Chapter 12: Cardiac Stress Testing
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Why may a doctor order an exercise stress test for a patient?
Their ECGs may appear normal
Exercise electrocardiography
Non-invasive type of cardiac stress testing that uses an exercise treadmill while their ECG is continuously monitored. The level of exercise is increased as the test goes on.
Other names for electrocardiography
Exercise tolerance test
Treadmill stress test
Stress ECG
Exercise treadmill test
What does common exercise electrocardiography equipment include?
A treadmill, an ECG machine, and a monitor
Noninvasive
Procedure that does not require entrance into a body cavity, tissue, or blood vessel
Who monitors the patient during the stress test?
Cardiologist and in same cases advanced cardiac life support certified professionals
What happens during the test?
Patient is asked to walk on a treadmills. The level of exertion is increased as the test progresses.
What other things are monitored during a stress test beside the ECG?
blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and physical appearance
Toward the end of each exercise stage, what is obtained?
Blood pressure and a 12-lead ECG
What is the patient asked to report during the test?
any chest pain, dizziness, shortness of breath or other symptoms
What is the goal of a treadmill test?
To exercise the heart and evaluate how it responds to the stress of exercise
What is your role as a healthcare professional?
To provide patient instruction and monitor patient during the procedure by taking blood pressure and other measurements. You also observe patient and apply/remove electrodes.
What are some basic responsibilities during an electrocardiograph
Always know location of crash cart and AED

Make sure you always report abnormalities such as ______ or ______ to the physician.
Tachycardia; tachypnea
Why is exercise electrocardiography considered non invasive?
It does not require an entrance into a body cavity, tissue, or blood vessel
Name at least three responsibilities you will have during electrocardiography
Provide for safety and prepare for emergencies
Explain, obtain, and prepare patient prior to procedure
Monitor the patient including blood pressure and 12-lead ECG
Exercise electrocardiography is used to evaluate how the heart and blood vessels respond to and it is used for what conditons?
physical activity
When is treadmill stress testing typically pefromed?
When a physician suspects a cardiac problem, most commonly coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease
due to atherosclerosis which occurs when plaque forms in blood vessels from an accumulation of excess fat
If a patient has CAD, what happens to blood flow?
It will not increase in response to exercise because the arteries are narrowed or obstructed
What is a ST depression?
An abnormally low ST segment below the normal baseline of the ECG. It may indicate myocardial ischemia, which can occur during exercise electrocardiography.

How does CAD affect the ECG tracing
ST depression which may indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction and should be reported to the doctor
What are other causes of ST depression?
Certain medications, hypothermia, hypokalemia
What is angina?
An oppressive pain or pressure that occurs when heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen due to partial or complete blockage of coronary artery. Symptoms include: weakness, shortness of breath, palpitations and dizziness.
Chemical stress test
Stress test performed after administering medications that cause the heart rate to increase or the coronary blood vessels to dilate; performed on patients who cannot perform the exercise required in a regular stress test
When is a chemical stress test used?
When the patient is unable to run or walk on a treadmill or use an exercise bike due to age, injury, or physical defect
T/F: Chemical stress tests can conducted using nuclear testing or in combination with echocardiography.
True
How is a chemical stress test conducted?
Requires one or more IVs for the introduction of a stressing chemical such as Adenocard, Persantine, dobutamine
Nuclear Stress Test
A stress test in which radionuclides are administered to trace the path of blood through the heart
Nuclear Stress Test Process
Nuclear medicine technologist inject patient with a stressing chemical. Then prior to the end of the stressing cycle, the tech injects a radioactive tracer. Then patient is scanned with a gamma camera.
Gamma Camera
Camera that records the gamma radiation emitted by radioactive tracers in patient’s blood.
How are the patients positioned for a nuclear stress test?
Lying on their back or sometimes sitting upright with arms above their head
What is an additional feature of nuclear testing?
3 lead ECG
Gate
a selective technique in which a gamma camera is triggered by specific events captured by a three lead ECG monitor
What kind of factors can affect nuclear stress test?
Diet
Female breast
Echocardiogram
Noninvasive diagnostic test that uses sound to study the heart, heart valves, and blood vessels.
Stress echocardiogram
A test that combines an exercise stress test with an electrocardiogram to assess left ventricular wall motion before and immediately after exercise.
When is a stress echo considered normal?
If the LV wall motion is normal at rest and within 45-60 seconds of achieving the target heart rate poststress.
When is ischemia suspected?
when a change is seen in the LV wall shape or contractility with exercise
How does echo work?
It directs beams of US waves through the chest wall, which are echoed by the heart tissues providing motion pictures of the heart
What are the phases of a stress electrocardiogram?
Resting echo phase, immediate post exercise scan, and recovery phase scan
What kind of images does the sonographer obtain during the resting phase?
Four specific LV wall motion images with patient lying on their left side with head slightly elevated
When is the treadmill stopped for stress echo?
When the pt achieves 85-100% of target heart rate during exercise portion.
