Introduction to Mechanotransduction in BENG 480/580
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Mechanotransduction
Process by which cells sense mechanical signals.
BENG 480/580
Course code for graduate-level mechanotransduction class.
Prof Caymen Novak
Instructor for the mechanotransduction course.
Winter 2025
Term during which the course is offered.
Class Layout
Structure includes quizzes, lectures, and discussions.
Engineering Lab
Location for lectures and labs in the course.
Quiz Duration
15 minutes at the beginning of each class.
Lecture Duration
Approximately 60 minutes of instructional content.
Journal Club Discussion
30-minute session for analyzing journal articles.
Lab Duration
60 minutes for hands-on activities and experiments.
Grading Breakdown
Total of 100% across various assignments.
Homework Weight
Accounts for 10% of the overall grade.
Journal Clubs Weight
Contributes 10% to the final grade.
Quizzes Weight
30% of the total course grade.
Labs Weight
15% of the overall course grade.
Final Project Weight
30% based on group presentations and reports.
Participation Weight
5% for active involvement in discussions.
Final Project
Group project focusing on assigned organ systems.
Organ Systems
Topics include musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems.
Journal Club Requirements
Read, annotate, and discuss assigned articles weekly.
Annotation Requirement
Annotated articles must be submitted for grading.
Discussion Participation
Active engagement monitored during journal club sessions.
Research Evaluation
Assess goals, hypotheses, and findings of studies.
Future Directions
Consider next steps for research based on findings.
Mechanotransduction
Cells convert mechanical stimuli into biochemical signals.
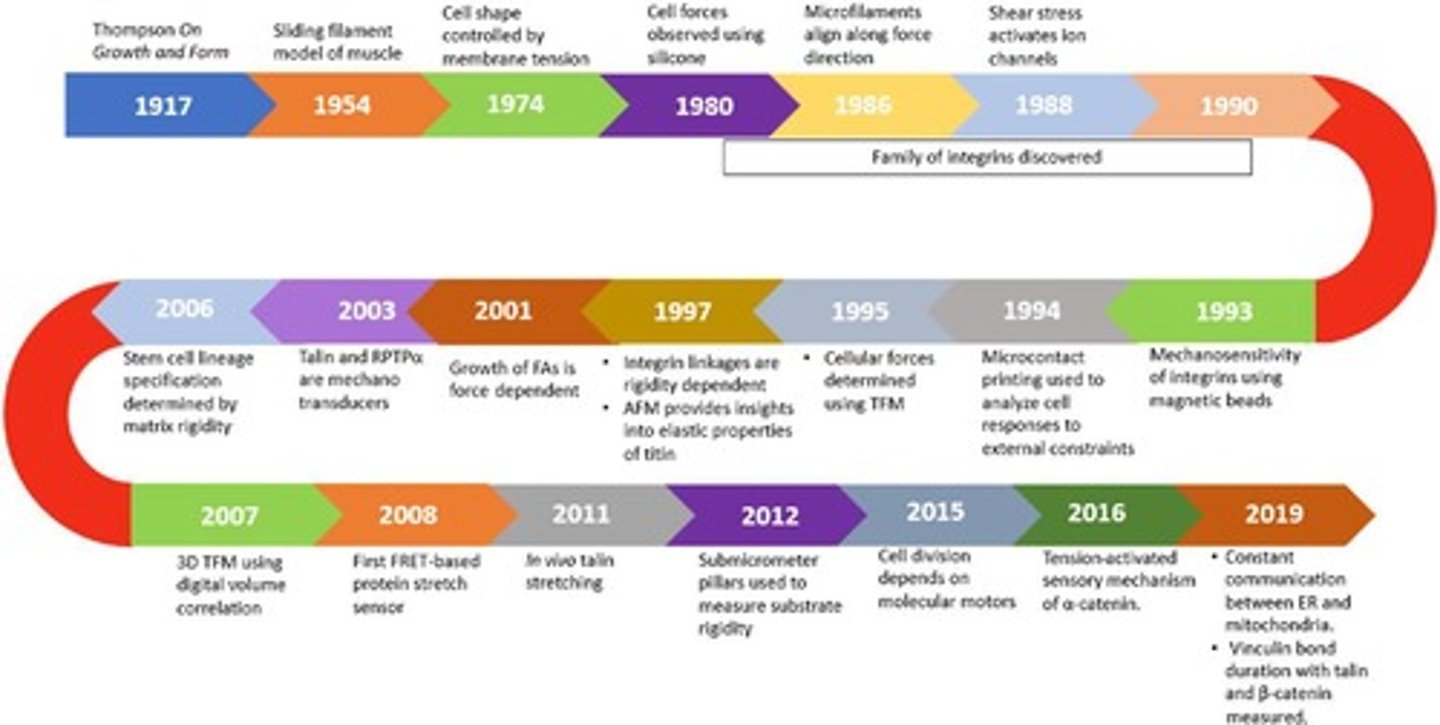
Focal Adhesions
Cell structures that anchor cells to the extracellular matrix.
