food tech GCSE
1/462
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
463 Terms
What is protein needed for?
-growth (e.g. nail/hair growth)
-repair (repairing muscles after illness/ injury)
-maintenance (e.g. making enzymes for digestion)
What are non-essential amino acids?
amino acids our bodies can make
What are essential amino acids?
amino acids we have to eat
What are HBV proteins?
-high biological value
-contain all the essential amino acids we need
-found in meat, fish, poultry, eggs, cheese, milk, soya beans, quinoa
What are LBV proteins?
-low biological value
-missing 1+ essential amino acids
-only found in plant sources (peas, lentils, nuts, seeds)
What is protein complementation?
-the combination of different LBV proteins to get all the essential amino acids (pitta+hummus)
How much more protein do pregnant women need?
6g more to help baby grow/more when breastfeeding
What can an excess of protein lead to?
Puts pressure/ strain on the organs processing proteins (liver, kidneys), which can be dangerous
What can a deficiency of protein lead to?
-growth is slowed down
-immune system can't work properly (wounds don't heal as fast, more infections)
-can lead to oedema
What is oedema?
-caused by deficiency of protein
-a build up of fluid in the body that causes swelling (often around the feet)
What is soya?
-alternative protein
-plant based HBV protein
-Must be cooked to remove toxicity
What is mycoprotein?
-alternative protein
-traditionally made from a mushroom like fungus and egg white
-Tthere are now vegan alternatives that use potato starch
What is TVP?
-textured vegetable protein
-made from soya beans (soya flour)
-soya flour is used to make a dough which when baked has a meat like texture
What do fats provide?
-concentrated energy
-nutrients (fat soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E, K)
-bodies use fat to make cholesterol (essential part of cell membranes)
What are fats made of?
-triglyceride (1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids)
-fatty acid chains are made of carbon and hydrogen
Are saturated fats healthy or unhealthy?
-unhealthy (especially in large amounts)
-too much saturated fat in the diet can increase cholestorol levels in the blood (increased risk of CHD)
What are saturated fats?
-solid at room temperature
-generally from animal sources
Are unsaturated fats healthy or unhealthy?
-generally healthier
-generally soft/liquid at room temperature
-replacing saturated fats with unsaturated has been shown to lower blood cholesterol
Where are unsaturated fats found?
-from vegetable sources
What are monounsaturated fats?
-contain one C=C double bond in their carbon chains
-found in olive oil, almonds, peanut butter, avocados
What are polyunsaturated fats?
-contain more than one C=C double bond
-found in sesame oil, soybean oil, seeds and oily fish
What percentage of our daily food energy should fat make up?
less than 35% (less than 11% from saturated)
How many grams of fat should an average adult consume?
70g (max 20g from saturated)
What can an excess of fat lead to?
-too much saturated fat can increase blood cholesterol levels
what can increased blood cholesterol levels lead to?
-cholesterol builds up in blood vessels and restricts blood flow around body
-increases the risk of high blood pressure, strokes, heart attacks, and CHD
what can a deficiency of fat lead to?
- Less fat soluble vitamins are absorbed by the body
What are fat soluble vitamins?
A, D, E, K
What are sugary carbohydrates?
-e.g. glucose, fructose
-can be divided into monosaccharides and disaccharides
What are starchy carbohydrates?
-contain lots of nutrients such as B vitamins, iron and calcium
-wholegrain starch foods have a really high fibre content
What are monosaccharides?
-simple carbohydrates (sugar)
-the most basic sugar molecules
-e.g. glucose, fructose
What are disaccharides?
-simple carbs (sugar)
-made up of 2 monosaccharides
-e.g. sucrose (made of glucose and fructose)
What are polysaccharides?
-complex carbohydrates, including starchy carbs
-take longer to digest, providing a slower release of energy
-made of lots of monosaccharides joined together
What does the body do to simple carbs?
-rapidly digests them
-making blood sugar levels rise quickly
-providing a short burst of energy
What is the glycaemic index?
-GI
-rates carbohydratres on how quickly they affect blood sugar levels
-helpful to people with diabetes (allows them to choose low GI carbs to avoid surges in blood sugar levels)
How much of our energy should come from carbs?
-50%
What happens if we have an excess of carbs?
-Will convert into fat
-tooth decay
-can lead to type 2 diabetes
What can a deficiency in carbs lead to?
-blood sugar levels drop, can cause hunger, dizziness, and tiredness
-body will use another source of energy, stored fat
-if you also have a fat deficiency, our bodies use up proteins, causing us to lose muscle, making us weaker.
What is vitamin A used for?
-good eyesight (night vision)
-growth
-healthy immune system
-healthy skin
-antioxidant
What are sources of vitamin A?
-retinol (liver, butter, oily fish, eggs)
-can be made from carotene (margarine, orange/yellow fruit/veg)
What can an excess of vitamin A lead to?
-can weaken bones
-should be avoided during pregnancy
What can a deficiency of vitamin A lead to?
-night blindness
-weaker immune system
-stunted growth
What is vitamin D used for?
