2.3 Metallic Bonding and 2.4 Models to Materials
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is metallic bonding?
Electrostatic attraction between delocalised free moving electrons and the positively charged metal ions.
Characteristics of a metal?
low relative electronegativity
great conductor of heat and electricity
lustrous
sonorous
high MP BP
malleable + ductile
tends to corrode
Why is metal malleable?
metallic bonds are non directional (uniform charge across the structure as electrons as electrons are shared across multiple atoms in all directions)
this allows layers of cations to slide past each other rearranging the shape of the lattice
without breaking the electrostatic attaction
Why can Metals conduct heat?
when metals are heated, the the cations in the metal lattice vibrate more vigotously
these vibrating cationns transfer their kinetic energy as they collide with neighbouring cations
the cations vibrate and transfer the heat to the delocalised electrons that can move and tranfer the heat rapidly throughout the metal
What determines rge strength of a metallic bond?
the greater the charge on the metal ion, the more delocalised electrons + higher charge difference
strong electrostatic attraction
Trend in Period 3 metals
MP increases from left to right
as their is a decrease in ionic radius
increase in ionic charge
and increased electron density
Transition metals:
metals that partially fill the D orbital as an atom or an ion
exception: Cu : [Ar] 4s1 3d10
why do transition metals have a higher melting point than group 1 and 2?
the electrons in the D sublevel become delocalised as well as the electrons of the outer level
increased electron density means stronger electrostatic forces of attraction (cations + electrons)
lots of heat energy to break attraction
What is elastic mtaerial?
materials that will change hspae when subjected to a force and return to thier original shape after the force is removed
What is a plastic material?
A material that changes and retains its deformed shape evn after the extrenal force is removed
Semiconductor:
A poor electrical conductor but bettwe when heated, illuminated or impure
Alloys:
when a pure metallic element is mixed with other metalic or non-metallic elements (mixtures)
ions of diff elemts are bound togetehr by delocalised electrons
Why are alloys stronger than pure metals?
alloys have a non-uniform packing of cations in the lattice
atoms of different sizes which distort/disrupt the regular arrangement of cations
this makes it more difficult for the layers to slide over eachother
Name 4 examples of alloys?
Brass, Steel, Stainless Steel and Bronze
Brass:
copper and zinc
strong + resistant to corrosion
door hing
Stainless Steel:
Iron, Chromium, nickel, carbon
corrosion resistant
cutlery, surgical instruments
Bronze:
copper and tin
hard + strong, resistance to corrosion
medals, sculptures, ship fittings
Polymer:
Covalently bonded macromolecules characterised by low thermal and eletcrical conductivity
Examples of Natural polymers:
cellulose
DNA
Starch
Examples of synthetic polymers:
polyester
nylon
teflon
Properties of Plastic:
low weight: polymers are loosley packed so will be less dense
unreactive: additon polymers from alkenes are saturated- no more bonds left
water resistant: hydrocarbon chains are hydrophobic
strong: lots of covalent bonds
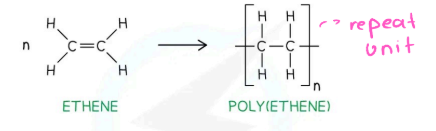
Ethene into Polyethene:
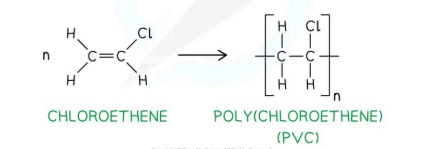
Chloroethen into Polychloroethene:
Propene into Polypropene:
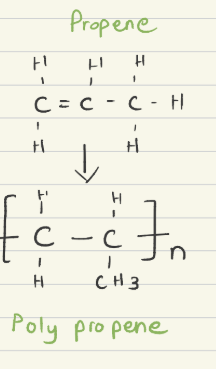
Diacid + Diamine →
Polyamide
To form a polymer a molecule must have atleast:
2 reactive functional groups or else an esther is formed
Coordination Bond:
when both the electrosn from the pair are from the same atom
benefits and engatives of bioplastics:
+ves: can be degraded quickly without releasing CO2 so don’t pollute the planet + can be made from renewable feed stocks
-ves: can be broken down quicky so may not functional in the longterm + it can cause eutrophicatiob