6.2 Influences upon the supply of labour to different markets
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
the supply of labour is influenced by
monetary and non monetary factors
what does the supply curve of labour show
the relationship beteen the wage rate and the number of workers willing to work in an occupation
examples on non monetary factors that influence the supply of labour
working conditions (safety, comfort)
job satisfaction
work life balance (remote work, flexible hours, unsociable hours)
job security
location
career progession/opportunities
perks and benefits (staff discounts, anual leave)
what is the difference between how changes in monetary and non monetary factors are shown graphically
non monetary → shift in the supply of labour
monetary → movement along the supply curve
causes of a shift in the market supply of labour curve
migration
education & training
changes in non monetrary factors
changes in income tax or benefits
demographic changes
changes in alterntive opportunities
changes in social attitudes
explain the impact of changes in income tax and benefits on the supply of labour
lower taxes → restore personal incetives → opportunity cost of not working increases → shifts supply to the right
lower benefits → reduces the replacement ratio → makes working more attractive
explain the impact of the changes in migration on the supply of labour
increased immigration → increases the labour pool → supply to the right
increced emmigration → fewer workers → supply to the left
case study on the impact of migration on the supply of labour
Afer UK left the EU, it lost access to the free movement of labour under the single market, led to a reduction in EU migrant workers due to tighter immigration rules
the number of HGV drivers fell by 50000 in 4 years
lead to severe shortages → delays in fuel and food deliveries → supply chain disruptions
policy response: UK added HGD, to the shortage occupation list → granted temporary visas
Evaluation: short term vs long term impact (in long run can work on domestic training schemes)
how do changes in demographics and social attitudes effect the supply of labour
social attitudes change eg more working mothers → increase supply of labour
demographic changes → eg increassing the retierment age
statistic on working mothers
rise form 66% in 2002 to 76% in 2021
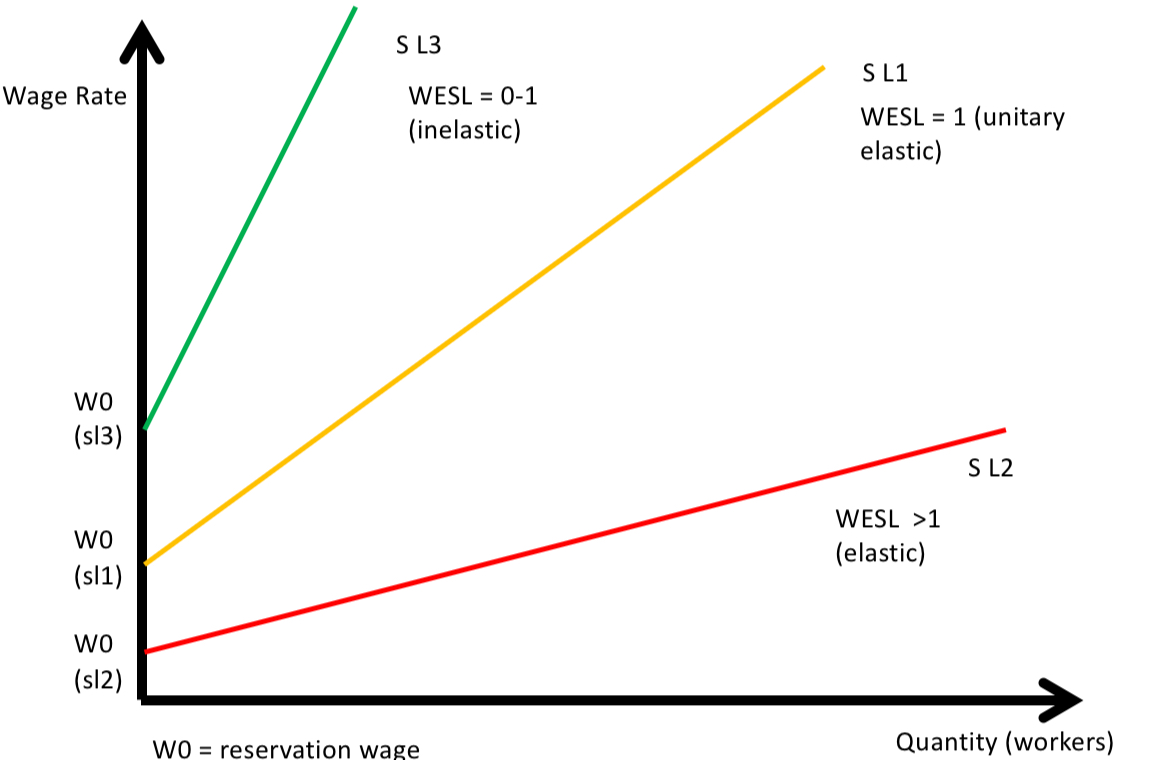
determinants of PES of labour
skill level and training ease
government regulations
apeal of job
long run or short run
geographical and ocupational mobility
how does regulation impact supply of labour (dental case study)
Reservation wage
the lowest wage any worker is willing to accept (W0)