AICE Environmental Management Ultimate Review 2022
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Name the oceans of the world.
Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, Southern
Name the continents
Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, South America
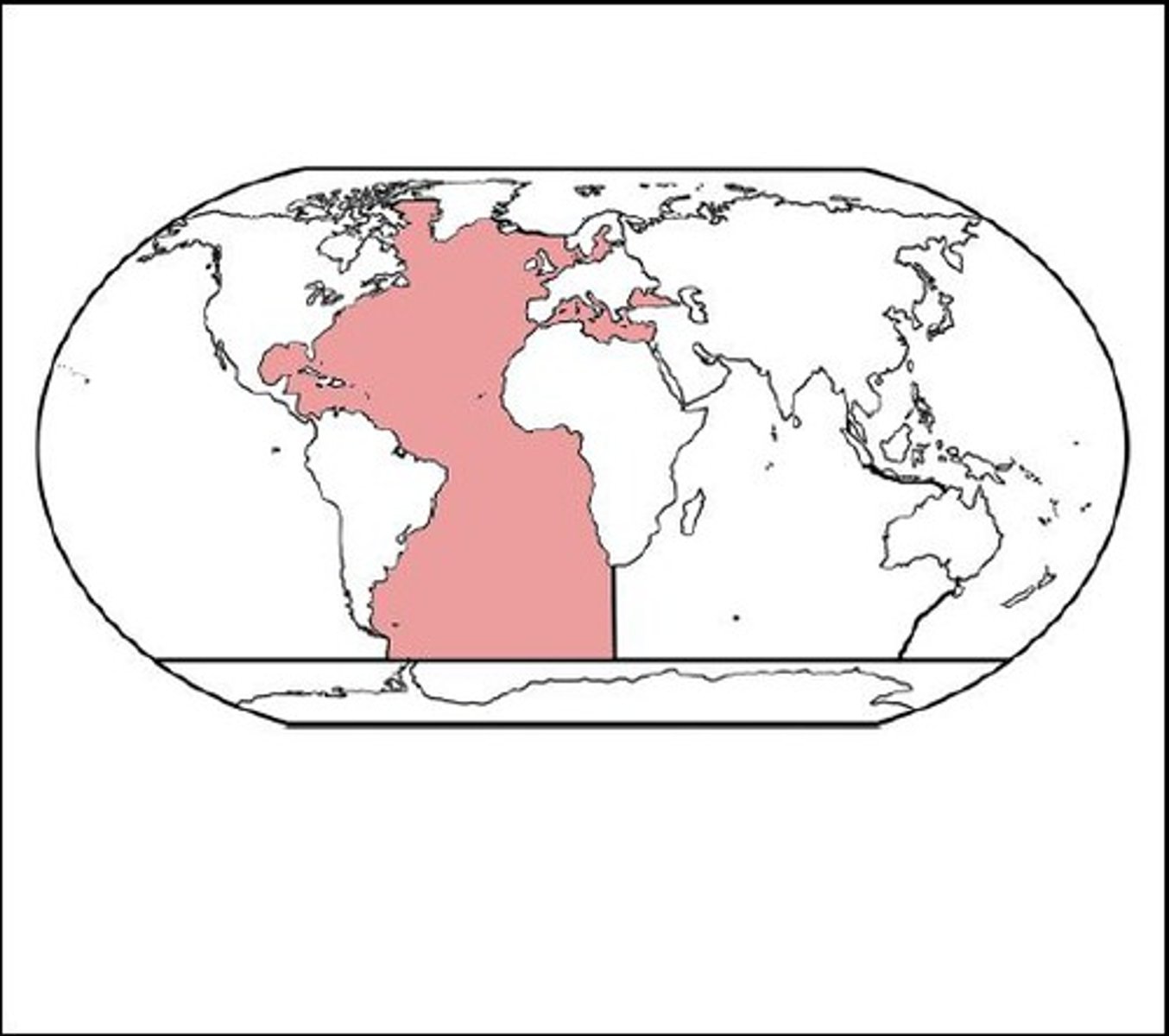
Where is the Atlantic Ocean?
