Atomic Structure
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
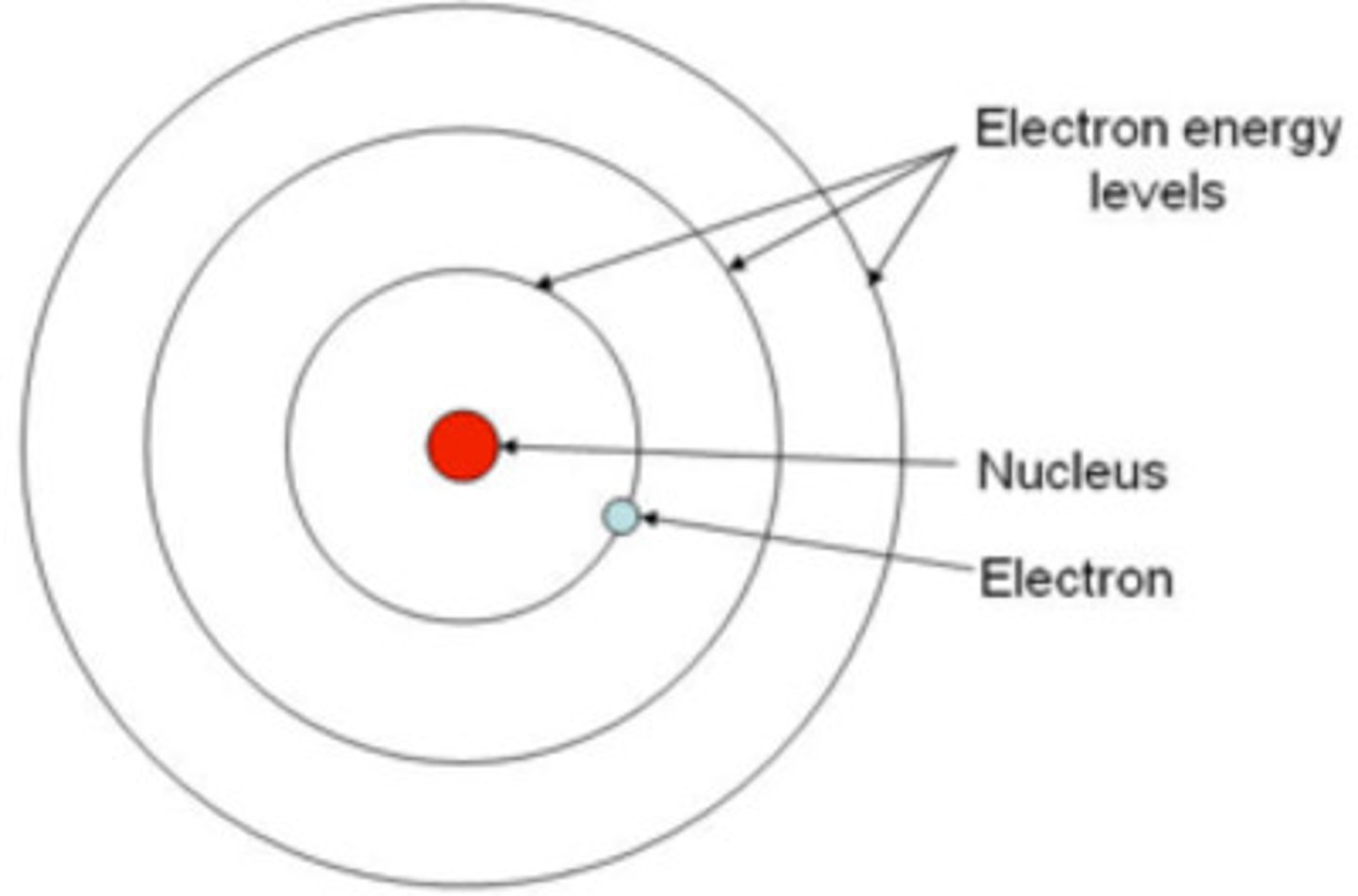
Bohr Model of Atom:
Relative atomic mass of a Neutron
1
Relative atomic mass of a proton
1
relative atomic mass of an electron
1/1840
relative atomic charge of neutron
0
relative atomic charge of a proton
+1
relative atomic charge of am electron
-1
Behavior of the particles in an electric/magnetic field if they have the same speed
- the electron will have a more acute/angular deflection because it has less energy (since mass is smaller)
- Proton will have a constant deflection because it has more energy (since mass is larger)
