Chad's Gen chem
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
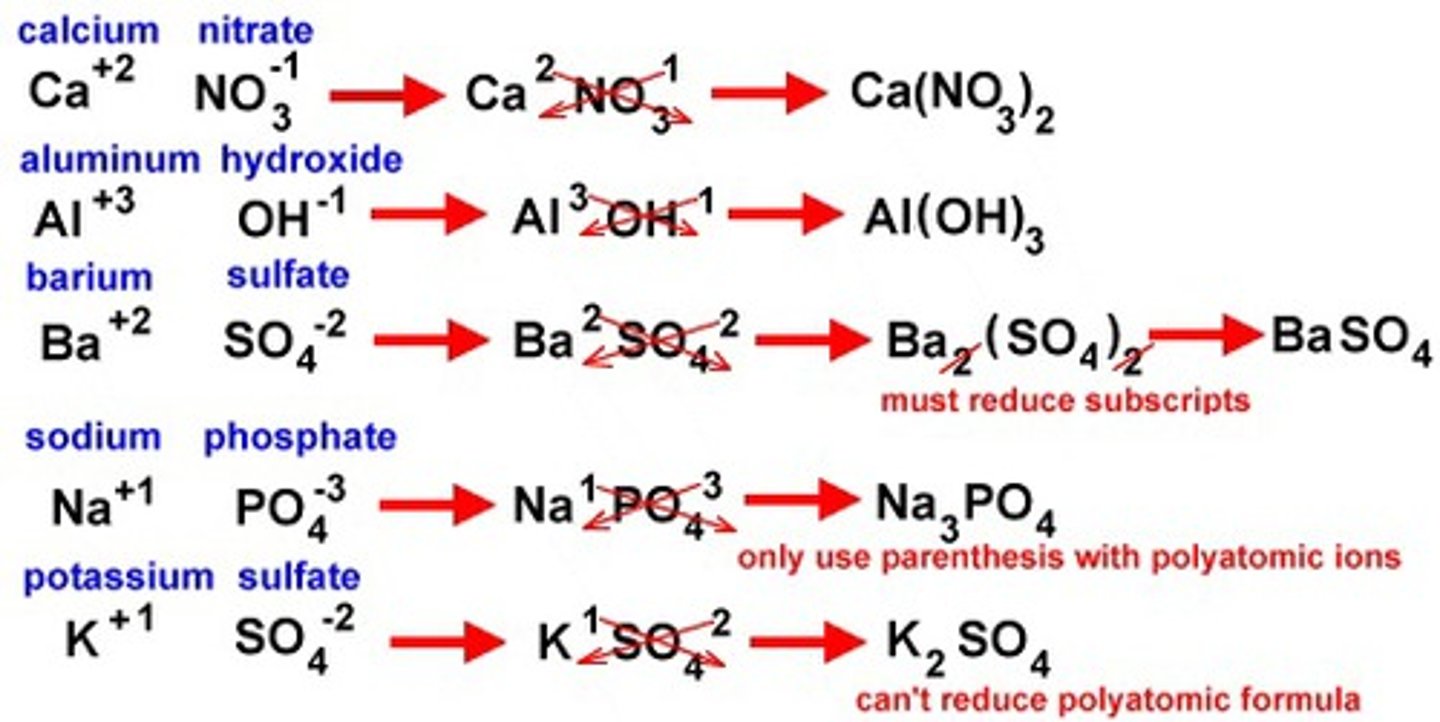
How to name an ionic compound (polyatomic/ metal + nonmetal)
1. Name the metal (polyatomic cation)
2. State the oxidation state as a roman numeral in parenthesis (EXCEPT FOR: Group 1 or 2, Al, Zn, Cd, Ag)
3. Name the non-metal (or polyatomic) with -ide ending
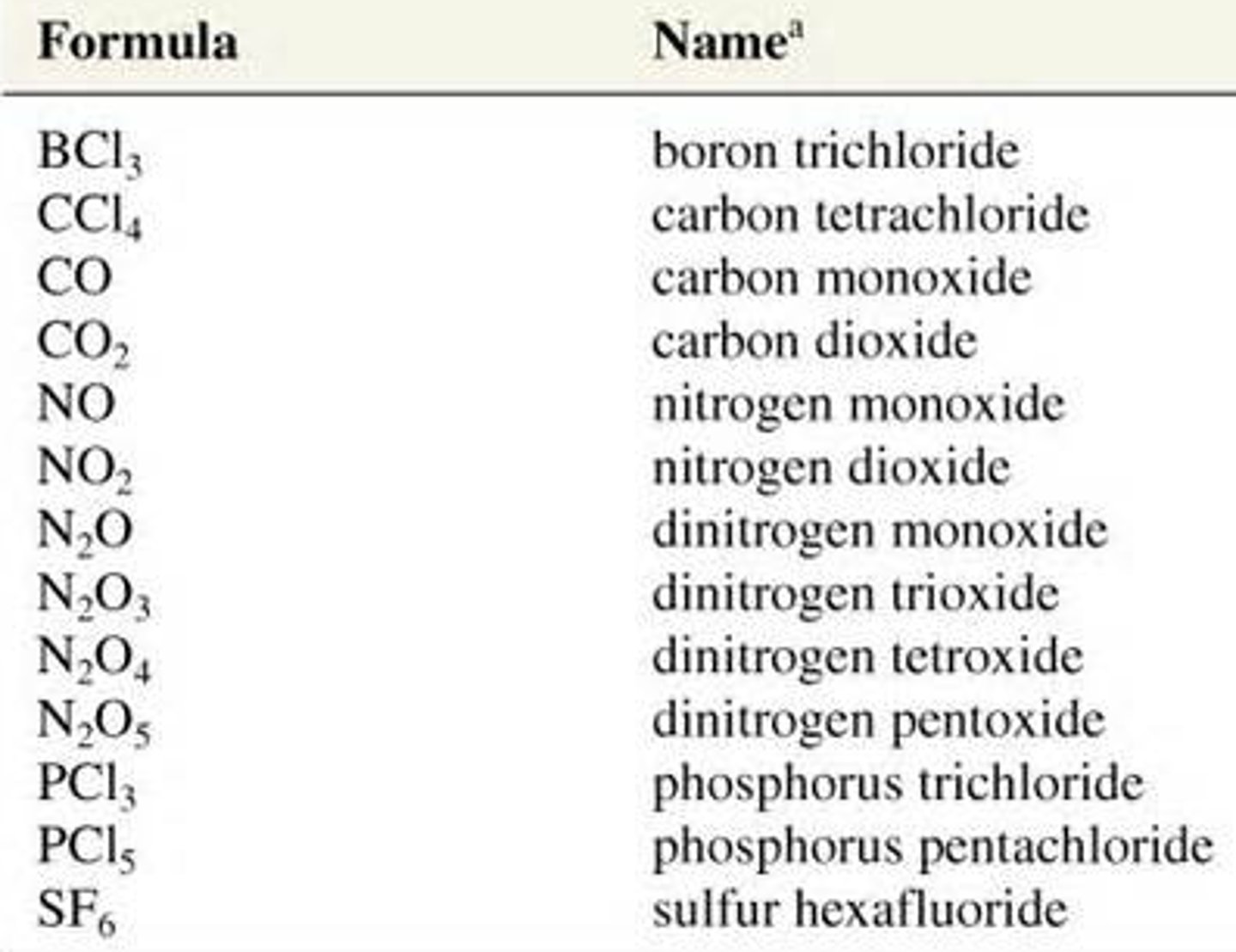
How to name molecular compounds?
