Botany | Exam 3 Study Guide | Dr. Sara Browning | PBA Fall 2024
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
homologous features
similar features that originated in a shared ancestor
analogous features
share similar function, but not common ancestry
phylogenetic
A family tree that shows the evolutionary relationships thought to exist among groups of organisms
systematics
study of the diversity of life and the evolutionary relationships between organisms
cladistics
A phylogenetic classification system that uses shared derived characters and ancestry as the sole criterion for grouping taxa.
clade
A group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants.
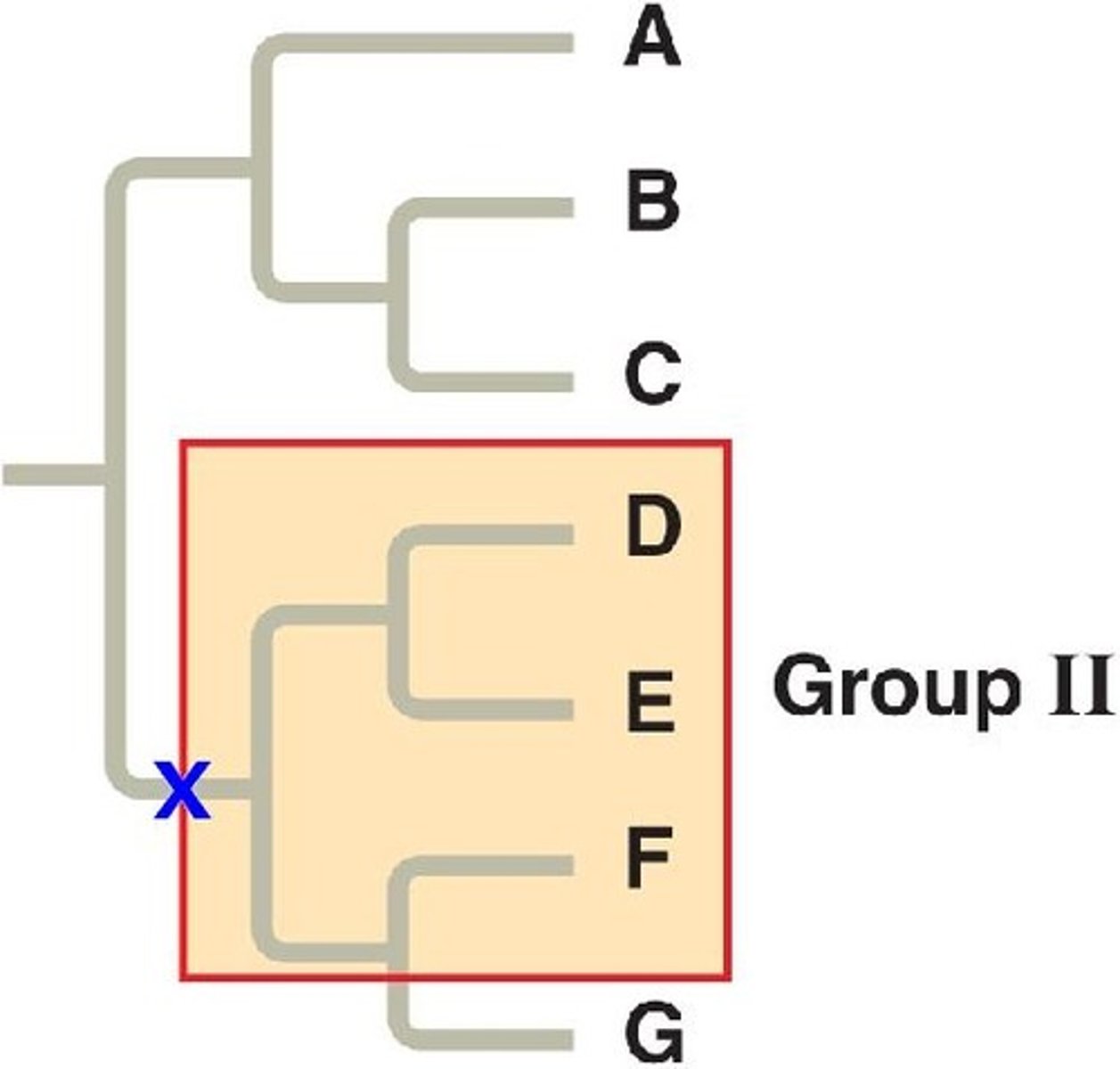
monophyletic
ALL descendants came from one common ancestor
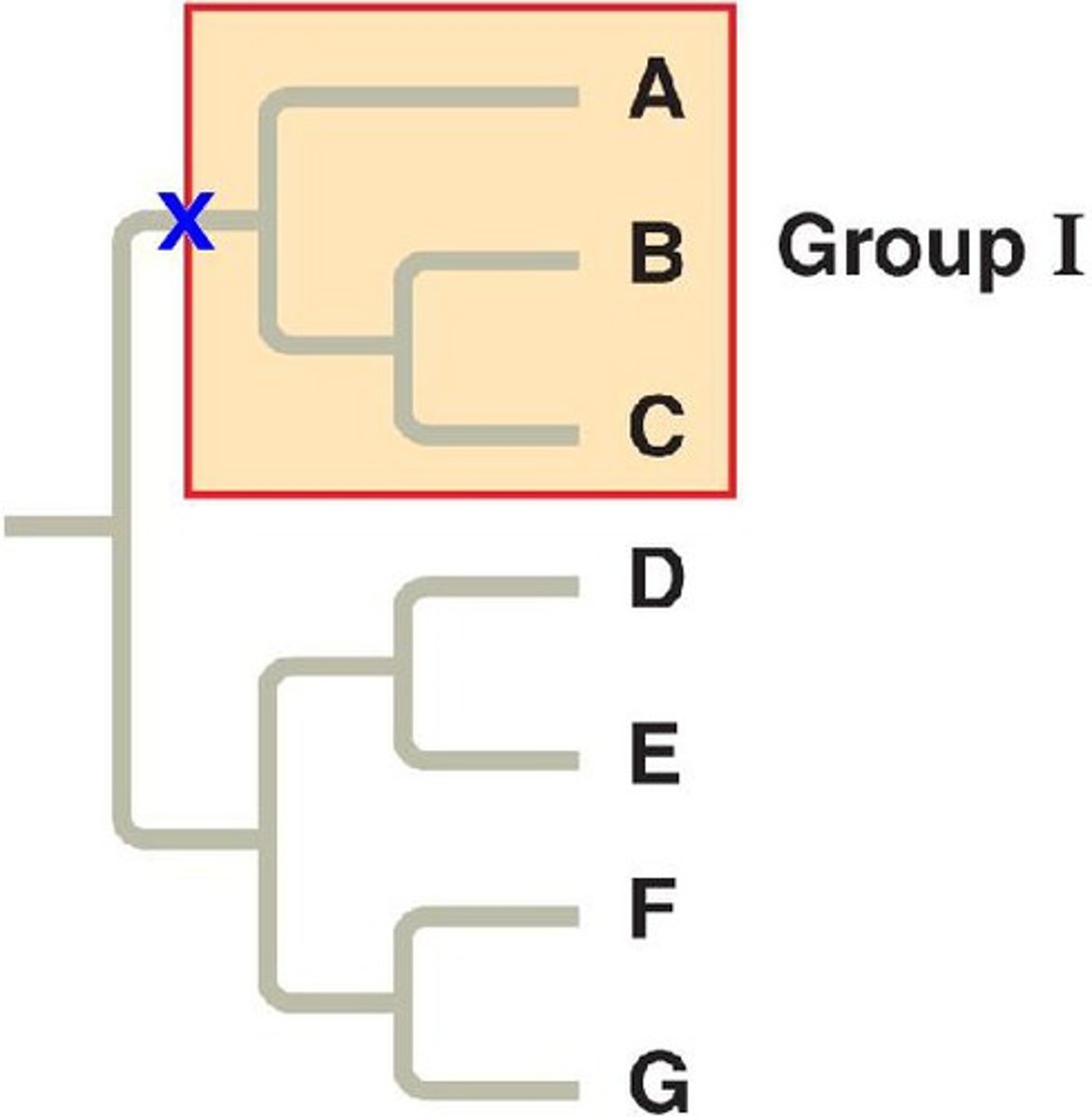
polyphyletic
pertaining to a group of taxa derived from two or more different ancestors
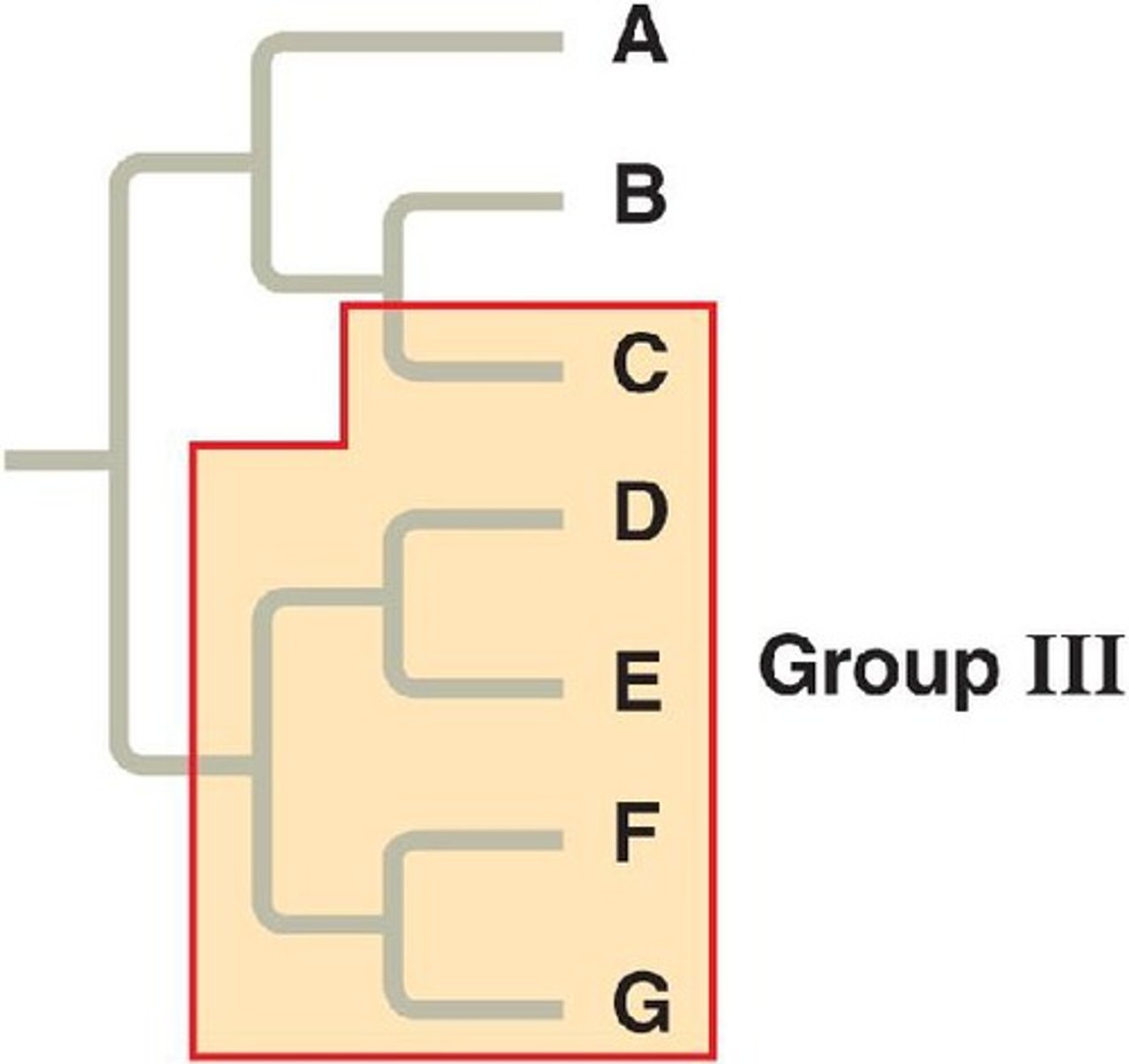
paraphyletic
Pertaining to a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants.
synapomorphy
shared derived character
barcoding
molecular biology technique in which one or more short gene sequences taken from a well-characterized portion of the genome is used to identify a species
phylocode
System of classification of organisms based on evolutionary relationships: Only groups that include a common ancestor and all of its descendents are named.
algal blooms
an explosion of algae in water that causes the loss of oxygen in the water.
eutrophication
A process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria.