- Neutron will not deflection since it has no charge
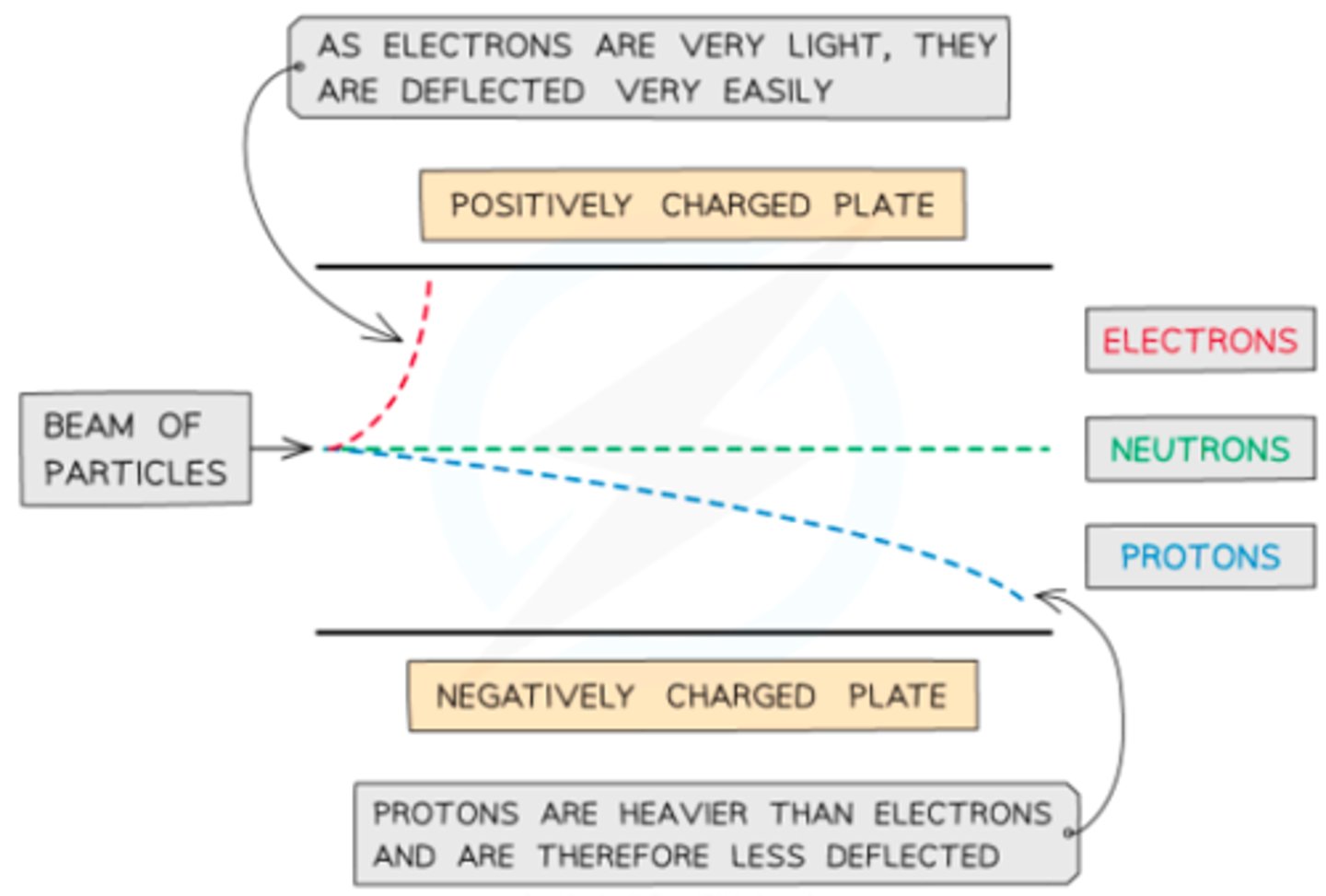
Behavior of particles in an electric/magnetic field if they have the same energy:
- Electrons & Protons will deflect the same amount to their respective electrode
- Neutron remain deflected
Role of protons in the atom:
responsible for the identity of the atom
Role of neutrons in atom:
gives rise to the existence of isotopes
What is an isotope?
atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
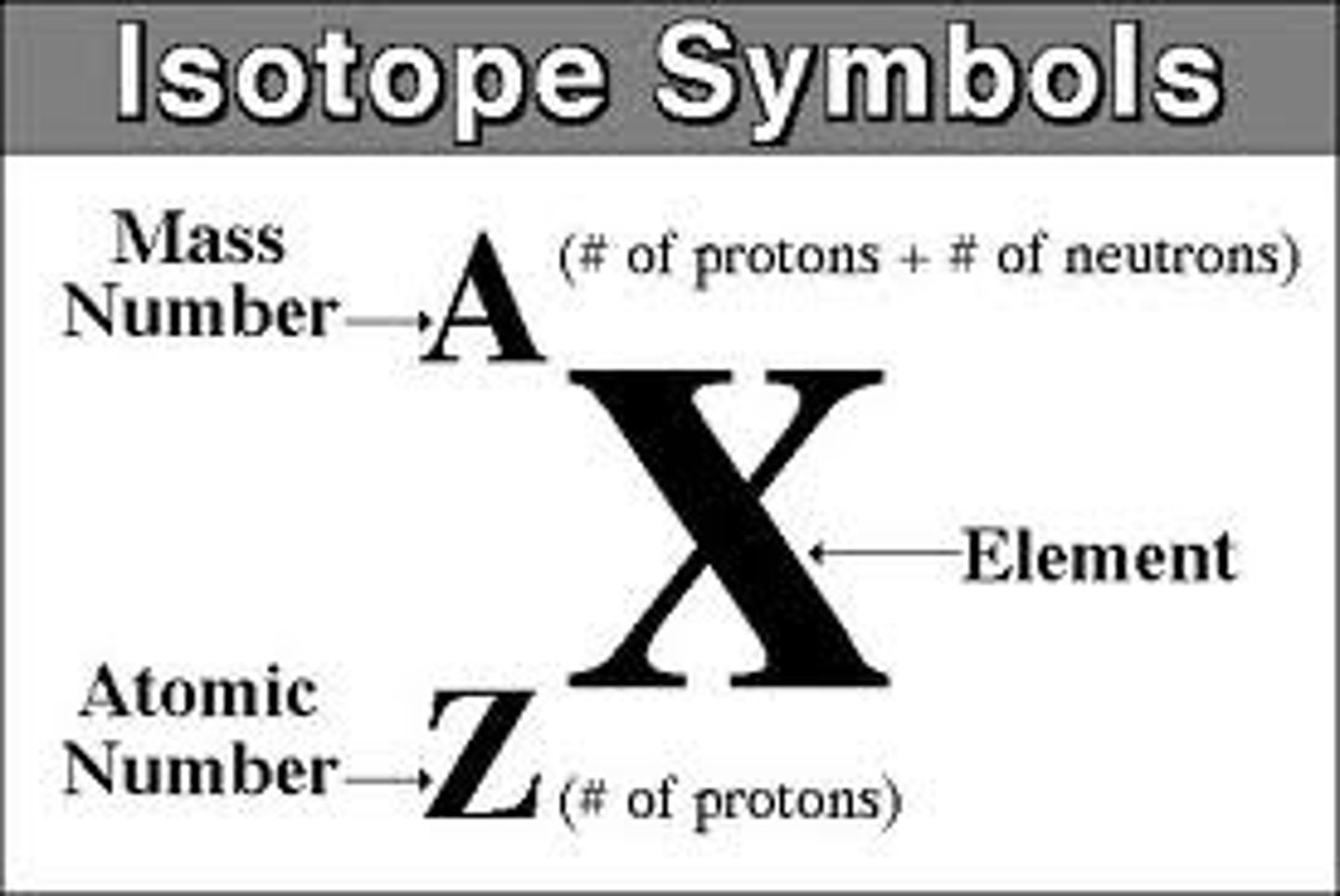
What is relative atomic mass, Ar?