East coast of US
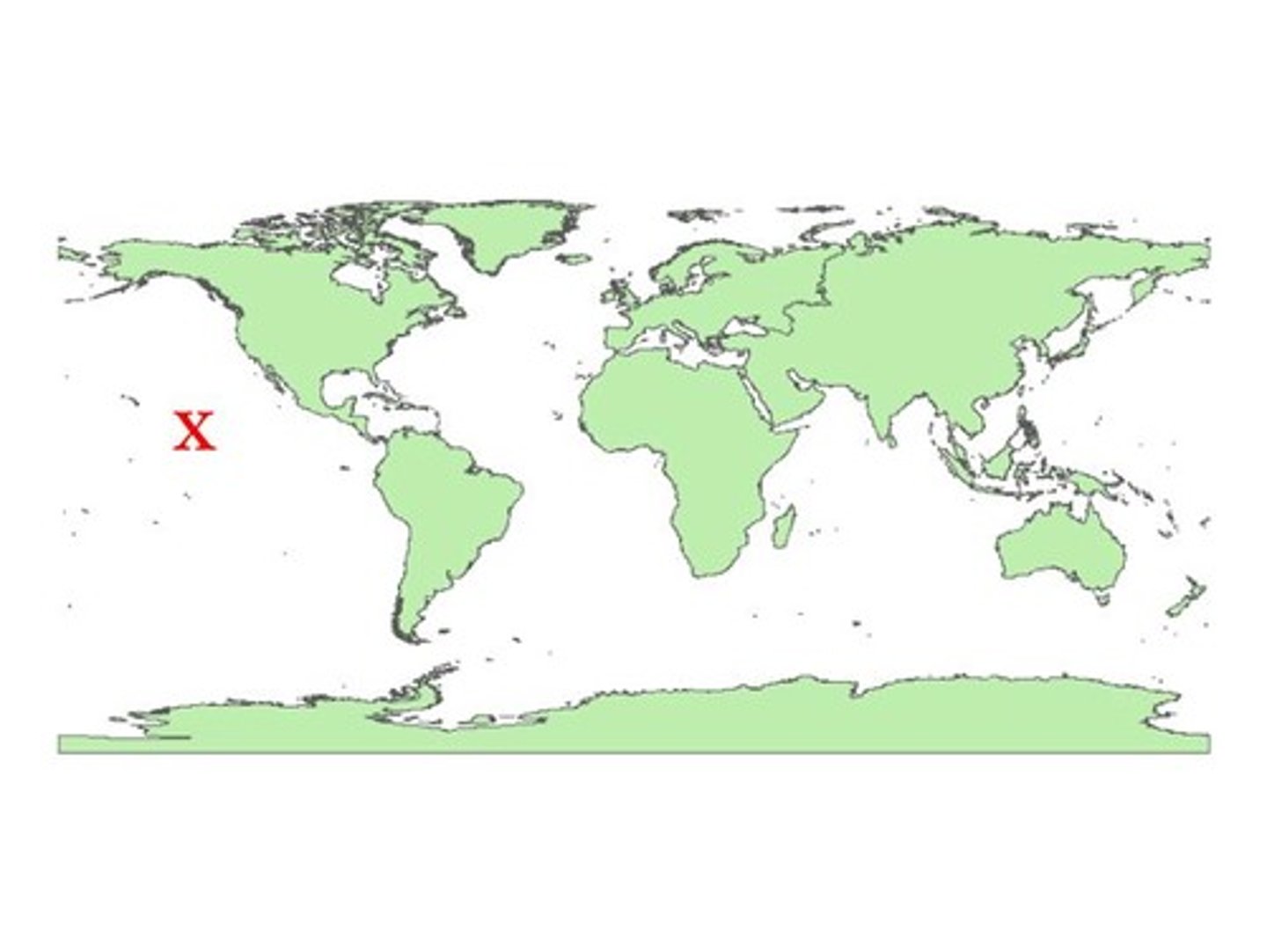
Where is the Pacific Ocean located?
