Barriers to growth and development
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
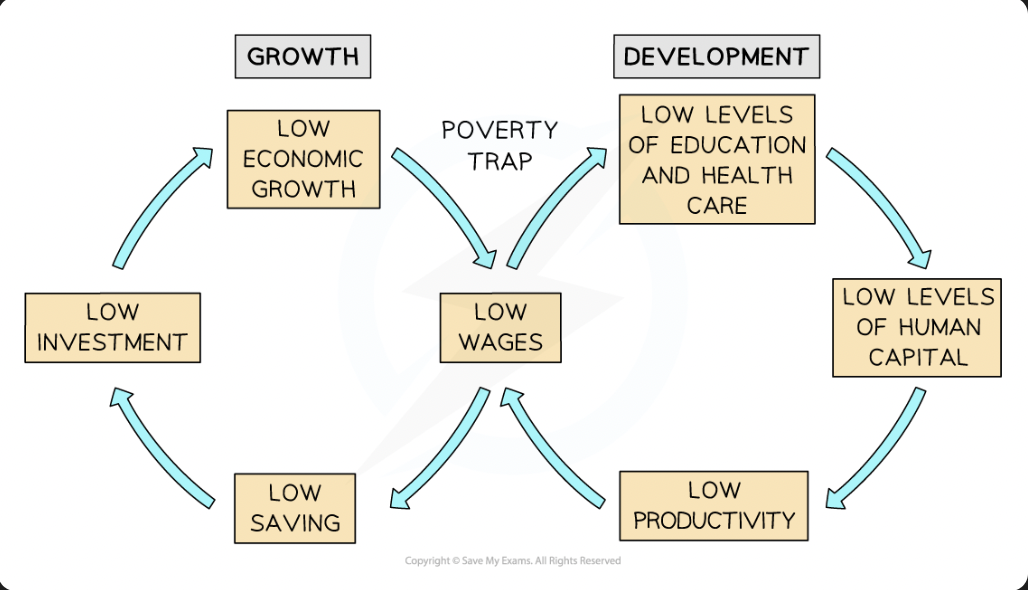
poverty traps
there are many causes of poverty, but poor countries exhibit several common characteristics
a poverty trap is a combination of factors that causes poverty to be self-perpetuating with low income as the cause
development:
low wages: intersection of economic growth and development and are the major cause of poverty
usually the result of unemployment
low levels of education and healthcare
cost money thus not accessible to those with lower wages
low levels of human capital
low education/healthcare leads to low level of human capital, reducing productivity
low productivity
results in low wages, cycle continues
growth
low wages
low saving
low wages means its harder to save because any money is spent on necessities
low investment
savings drive investment as firms are able to borrow money from banks. low savings = less money available for investment
low economic growth
investment is a component of GDP
economic barriers
rising income inequality
more equal distribution of income means more households able to consume wider range of goods
rich get richer poor get poorer
dependence on primary sector
primary sector produces primary commodities (goods arising from land FOP)
PES and PED for primary products is inelastic, meaning prices are volatile, affecting income, investment, employment of agricultural workers
one bad yield one year means economy suffers greatly
lack of access to international markets
trade is a significant source of higher incomes, leading to development
many countries can’t access more developed markets due to trade barriers
informal economy
economic activity not officially recorder, regulated or taxed
less gov revenue so less provision of merit goods, hence development
capital flight
when households/firms take money/resources out of a country due to low confidence
prevents consumption/investment, preventing growth & development
indebtedness
countries have to focus on repaying loans over investing in its economy, preventing growth & development
lack of access to infrastructure
good infrastructure reduces business costs and attracts FDI
makes it difficult to generate economic activity
low levels of human capital
lack of access to healthcare/education, less knowledge and productivity, less output, less growth, less income
geography
landlocked countries find it more expensive to import/export products bc no access to ports
tropical climates and endemic diseases
many diseases e.g malaria, dengue most common in tropical climates, hinder productivity and output of workforce and development
political and social barriers: institutional
institutional framework barriers - refers to functions of government
legal system
strong legal system builds confidence in an economy. this attracts overseas investment
less confidence means less investment hindering growth & development
tax structure
progressive tax system redistributes income from those with higher to those with lower, reducing inequality
banking system
lack of financial institutions means less borrowing for investment, hence less growth
property rights
includes both assets like land and copyrights/patents
lack of enforcement of this discourages investment (as its risky) and innovation (as others can copy)
other social/political barriers
lack of good governance
leads to insufficient use of resources and poor decision making - meaning laws that directly inhibit growth and development
corruption leads to diverting funds to groups that have bribed or lobbied, resulting in low growth and development
unequal political power & status
countries with low trade union membership leads to exploitation of workers through low wages and income inequality
gender inequality
increases income inequality leading to lower growth
reduces incentive for women to work, meaning loss of productivity and hence growth
evaluating barriers to growth and development
there are a common set of factors which prohibit economic growth and development however each country is unique and likely to have a different combination of factors which are more prominent
understanding context of the country is vital to evaluating how significant the barrier is
e.g Romania has a history of corruption, reducing its development
e.g India has infrastructure problems limiting its ability to grow