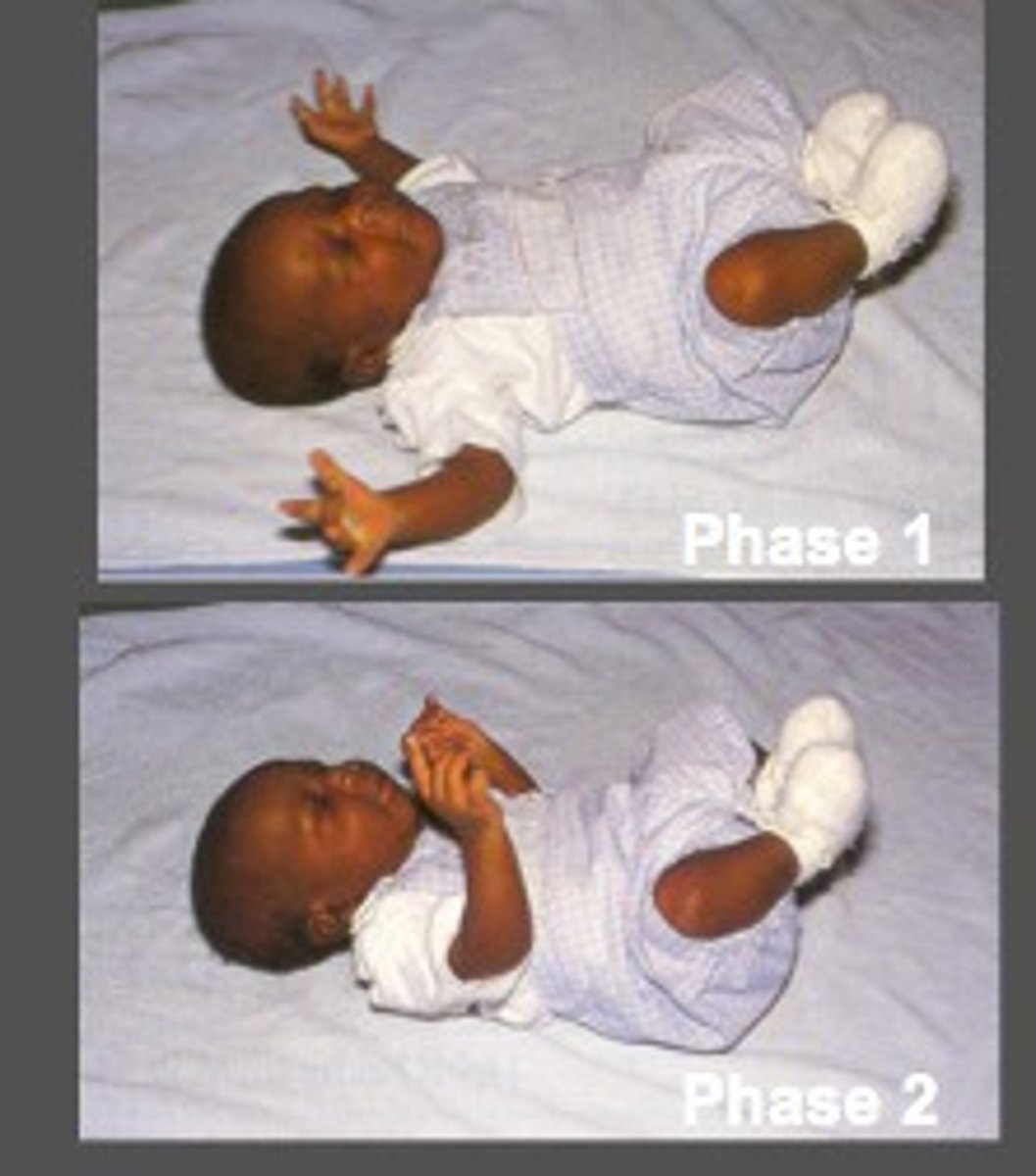
ATNR
turn head to side, baby will extend on face side and flex on skull side (en guarde)
- develops 20 weeks gestation
- integrates 4-5 months
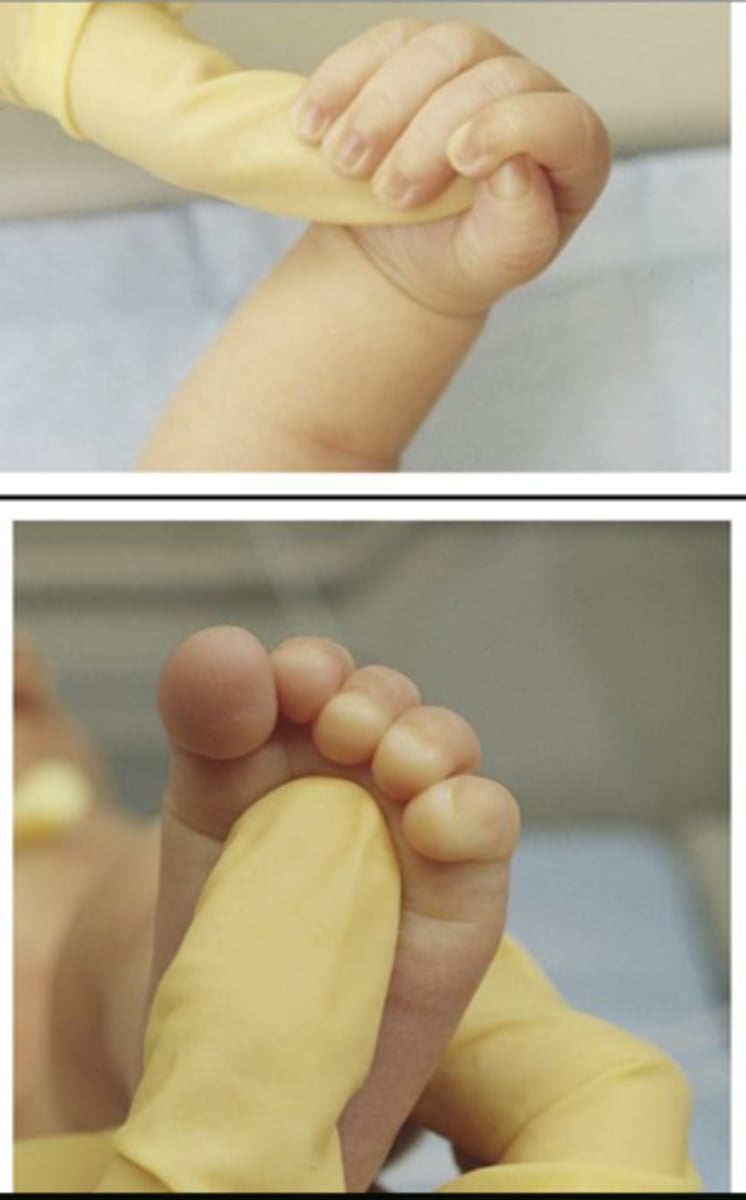
palmar/plantar
touch palm or ball of foot, baby will close hand or curl toes around object
- develops 28 weeks gestation
- integrates:
- palmar: 4-7 months
- plantar: 9 months
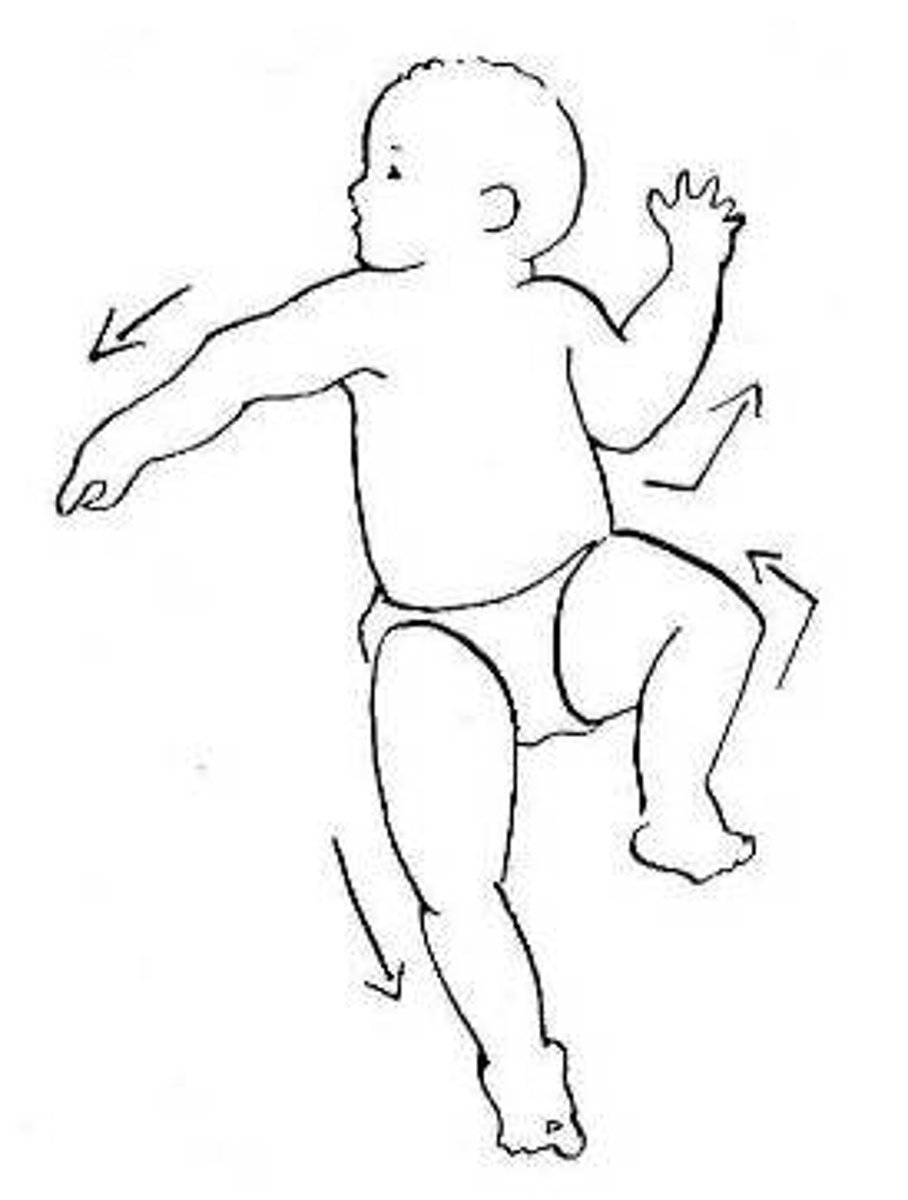
tonic labyrinthine
prone or supine position
supine: extend neck and limbs
prone: flex neck and limbs
- develops by 2 weeks
- integrates 4 months
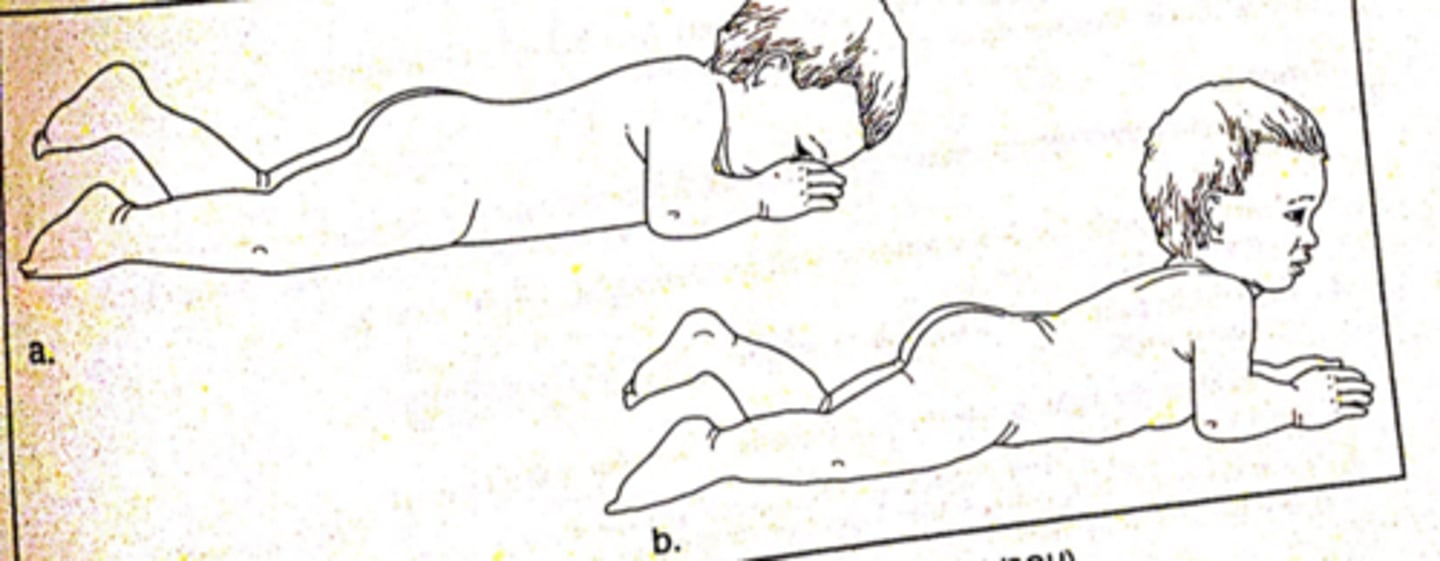
landau