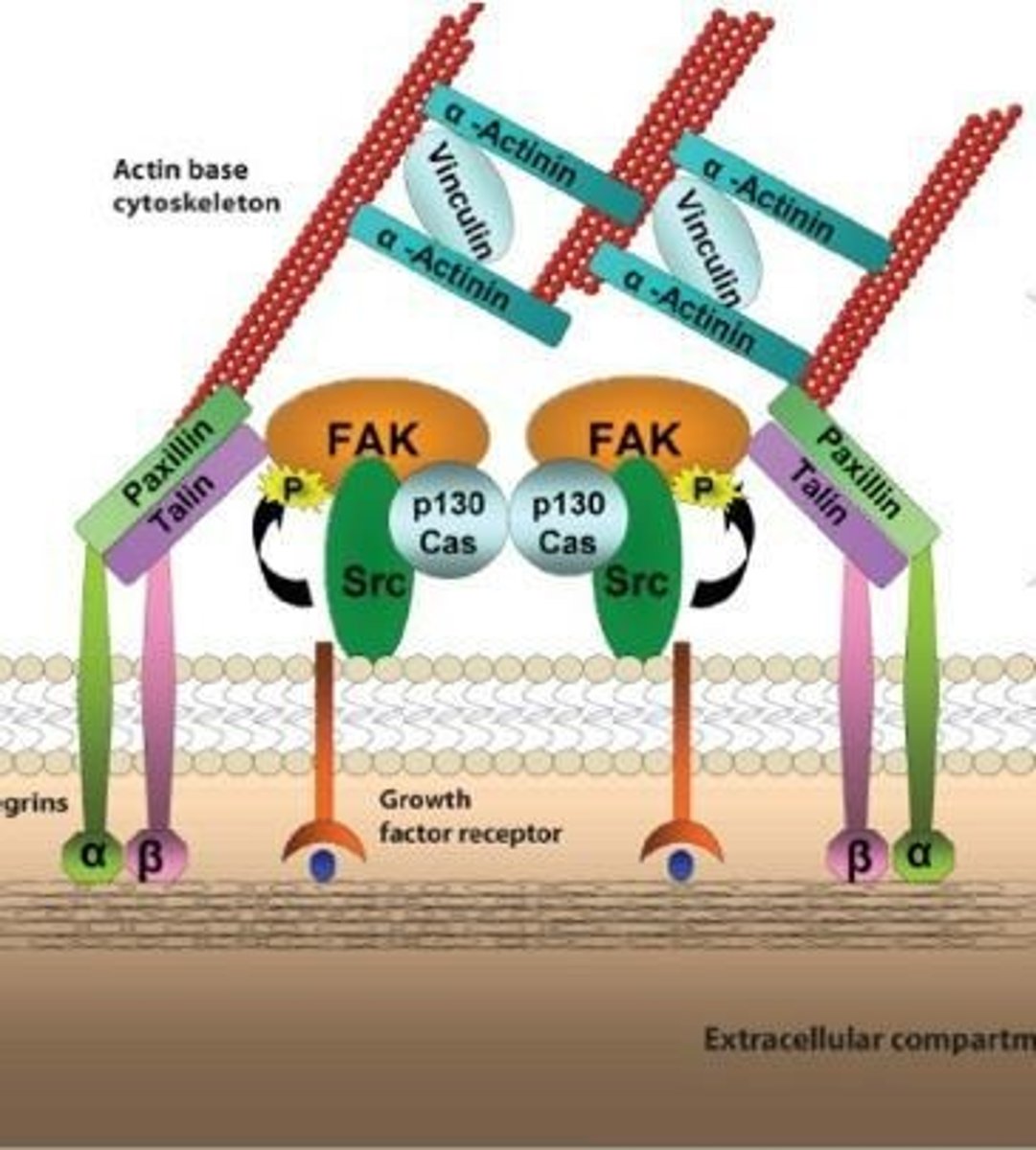
YAPTAZ
Protein involved in mechanotransduction pathways.