-helps the body absorb various mineral (e.g. calcium)
-so helpful for the development of healthy bones+teeth
Where is vitamin D found?
-oily fish
-egg yolks
-produced when the skin is exposed to sunlight
What can an excess of vitamin D lead to?
-makes you absorb too much calcium (can lead to kidney damage)
What can a deficiency of vitamin D lead to?
-can lead to bone diseased (osteomalacia, rickets, osteoporosis)
What is osteomalacia?
softening of the bone
Why do you need vitamin E?
-keeps skin+eyes healthy
-improves immune system
-antioxidant (may protect us from free-radicals)
What are sources of vitamin E?
-leafy greens
-nuts
-vegetable oils
What can an excess of vitamin E do?
-can interfere with blood clotting
-cause nausea
-blurred vision
What can a deficiency of vitamin E lead to?
-weak muscles
-problems with sight
What does vitamin K do?
-helps blood clotting so heals wounds
-maintains immune system
-maintains bones
What are sources of vitamin K?
-leafy greens
-cereals
-vegetable oils
What can an excess of vitamin K lead to?
there is no excessive level of vitamin K
What can a deficiency of vitamin K lead to?
-extremely rare in adults
-can cause uncontrolled bleeding in newborns
What happens to unused fat-soluble vitamins?
stored in fat tissue
What are water-soluble vitamins?
vitamins that dissolve in water, aren't generally stored in the body, so we need to take them in daily
What are water soluble vitamins?
B and C (Before Christ, Christ walked on WATER)
What is the function of vitamin B?
-helps energy release from foods
-helps maintain a healthy nervous system
-Crucial for growth
What is the function of vitamin C (ascorbic acid)?
-protects the body from infection + allergies
-keeps blood vessels healthy + heals wounds
What can a deficiency in Vitamin B lead to?
-tiredness
-weak muscles
-beriberi (in severe cases)
What is beriberi?
-a disease that affects the heart, blood vessels and nervous system
What is pellagra?
-Vitamin B deficiency
-a disease causing fatigue, depression and loss of memory
What can a deficiency in vitamin C (ascorbic acid) lead to?
-anaemia
-scurvy (tiredness and bleeding gums)
-too little can increase the risk of cancer
What can an excess of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) lead to?
-stomach pain
-diarrhoea
Why should you prepare fruit/veg just before you need to use it?
because once they are exposed to air, they start losing vitamin C
Why shouldn't you leave your fruits/veg to stand in water?
-because vitamins B and C dissolve in water
-steaming/microwaving are the best ways to keep the water-soluble vitamins
What are free radicals?
-chemicals we encounter daily
-they can damage our body's cells
-leading to cancer/heart disease
What are antioxidants?
-vitamins A, C and E
-many people believe they protect us from free radicals
What is calcium needed for?
-strong bones+teeth (especially in growing children)
-healthy nerves and muscles
-blood clotting
What can an excess of calcium lead to?
-excess is stored in organs like the kidneys
-can increase the risk of kidney tones
-could even stop kidneys working
What can a deficiency of calcium lead to?
-too little in childhood can lead to rickets/osteoporosis as bones become weaker
-slow down blood clotting
What is iron needed for?
-to form part of haemoglobin (gives red blood cells their red colour)
What can an excess of iron lead to?
-can cause stomach pains/nausea
-constipation
-in extreme cases can cause death
What is sodium needed for?
-controls the body's water content
-helps our nerves+ muscles to function
What can an excess of salt lead to?
-lead to high blood pressure
-leads to heart disease
What can a deficiency of salt lead to?
-nausea
-muscle cramps
What is phosphorus needed for?
-healthy bones and teeth
What are sources of phosphorus?
-protein rich foods
-meat, fish, dairy products, nuts, beans, cereals
What can an excess of phosphorous do?
-can make it harder to absorb calcium
What can a deficiency in phosphorous lead to?
-weak muscles
-painful bone
What does flouride do?
-strengthens teeth
-hardens tooth enamel
-helps prevent tooth decay
What can an excess of fluoride lead to?
-brown coloured teeth
-bone problems
-cancer
What can a deficiency of fluoride lead to?
-weak teeth/enamel (leads to tooth decay)
What is iodine needed for?
to make some hormones in the body
What is iodine found in?
seafood, dairy foods and vegetables
What can a deficiency of iodine lead to?
-a serious lack of iodine can cause goitre (neck swelling)
-complications in new born babies
What can a lack of fibre lead to?
-constipation
-bowel/colon cancer
-high blood pressure
How much fibre do we need?
-average adult should have 30g a day
-young children need less as the "fullness" fibre gives people can stop them from eating more important nutrients
How much water is in our bodies?
-60%
-found in every cell
-found in fluids (blood, sweat, saliva)
Why do our bodies need water?
-Eliminates waste
-Controls body temperature (sweating)
-Aids the process of digestion
EATWELL GUIDE what fraction of your daily food intake should fruit/veg make up?