ventral suspension, baby extends head, back, and hips in sequence (superman)
- develops about 3 months
- integrates 12-24 months
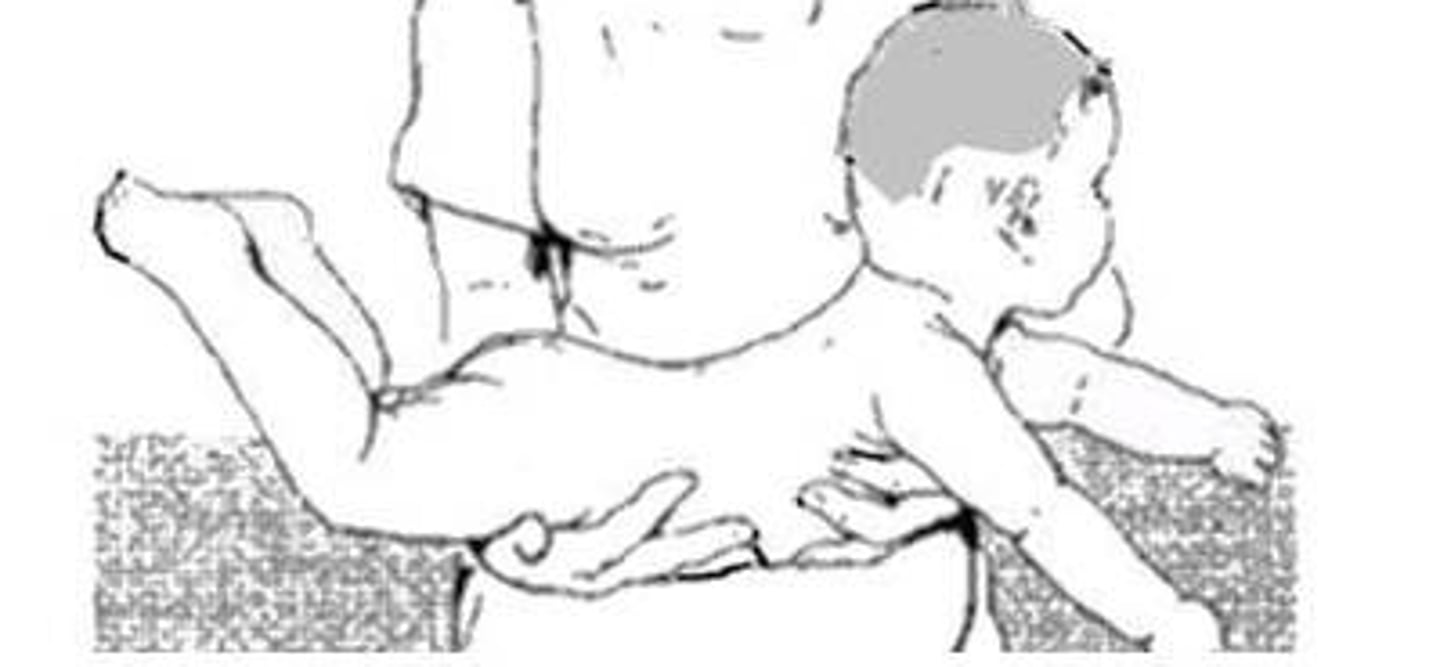
STNR
in supported sitting, flex or extend head
arms will flex and legs will extend (head flexes) or opposite
- develops 4-6 months
- integrates 8-12 months
- basis for crawling
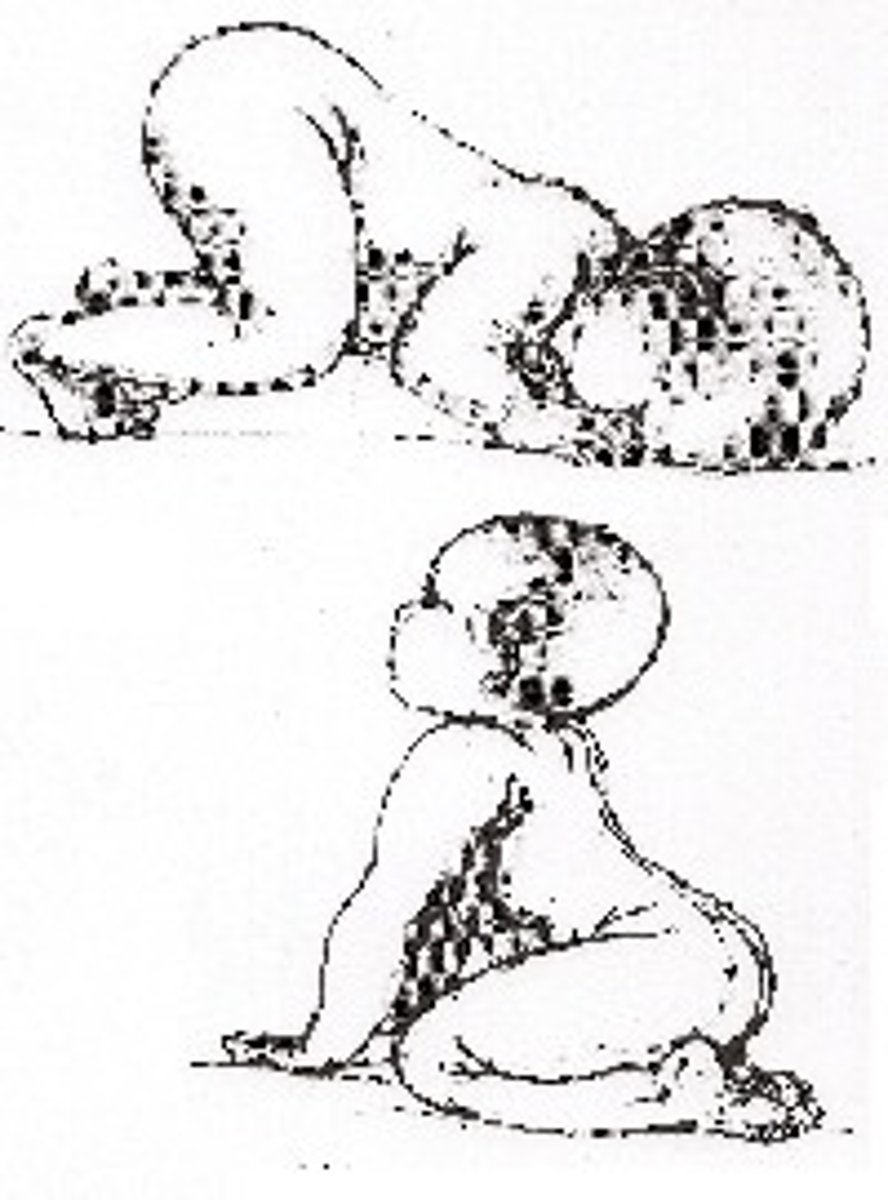

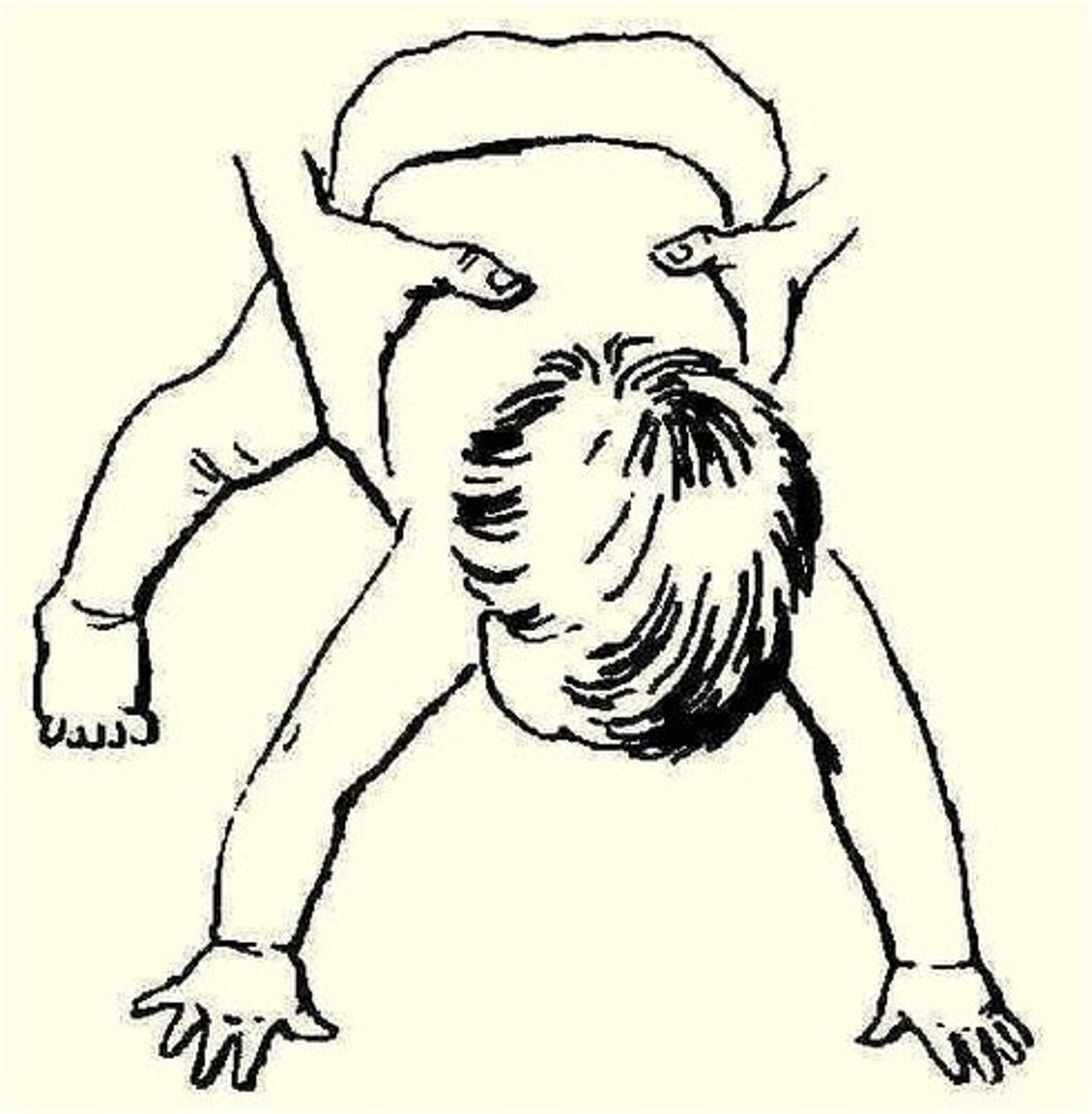
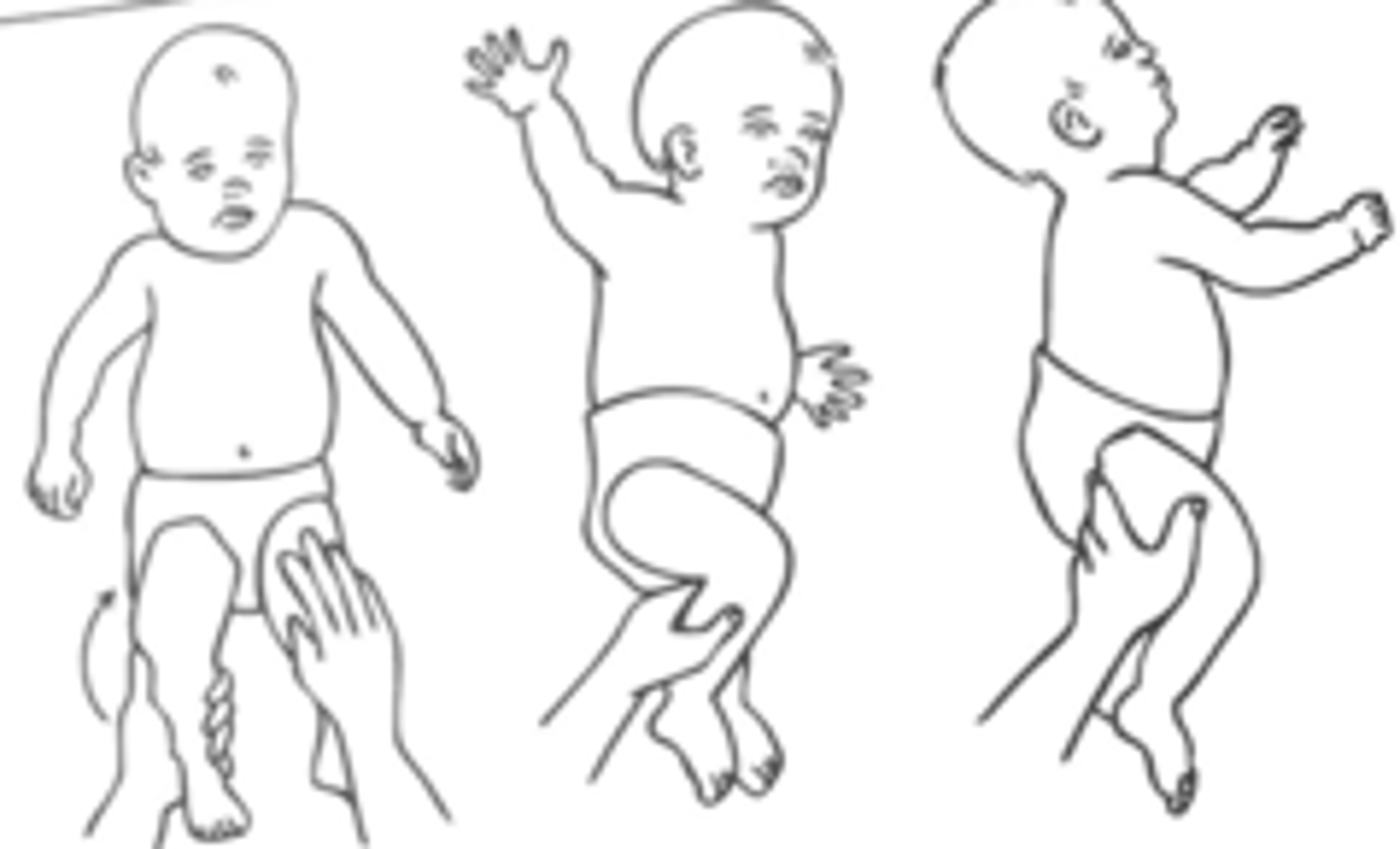
parachute
support child in prone and lower toward support surface
baby will extend arms with open hands
- develops 8-9 months
- should not go away (protective)
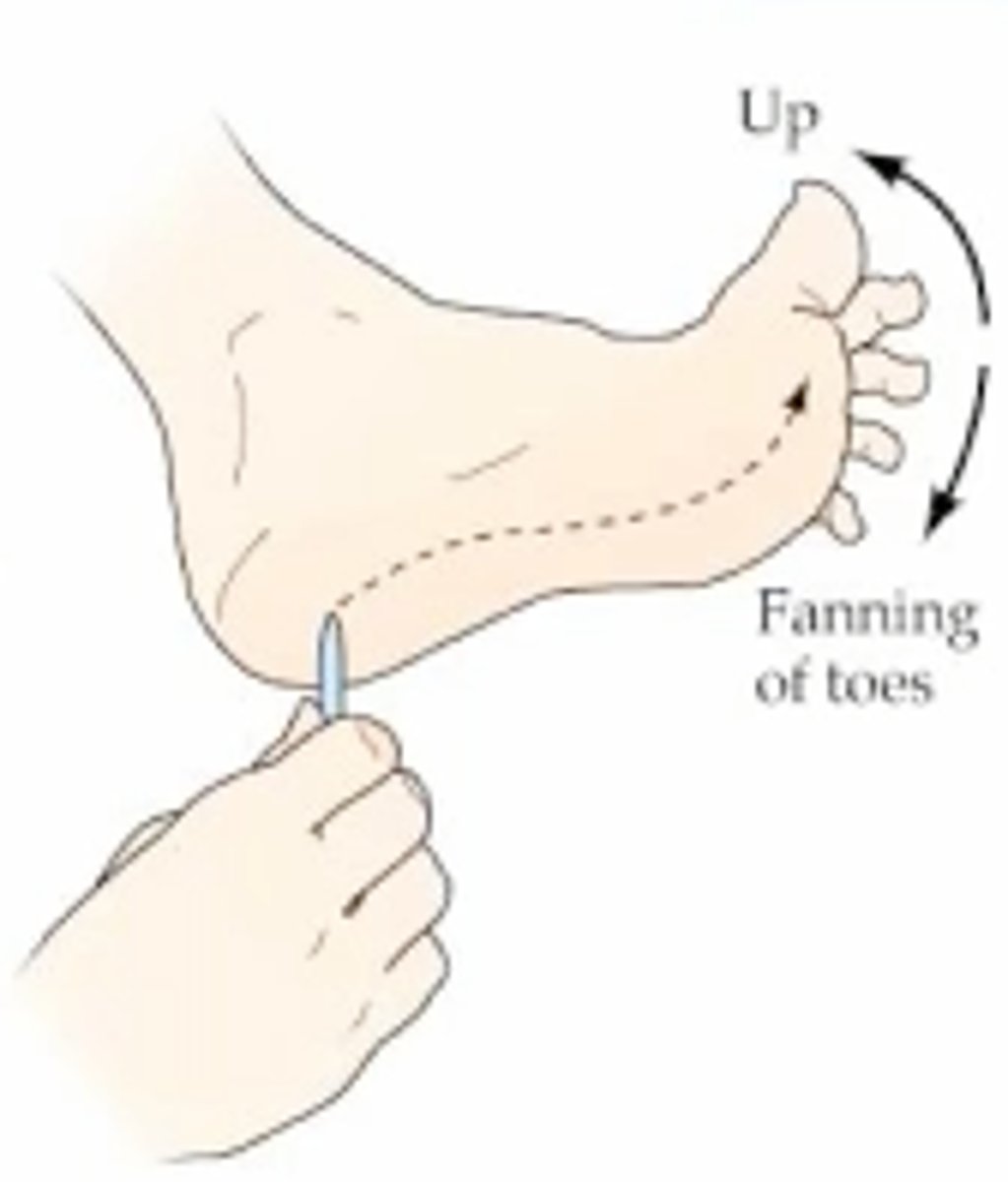