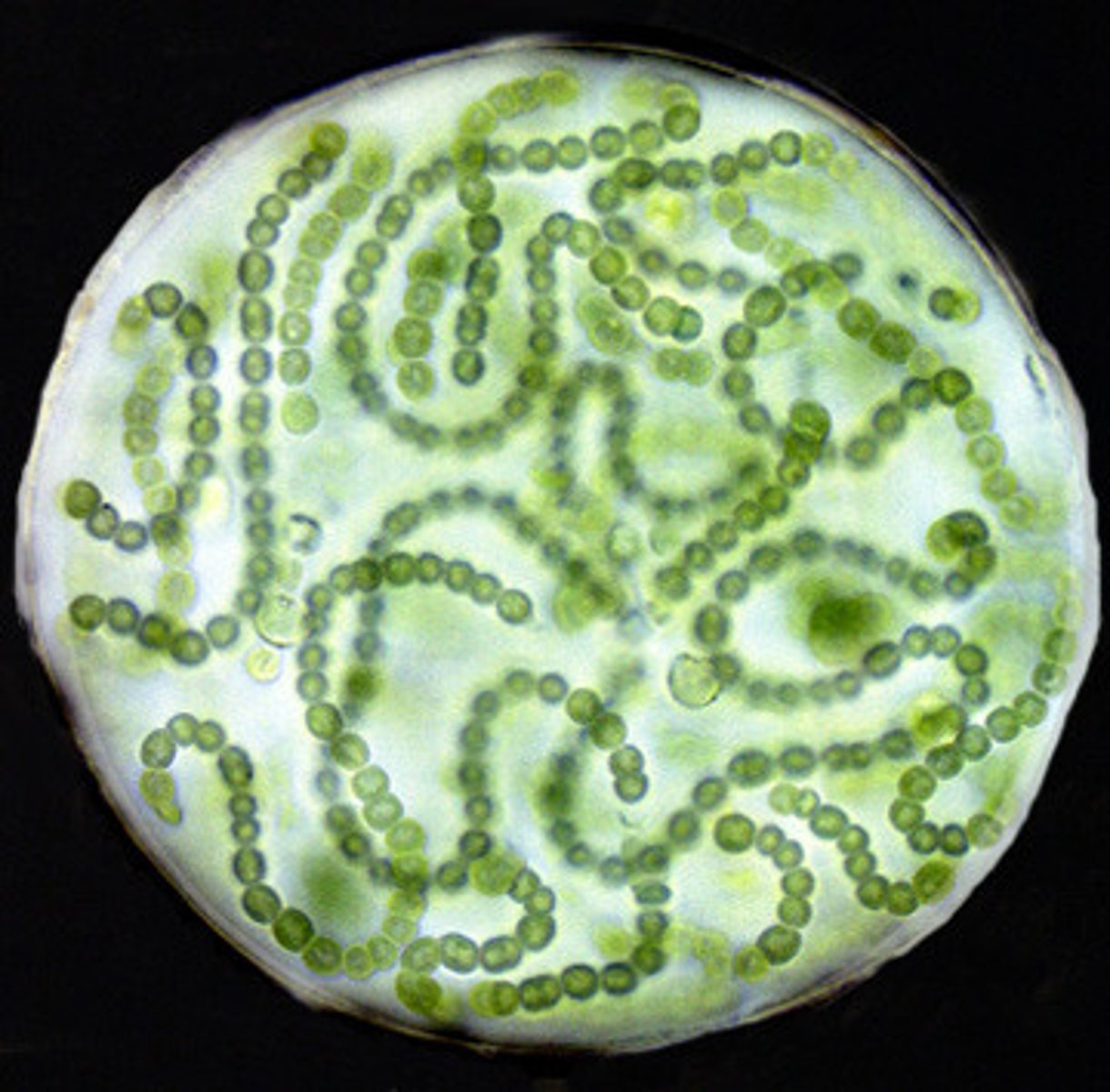
heterocyst
a specialized cell that engages in nitrogen fixation in some filamentous cyanobacteria
Prochlorococcus
most abundant photosynthetic organism on the planet
mycelium
mass of hyphae
hyphae
The branching, threadlike tubes that make up the bodies of multicellular fungi
parasite
An organism that feeds on a living host
symbiont
The smaller participant in a symbiotic relationship, living in or on the host.
pathogen
An organism that causes disease
chitin
A structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods.