the mass of an atom compared to 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12
How to calculate Ar?
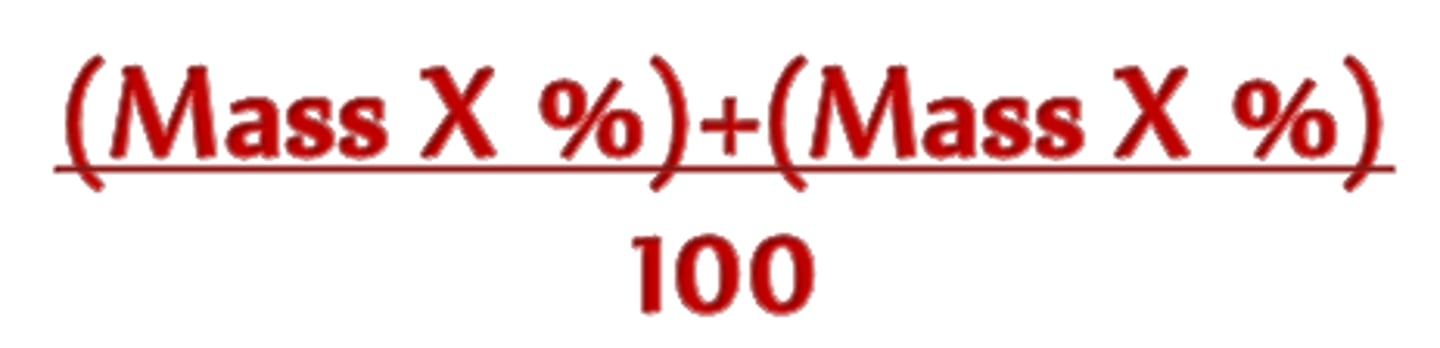
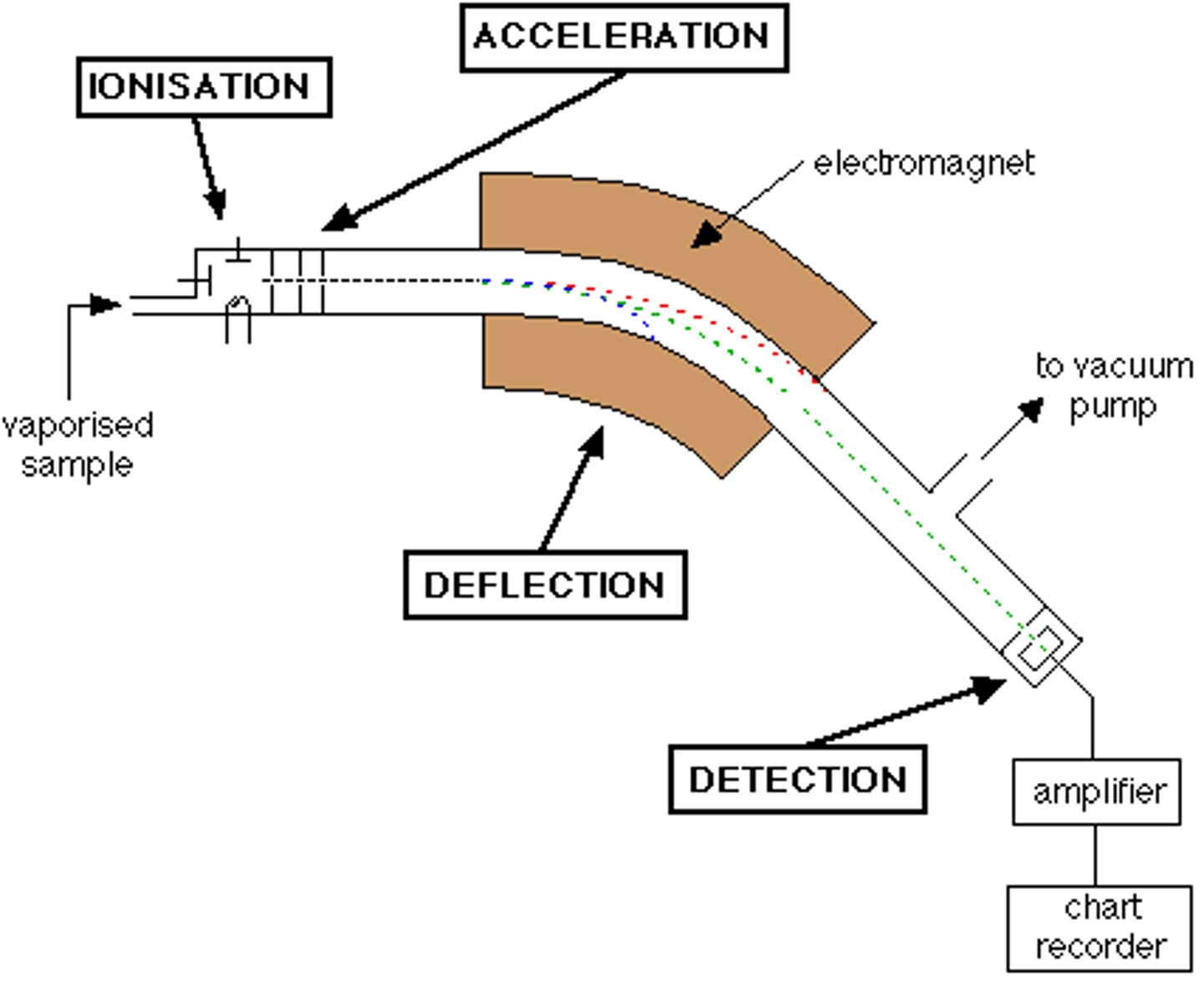
What is a mass spectrometer?