1. Prefix if first element has more than one atom + name of first element
2. Prefix of number of atoms of second element + root name of second element + ide
What is a binary acid
an acid that contains only two different elements: hydrogen and one of the more electronegative elements
Hydro-element-ic acid
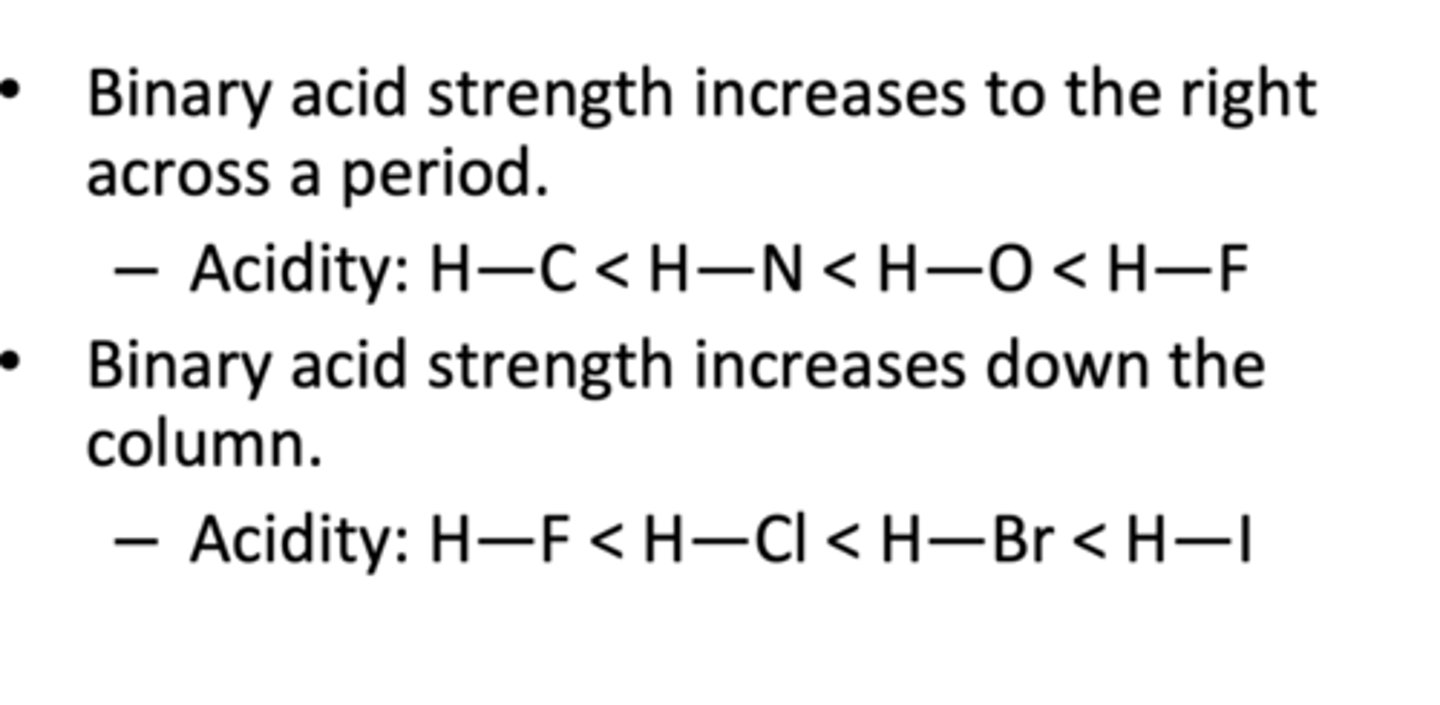
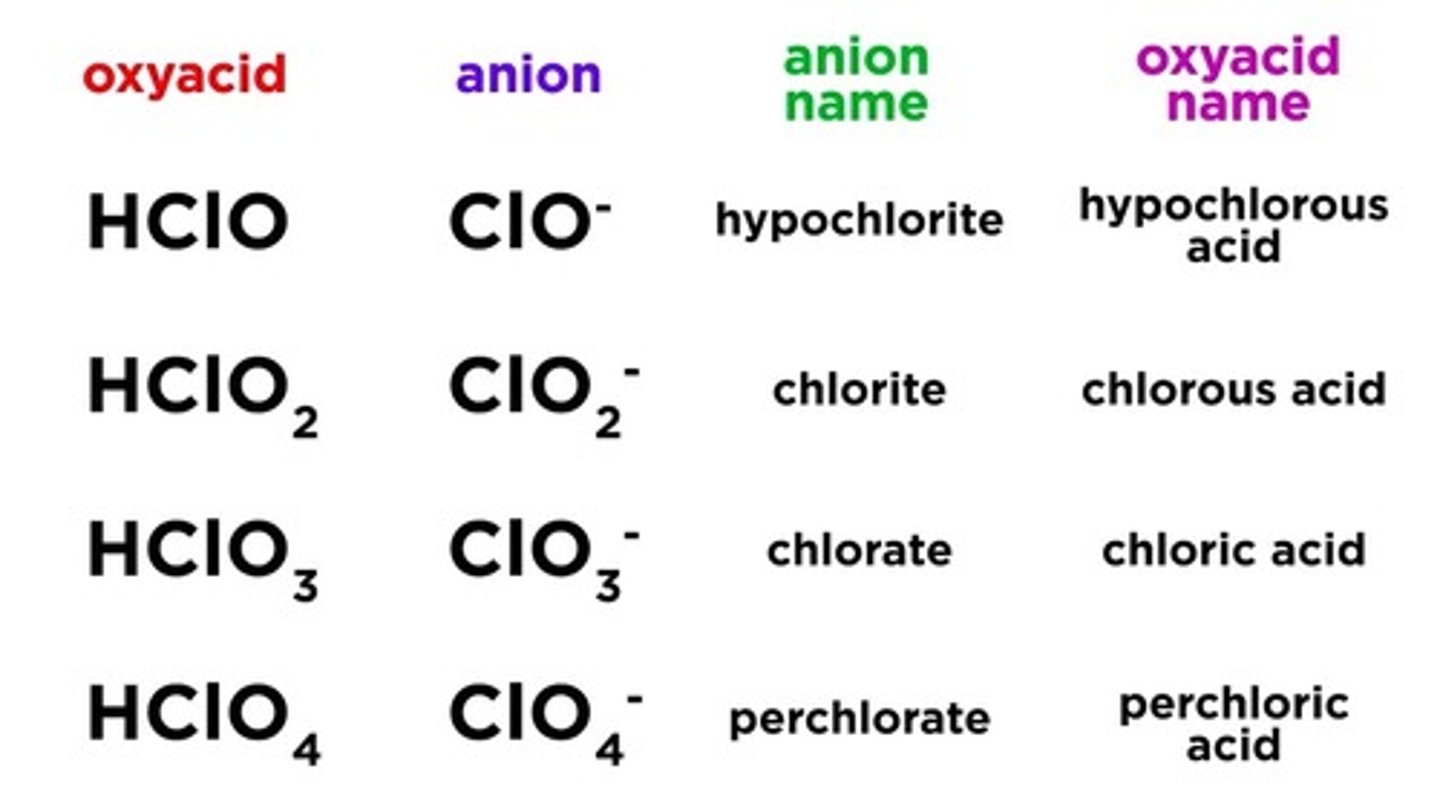
What are oxyacids?
