4.3 - Cardiac Conduction & ECG
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Within the Right Atrium, what are the autonomic cells called that start the heartbeat?
SA node
On the SA nodes’ own, what can they run the heartbeat to?
90 bpm
What does the AP started from the SA node trigger?
atrial muscle to contract
From the SA node, where does the electrical current (that it started) go to?
AV node
Does the action potential HAVE to go through the AV node ot get to the ventricle?
yes
What is the heartbeat (on its own) that the AV node can have?
60 bpm
What is the AV node attatched to?
bundle of his
The AV node then sends the AP (through bundle of His) to ?
purkinje fibers
Where does the AP spread to then from the Purkinje fibers?
ventricles
When purkinje fibers send the AP to ventricles, it causes them to?
contract
What is the hb the purkinje fibers cause alone?
20-40 bpm
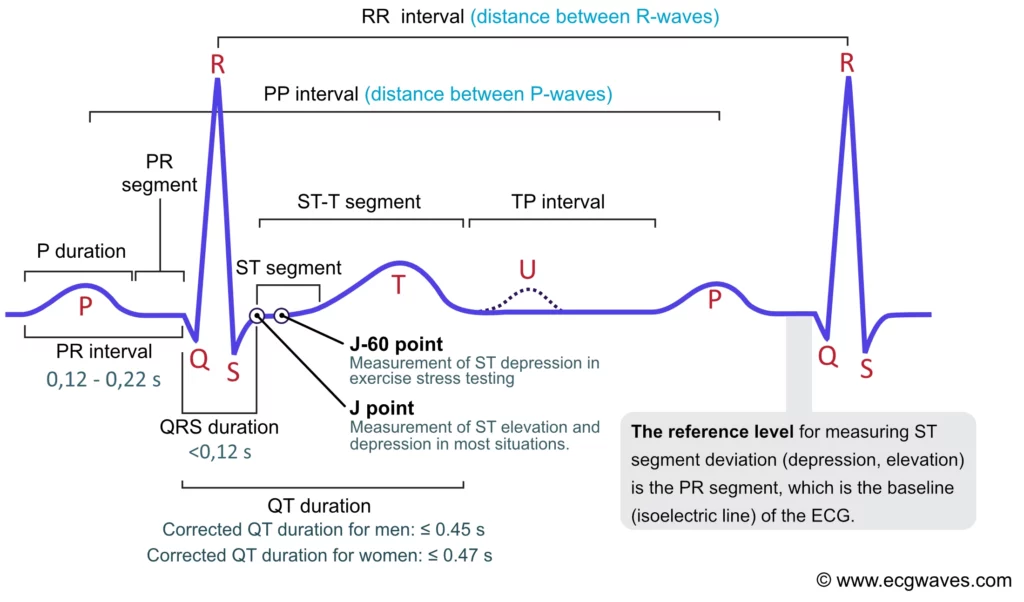
Does each heartbeat have a distingtive set of waves?
yes
When the SA node sends AP to AV node, does the AV node immedieately send it to the purkinje fibers?
no
Why doesn’t the AV node send the AP to the Purkinje fibers?
the atria is already contracting (building pressure) so it needs to wait until it’s relaxed to start contracting the ventricles
Which node is the fastest?
SA node
So the SA node ____ the action potentials.
directs
Are all the nodes/fibers autorhthmic cells?
yes
If the SA node fails to start AP for heart contraction, what’s the backup node?
AV node
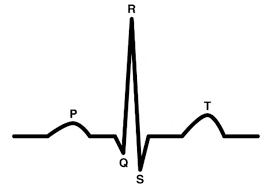
The first wave is P wave; what is happening in this wave?
depolarization is spread across atria
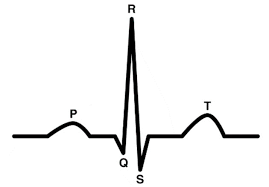
Q wave - (we don’t rly need to know Q or S); but what’s causing this little wave?
bundle of his
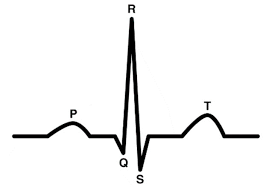
R wave - what’s occuring in this wave?
depolarization is spreading across ventricles
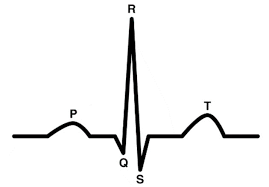
T wave - What’s happening here?
repolarization of the ventricles
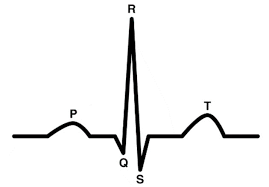
Between the P to R waves, what is this?
atrial twitch
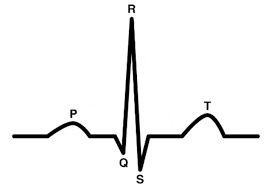
Between R to T waves, what is this?
ventricular twitch
Where is atria repolarization happening?
around the same time R wave occurs
But, R wave is so large, it drowns out the _____ ________ _____. (3)
atria repolarization wave (ECG don’t pick it up)
In Cardiac Cycle, all fluid moves by ______ ______. (2)
pressure differences
What’s the 1st Step of the Cardiac Cycle?