an analytical tool used to measure the mass and relative abundance of each isotope in a sample of naturally occurring element.
chemical Rxn. vs Nuclear Rxn: location
Reactions occur in the valence shell of a chemical rxn. while they occur in the nucleus of a nuclear rxn.
Chemical rxn. vs Nuclear rxn: Particles involved
chem. rxn: valence electrons
nuclear rxn: protons and neutrons
Chemical rxn vs Nuclear reaction: objective
both strive to achieve "stability"
What does stability mean for chemical reactions?
obtaining a full valence shell
What does stability mean for nuclear reactions?
having a stable proton to Neutron ratio
What is radioactivity?
the phenomenon where an unstable nucleus achieves stability via decomposition to produce a more stable nucleus with the release of radiation
Types of radioactive particles
alpha, beta, gamma
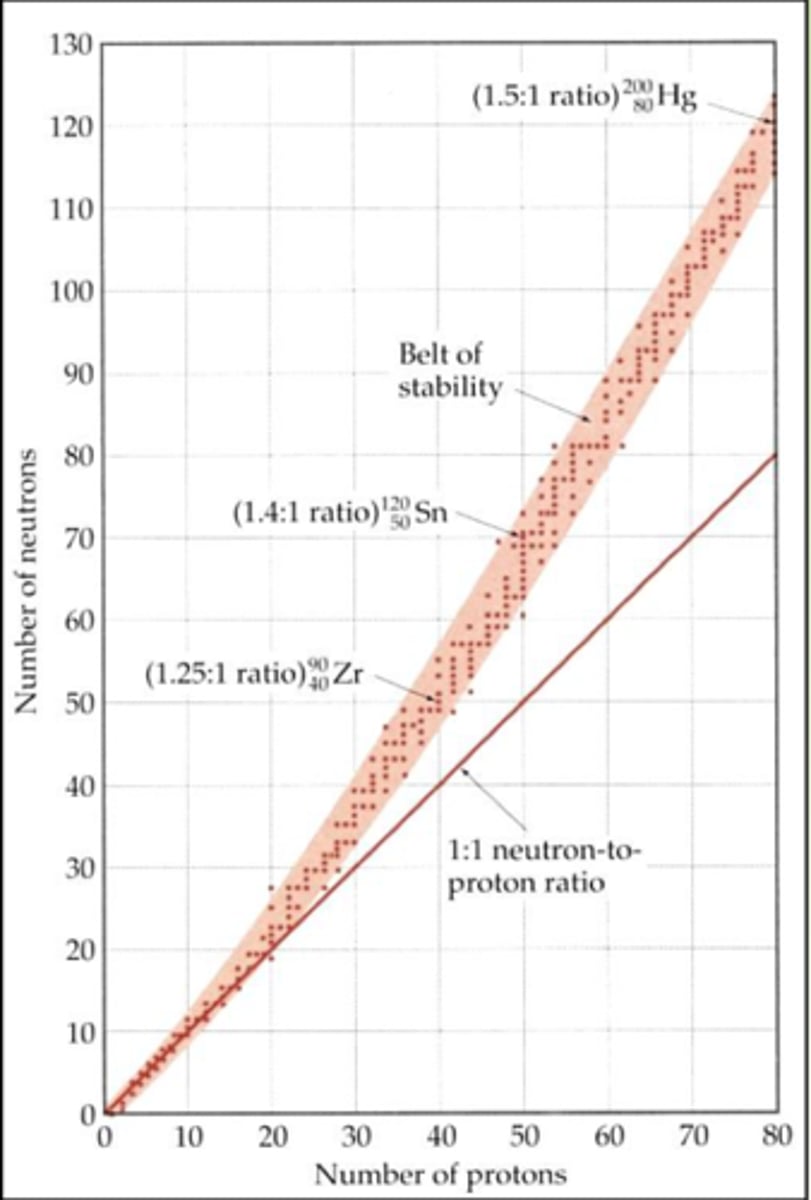
Band of stability:
characteristics of beta radiation (β)
- can pass through paper
- can be stopped by aluminum foil
characteristics of gamma rays (γ)
- released along w/ other forms of radiation
- can be stopped by lead/thick concrete
- it's essentially pure energy
characteristics of alpha radiation (α)
can be stopped by paper
Why is the proton-neutron ratio important in an atom?
- neutrons are made up of a proton and an electron
- the electron within the neutron "prevents" the electrons in the shell from being attracted to the proton in the neutron
- the ekectrons are repelled from each other
- keeps the electrons in in their shells
How does a beta particle convert a neutron to a proton?
- a beta particles is essentially an electron (it has a -1 charge and no mass num)
- the emission of a ß-particle will increase the atomic num but maintenance in the mass num.