acids that contain hydrogen, oxygen, and a third element (usually a nonmetal)

How to name binary acids
hydro_____ic acid

how to name oxyacids
1. Omit "hydrogen"
2.Start with the root name of the anion
3. Replace -ate with -ic, or -ite with -ous
4. Add "acid"
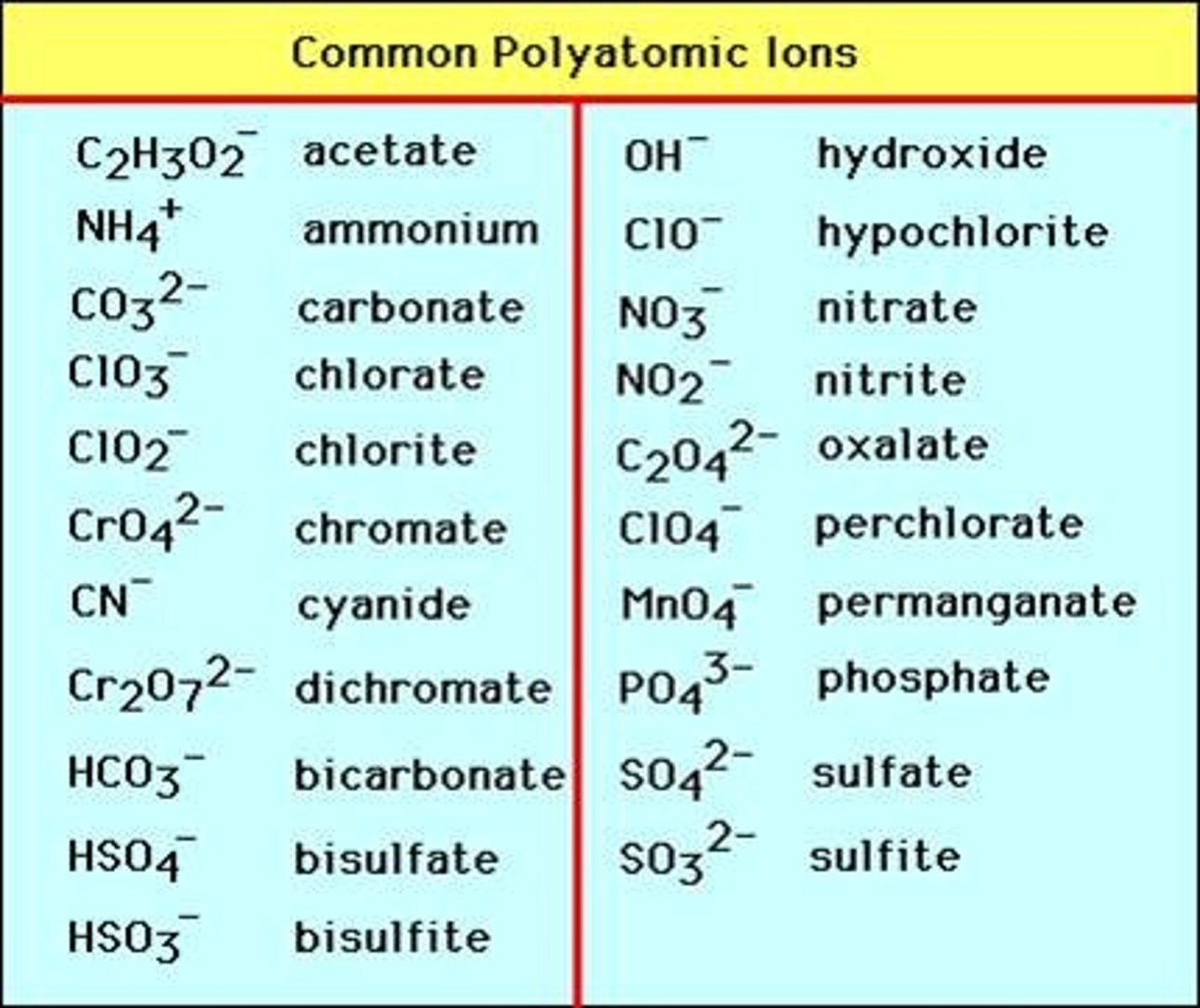
What are polyatomic ions?
A charged particle with two or more atoms
What is Terra
10^12
What is Giga
10^9
What is Mega
10^6
What is kilo
10^3
What is centi
10^-2
What is milli
10^-3
what is micro
10^-6
what is nano
10^-9
what is pico
10^-12
what is femto
10^-15
ft to inches
1 ft = 12 inches
inch to cm
1 inch = 2.54 cm
cm to meter
100 cm = 1 m
What is density?
mass/volume
Atomic weight
protons + neutrons (Average of the mass numbers of all isotopes)
molecular weight (MW)
the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule

Accuracy
how close a measurement is to the true value
Precision
a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another
who is the most precise lab equipment?
volumetric pipet> buret/ volumetric flask > graduated cylinder > beaker/erlenmeyer flask
dilutions formula
M1V1=M2V2
% error formula
(actual-theoretical)/theoretical x 100
% yield formula
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
Absorbance equation
absorbance= ecl
e: molar extinction coefficient - higher for things that are bright
c: sample concentration
l: path length- distance bw light source and spectrophotometer
How do you heat a test tube?
in water
How do you dilute strong acids?
Add acid to water, swirl or stir the solution and be careful of the heat produced
Absorbance is directly proportional to
concentration and path length
when pressure increases
volume decreases
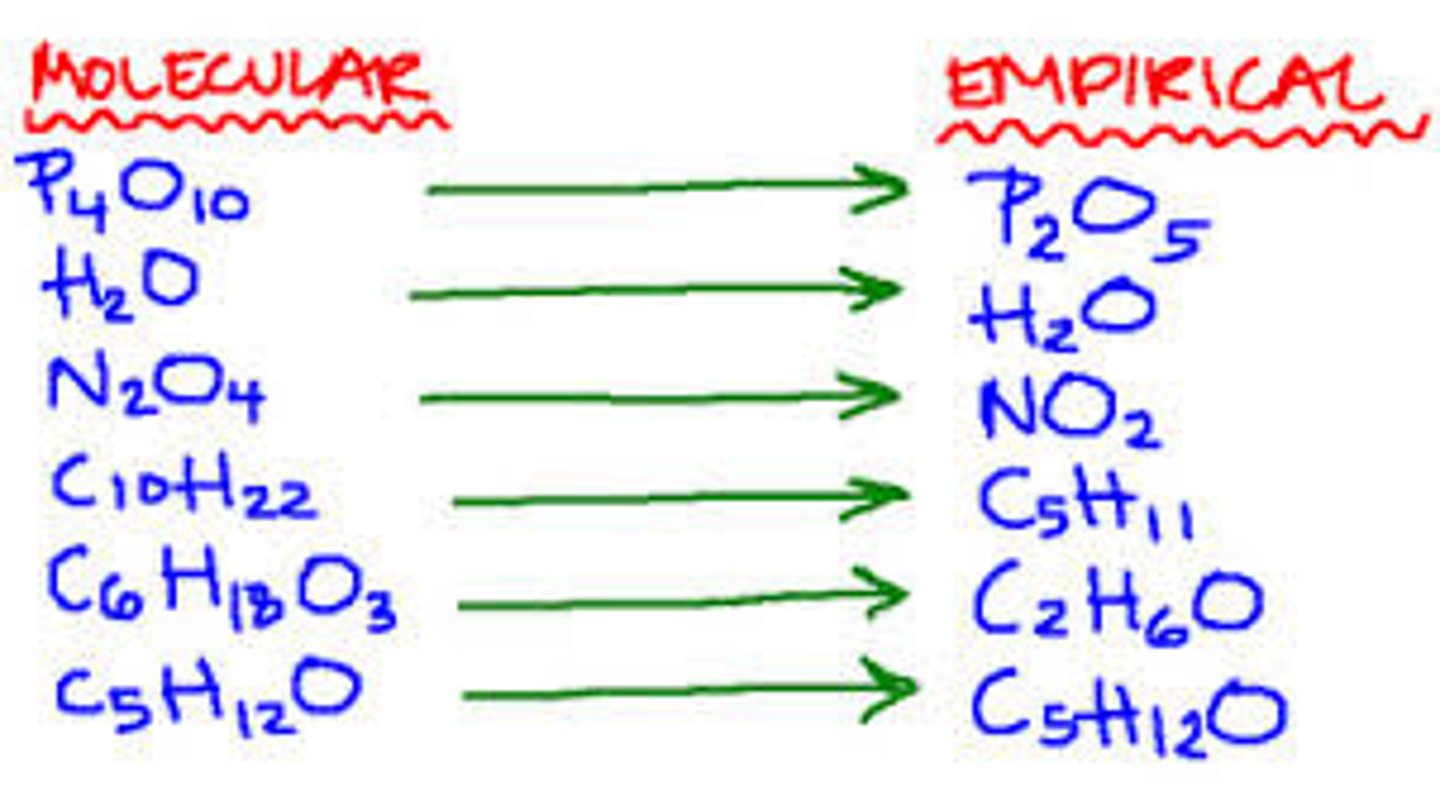
empirical formula
a chemical formula showing the ratio of elements in a compound rather than the total number of atoms
percent composition formula (molar mass)
mass of element/molar mass x 100
percent composition formula
mass of element/mass of compound x 100
1 mole =
6.02 x 10^23 molecules
How to balance a chemical equation
1. make sure each individual compound makes sense (is neutral) 2. take inventory of the atoms for each side of the equation. 3. Add coefficients which should help to make the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. 4. Check the equation by taking another inventory on each side.
limiting reactant
the reactant that limits the amount of the other reactant that can combine and the amount of product that can form in a chemical reaction

What did dalton do?
proposed the atomic theory

What did thompson do?