babinski
firm stroke along lateral border of sole, big toe extends and others fan out
- should integrate within 2 years
- abnormal after age 2
difficulty eating if head turn, may cause scoliosis
if the ATNR doesn't integrate what will be hard for the baby?
difficulty releasing voluntarily
if the palmar/plantar grasp doesn't integrate what will be complicated?
difficulty with midline control and tracking
if the rooting reflex doesn't integrate what will be complicated?
walking, too much extension of LEs
if positive support doesn't integrate what will be complicated?
poor trunk control, possible scoliosis
if galant doesn't integrate what will be complicated?
difficulty with sitting balance
if moro doesn't integrate what will be complicated?
phasic bite
A reflex that is characterized by a rhythmic opening and closing of the jaw when the gums are stimulated. Appears around 28 weeks gestation.
- if the baby clamps down, this is not normal
impacts rolling, need asymmetrical pattern
if tonic labyrinthine doesn't integrate what will be complicated?
postural control
Controlling the body's position in space for the dual purposes of stability and orientation
postural orientation
ability to maintain relationship between body segments and between body and environment for a task
postural stability
ability to control the COM in relationship to the BOS
2
infants cannot sustain their head flexion/extension until about ____ months with their eyes 30 degrees below the horizontal
3
infants can sustain and track with their head by about _____ months
6
smooth visual tracking occurs by about _____ weeks
14
vision is adultlike by about _____ weeks
vision
primary system to start
feedback correction and anticipatory postural strategies
vestibular
drives postural activity to regulate head control and reference gravitational forces
- hasn't had practice working until birth
- develops later
somatosensory
triggers postural activity related to body positioning and righting