The quantum mechanical model of the atom:
What does Pauli's Exclusion Principle state?
that 2 electrons in the same orbital cannot have the same quantum numbers
what does Heisenberg's uncertainty principle state?
that it is impossible to know both the velocity & location of an electron at the same time
What does Hund's rule state?
that electrons fill the orbitals singly at first, then they pair
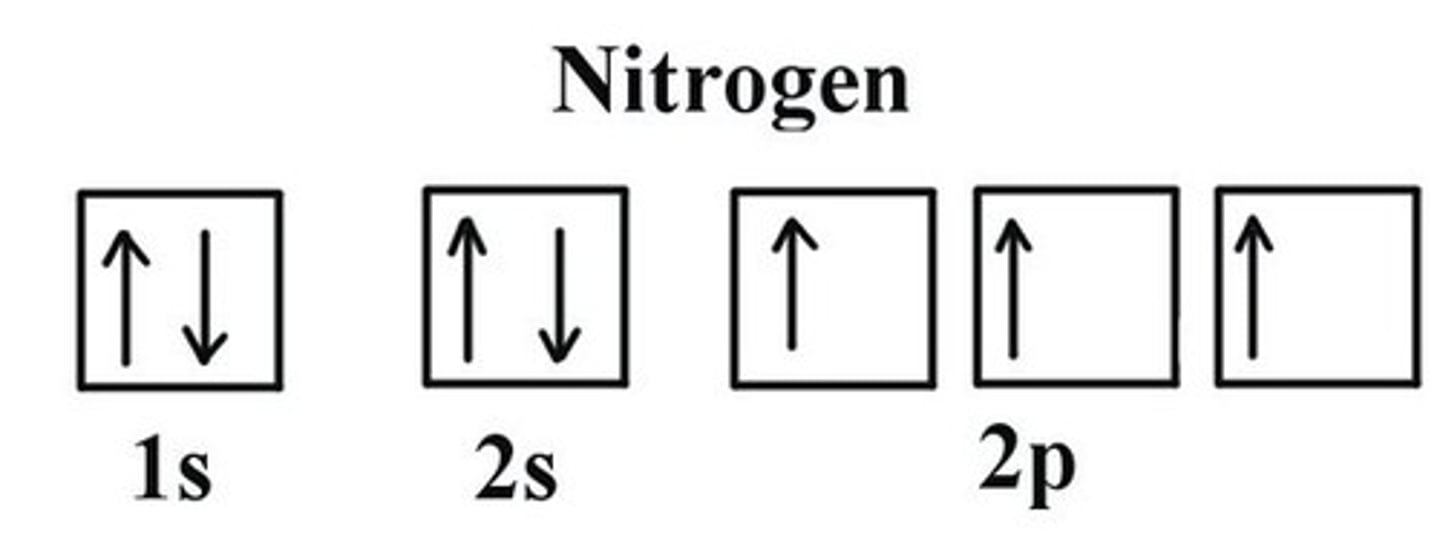
What does the Aufbau Principle state?
that electrons fill the LOWER energy orbitals FIRST then fill the higher energy orbitals
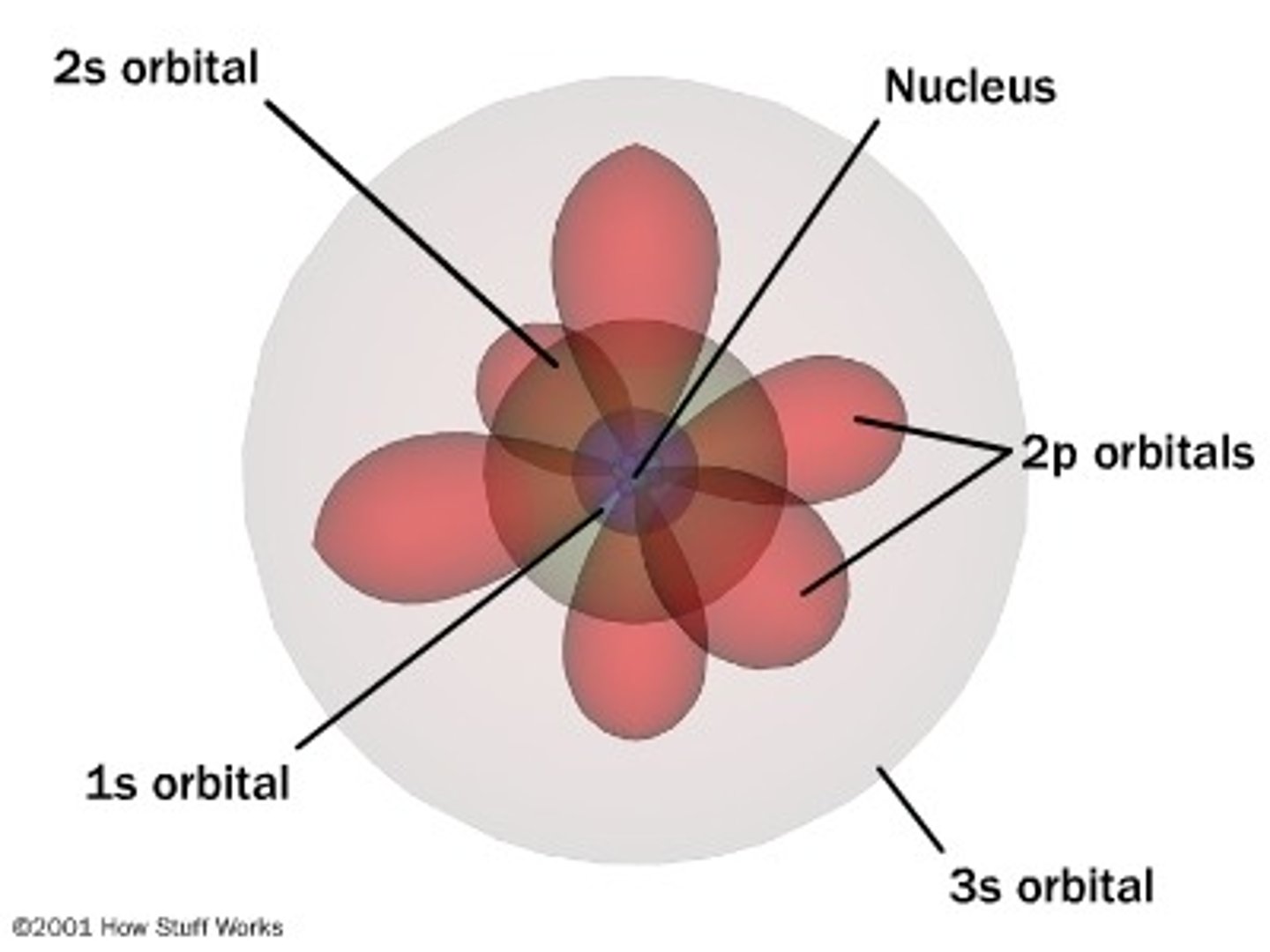
What is an orbital?