E-cadherin
Adhesion molecule important for cell-cell adhesion.
N-cadherin
Adhesion molecule involved in fibroblast-cancer interactions.
Elastomeric Substrates
Materials that can change shape under mechanical stress.
Mechanogenetic Gene Circuit
Synthetic system for controlling gene expression via mechanics.
Vascular Regeneration
Restoration of blood vessel function and structure.
Bioreactor Systems
Controlled environments for growing biological tissues.
Credit Hours
Units representing the time commitment of a course.
Anticipated Workload
Estimated hours required outside of class per week.
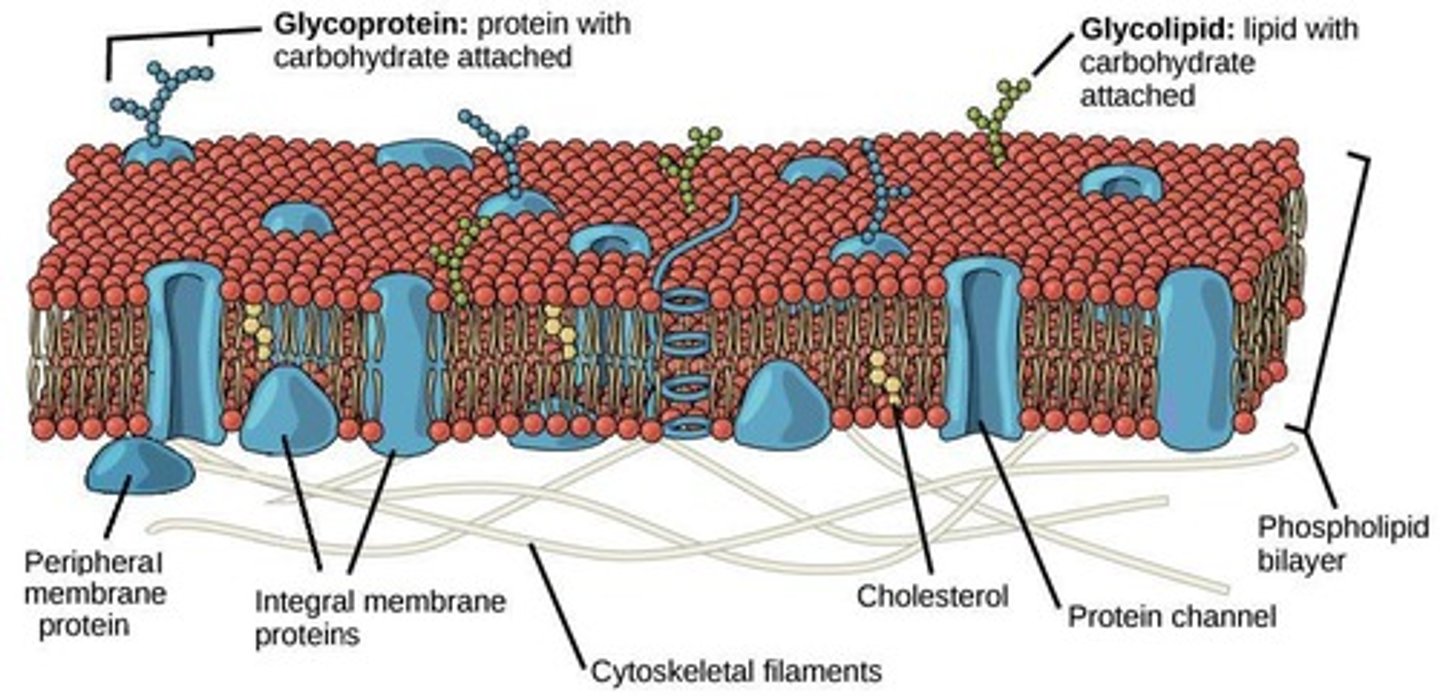
Cell Membrane
Barrier that regulates entry and exit of substances.