Left of South America
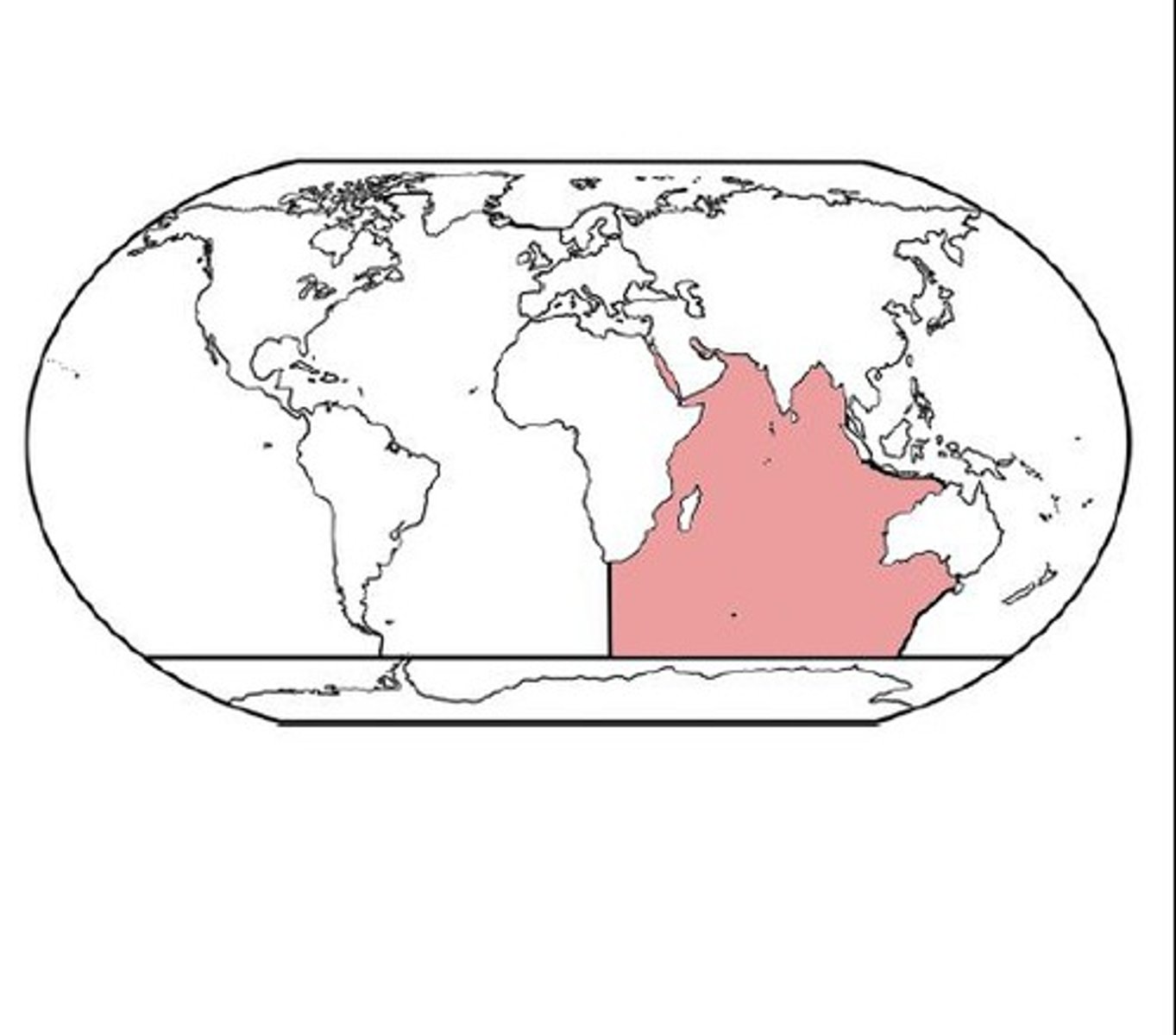
Where is the Indian Ocean?
South India
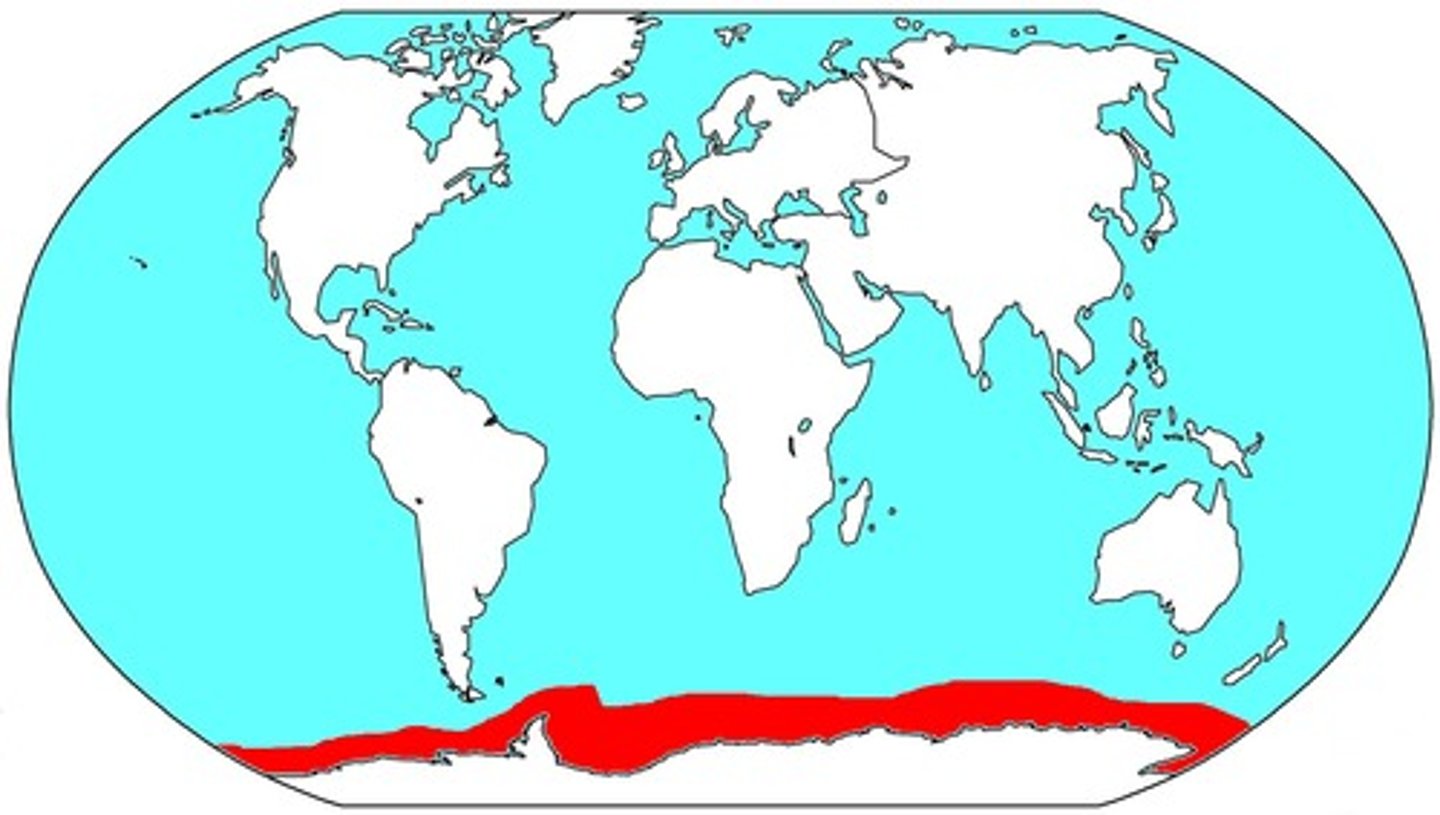
Where is the Southern Ocean?
Above Antarctica
Where is the Arctic Ocean?
North Pole
Where is Africa located?
Below Europe
Where is North America
USA, Canada, Greenland, gulf of mexico ect.
Where is South America
Below North America
Where is Europe?
Uk, iceland, france, ukraine, finland ect.
Where is Asia?
Russia, china, india, japan ect.
Where is Antarctica?
South Pole
Where is Oceania?
australia, new zealand, papua new guinea ect.
low-income countries
nations with little industrialization and low levels of national and personal income
high-income countries
nations with highly industrialized economies; technologically advanced industrial, administrative, and service occupations; and relatively high levels of national and personal income
middle-income countries
nations with industrializing economies, particularly in urban areas, and moderate levels of national and personal income
Sustainability
meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Describe the need to use our resources sustainably.
We need to use our resources sustainably because at the current rate we will not have enough for future generations. We need to scale back our use of resources and be more efficient with the ones we have
Water Cycle
The continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back
Percipitation
water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth as rain,sleet , or snow
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
driving force of the water cycle
sun
Evaporation
The change of a substance from a liquid to a gas
largest reservoir of water
oceans
Cryosphere
A term referring to all water that is temporarily frozen in polar ice caps, snow, permafrost, and glaciers
Interception
Water being prevented from reaching the surface by trees or grass
Infiltration
the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
surface runoff
Water flowing off the land into bodies of surface water.
Through flow
movement of water through soil
