AP Psychology Unit 1: RESEARCH METHODS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it

Double Blind Procedure
An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo. Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies

Independent Variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated--the variable whose effect is being studied
Dependent Variables
The outcome factor -- the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable

Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance ,thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups

random sample
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion

Scatter plot
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables. The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation
Illusory Correlation
the perception of a relationship where none exists; the basis for many superstitions
Case Study
An observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles

Survey
A technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of people, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of them

Naturalistic Observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other.
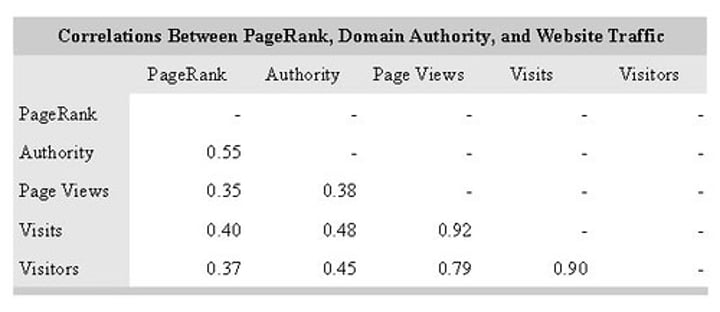
Experiment
A research method in which one or more factors (IV) are manipulated to observe the effect on a behavior/mental process (DV)

Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances

Operational Definition
A statement of the procedures used to define research variables. Ex human intelligence -- what an intelligence test measures.

Theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations
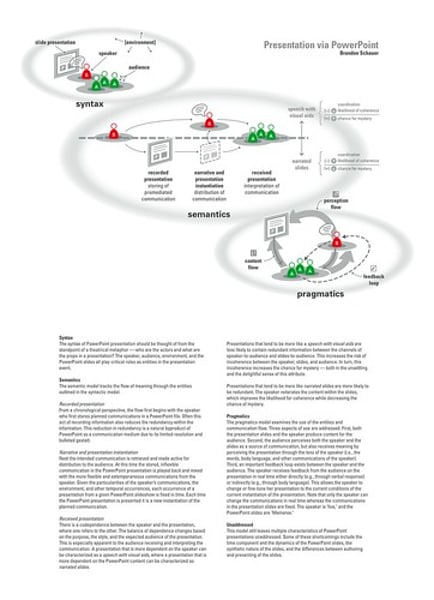
Hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory

Population
all the cases in a group, from which samples may be drawn for a study
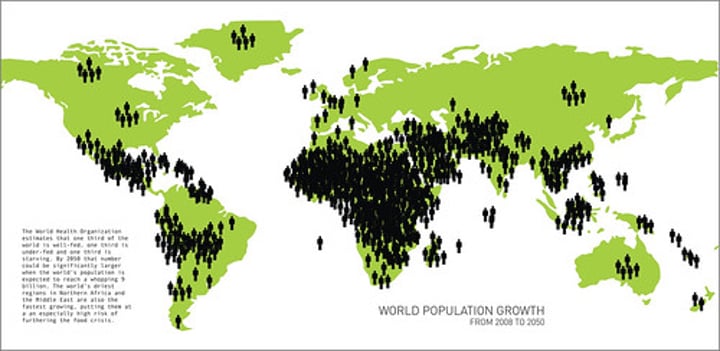
representative sample
a sample that resembles the population
Correlation Coefficient
a statistical index of the relationship between two things (from -1 to +1) extent to which two factors vary together; how well either factor predicts the other
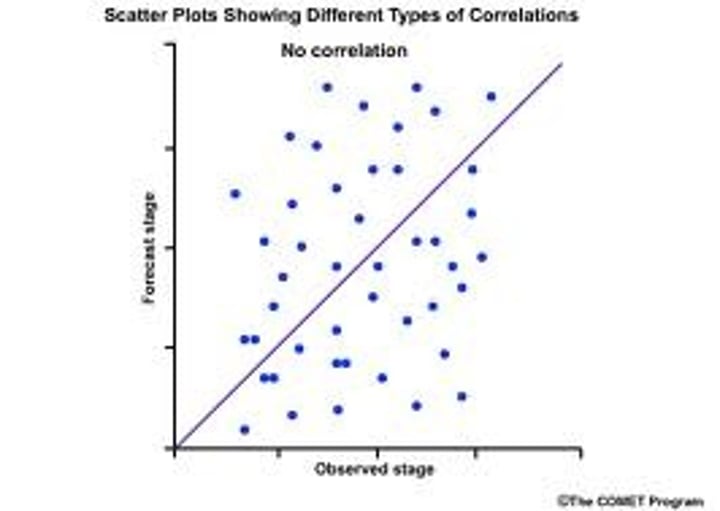
Placebo Effect
experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by administration of an inert substance or condition

Experimental condition
in an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
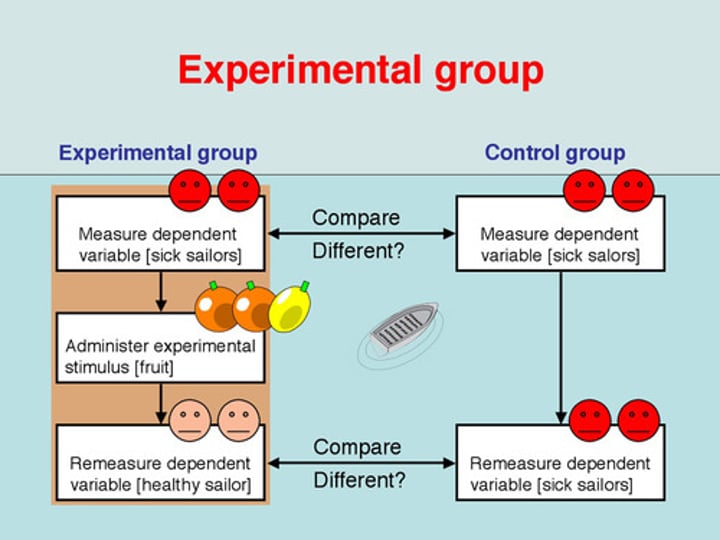
Control condition
in an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.

Confounding Variable
a factor other than the independent variable that could influence the dependent variable

overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
sampling bias
A problem that occurs when a sample is not representative of the population from which it is drawn.
wording effects
when a specific word used in a question affects how respondents answer the question or the order of the questions
Hawthorne effect
A change in a subject's behavior caused simply by the awareness of being studied
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
causation
the relationship between cause and effect; in psychological research causation can only be est. by experiment