ISA + pipelining
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
5 factors to consider when picking an ISA
instruction length
operands/instruction type
memory organisation
addressing modes
operations available
3 main measures for an ISA
memory space (RAM as expensive)
instruction complexity
number of available instructions
endianness
byte ordering, how data is stored
ordering of bytes of data
little endian machines
LSB → MSB
flexible for casting
16 to 32 bit integer address doesn’t require any arithmetic
big endian machines
MSB → LSB
natural
sign of number obvious by looking at byte at address offset 0
strings and integers are stored in same order
3 types of register architectures
stack architecture
accumulator architecture
general purpose register architecture
tradeoff is between simplicity and cost of hardware, and execution speed and ease of use
stack architecture
instructions and operands taken from stack
cannot be accessed randomly
stack machine
use 1 and 0 operand instructions
instructions operate on elements on top of stack
access instructions are push and pop that need 1 memory address operand
accumulator architecture
1 operand of binary operand is stored in accumulator
one operand in memory, creating bus traffic
GPR architecture
registers used instead of memory
faster than ACC architecture
longer instructions
3 types of GPR architecture
memory-memory: 2/3 operands in memory
register-memory: at least 1 operand in register
load-store: no operands in memory
move data to CPU, work with it, move out when done
immediate addressing
data is part of instruction
direct addressing
address of data is given in instruction
indirect addressing
address of address of data is given in instruction
index addressing
uses register as offset (index , for index addressing, base for base addressing)
added to address in operand to find effective address of data
register addressing
data located in a register
register indirect addressing
register stores address of address of data
stack addressing
operand assumed to be on top of stack
FDE broken down into instruction level
fetch instruction
decode opcode
calculate effective address of operand
fetch operand
execute instruction
store result
theoretical speed offered by pipeline
each instruction is a task T, no. of tasks is N
Tp is time pers take, K is number of stages in pipeline
for no pipelining, time is NKtp
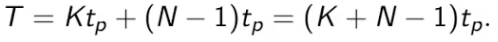
pipeline speed up equation

3 pipeline hazards
resource conflicts
data dependencies
conditional branching