biopsych ch9 & 10
1/82
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Adequate Stimulus
The energy form for which a receptor is specialized.
Agraphia
The inability to write due to brain damage.
Alexia
The inability to read due to brain damage
Angular Gyrus
Damage results in alexia and agraphia.
Brocas or Expressive Aphasia
Language articulation impairment caused by damage to left frontal lobe anterior to motor area
Wernickes Receptive aphasia
is a language comprehension (written and spoken) impairment resulting from damage to the left temporal lobe. (word salad phrases)
Auditory Object
A sound that we recognize as having an identity that is distinct from other sounds
Basilar Membrane
membrane in the cochlea that separates the cochlear canal from the tympanic canal
Cochlea
snail-shaped structure where the ear’s sound-analyzing structures are located.
Cochlear Canal
middle canal in the cochlea, which contains the organ of Corti
Cocktail Party Effect
ability to sort out meaningful auditory messages from a complex background of sounds
Coincidence Detectors
Neurons that fire most when they receive input from both ears at the same time; they are involved in sound localization
Complex Sound
sound composed of more than one pure tone
Dyslexia
impairment of reading, which can be developmental or acquired through brain damage (near wernickes area)
Eustachian Tube (between the middle ear and the oral cavity)
equalize air pressure differences between the outside of the head and the middle ear
Frequency
the number of vibrations or cycles per second of a sound wave, measured in Hertz (Hz)
Frequency-Place Theory
hypothesis that frequency following individual neurons accounts for the discrimination of frequencies up to about 200 Hz (higher frequencies are represented by the place of greatest activity on the basilar membrane)
Frequency Theory/Telephone theory
frequency of a sound is represented in the firing rate of each neuron or a group of neurons(limited by refractory period)
Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF)
frequency alterations to a sound as it passes through the pinna and auditory canal, a cue for locating the direction of a sound source
Inner Hair Cells
about 3,500 hair cells located on the basilar membrane toward the inside of the cochlea’s coil producing the majority of auditory signal
Intensity
physical energy in a sound; the sound’s amplitude
Interaural Level Difference
binaural cue to the location of a sound coming from one side that results from the sound shadow created by the head and most effective above 2000 to 3000 Hz
Interaural Timing Difference (ITD)
binaural cue to the location of a sound coming from one side due to the time the sound requires to travel the distance between the ears; most effective for low-frequency sounds
Language
structured system of communication with a common set of grammatical and organizational rules
Language Acquisition Device
A part of the brain hypothesized to be dedicated to learning and controlling language
Loudness
our experience of sound intensity
Organ of Corti
sound-analyzing structure on the basilar membrane of the cochlea
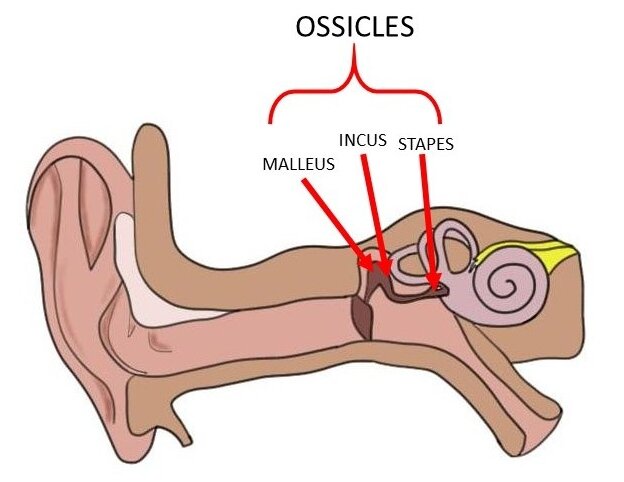
Ossicles
Tiny bones in the middle ear that operate in lever fashion to transfer vibration from the tympanic membrane to the cochlea
Outer Hair Cells
amplify the cochlea’s output and sharpen frequency tuning, possibly by adjusting the tension of the tectorial membrane
Perception
interpretation of sensory information
Phonological Hypothesis
idea that the fundamental problem in dyslexia is impaired phoneme processing
Pinna
the outer ear.
Pitch
experience of the frequency of a sound
Place Theory
theory that states that the frequency of a sound is identified by the location of maximal vibration on the basilar membrane and which neurons are firing most
Planum Temporale
area in each temporal lobe and the location in the left hemisphere of Wernicke’s area that is larger on the left in most people
Prosody
use of intonation, emphasis, and rhythm to convey meaning in speech
Pure Tone
A sound consisting of a single frequency
Receptor
cell, often a specialized neuron, suited by its structure and function to respond to a particular form of energy, such as sound
Sensation
acquisition of sensory information
Tectorial Membrane
shelf-like membrane overlying the hair cells and the basilar membrane in the cochlea
Telephone Theory
A theory of auditory frequency analysis, which stated that the auditory neurons transmit the actual sound frequencies to the cortex.
Tonotopically Organized
neurons from adjacent receptor locations project to adjacent cells in the auditory cortex, forming a tonotopic map
Tympanic Membrane
The eardrum, a very thin membrane stretched across the end of the auditory canal; its vibration transmits sound energy to the ossicles.
Volley Theory
hypothesis of auditory frequency analysis that states that groups of neurons follow the frequency of a sound when the frequency exceeds the firing rate capability of a single neuron.
pathway to auditory nerve
auditory nerve enters brain stem, information from both ears integrated, inferior colliculi, to medial geniculate nuclei, to auditory cortex in temporal lobe
Accommodation
Changing of the lens shape to focus light onto the retina (ciliary muscles contract to make the lens rounder for a near object and relax to flatten the lens for a far object)
Binding Problem
The question of how the brain combines all visual information about an object into a unitary whole
Blindsight
ability of cortically blind individuals to respond to visual stimuli that are outside conscious awareness
Color Agnosia
Loss of the ability to perceive colors due to brain damage
Color Blindness (color vision deficiency)
A condition when one or more color-sensitive cones is functionally impaired or absent, leading to difficulty distinguishing certain colors.