He discovered the electron and used the cathode ray tube for experiments
What did Milikan do?
• Milikan designed and carried out the famous oil-drop experiment
• This measured the charge on electrons which meant that their mass could be calculated
What did Rutherford do?
discovered the nucleus using the gold foil experiment
atomic orbitals are
s, p, d, f
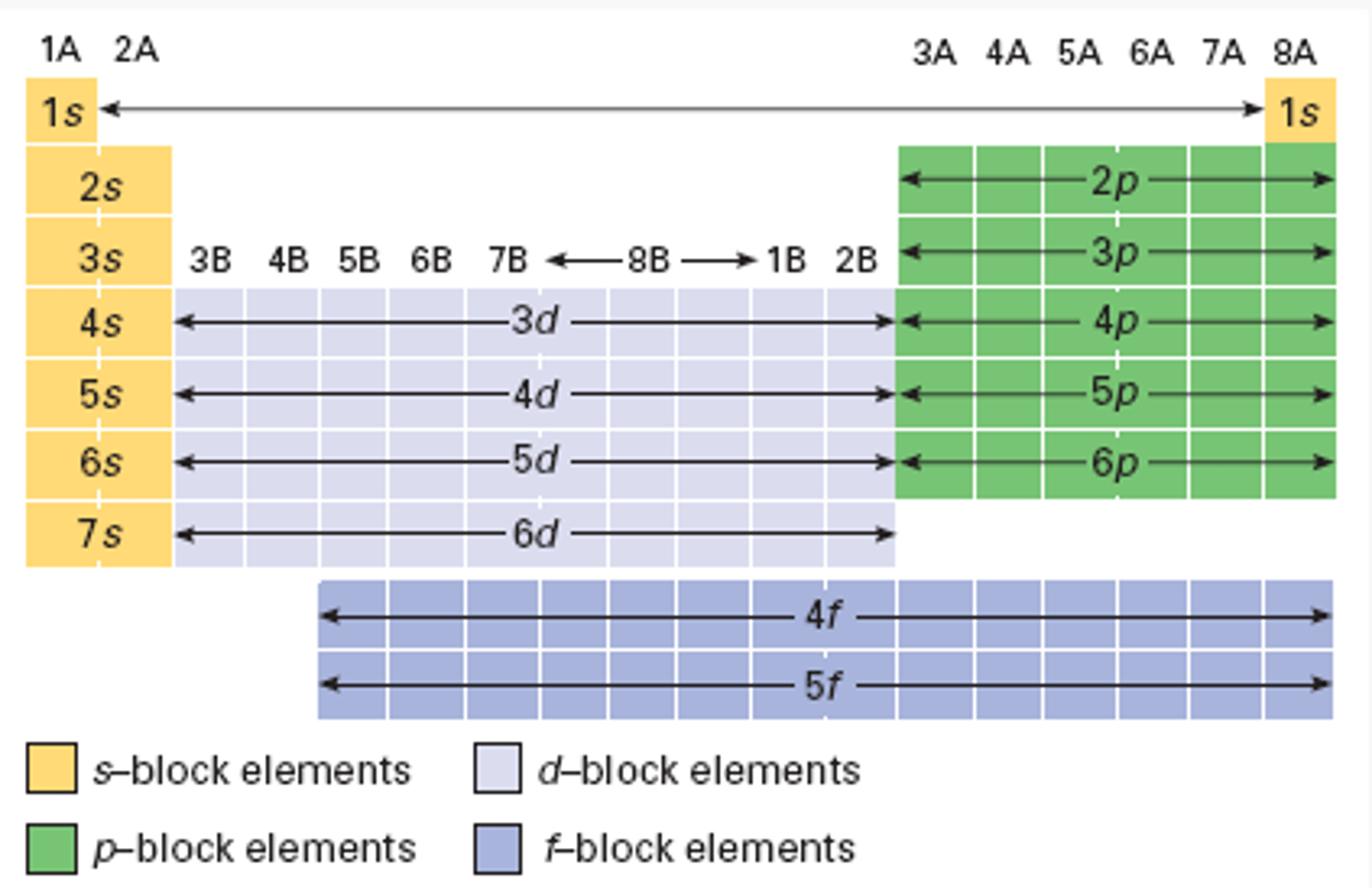
quantum numbers values
n: 1,2,3...
l: 0,1,...,(n-1)
ml: -l to l
ms: 1/2 or -1/2
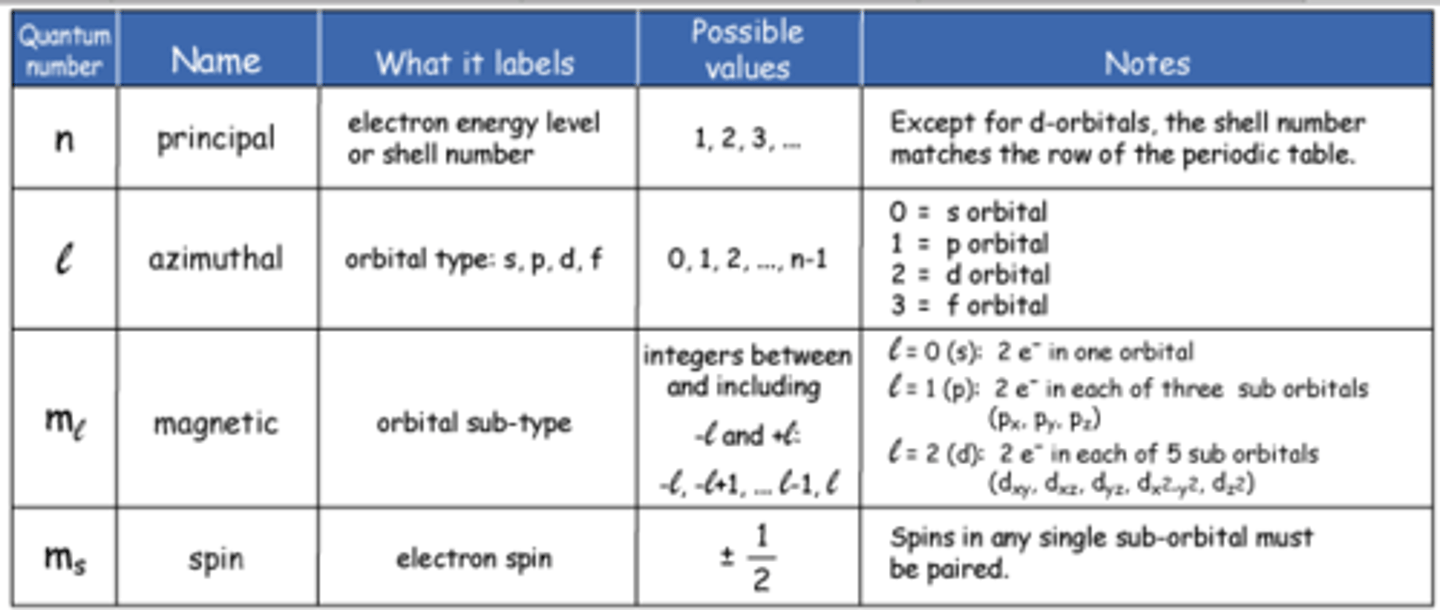
ground state electron configuration
the lowest energy electron configuration for an atom or molecule
excited state
a state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground state because when an atom absorbs energy, its electrons move to a higher energy level

Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
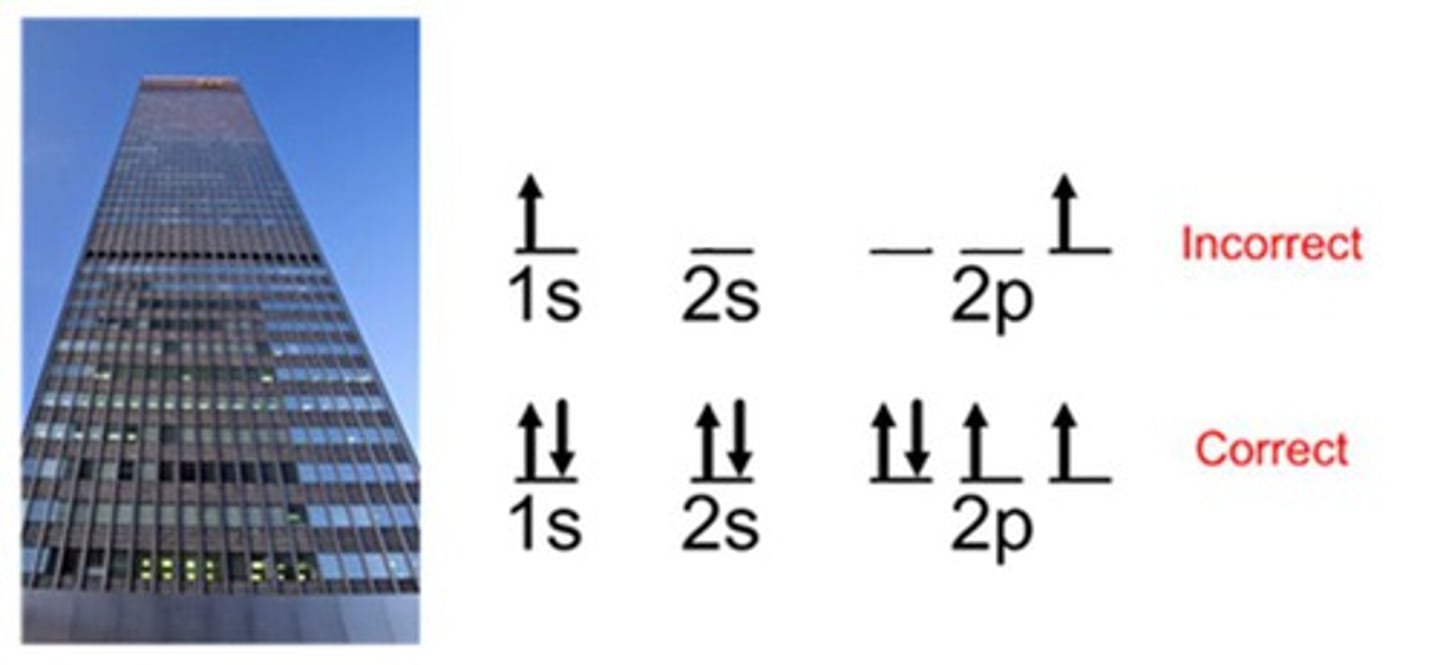
Hund's Rule
states that single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal-energy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbitals

Pauli's Exclusion
no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers
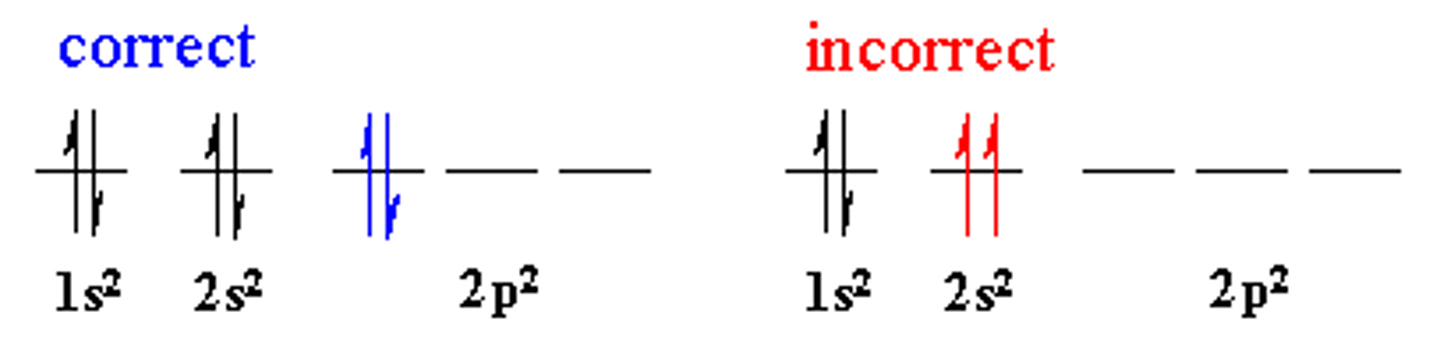
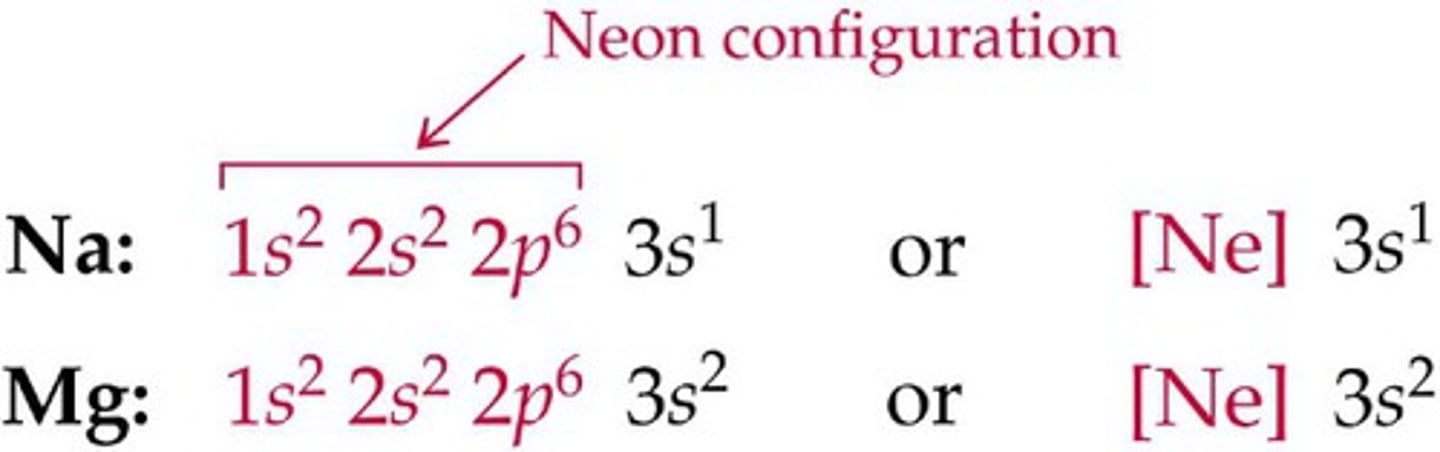
noble gas configuration/notation
an outer main energy level occupied, in most cases, by eight electrons. It's a way of simplifying an element's electron configuration by comparing it to the closest noble gas that has a lower atomic value.
