endocrinology
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lab practical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
chemical communication
composed of endocrine glands and hormones
endocrine glands:
ductless and have rich blood supply
hormones:
secreted into the bloodstream
can travel to anywhere in the body and interact with any cell that has an appropriate receptor
hormone receptors are specific binding sites embedded in the cell membrane or located elsewhere in the cell
interacts with a particular hormone/class of hormones
types of hormonal stimulation
hormonal stimulation, humoral stimulation, & nervous system stimulation
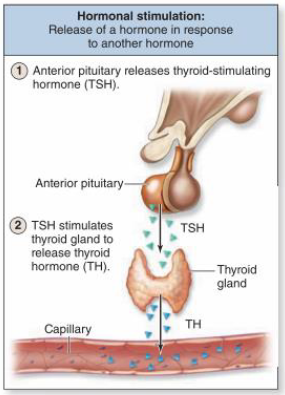
hormonal stimulation
release of a hormone in response to another hormone
i.e. anterior pituitary releasing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) → TSH stimulates thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH)
humoral stimulation
release of a hormone in response to changes in level of nutrient or ion in the blood
i.e. blood glucose levels increase → stimulates pancreas to release insulin to lower blood glucose levels
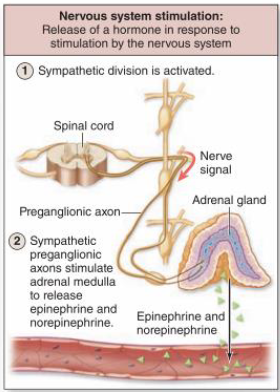
nervous system stimulation
release of a hormone in response to stimulation by the nervous system
i.e. sympathetic division is activated → sympathetic preganglionic axons stimulate adrenal medulla to release epinephrine & norepinephrine