- collects information, learning to interpret
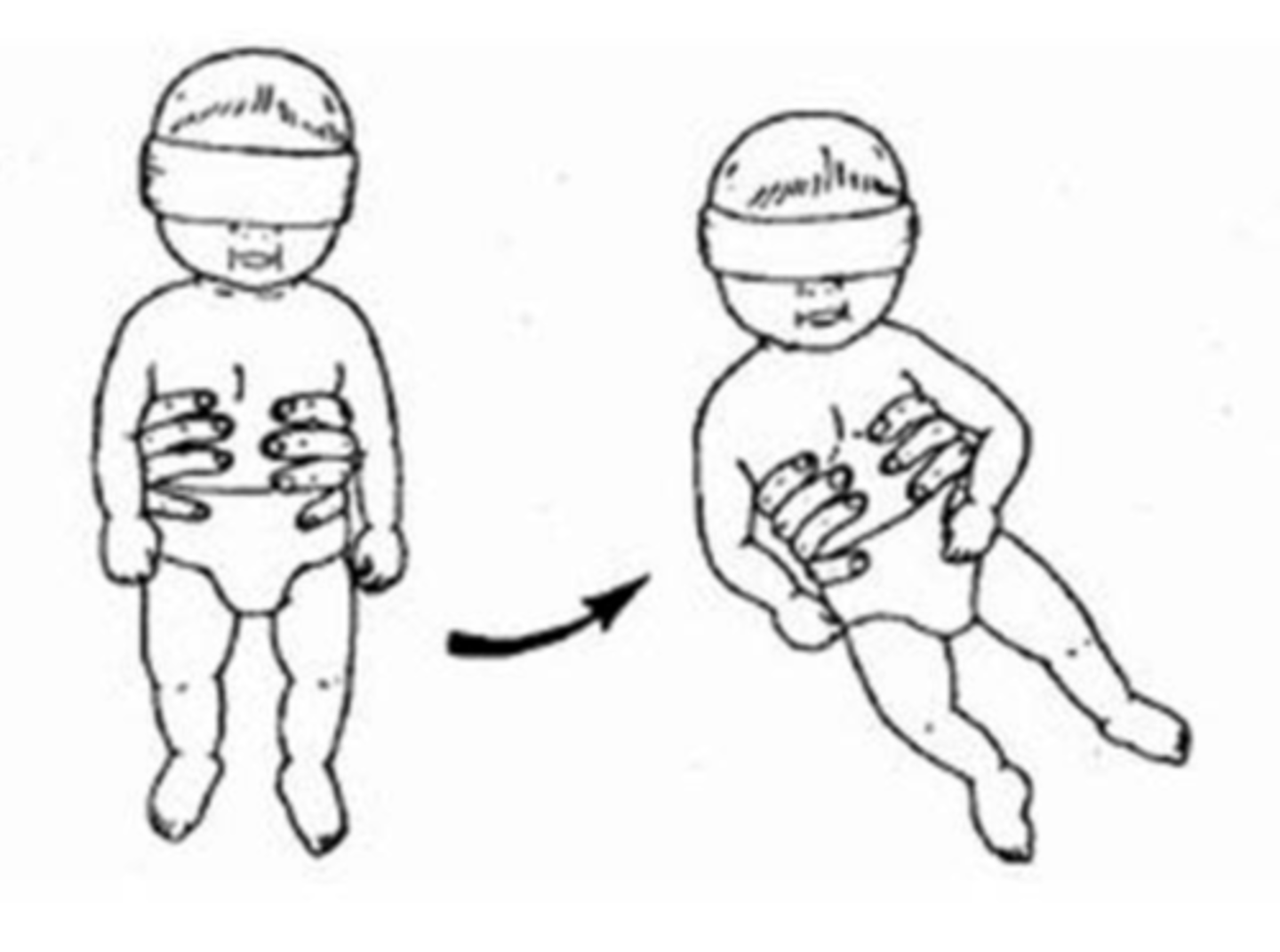
labyrinthine righting reflex
tilt infant in vertical suspension with eyes covered
- baby should orient their head to vertical
- onset birth-2 months
optical righting reflex
same as labyrinthine without eyes covered
BOH (body righting reflex acting on head)
body contacts surface
lift head away from surface (so they don't suffocate)
- onset birth-2 months
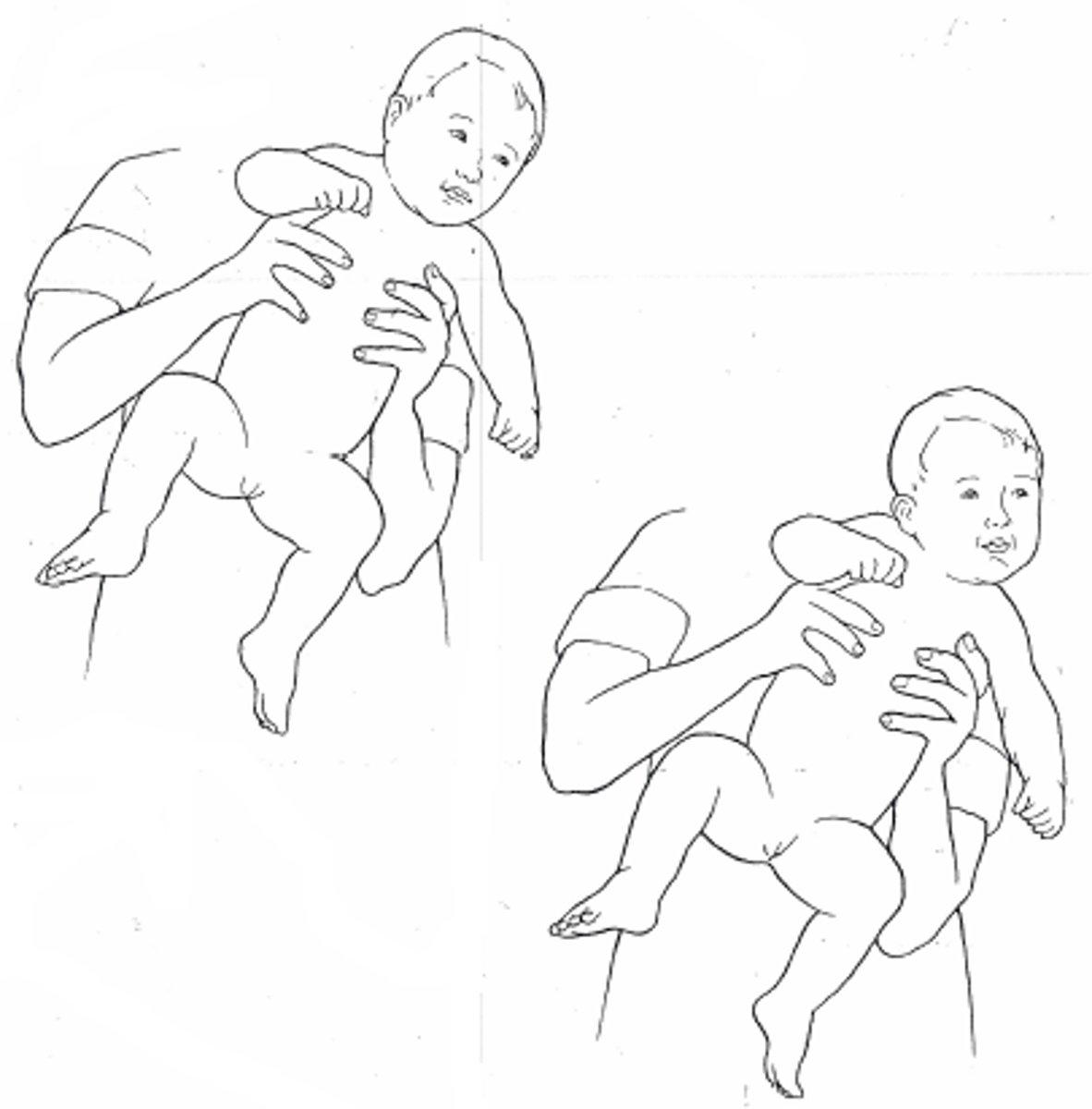
NOB (neck righting reflex)
turn head of infant in supine
body turns toward head
- onset 34 weeks, integrates 4-6 months