a region where there is a high probability of finding an electron
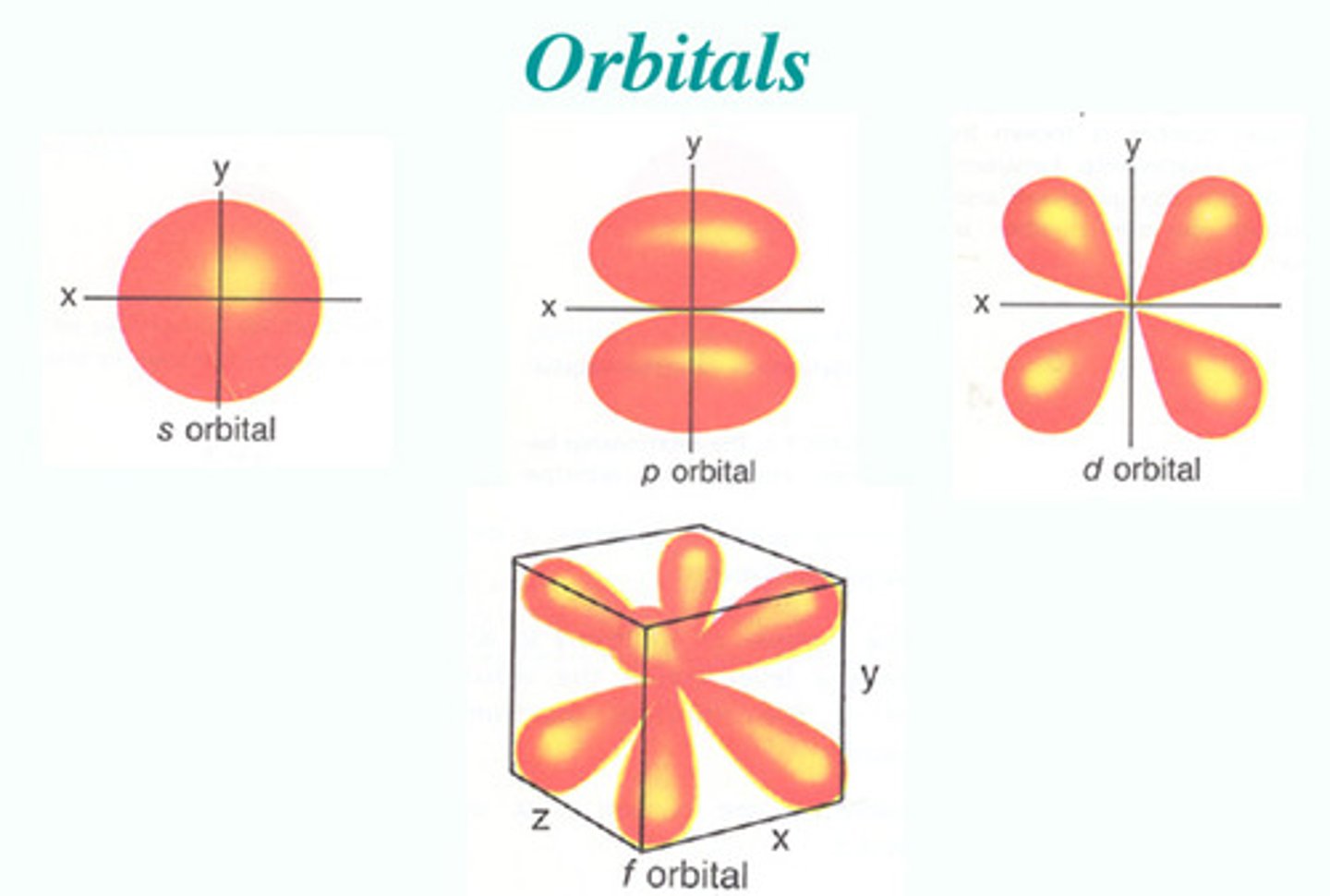
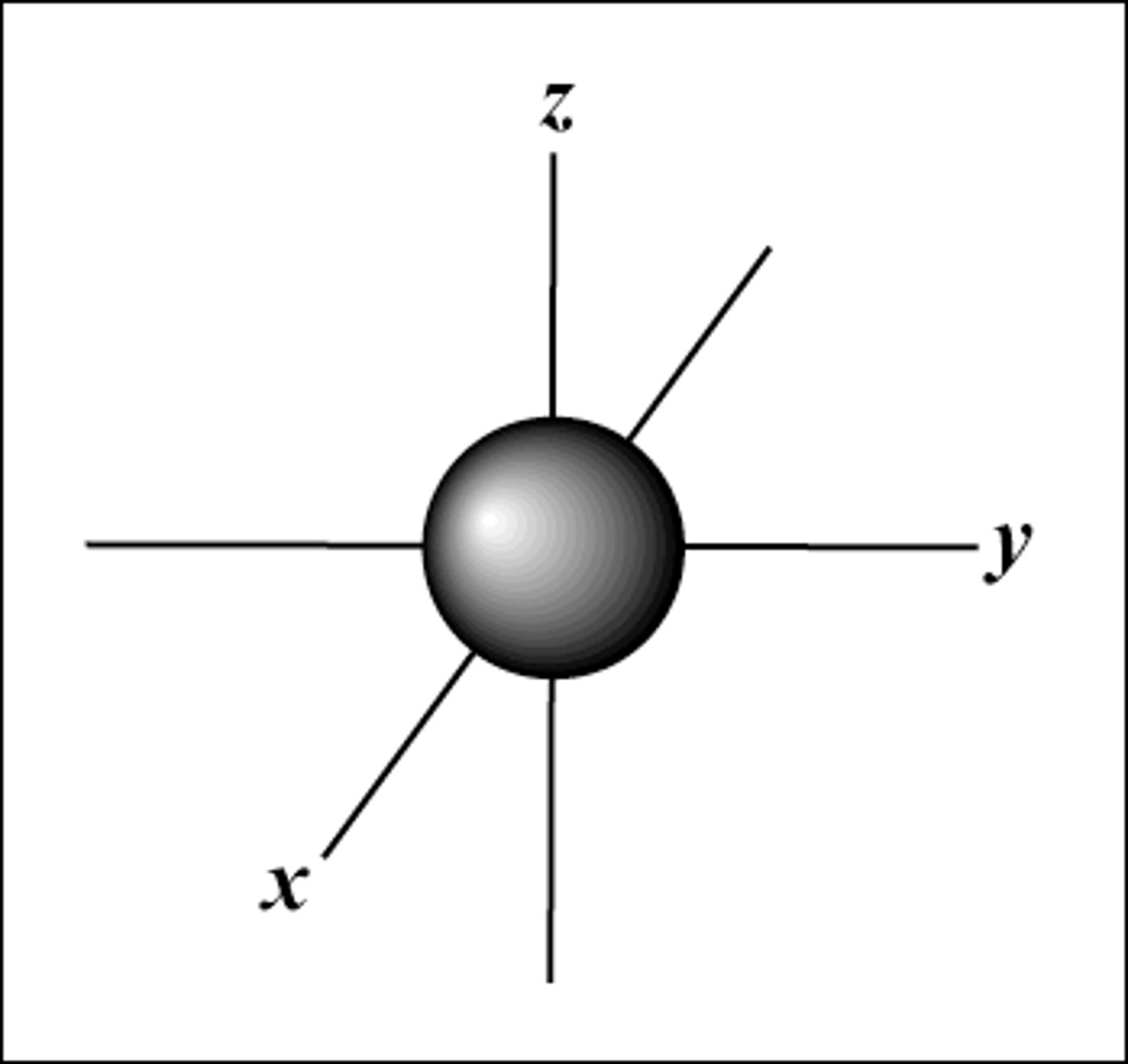
