Orthopedics: Lower Extremity
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
With damage to the hip what nerve and artery are we concerned about?
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Sciatic nerve
Most commonly strained quadriceps muscle
MOI: Kicking, esp. if foot hits an object mid-kick
Symptoms: Acute anterior thigh pain, worsened with hip flexion/knee extension
Rectus Femoris Strain (Hip Flexor Strain)
Treatment:
Strain: RICE, rehab
Proximal rupture: consider surgery
Symptoms: Groin pain, ↓ ROM (especially with flexion + internal rotation)
Femoral head = NOT round
Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI)
Type:
CAM
Symptoms: Groin pain, ↓ ROM (especially with flexion + internal rotation)
Acetabular abnormality
Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI)
Type:
Pincer
What is a MIXED Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI)?
We see CAM (femoral head abnormality) and Pincer (acetabular abnormality)
Direct blow to iliac crest or greater trochanter (contact sports)
Symptoms: Bruising, tenderness
Hip Pointer (Iliac Crest Contusion)
Treatment: RICE, NSAIDs → early ROM & resistance exercises
most common
Dashboard injury, hip flexed → posterior force
Position: Shortened, flexed, internally rotated, adducted hip
Posterior Hip Dislocation
Management:
Early reduction <6 hrs
Closed reduction (pop back into place) or open reduction (surgery)
Less common
Position: Externally rotated, abducted, flexed hip
Anterior Hip Dislocation
Management:
Early reduction <6 hrs
Closed reduction (pop back into place) or open reduction (surgery)
What three major complications can arise from hip dislocations (posterior/anterior)?
Posterior Complications: Sciatic nerve injury, AVN (medial circumflex artery), chondrolysis
Anterior Complications: Femoral artery/nerve injury, AVN
How do you treat a femur fracture?
Intramedullary nail
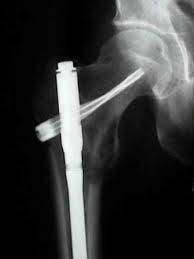
MOI:
Direct blow (fall, dashboard)
Indirect (eccentric quad contraction)
Symptoms:
Inability to extend knee
Hemarthrosis, swelling
Complication:
popliteal artery rupture
Patella Fracture
Treatment:
Immobilization (extension cast/brace) if nondisplaced
Patellectomy if severe
Lateral = most common
Causes: Shallow trochlea, ligamentous laxity, MPFL rupture
Symptoms: Knee buckling, + patellar apprehension
Patellar Instability/Dislocation
Treatment:
Reduction + conservative care (PT, NSAIDs)
MPFL repair/reconstruction if recurrent
Valgus force (blow to lateral knee), often with medial meniscus tear
Symptoms: Medial knee pain, instability, swelling
Tests:
↑ laxity with valgus stress
MCL Injury (Medial Collateral Ligament)
Treatment: Brace, surgery if complete tear
Varus force (blow to medial knee), less common in isolation
Symptoms: lateral knee pain, swelling, instability
Tests:
↑ laxity with varus stress
LCL Injury (Lateral Collateral Ligament)
Treatment: Brace, surgery if complete tear
Traumatic (younger athletes) vs. Degenerative (elderly)
Medial > lateral, except acute ACL → lateral
Symptoms: Locking, popping, joint line tenderness
Tests: +McMurray, +Apley
Zones:
Red zone (outer third): vascular, heals well
White zone (inner): avascular, poor healing
Meniscal Tear
Treatment:
Young: Repair or meniscectomy
Older: RICE, PT
Which meniscal tear is more common? (Medial vs lateral)
Medial meniscus more common UNLESS
ACL tear then lateral is more expected
MOI: Non-contact pivot or hyperextension and severe force directed anteriorly with the knee “semi-flexed”
Risk: Women more likely (↑ Q-angle)
Symptoms: “Pop,” swelling, instability
Tests: +Lachman (best), +Anterior drawer
ACL Tear (Anterior Cruciate Ligament)
Treatment:
Low demand: PT
High demand: Surgical reconstruction
What is O'Donoghue’s Triad (“Terrible Triad”)?
ACL + MCL + medial meniscus
Valgus force mechanism
Note: WE NOW KNOW that the Lateral meniscus is often torn in acute ACL injury
MOI: Dashboard injury (tibia pushed posteriorly)
Symptoms: Instability, difficulty walking
Test: +Posterior drawer
PCL Tear (Posterior Cruciate Ligament)
Treatment: Conservative unless other ligaments injured
Cause: repetitive trauma/pressure to knee; “Housemaids knee”
Symptoms: pain with AROM, swelling anterior to patella, warmth
Prepatellar Bursitis (most common)
Etiology: obesity and overuse in athletes
Symptoms: sharp non-radiating pain on medial tibia just below knee
Muscles affected: Semitendinosus, Gracilis, Sartorius
Anserine Bursitis
With Anserine Bursitis, what muscles are affected?