Atrial and Ventricular Diastole
Diastole means
relaxed
In Atrial and Ventricular Diastole (1st) - What pressure is greater, atrial or ventricular?
atrial (pressure is greater)
Why is atrial pressure bigger in 1st step?
blood is entering atria from systemic circuit
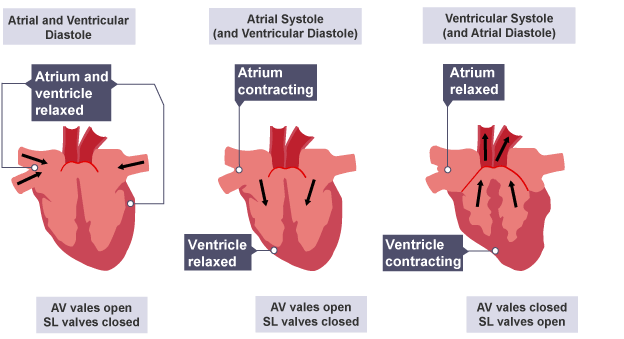
In Atrial and Ventricular Diastole (1st) - What valves open to drain atria blood into ventricles?
Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid/bicuspid)
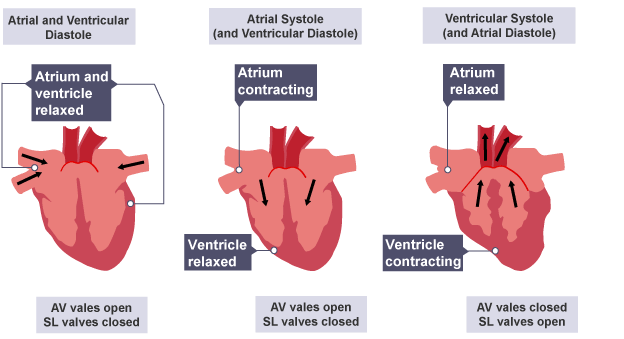
In Atrial and Ventricular Diastole (1st) - About how much blood are the ventricles passively getting? (means no contraciton yet, just pressure build up)
3/4
In Atrial and Ventricular Diastole (1st) - Is arteriole or ventricular pressure greater?
arteriole
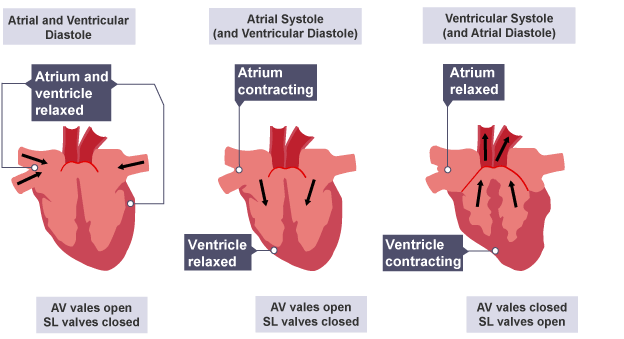
Although in 1st, arteriole valves (aorta/pulmonary trunk) are GREATER, will they allow blood to backflow into ventricles?
no
So in 1st step, the Semilunar valves are ____.
shut
What’s the 2nd Step of the Cardiac Cycle?
Atrial Systole
Systole means?
contraction
In Atrial Systole (2nd) - Contraction of the atria begins, so it’s starting the _ _____.
P wave
When the P wave starts, that means the atria is beginning their _____.
twitch
In Atrial Systole (2nd) - It pushes more blood to go from atria →
ventricles (topping them off)
What’s the 3rd step of the Contractile Cycle?
Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (Early ventricular systole)
In Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (3rd) - The ____ are contracting creating very high pressure.
ventricles
In Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (3rd) - At this point, when ventricle pressure is builiding, which has higher pressure ventricles or atria?
ventricles
In Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (3rd) - Since ventricle pressure is higher, what valves close
AV valves (no backflow!)
The closing of the AV valves creates the first ____ _____
heart sound (lub)
In Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (3rd) - Is ventricular pressure greater or less than arteriole pressure?
less than
In Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (3rd) - So this step is the start of the __ _____.
R wave
In Isovolumic Ventricular Contraction (3rd) - It’s also the start of ______ ______.
ventricular twitch
What’s the 4th step of the Cardiac Cycle?
Ventricular Ejection (late ventricular systole)
In Ventricular Ejection (4th) - The MOMENT the ventricular pressure > (greater than) arterioles, ____ valves open.
SL
In Ventricular Ejection (4th) - Where does blood go after SL valves open? (2)
pulmonary artery, aorta
In Ventricular Ejection (4th) - Simultaneously to arterioles getting blood, the ___ is also filling up again.
atria (cycles starting again kinda)
In Ventricular Ejection (4th) - Since blood is pushed from ventricles, they begin to relax (less pressure) which stimulates the __ _____.
T wave
What’s the 5th step of the Cardiac Cycle?
Isovolumic ventricular Relaxation (early ventricular diastole)
In Isovolumic ventricular Relaxation (5th) - Is ventricular or arteriole pressure lower?
ventricular
In Isovolumic ventricular Relaxation (5th) - What valves CLOSE to prevent backflow?
SL valves
The closing of the SL valves closing indicates the _____ ______ _____ .
second heartbeat sound (dub)
In Isovolumic ventricular Relaxation (5th) - Is ventricular pressure greater or less than atrial pressure?
greater
So since ventricular pressure is greater, what valves are still closed?
AV valves
In Isovolumic ventricular Relaxation (5th) - Ventricles are trying to _____.
relax
In Isovolumic ventricular Relaxation (5th) - Once ventricles are fully in diastole, what step occurs?
step 1!