comparison of nervous and endocrine system
mode of transport
nervous: axon
endocrine: blood
speed of response
nervous: instant/milliseconds
endocrine: delyated/seconds
duration of response
nervous: miliseconds/seconds
endocrine: minutes/days
for hormones concentration in blood determines strength of response
patterns of hormone secretion
chronic, acute & episodic (cyclic)
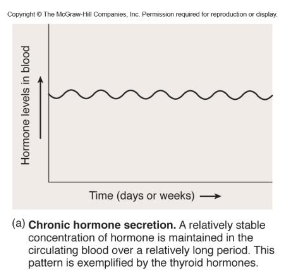
chronic hormone regulation
maintenance of relatively constant concentration of hormone
i.e. thyroid hormone
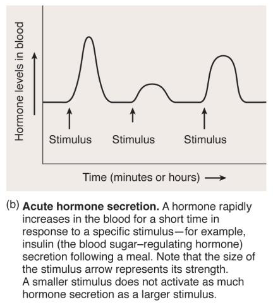
acute hormone regulation
epinephrine response to stress
very strong and quick
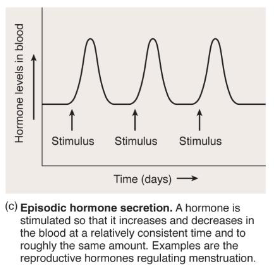
episodic (cyclic) hormone regulation
female reproductive hormones
factors that control concentration of hormones
rate of secretion
metabolic clearance rate (MCR)
rate of disappearance of hormone from plasma/concentration of hormone
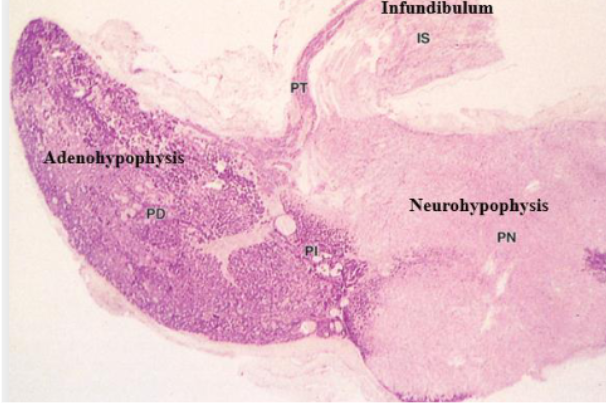
regions of the hypothalamus
Anterior portion → adenohypophysis
Stains much darker
Posterior portion → neurohypophysis
Stains lighter
Infundibulum: attaches pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
In the hypothalamus
Paraventricular nucleus: produces the hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland
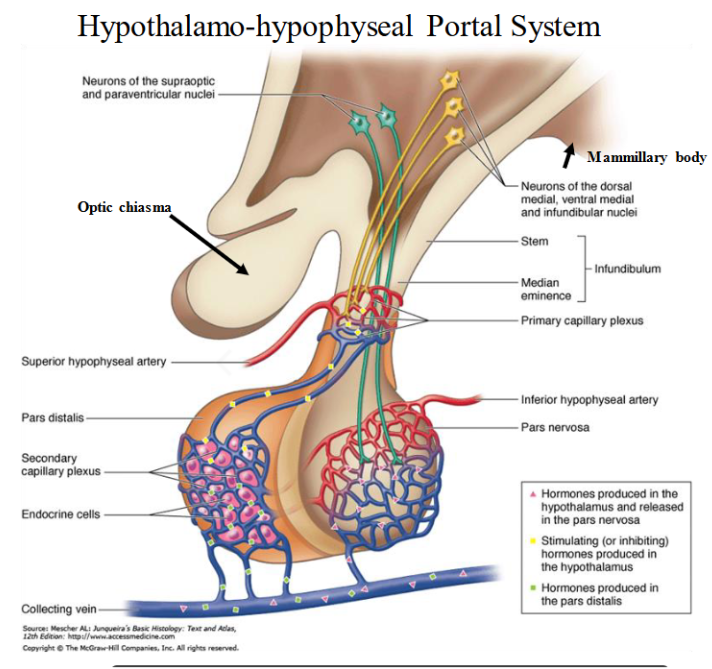
hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
portal system which connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
portal system consists of two capillaries
transports and exchanges hormones
prolactin
anterior pituitary hormone
stimulates milk production
target: breast
growth hormone
anterior pituitary hormone
stimulates growth in childhood
maintains healthy bone in adulthood
targets: skeletal system
adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)
anterior pituitary hormone
stimulates production of cortisol
fights stress hormone— controls BP and sugar levels under stress
targets: adrenal cortex on kidneys
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
anterior pituitary hormone
regulates metabolism, energy balance, growth, and NS activity
targets: thyroid gland
luteinizing hormone (LH)
anterior pituitary hormone
stimulates testosterone production in men
stimulates ovulation in women
target: testes & ovaries
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
anterior pituitary hormone
promotes sperm production in men
stimulates the ovaries to develop and estrogen production in women
target: testes & ovaries
melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
anterior pituitary
stimulates melanin production → helps protect skin from UV rays
target: skin
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH, or vasopressin)
posterior pituitary hormone
regulates water balance in body and sodium levels in the blood
target: kidneys
oxytocin
posterior pituitary hormone
stimulates milk flow during breastfeeding
promotes labour during childbirth
promotes bonding between mother & child
target: breast & uterus
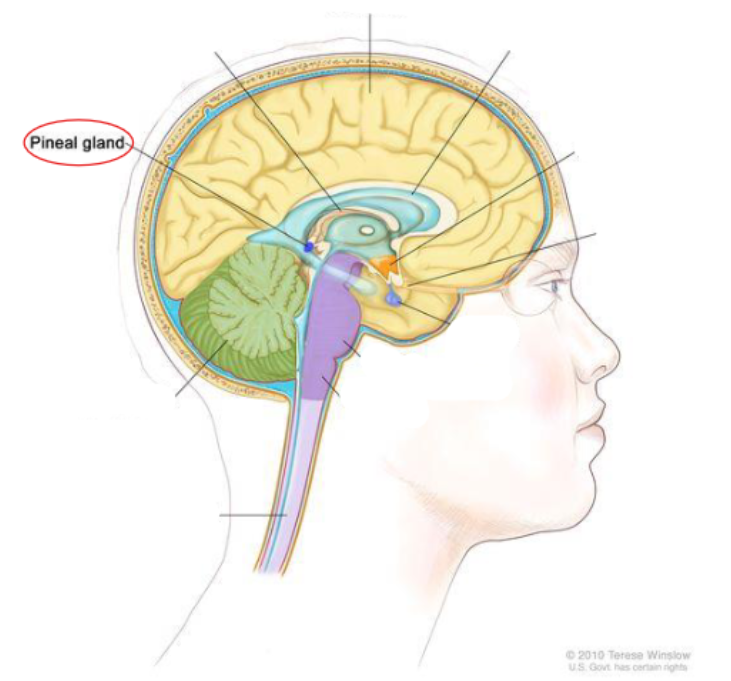
pineal gland
Pineal gland: secretes melatonin
Controlled by the amount of light seen by the eyes each day
Helps regulate the sleep cycle
Pathway: light signals from eyes → suprachiasmatic nucleus of hypothalamus → pineal gland → pineal secretion
made up of pinealocytes
Pinealocytes: manufacture melatonin in the absence of light and serotonin in the presence of light
Brain sand: calcified granular material located in the intercellular spaces
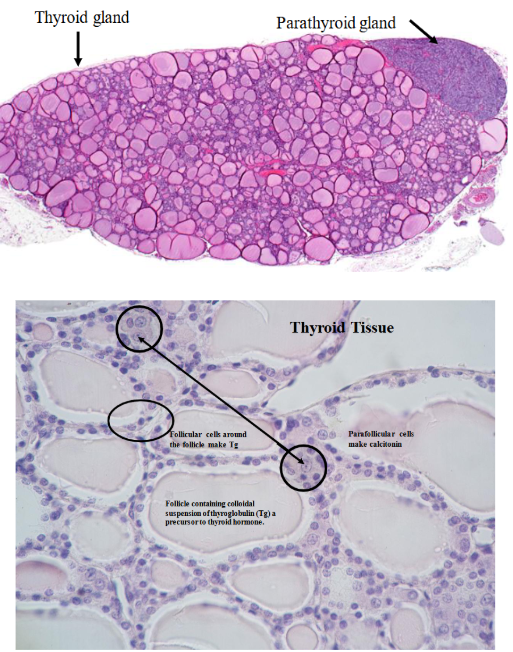
thyroid glands
Located in the trachea of the neck
Contains parathyroid glands
Secretes triiodothyronine (T3): iodine-containing hormone
Secretes thyroxine (T4) → eventually converted into T3
Monitors metabolism
regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Follicular cells: make thyroglobulin
Parafollicular cells: secretes calcitonin → decreases blood calcium levels
Parathyroid hormone secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH): releases calcium from the bones to be put into the bloodstream
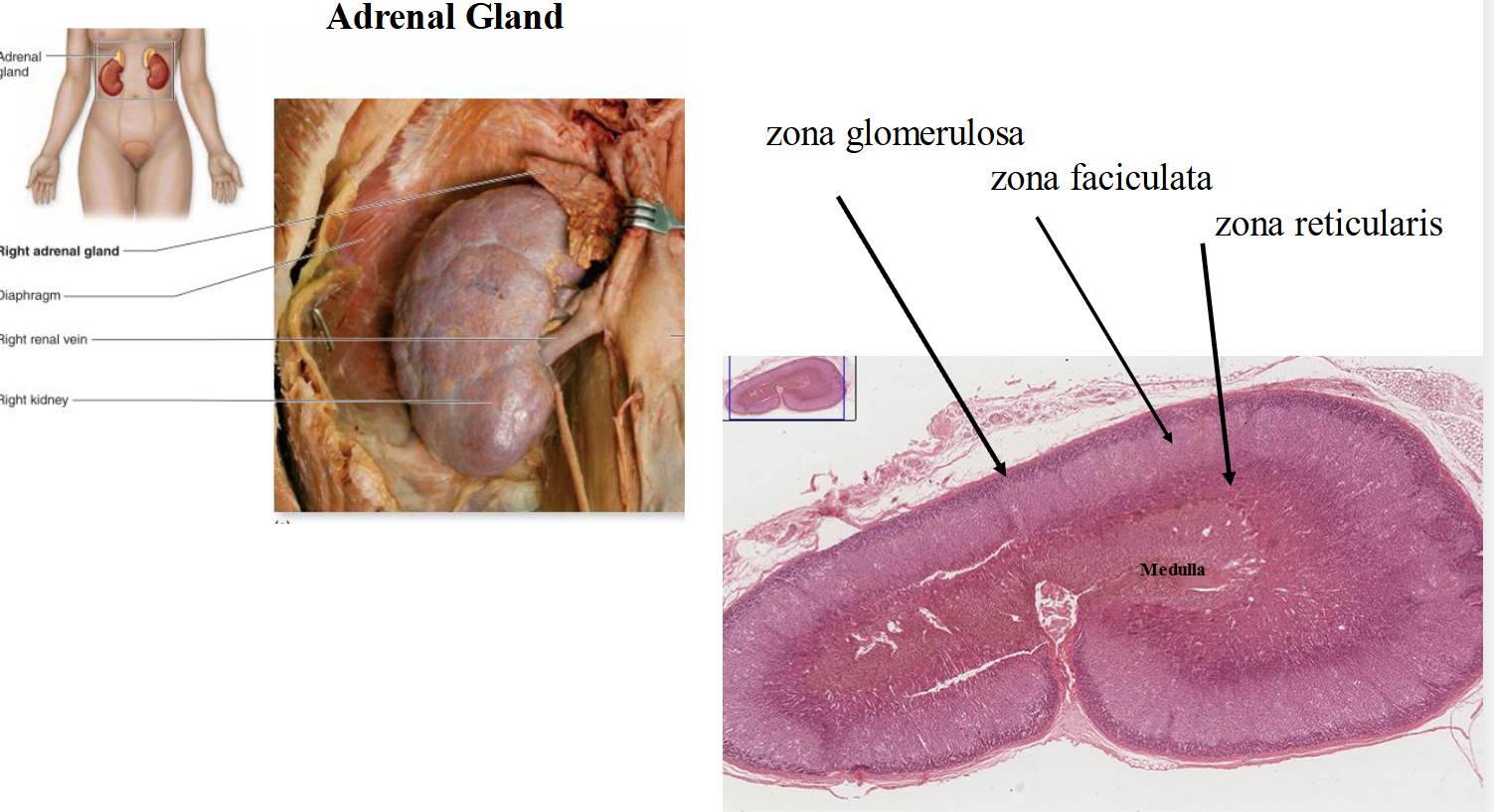