Sartorius, Gracilis, Semitendinosus (SGT.)
MOI: Popliteal swelling from synovial fluid buildup
Can mimic DVT if ruptured
Generally asymptomatic but may cause posterior knee pain
Baker’s Cyst or Popliteal Cyst
What compartment is most commonly affected in Compartment Syndrome?
Anterior compartment (lower leg)
Cause: Fracture, crush injury, reperfusion injury
Anterior = most common
6 Ps: Pain out of proportion, paresthesia, pallor, pulselessness, paralysis, poikilothermia
Dx: >30 mmHg compartment pressure
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Treatment:
Emergency fasciotomy
What compartment?
Numbness: first web space (of toe)
Action causing pain: plantar flexion
Anterior compartment
What compartment?
Numbness: dorsum of foot
Action causing pain: inversion and dorsiflexion (of foot)
Lateral compartment
What compartment?
Numbness: lateral foot
Action causing pain: dorsiflexion
Superficial Posterior compartment
What compartment?
Numbness: plantar aspect of foot
Action causing pain: dorsiflexion
Deep Posterior compartment
Causes: exercise with repetitive motions
Symptoms: achy, crampy, squeezing pain or pressure, reproduceable by the patient
Cessation of exercise usually decreases pain
Chronic (Exertional) Compartment Syndrome
Risk factors: Virchow’s triad (stasis of blood flow, hypercoagulability, endothelial damage)
Symptoms:
Unilateral swelling, pain, warmth
+Homan’s sign (pain on dorsiflexion)
Dx: Duplex ultrasound, D-dimer
DVT / VTE (Deep Vein Thrombosis/ Venous Thromboembolism)
How do you treat DVT / VTE?
Anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin (warfarin) or LMWH
Most common ankle sprain
Ligaments: ATFL (most common)
MOI: Foot rolls outward
Symptoms: Lateral ankle pain, swelling, bruising
Tests: + Anterior drawer test
XRAY depending on “Ottawa” ankle rules
Low Ankle Sprain – Inversion (lateral)
Treatment: RICE, brace, PT; surgery rarely needed
Ligament: Deltoid ligament
Less common, more severe
MOI: Foot rolls inward
Symptoms: Medial ankle pain/swelling; possible fibula or syndesmosis injury
XRAY depending on “Ottawa” ankle rules
Low Ankle Sprain – Eversion (medial)
Treatment
RICE, brace, longer rehab; consider imaging for fracture
Injury to syndesmosis (AITFL) —> Anterior Inferior Tibiofibular Ligament
MOI: External rotation + dorsiflexion
Test: Squeeze test, external rotation test
High Ankle Sprain
Treatment:
Longer rest, possible surgery
Zone: ~6 cm above calcaneal insertion (hypovascular zone)
MOI: Push-off during running/lateral movement
Symptoms: Sudden “pop,” feels like “getting kicked in back of ankle,” inability to plantarflex
Test: +Thompson test
Achilles Tendon Rupture
Treatment:
Non-surgical: Plantarflexion cast
Surgical: Tendon repair
Get a ________ xray if:
Pain in the malleolar zone AND:
Bone tenderness at the posterior edge or tip of the lateral malleolus (distal 6 cm), OR
Bone tenderness at the posterior edge or tip of the medial malleolus, OR
Inability to bear weight both immediately after injury and in the ER (4 steps)
Get an ankle x-ray
Get a _______X-ray if:
Pain in the midfoot zone AND:
Bone tenderness at the base of the 5th metatarsal, OR
Bone tenderness at the navicular bone, OR
Inability to bear weight both immediately after injury and in the ER (4 steps)
Get a foot x-ray
What is the Ottawa rules mnemonic?
Mnemonic:
“In Ottawa, we drink Fine MALBEC”
FI – Fifth Metatarsal
N – Navicular
MAL – Medial Malleolus
L – Lateral Malleolus
BE – Bear weight (4 steps)
C – Clinical Judgment
MOI: Sudden stretch at musculotendinous junction (sprinting)
Severe: Complete avulsion from ischium
Symptoms: Posterior thigh pain ± sciatic nerve symptoms (numbness/tingling from hematoma)
Proximal Hamstring Injury
Treatment:
Strain: RICE
Avulsion:
>3 cm retraction → early surgery
<3 cm → try non-operative