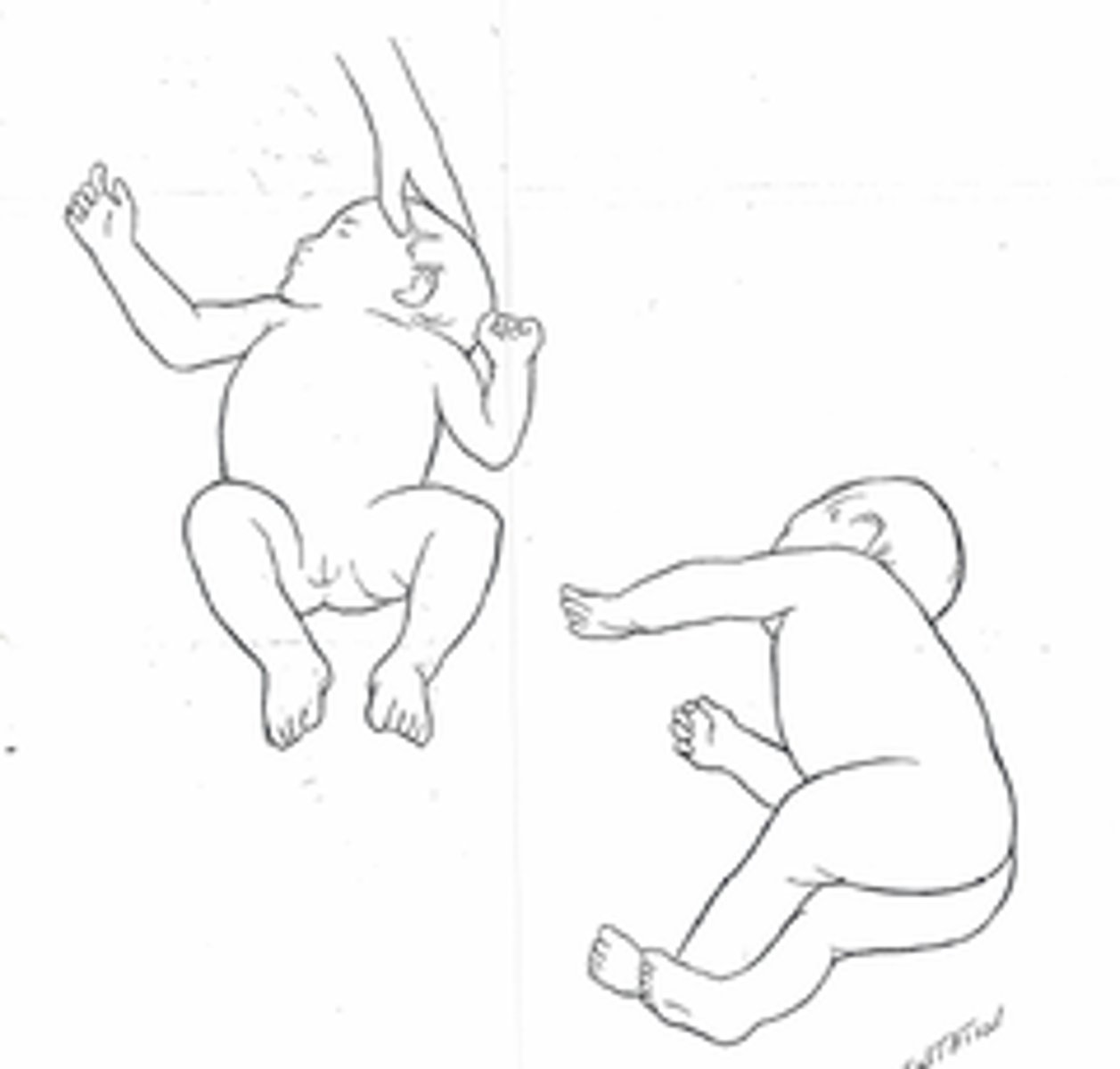
BOB (body righting reflex on body)
flex leg over supine body
upper body follows in log roll
symmetry
goals of righting reactions in pediatric PT are to improve ______ of reactions to both sides, midline control, and coordination of transitional movements
protective extension
a primitive reflex that develops shortly after birth in response to the new environment of gravity
-automatic reactions to a rapid loss of balance or weight shifting (protect from injury during a fall)
- most distinguishable at 10-12 months
- remains active throughout life
anterior, lateral, posterior
what order does protective extension occur in development?
equilibrium reaction
torso elongates on weight bearing side
torso lateral flexes to non-weight bearing side
extremities may abd on non-weight bearing side (shift more weight)
- may be some rotation
proactive balance control
- Feed-forward Control
- Anticipatory balance
- Postural responses in anticipation of a voluntary movement that may destabilize in order to maintain stability.
- Volitional shifts in COM
reactive postural adjustments
-development in standing is variable
-increased latency in children ages 4-6 years (period when visual dependence in transitioning to add somatosensory input)
-adult like response by 7-10 years