adrenal gland
Adrenal gland
Central area → adrenal medulla: secretes norepinephrine and epinephrine
Activated in response to stimulation by sympathetic preganglionic neurons
Zona glomerulosa: mineralocorticoids
Secretes aldosterone
Increases rate of sodium reabsorption by kidneys → increases sodium blood levels
Zona fasciculata: glucocorticoids
Secretes cortisol
Increases fat and protein breakdown
Increases glucose synthesis
Decreases inflammatory response
Zone reticularis: androgens
Weak androgen secreted → converted to testosterone by peripheral tissues
Stimulate public and axillary hair growth
Stimulates sexual drive in females
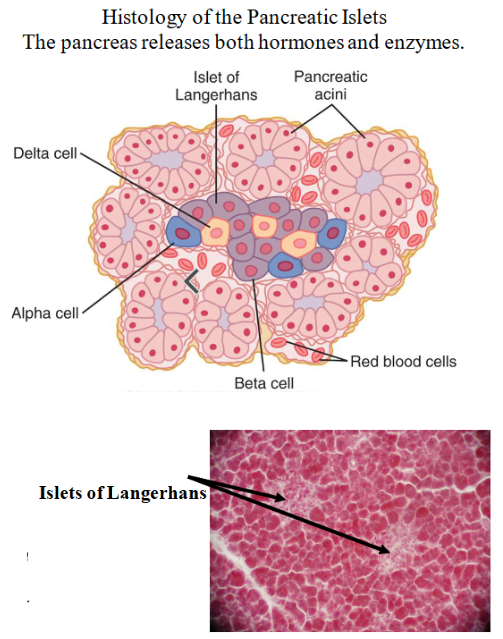
pancreas
Pancreas
Releases both hormones and enzymes
Located close to the small intestine → releases enzymes into the small intestine
Alpha cells produce glucagon → stimulates the breakdown of glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream
Beta cells produce insulin → tells the liver to store glucose in the form of glycogen
Delta cells produce somatostatin → inhibits secretion of insulin and glucagon
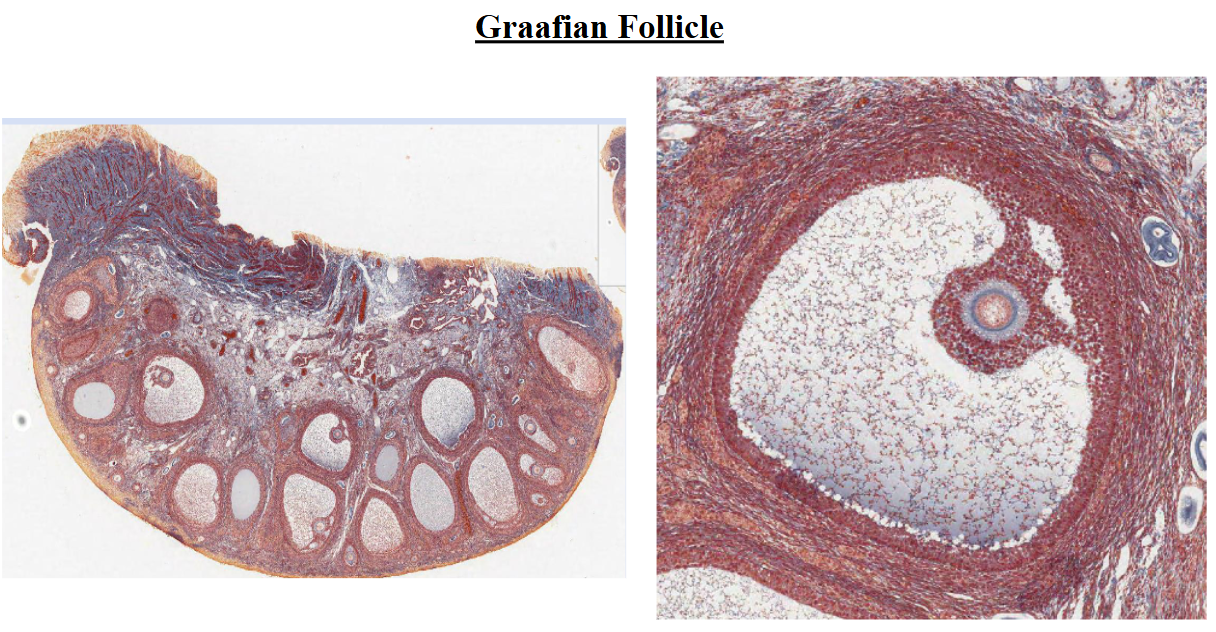
graafian follicle
a mature ovarian follicle
within the ovary
following ovulation, becomes corpus luteum
secretes estrogen and progesterone
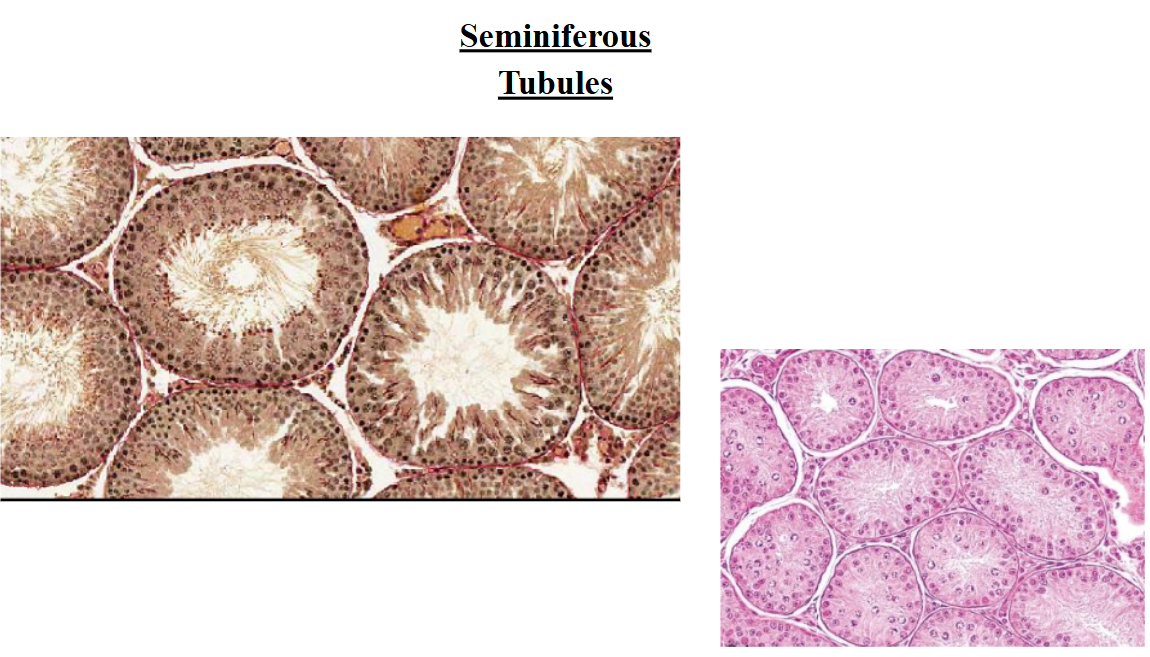
seminiferous tubules
produces mature sperm cells