Chemical stress echocardiogram
A stress echocardiogram is when the heart is stressed by chemicals instead of physical exercise
When the patient’s heart returns close to _____ _____ ____, the same four LV wall motion images are acquired to complete the _____ ______.
resting heart rate; recovery
What does the cardiologist do with the US scans?
assess for changes in LV motion and contractility, which can predict the presence of ischemia in one or more coronary arteries
Why is communication with the patient important?
It is our responsibility to ensure that the patient understand what will occur during the test and what the patient should report while test is in progress.
Why would it be necessary to use chemical stress testing?
Maybe the patient cannot exercise or has a limb missing
How should the patient prepare for the test?
Avoid consuming alcohol or caffeine for 24 hours prior to test
No tobacco
Not eat or drink anything 4 hrs prior to test
War comfy shoes and clothing
Informed consent
Affirms that the patient understands treatment, why it is being performed, etc.
What should you do if a pt does not understand why consent form is necessary?
Explain the legal requirements for informed consent and refer to physician if necessary
Pt does not understand procedure you could…
notify the licensed practioner and provide a brochure for patient to review
Patient is illiterate and unable to sign their name
Have a witness present and have the consent form marked with an X by patient and signed by witness and yourself
Patient is unable to sign because glasses are not available or because patient is blind
Make every attempt to obtain glasses and have patient sign to best of their ability
Which type of medications are usually stopped before a stress test?
Beta blockers
What are beta blockers?
Drugs used to treat hypertension
T/F: You may need to complete a pt hx
True
What type of info do you need from a patient for a pt history
Medical history, medications currently being taken, cardiovascular risk factors, and reason. Consent forms must be signed and witnessed.
T/F: You can tell the patient that exercise electrocardiography is about an hour.
False: patient should be informed this is not a TIMED test. Test may take from 45 minutes to 3 hours.
Stress testing is a noninvasive procedure…why is informed consent necessary?
Patients need to affirm they understand the procedure and risks.
Why should you obtain a list of the current medications the patient is taking before the stress test procedure?
Because certain medications should not be taken prior to the test
What do you need to prepare in advance for exercise electrocardiography?
BP equipment
Skin prep solution
Clippers
Gauze
Chest electrodes
Stress test unit
lead wires
Treadmill
adhesive tape
belt
crash cart
When patient arrives what should you do?
Make sure they followed guidelines for food, caffeine, etc
Observe if pt is dressed appropriately
Inquire if certain rx stopped
Complete pt hx
make sure consent form is signed and
Which is preferred clipping hair or shaving?
Clipping because shaving can leave skin brisk
Attach blood pressure cuff and then
place the precordial electrodes
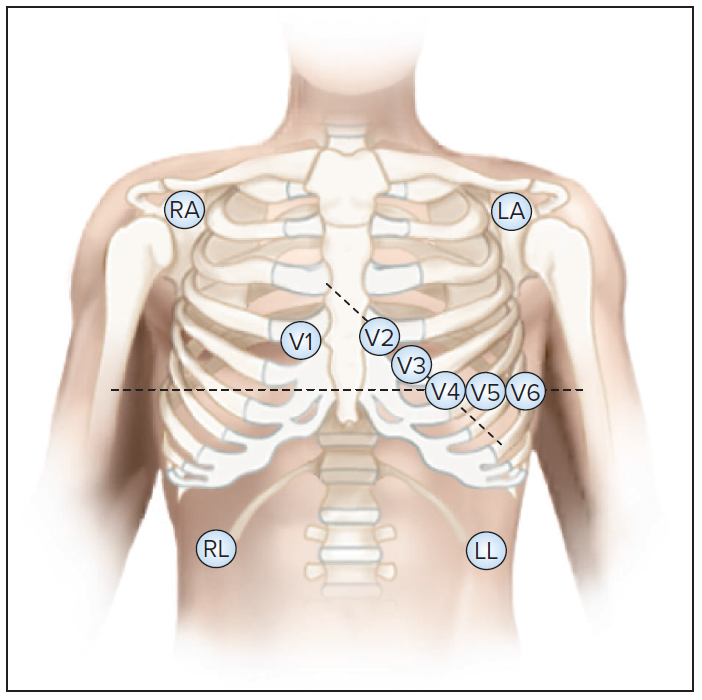
Where are precordial electrodes placed for an exercise ecg?
Same as a 12-lead
How are the limb leads different than a 12-lead ECG?
Limb sensors must be moved from arms and legs to upper chest and torso
To avoid artifacts, avoid placement electrodes near
patients belt
Mason-Likar Placement
Placement of electrodes for exercise cardiography
Any symptoms the patient complains of should be reported
to the physican
What equipment must be assembled before exercise electrocardiography can be performed?
bp equipment
chest electrodes
stress test unit
lead wires
treadmill
Stress test is divided into
2 or 3 minutes each
Each stage of the stress test is based on
protocols
What do the protocols include?