Basidiomycota
club fungi (mushrooms)
Ascomycota
sac fungi
Zygomycete
Member of a group of fungi characterized by a sturdy structure called a zygosporangium during sexual reproduction.
Glomeromycota
a group of fungi that form symbiotic relationships with the roots of trees
mold fungi
distinctly filamentous, microscopic or submicroscopic fungi that breakdown soil organic matter.
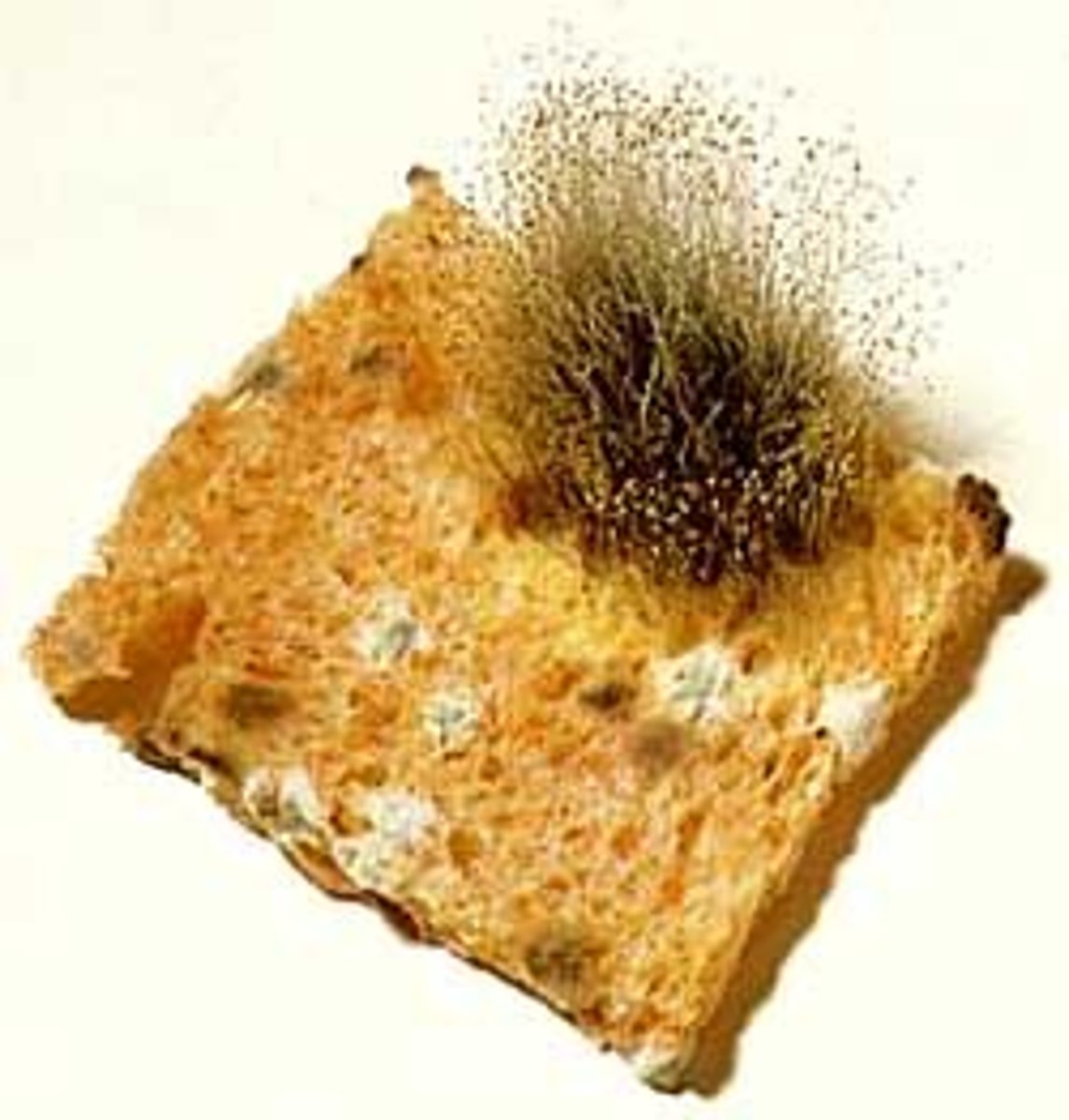

mildew
A type of fungus that affects plants or grows on inanimate objects, but does not cause human infections in the salon.