Characteristics of S-orbitals
- spherical
- simplest type of orbital
*each energy level begins with an S-orbital
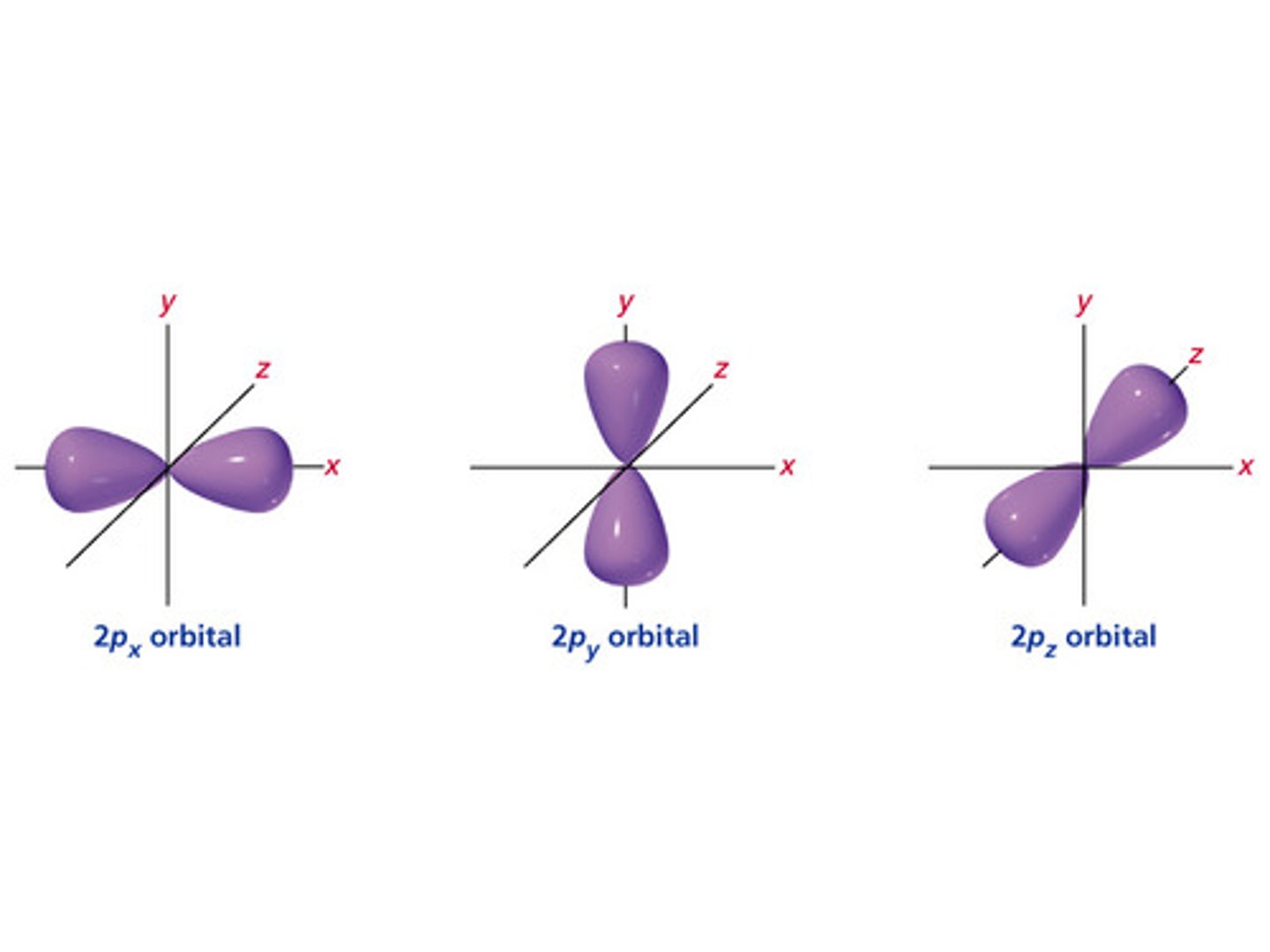
P-orbital
- there are 3 types
- has directional probability
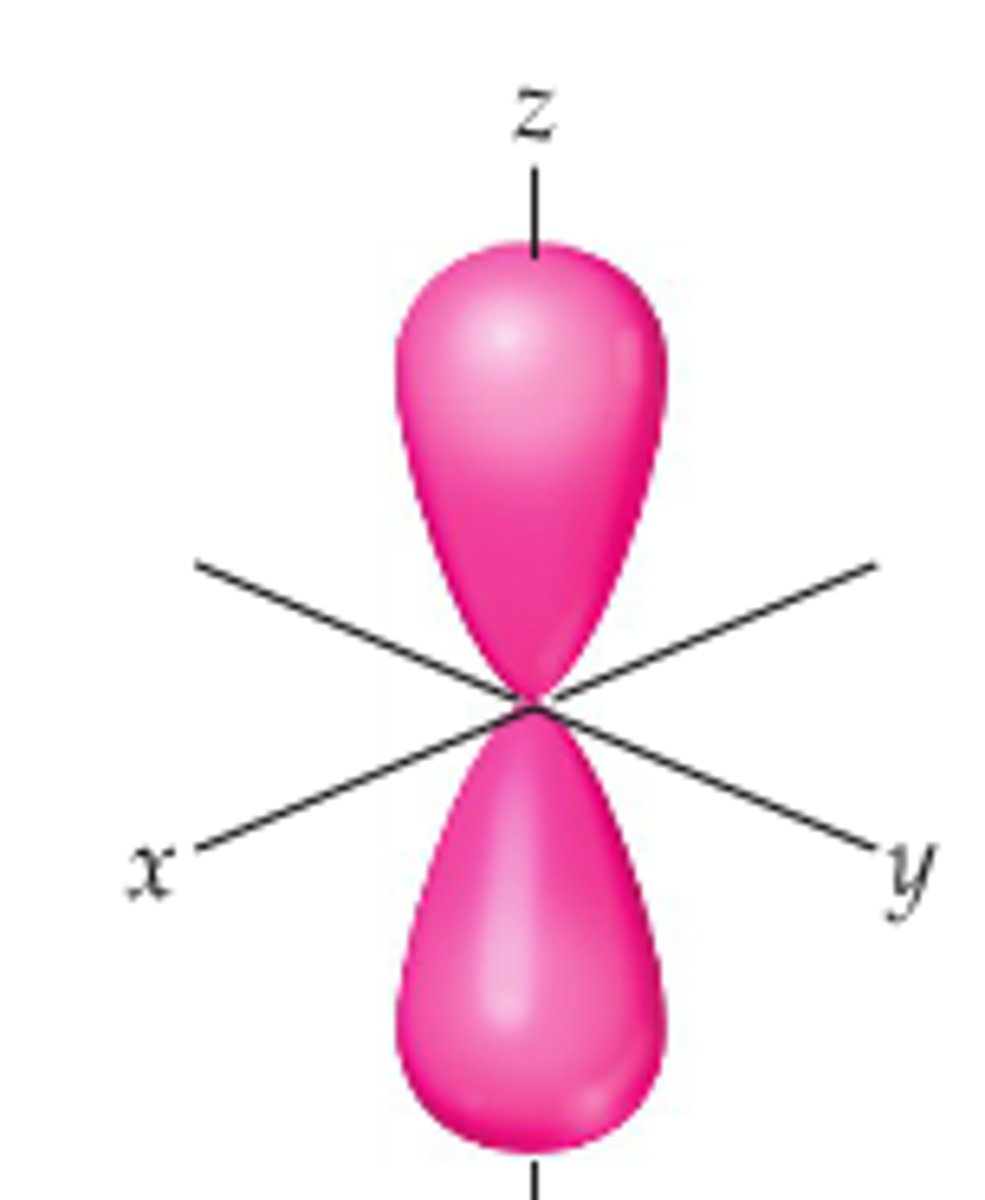
Types of P-orbitals