Special Relativity Year 3
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Why is Special Relativity… Special?
Because it is specific to flat space-times
Restate the first postulate of SR in terms of invariance
The laws of physics are co variant, frame invariant, and form invariant in flat space-times
Define an invariant
If an equation is invariant, it means it is completely general– you do not need to change the form of the equation, or the constants, to apply the equation to another relevant problem
Define form invariant
If an equation is form invariant, it means that the equation will retain the same form when applied to another relevant problem. For instance an inverse-square law would remain an inverse-square law
Define frame invariant
If an equation is frame invariant, it means that the equation does not change provided that the relative frame of the observer has been accounted for.
If an equation is not completely frame invariant then we might add some specificity to this description… For instance we might say that the equation is frame invariant if we consider only inertial frames.
Define Co-variant
This has a more mathematical meaning; in terms of relativity it means that the system of equations will adapt to the shape of the underlying space-time (so the “co” here means “with” as in “co-operate”), this is one of the properties of general laws of physics that enables them to comply with other forms of invariance.
What is the space-time interval S?
S is an invariant measure of space-time length
Where lengths contract and time dilates, this remains unchanged
What is the proper time?
The proper time is defined as the time interval between two events that occur at the same point in space in a particular reference frame
What are timelike separated events?
Events A and B are said to be timelike, or timelike separated if one will always lie within the light cone of the other
It is possible to choose a frame in which the two events will appear to occur at the same point in space, separated only by time
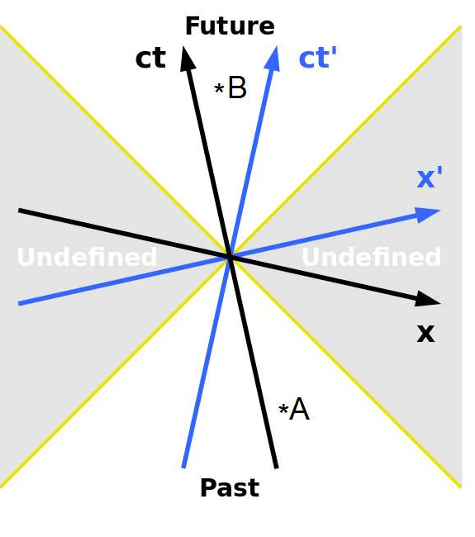
What are lightlike separated events?
Events A and B are said to be lightlike if only the photon world-line connects the two
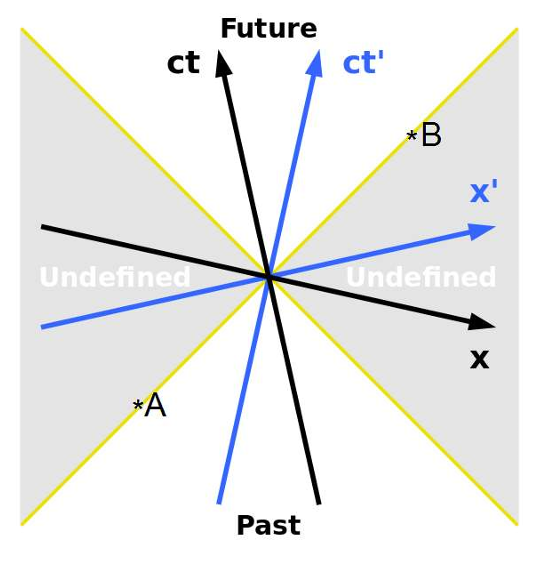
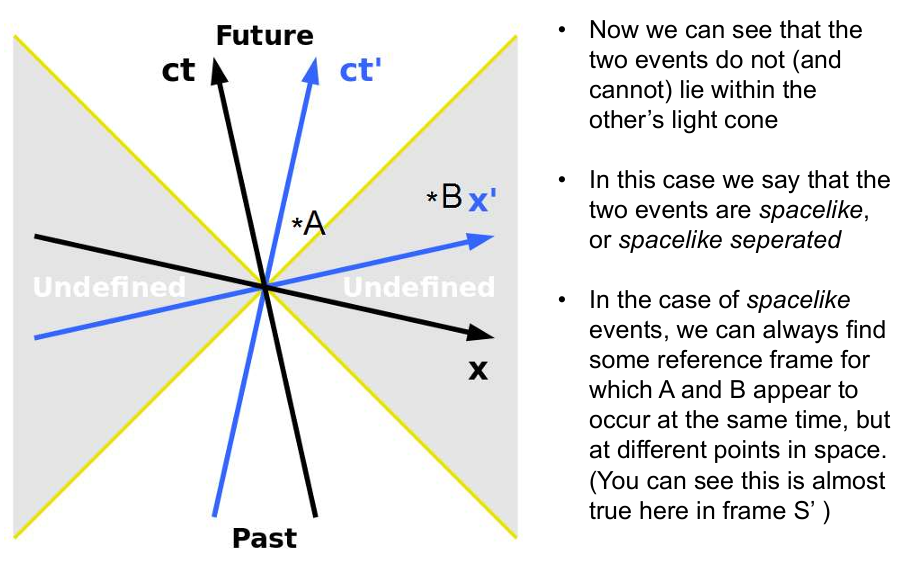
What are spacelike separated events?
Two events are considered spacelike if the two events do not (and cannot) lie within the other’s light cone
Define Minkowski Space
Minkowski space is a flat space time, a 4-space (x,y,z,ct)
What is meant by the twin paradox in Special Relativity?
Two twins, one leaves Earth to journey into space and back at close to the speed of light
To twin A, twin B ages more slowly due time dilation
Since in special relativity, no inertial frame is “special” and therefore to twin B, twin A appears to age more slowly
The paradox is resolved by noting that twin B is not in a IFR at multiple points in his journey