1/3 of your daily intake (at least 5 portions every day)
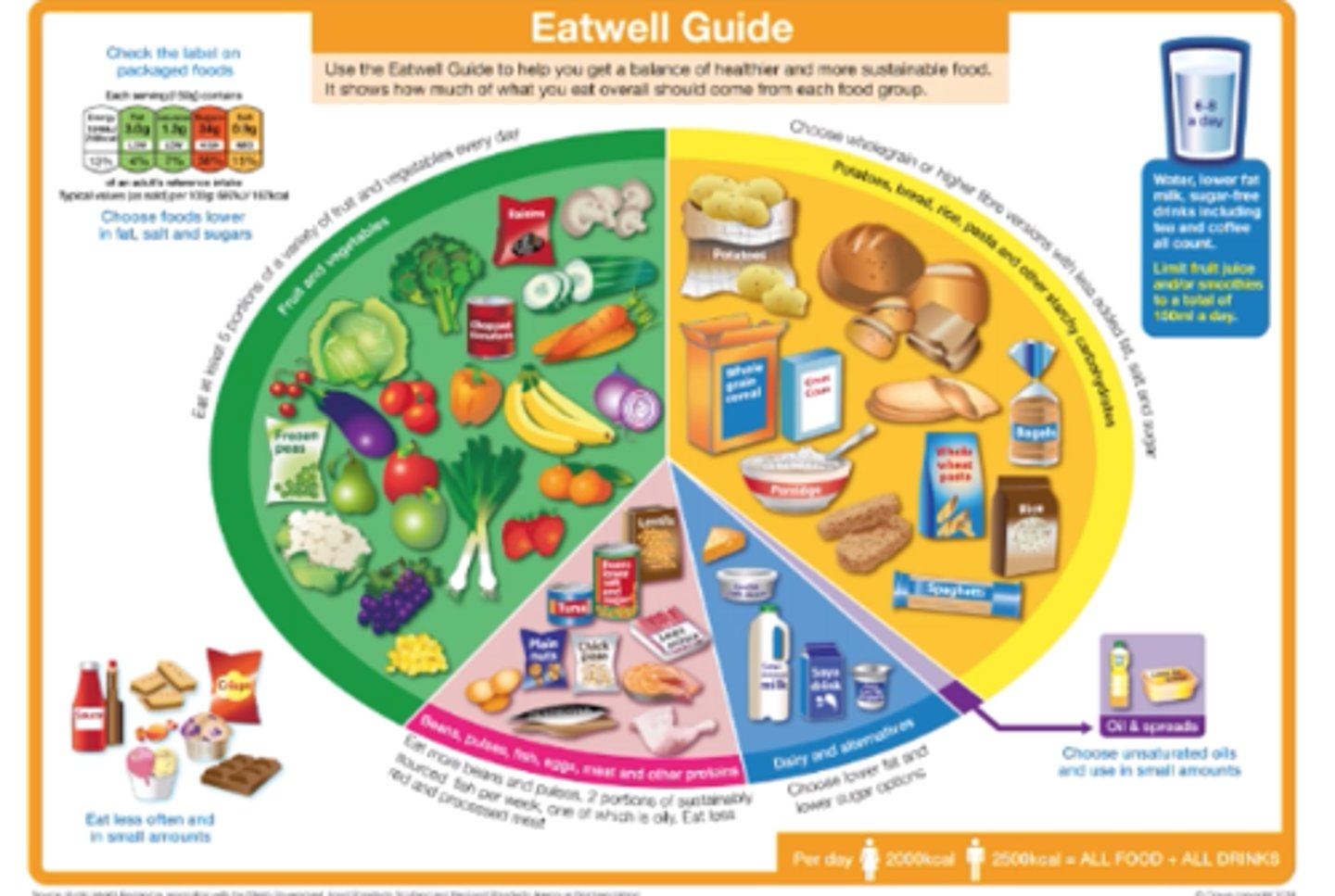
EATWELL GUIDE what fraction of your daily food intake should starchy carbs make up?
-1/3 of your daily intake (starchy food in every meal)
How much fluids should you have per day?
6-8 glasses (no more than 1 glass fruit juice a day)
How much salt should you have per day?
no more than 6g
Why is milk important to 2-5 year (young children) olds?
-gives children their daily calcium (although it is better to get from a range of foods)
-good source of vitamin A
-300ml a day
Why do 5-12 year olds (children) need carbs/fat?
-provide energy for growth/physical activity
-saturated fats should be eaten in moderation
Why do teens need protein?
-to cope with growth spurts
-boys tend to need more protein than girls as muscular tissue develops
Why do teens need iron/vitamin C?
-teenage girls lose iron when they have their period so it must be replaced or they could become anaemic
-vitamin C helps the body absorb iron
Why do teens need calcium/ vitamin D?
-skeleton grows quickly during this time
-these nutrients are neccesary as they help the skeleton reach peak size/bone density
Why is calcium/vitamin D important for adults/elderly?
-reduce the chance of bone diseases in later life
-women can quickly lose bone strength after menopause
-needed to keep the skeleton strong