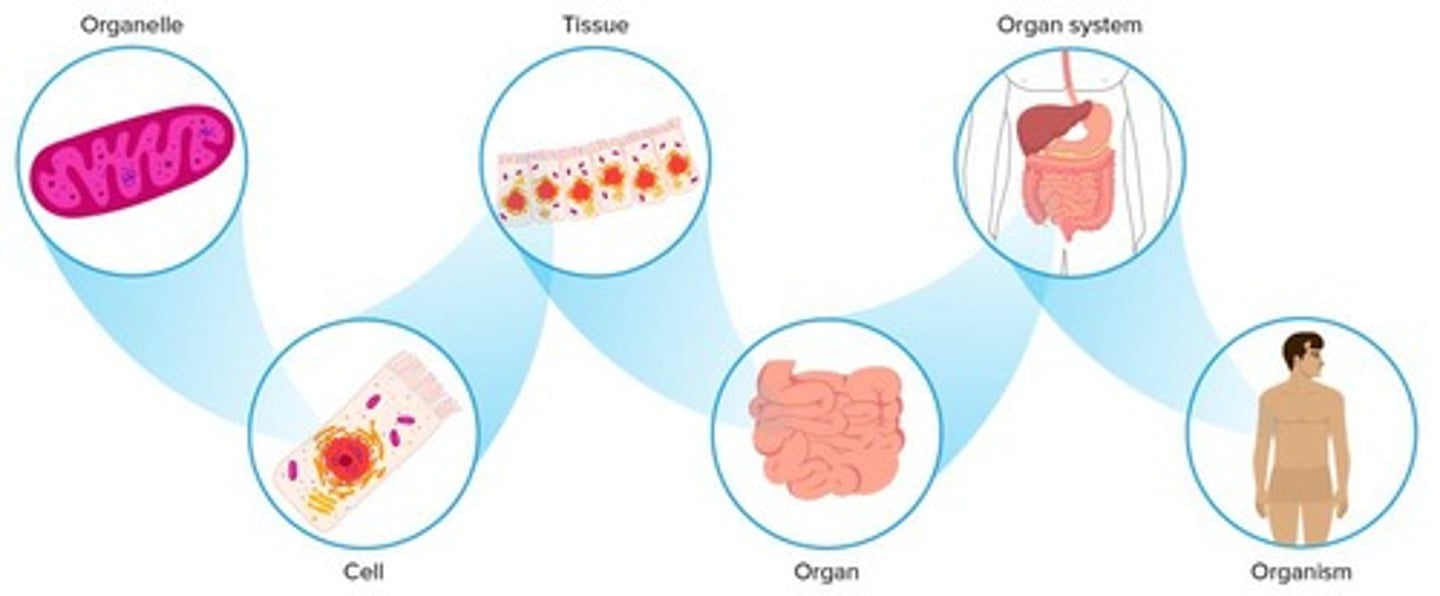
Hierarchy of Life
Organizational structure from cells to ecosystems.
Protein Synthesis
Process of creating proteins from amino acids.
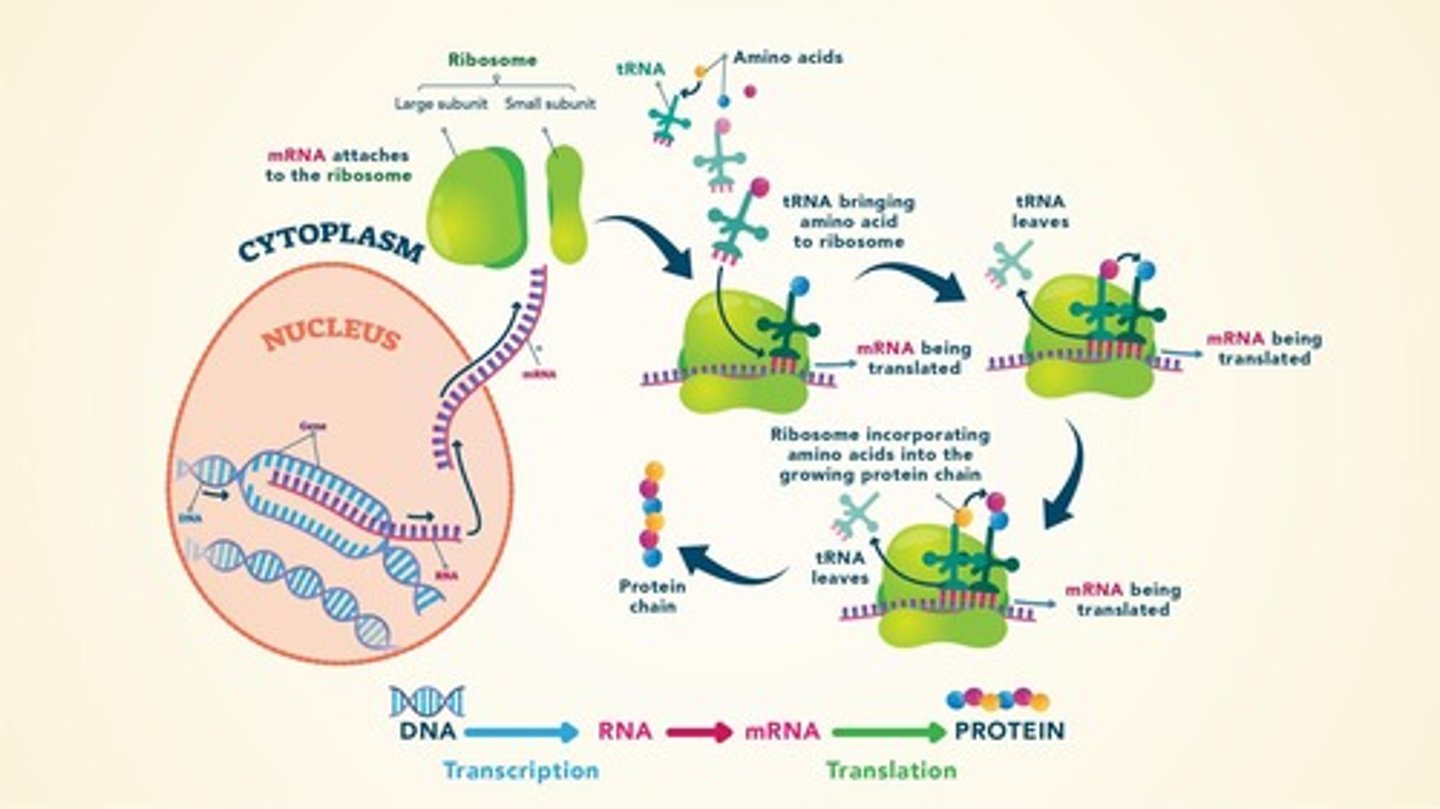
Gene Expression
Process by which information from a gene is used.
Cell Phenotype
Observable characteristics of a cell influenced by genetics.
Fluid Shear
Force exerted by fluid flow on surfaces.
Tissue Responses
Reactions of tissues to mechanical or biochemical stimuli.
Organ Responses
Reactions of organs to changes in their environment.
Proliferation
Increase in cell number through division.
Differentiation
Process by which cells become specialized in function.
Motility
Ability of cells to move and navigate their environment.
Protein Expression
Production of proteins based on gene instructions.
Tissue Adaptation
Changes in tissue structure or function in response to stimuli.
Wolff's Law
Bone adapts to mechanical stress through remodeling.
Murray's Law
Flow rate through artery scales with radius cubed.
Hemodynamic Shear Stress
Constant stress level at approximately 1 Pa.
Soft Tissue Remodeling
Tissue changes due to mechanical stress influences.
Circumferential Stress
Thickness changes in arterial wall from stress.
Calcification
Heart valve tissue responds to mechanical patterns.
Microgravity Bone Loss
Bone density decreases in low-gravity environments.
Magnitude of Stimuli
Strength and duration of mechanical forces applied.
Cellular Scale Forces
Microscale forces lead to larger physiological changes.
Estimating Forces
Magnitude, duration, and frequency of forces are estimated.
Modeling Mechanical Forces
Recreating forces in vitro for impact studies.
Endothelial Cell Response
Cells adjust behavior based on stress levels.
Circumferential Strains
Arterial wall strains range from 2 to 18%.
Bone Strain Sensitivity
Bone cells detect strains as small as 1000 µε.
Force Activation Threshold
Energy must exceed thermal energy for activation.
Resting Stress Levels
Baseline stress from actomyosin machinery in cells.
Internal vs External Forces
Cells sense both internal and externally applied stresses.
Actomyosin Contractions
Internal forces help cells probe mechanical environments.
Extracellular Matrix Cues
Mechanical signals influence cell differentiation.
Matrix Stiffness
Influences cellular behavior and tissue organization.
Physiological Models
Accurate models improve understanding of diseases.
Homework Assignments
Includes pipetting practice and journal club reading.