Ground water flow
Run-off that flows under ground
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
main gasses of the atmosphere
nitrogen • oxygen • carbon dioxide • argon • water vapour
What layer contains ozone
Stratosphere
function of ozone layer
Keeps most UV light from reaching Earth
Atmospheric layer where weather occurs
Troposphere
Explain the greenhouse effect and its role in maintaining Earth's temperature.
• ultraviolet radiation (shortwave radiation) passes through the Earth's atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface • some energy is re-emitted back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation (longwave radiation) • greenhouse gases absorb some of this infrared radiation and prevent it from leaving the atmosphere
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area
habitat
Place where an organism lives
Niche
Full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions
Abiotic Factors
Nonliving components of environment.
biotic factors
living and once living parts of an ecosystem
List the (3) types of biotic factors
Producers, Consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary), Decomposers
List the (7) abiotic factors of an ecosystem
Temperature - Humidity - Water - Oxygen - Salinity - Light - pH
Producers
Organisms that make their own food using the sun
Consumers
An organism that obtains energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms or their remains.
decomposers/detritivores
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
primary consumers (herbivores) eat
producers
secondary consumer
An organism that eats primary consumers
tertiary consumers (carnivores)
organisms in the fourth trophic level (eg, hawks and sea otters), which obtain their energy by eating secondary consumers
Describe how biotic factors affect the number and the diversity of organisms found within an ecosystem
Biotic factors impact the availability of food sources to secondary and tertiary consumers. They impact the populations of herbivores and producers. The more diversity in the ecosystem the more resilient it is to change.
Interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
grazing
act of feeding on plants
Predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
photosynthesis
the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
Formula for photosynthesis
6H₂O + 6CO₂ + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆+ 6O₂
pigment in the plant that captures light for photosynthesis
Chlorophyll
4 factors that affect photosynthesis
temperature, light intensity, amount of carbon dioxide and the availability of water.
Carbon stores
Places where carbon accumulates for a period of time such as rocks, oceans, atmosphere and plant matter.
trophic level
Each step in a food chain or food web
food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
food web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
What is transferred between organisms on a food chain/web
energy
energy pyramid
A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web
pyramid of biomass
A pyramid that illustrates the total mass of all the organisms in a trophic level.
pyramid of numbers
representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem
aerobic respiration
Breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen to create energy and carbon dioxide
Formula for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy
word formula for photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide + Water ------Sun------> Glucose + Oxygen
word formula for cellular respiration
oxygen + glucose > carbon dioxide + water + energy
Carbon Cycle Steps
1. Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration and combustion. 2. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis. 3. Animals feed on the plant passing the carbon compounds along the food chain. Most of the carbon they consume is exhaled as carbon dioxide formed during respiration. The animals and plants eventually die. 4. The dead organisms are eaten by decomposers and the carbon in their bodies is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. In some conditions decomposition is blocked. The plant and animal material may then be available as fossil fuel in the future for combustion.
Describe how the scientific method involves the interplay between observations and the formation, testing and evaluation of hypotheses.
Scientists make an observation which leads them to ask a question. They think of a possible solution or reasoning for the observation they made (hypothesis) and then design and analyze a test (experiment) to see if their reasoning was correct.
independent variable
variable that is manipulated/changed/whos effect is being studied.
dependent variable
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested.
Reliable Data
Data that is consistent and repeatable
Bias data
Occurs when the experimenter purposely manipulates the results in a way that will prove their hypothesis is true
Early climate data
limited amount of historical data, can be re-examined using proxy data such as ice cores, tree rings and coral growth rings.
present climate data
development of scientific theory • advances in technology (Satellites, Geospatial systems and monitoring, computer models)
random sampling
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
systemic sampling
select some starting point and then select every nth element in the population
transect sampling
a line randomly crosses a space and any organisms that are close to the line are counted.
factors influence suitability of sampling
size, ease of access, knowledge of the environment.
Quadrats
square frames (usually 1m x1m) used in estimating abundance in plants or slow-moving animals
Grid quadrat
The same as a frame quadrat but containing smaller internal division, used to estimate percentage cover
Open frame quadrat
used to measure the density per metre squared of organisms such as mussels or dandelions
Point quadrat
A horizontal bar on two legs with a series of holes set at intervals along its length, through which pins are dropped. Can be used to investigate the abundance and distribution of organisms in an area.
Pitfall trap
Sampling technique used to trap animals living on the soil surface or in leaf litter.
Sweep netting
sampling method using a fine net swept through the air and then closed at the neck. Used for sampling flying insects
Beating trays method
A cloth that is usually stretched out using a frame. The frame is then held under a tree or shrub and the foliage is then shaken. Invertebrates fall from the foliage and land on the cloth. They can then be examined or collected.
Kick sampling
Used to study river organism, sediment is kicked up and a net downstream catches any organisms for a set period of time
light traps
A method of sampling populations of night-flying organisms that are attracted to lights, especially moths.
Capture-mark-recapture
The method involves capturing a number of animals, marking them, releasing them back into the population, and then determining the ratio of marked to unmarked animals in the population. Also known as The Lincoln Index, a process which is used to estimate the size of populations which are very mobile and difficult to survey.
Water turbidity
Turbidity (from sediment) reduces the amount of light penetrating the water column, thus depressing primary productivity.
questionaire data
facts and figures obtained by asking people about their attitudes, awareness, intentions, and behaviors
Lincoln Index
a way to measure the abundance of small motile organisms
(catch 1 x catch 2) / marked in catch 2
Simpson's Index of Diversity
a measure of biodiversity that takes into account both species richness and species evenness.