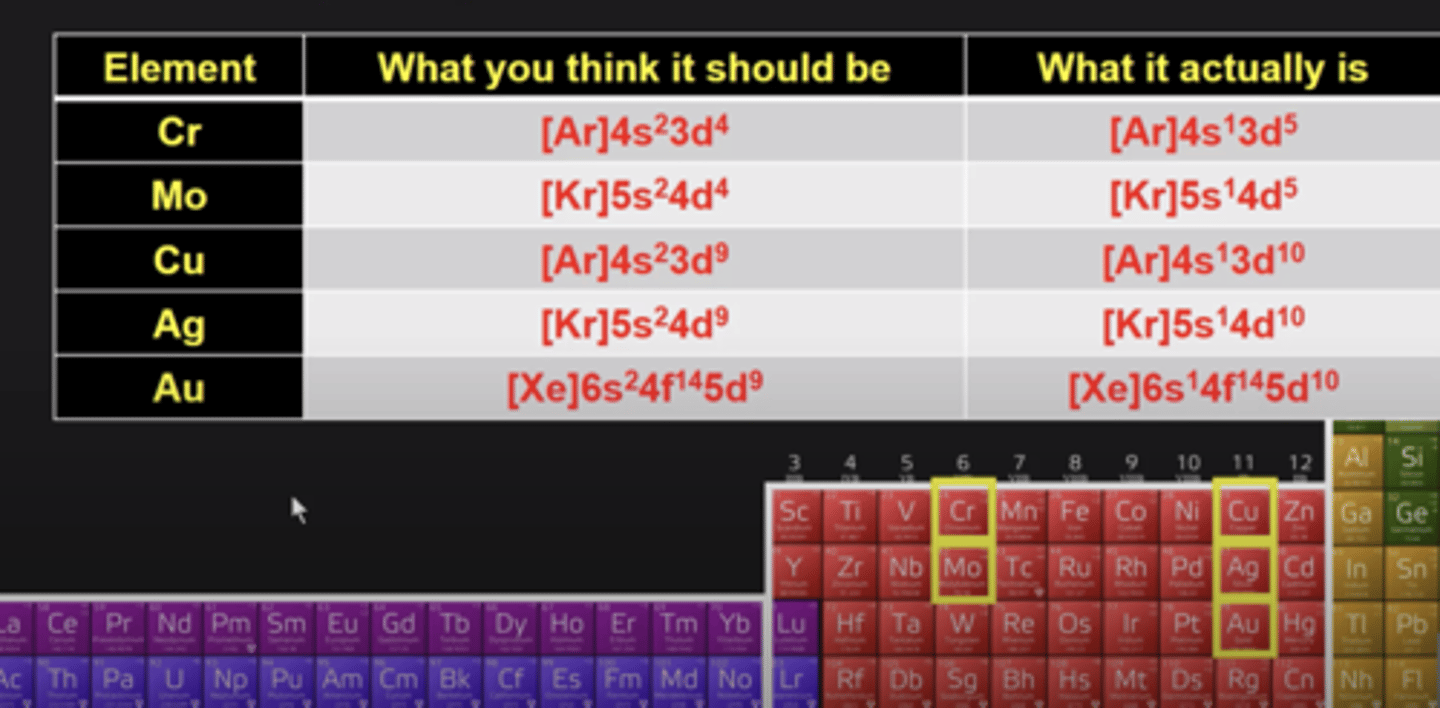
electron configuration exceptions
Cr, Mo, Cu, Ag, Au
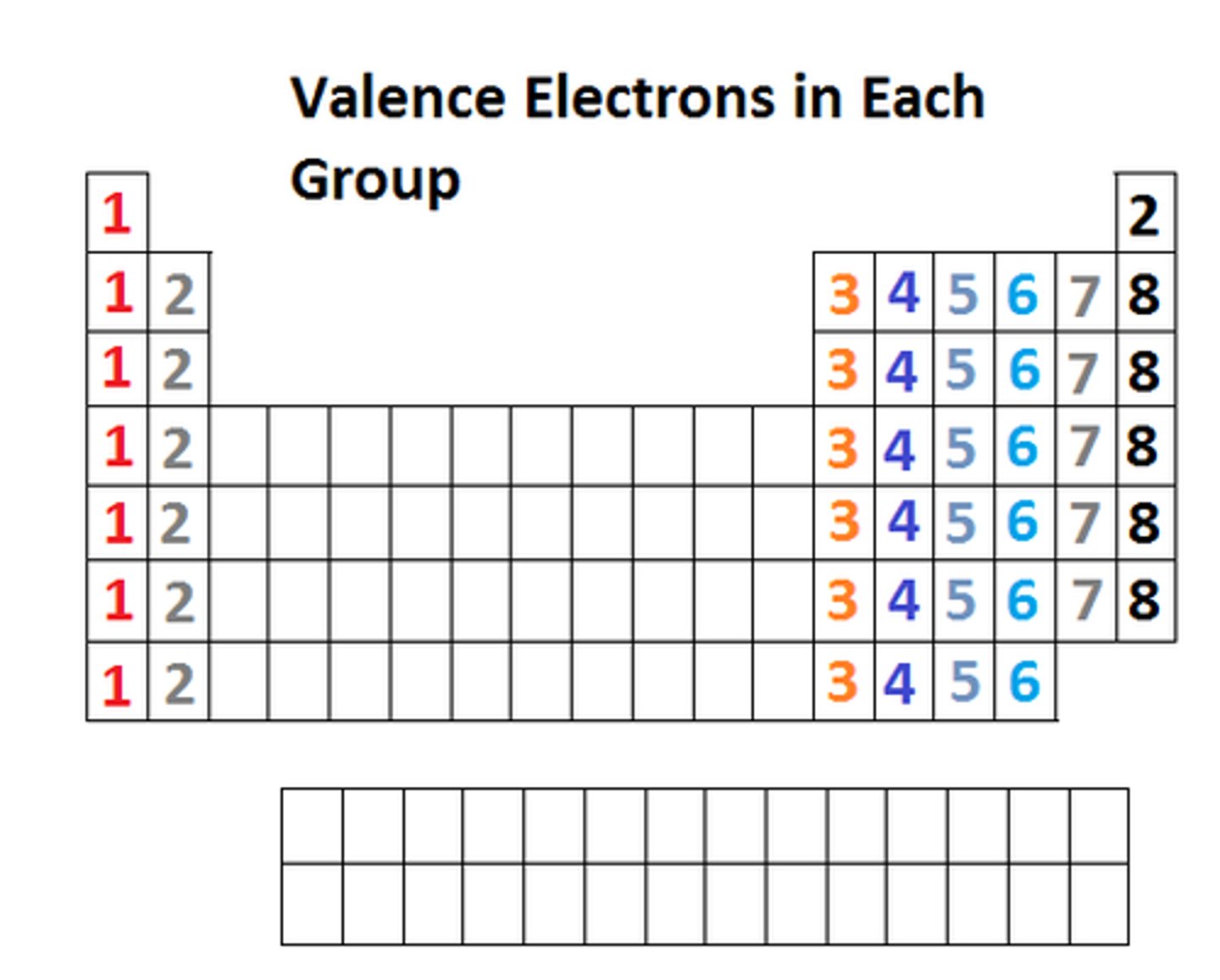
Valence electrons are
electrons in the outermost energy level
Ion Configuration
configurations where you write the electron configuration for the closest Noble Gas.