Color Constancy
The ability to recognize the natural color of an object regardless of the brightness or wavelength of illuminating light.
Complementary Colors
Colors that cancel each other out to produce a neutral gray or white.
Complex Cell
A type of cell in the visual cortex that continues to respond (unlike simple cells) when a line or an edge moves to a different location.
Dorsal Stream
The visual processing pathway that extends into the parietal lobes; concerned with the location of objects in space.
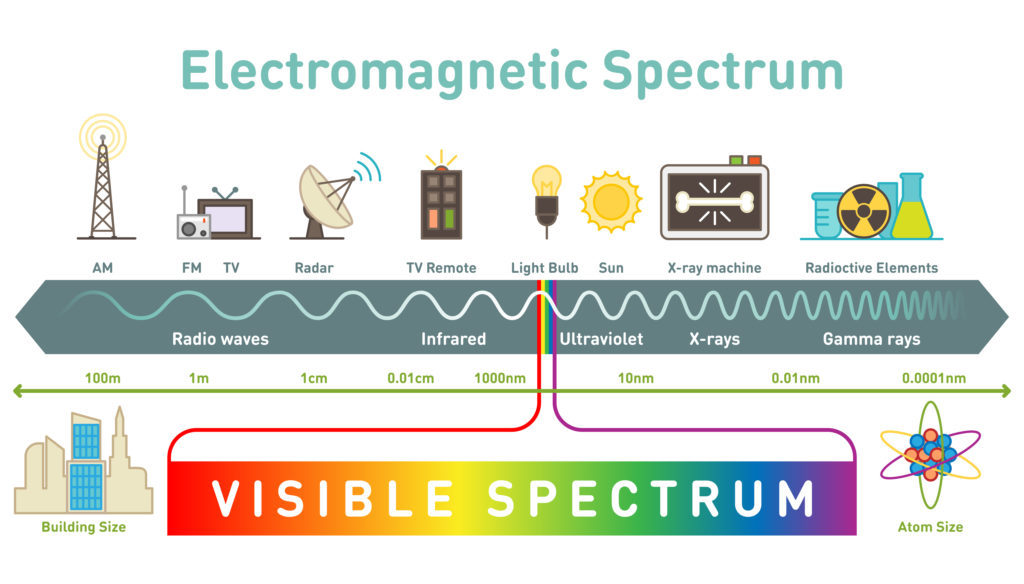
Electromagnetic Spectrum
energy forms, ranging from high-frequency gamma rays at one extreme to very-low-frequency electrical currents on the other.
Form Vision
detection of an object’s boundaries and features, such as texture.
Fovea
area in the middle of the retina in which cones are most concentrated and visual acuity and color discrimination are greatest
Fusiform Face Area (FFA)
A part of the inferior temporal lobe important in face identification
Hierarchical Processing
A type of processing in which lower levels of the nervous system analyze their information and pass the results on to the next higher level for further analysis.
Iodopsin
group of three photopigments found in cones; one form is sensitive to red light, one is sensitive to green light, and one is sensitive to bluish-violet light
Lateral Inhibition
A method of enhancing neural information in which each neuron’s activity inhibits the activity of its neighbors and in turn its activity is inhibited by them.
Magnocellular System
A division of the visual system, extending from the retina through the visual association areas, specialized for brightness contrast and for movement.
Modular Processing
The segregation of the various components of visual processing in the brain into separate locations
Movement Agnosia
Impairment of the ability to perceive movement (most common is radial impairment)
Negative Color Aftereffect
The experience of a color’s complement following stimulation by the color (red would stimulate green on a blank wall)
Object Agnosia
Impairment of the ability to recognize objects visually.
Opponent Process Theory
A color vision theory that attempts to explain color vision in terms of opposing neural processes (two receptors blue/yellow and red/green)
Parvocellular System
A division of the visual system, extending from the retina through the visual association areas, that is specialized for fine detail and color.
Photopigments
Light-sensitive chemicals in the visual receptors that initiate the neural response.
Prosopagnosia
An impairment of the ability to visually recognize familiar faces.
Receptive Field
area of the retina from which a cell in the visual system receives its input.
Retina
structure at the rear of the eye, which is made up of light-sensitive receptor cells and the neural cells that are connected to them
Retinal Disparity
A discrepancy in the location of an object’s image on the two retinas; a cue to the distance of a focused object.
Retinotopic Map
A map of the retina in the visual cortex, which results from adjacent receptors in the retina activating adjacent neural cells in the visual cortex.
Rhodopsin
The photopigment in rods that is sensitive to all wavelengths of visible light.
Simple Cell
A cell in the visual cortex that responds to a line or an edge that is at a specific orientation and a specific place on the retina.
Spatial Frequency Theory
The idea that visual cortical cells do a Fourier frequency analysis of the luminosity variations in a scene (cells tuned to a high freq:edge or low freq: light to shadow)
Synesthesia
condition in which stimulation in one sense triggers an experience in another sense
Trichromatic Theory
The hypothesis that three color processes account for all the colors we are able to distinguish (r,g,b) concept tv operates on
Ventral Stream
The visual processing pathway that extends into the temporal lobes; it is especially concerned with the identification of objects.
Visual Acuity
ability to distinguish visual details
Visual Field
The part of the environment that is being registered on the retina.
Visual Word Form Area (VWFA)
An area in the human inferior temporal lobe involved in reading words.