C4.1 Populations & Communities
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What defines a population? What happens if populations are isolated?
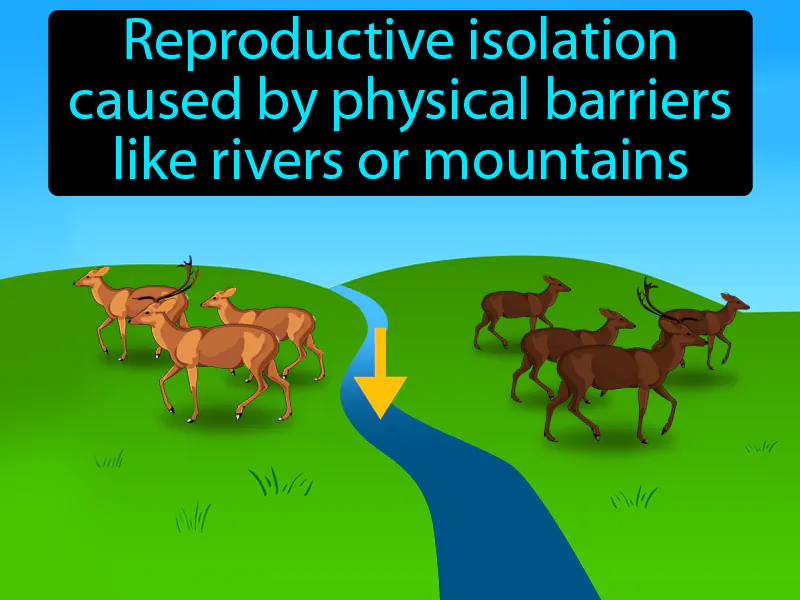
A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a defined area at the same time.
If populations are isolated from one another, this leads to reproductive isolation, where they can no longer exchange genetic material with one another.
What is the Capture-Mark-Recapture method?
Since Quadrat sampling only works for sessile organisms that cannot move;
The Capture-Mark-Recapture method is used to estimate the size of a population of animals by capturing them temporarily, marking them, releasing them, and then recapturing them to see how many are marked;
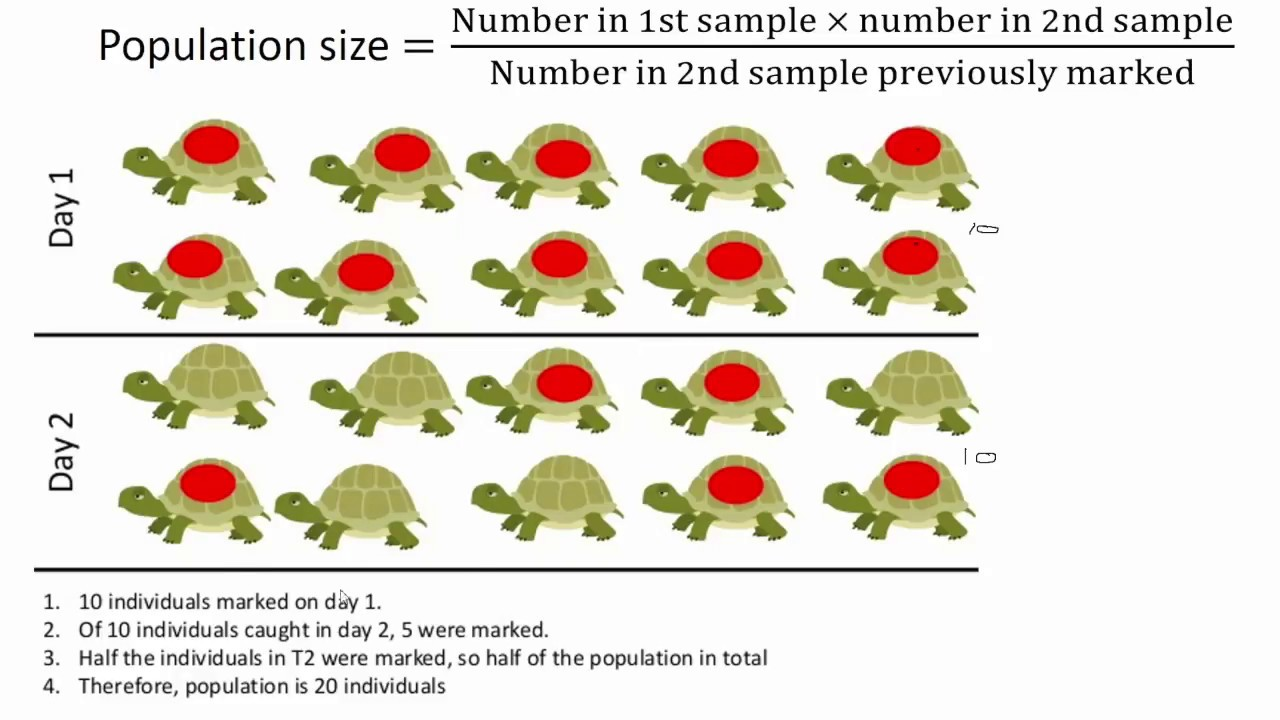
What is the Lincoln Index formula used for?
The Lincoln index formula is used for estimating population size in the capture-mark-recapture method;
The formula is the following:

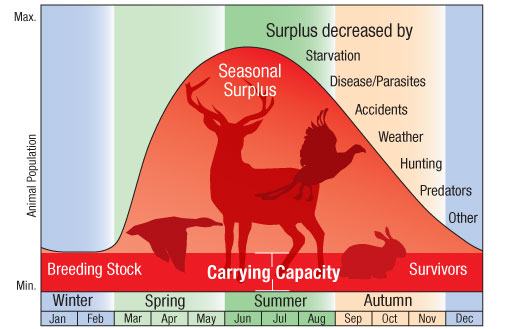
What is Carrying Capacity?
The Maximum Population size that an environment can support, given that there are enough available resources and proper conditions in a habitat.
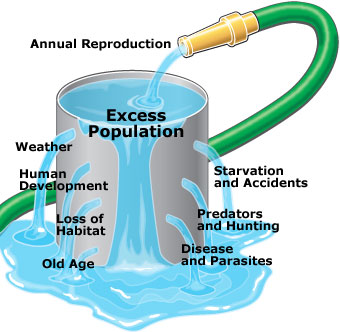
What are density-dependent factors? what are density independent factors?
Density dependent factors are factors that become stronger and more increased at higher population density; For example; Disease, Predation
Density independent factors are one that are equally as impactful, regardless of the density of a population; Examples are: Climate change, and Natural Disasters
What happens to a population when an environment reaches its carrying capacity?
Once an environment reaches its carrying capacity, resources become scarce, and the population curve begins to flatten.
Also, if population numbers do start to exceed that of the carrying capacity; then density dependent factors come into play, like: competition, starvation, disease, or predation. These will increase to cause a population decline.
How does the predator-prey cycle work?
When prey numbers increase, predator populations also increase because more food is available.
As predators increase, they consume more prey, reducing the number of prey.
Fewer prey means more predators struggle to find food, until predator numbers start to drop.
This allows the prey population to regenerate and restart the cycle.

What is Top-Down and Bottom-Up control?
Top-Down control is when higher trophic levels control/regulate lower trophic levels, usually due to predation;
Bottom-Up control is when lower trophic levels control/regulate higher trophic levels usually because of resource + nutrient availability.
Can you give an example of top-down control?
Top down: Herbivores controlling the population of plants; Like grazing animals preventing vegetation from overgrowing
Bottom up: Food availability regulating population growth; For example: plants depending on light intensity to grow.