Length of time of exercise and incline
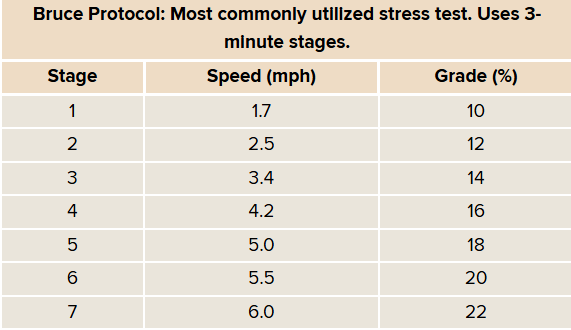
Bruce Protocol
ECG recordings are made continuously during and after exercise
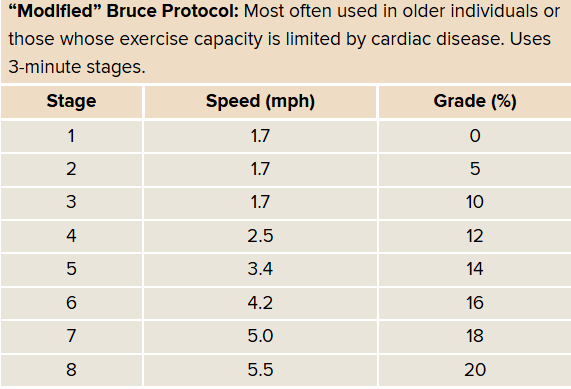
Modified Bruce Protocol
for patients with limitations due to age or hx of cardiac disease
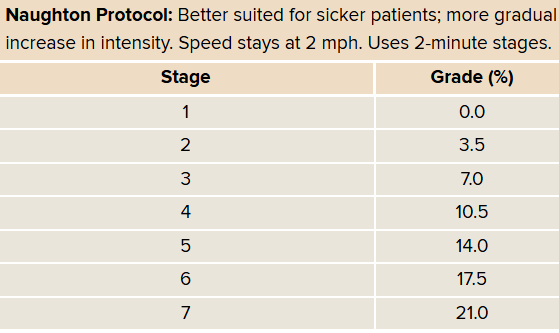
Naughton protocol
for really sick patients
How can you reduce pt fears?
Maintaining confidence
Answering questions
Following safety precautions
The entire exercise period lasts up to
15 minutes but may vary
What happens at the end of each exercise?
Blood pressure is taken and level of exercise is increased
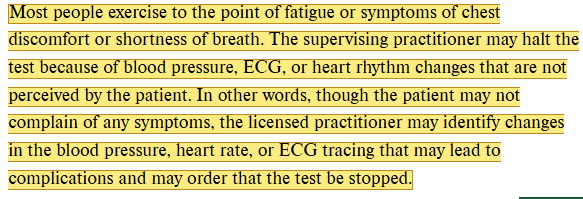
When does exercise stop?
Why patient reaches symptoms, fatigue or physician notices an issue
Target heart rate
measurement needed to truly exercise the heart

How do you calculate target heart rate?
220-pt age x by a percent
Submaximal
Target heart of 220 minus the age multiplied by a percentage between 60 and 85. THR = [(220 − age) × 0.60] to THR = [(220 − age) × 0.85]
Maximal
Target heart rate of 220 minus the age of the patient.
Rate pressure product
Systolic blood pressure multiplied by the heart rate; also known as double product.
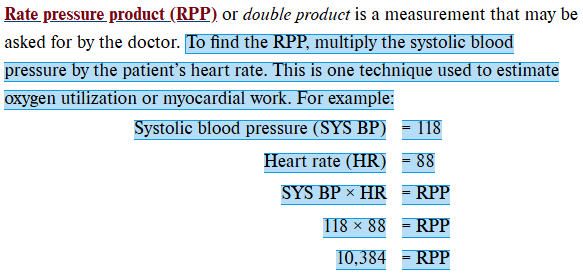
What are the two main factors determining the workload of the heart?
Systolic blood pressure and heart rate
A person with good blood supply and a strong heart should have a
lower RPPA
person who has a disruption of blood supply to the heart and a weaker heart muscle
higher RPP
A patient who recently has a heart attack
Noughton protocol
A 46 year old pt during a yearly physical
Bruce protocol
Patient with hypertension and chest pain
Modified bruce protocol
The period from when the patient ends their exercise but is still monitored is called the
cooling off period and lasts from 6-15 minutes
What is the goal of the cooling off period?
For the patients BP and heart rate to return to the pretest numbers
What factors are used to interpret the results of exercise electrocardiography?
Presence of ECG changes and symptoms
Heart rate and rhythm
Blood pressure
Changes in oxygen saturation
What is an inconclusive test?
A test with questionable results but does not mean necessarily there is an abnormality or potential of an abnormaility
What should the patient do after testing?
rest for several hours
Avoid extreme temperatures
Avoid stimulants

Stress testing is considered a good method to detect
early coronary vascular disease
What percentage of adults have false positive results?
5-15%
False Positive
When a diagnostic test indicates that disease is present but, in reality, no disease is present. A false positive is never considered a negative result. It is a positive result, albeit a falsely positive one.