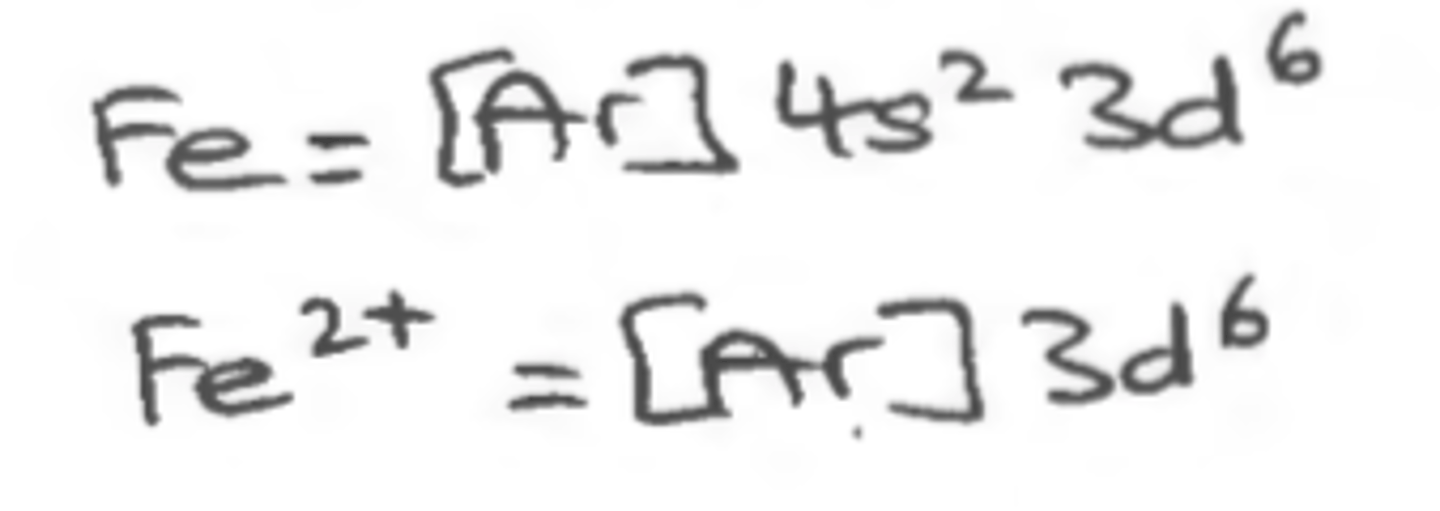
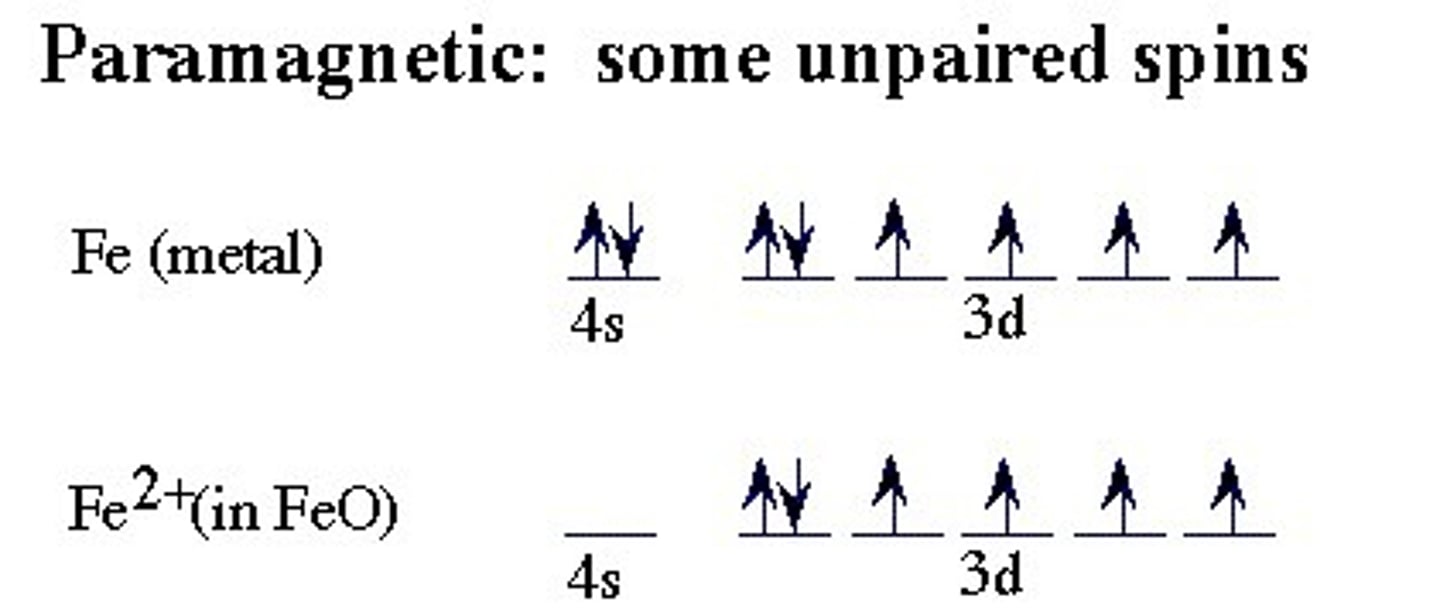
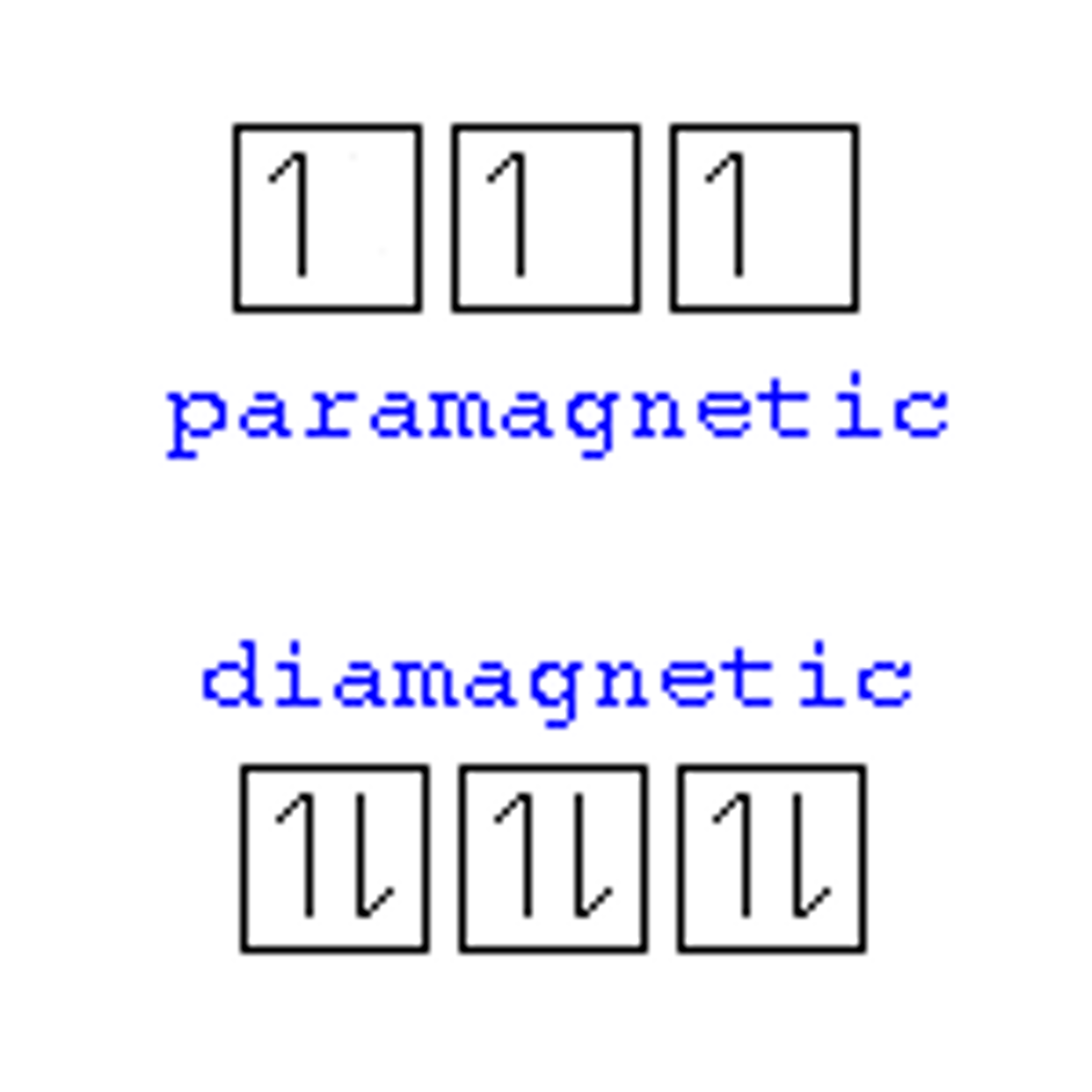
paramagnetic
Atom or substance containing unpaired electrons and is consequently attracted by a magnet.
diamagnetic
All electrons are paired; slightly repelled by a magnetic field.
electromagnetic radiation equation
c=λv (where c=speed of light=3.00 x 10^8 m/s, λ=wavelength, v=frequency)

Planck's equation
∆E = hf, electromagnetic energy is quantized and only comes in discrete units related to the wave frequency. H= 6.6x10^-34 J*s
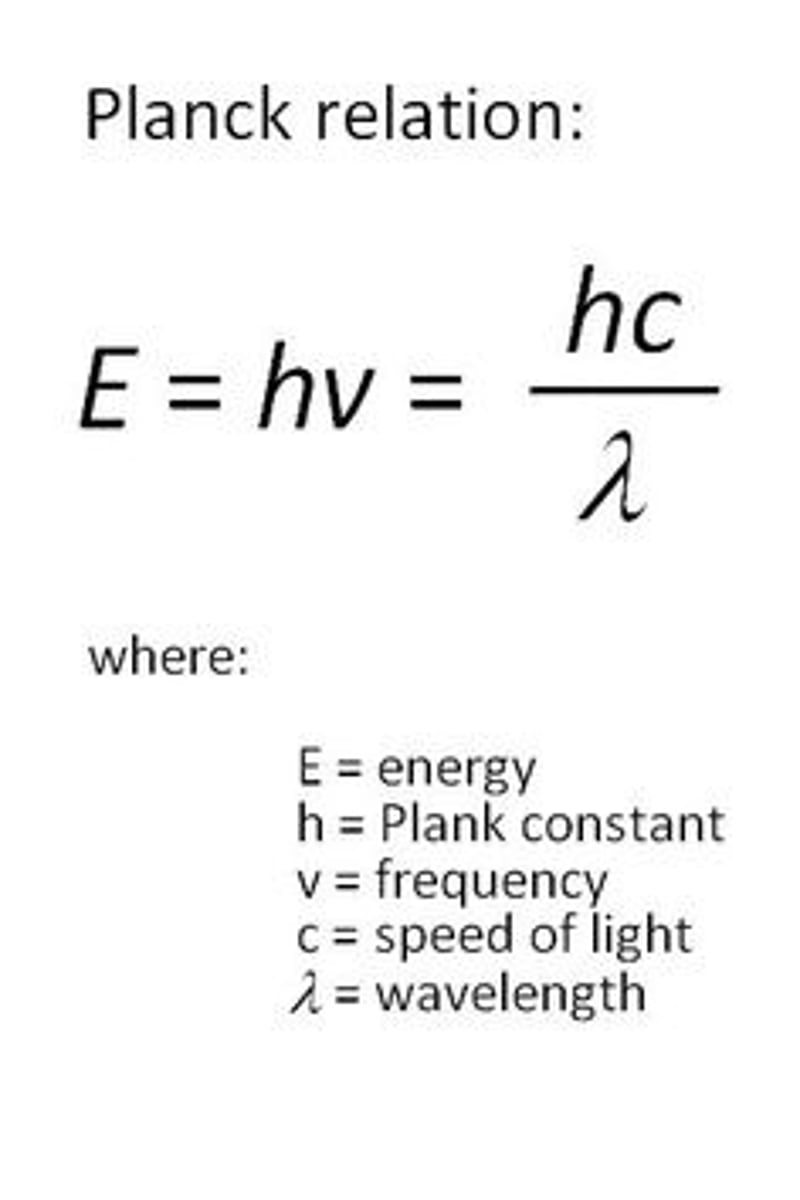
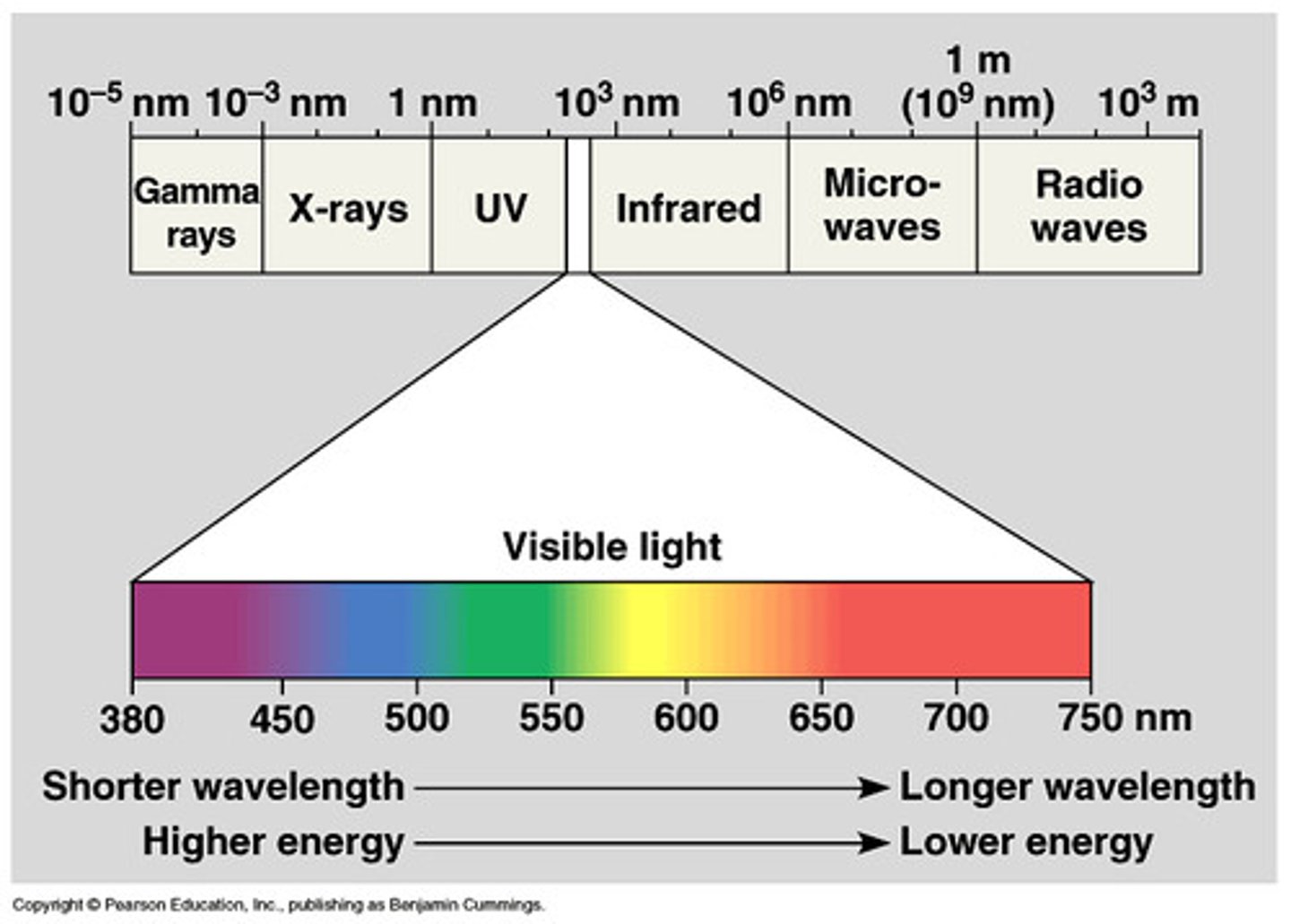
electromagnetic spectrum
the complete range of electromagnetic waves placed in order of increasing frequency