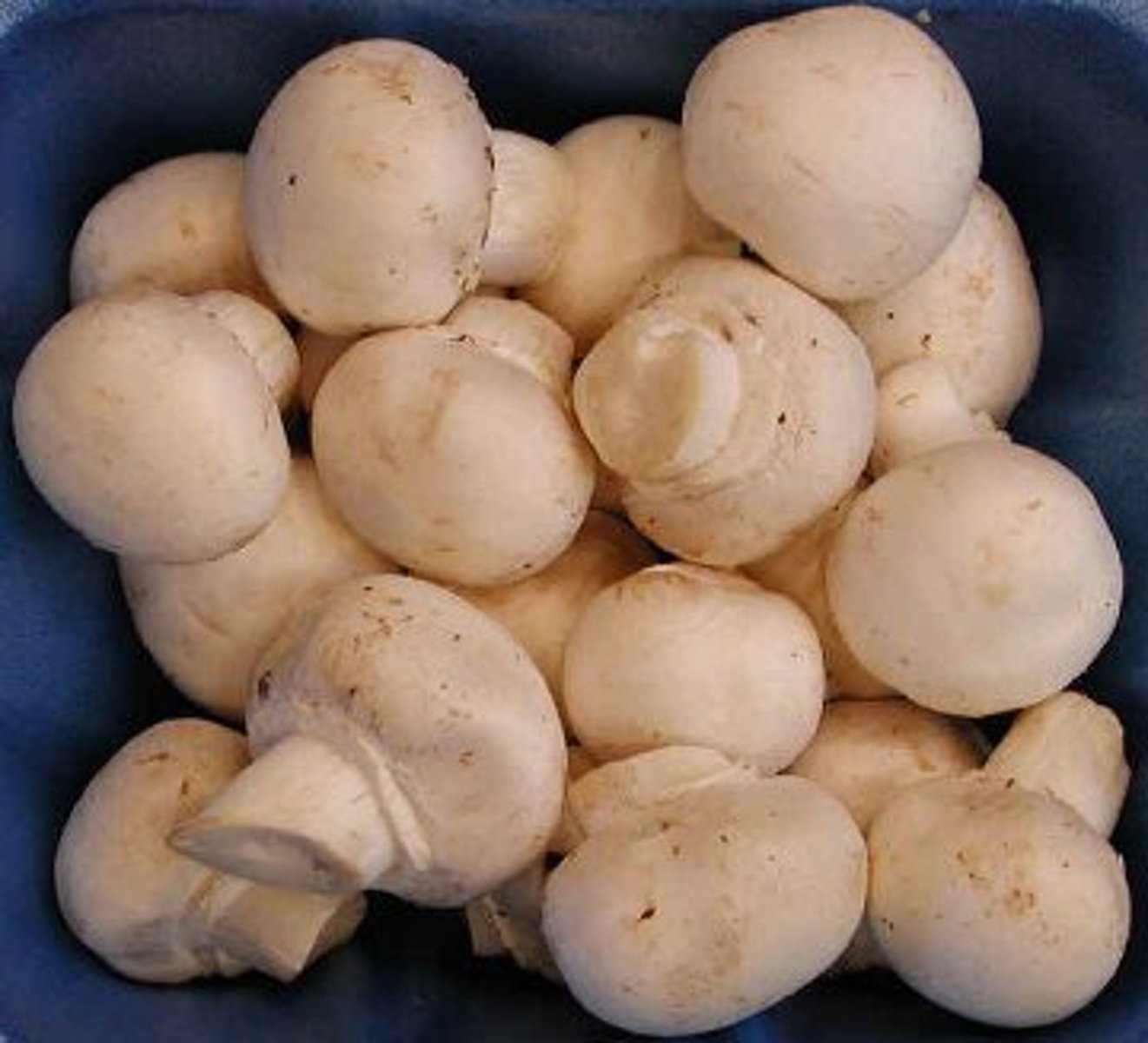
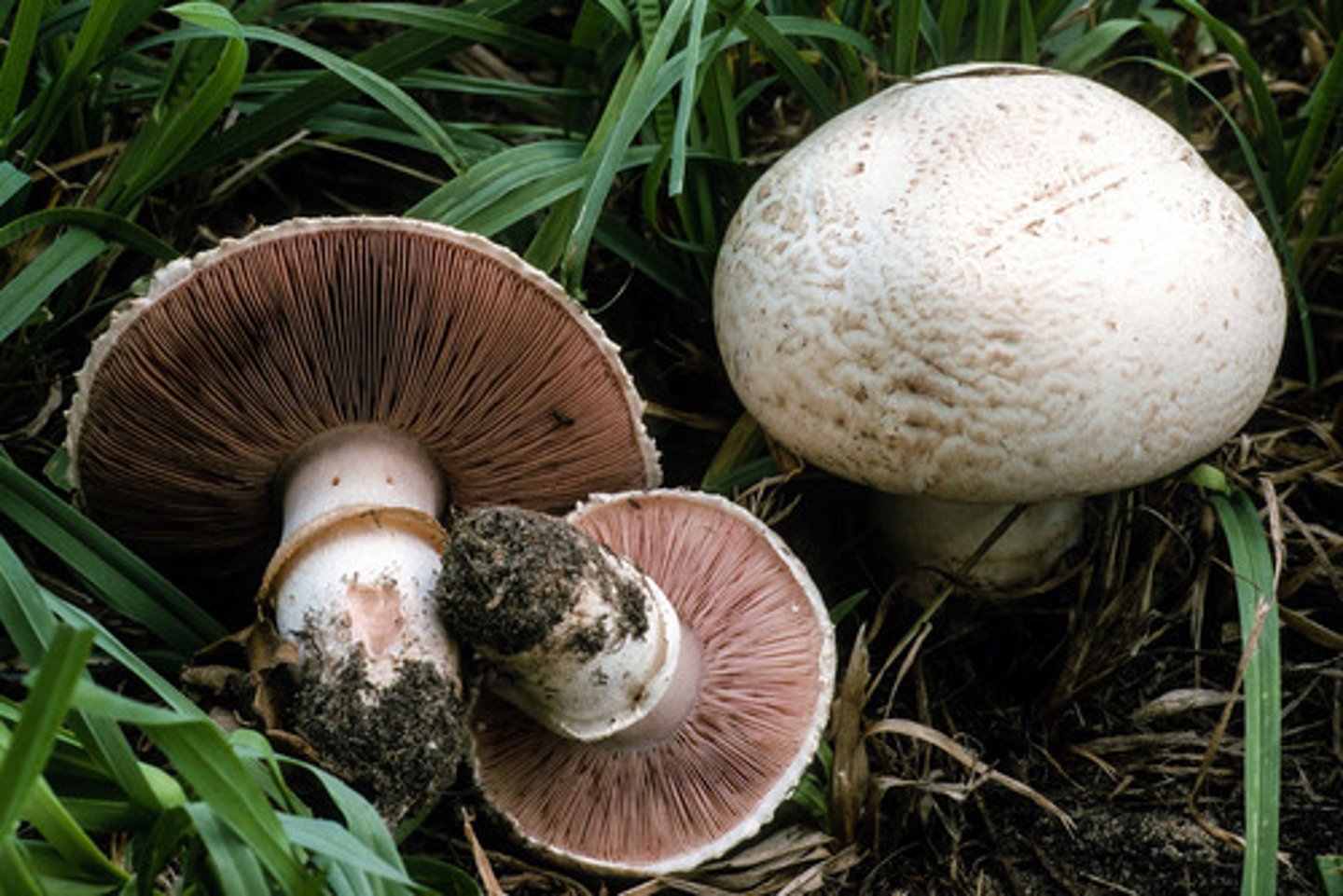
mushroom
a fleshy spore-producing growth of certain fungi

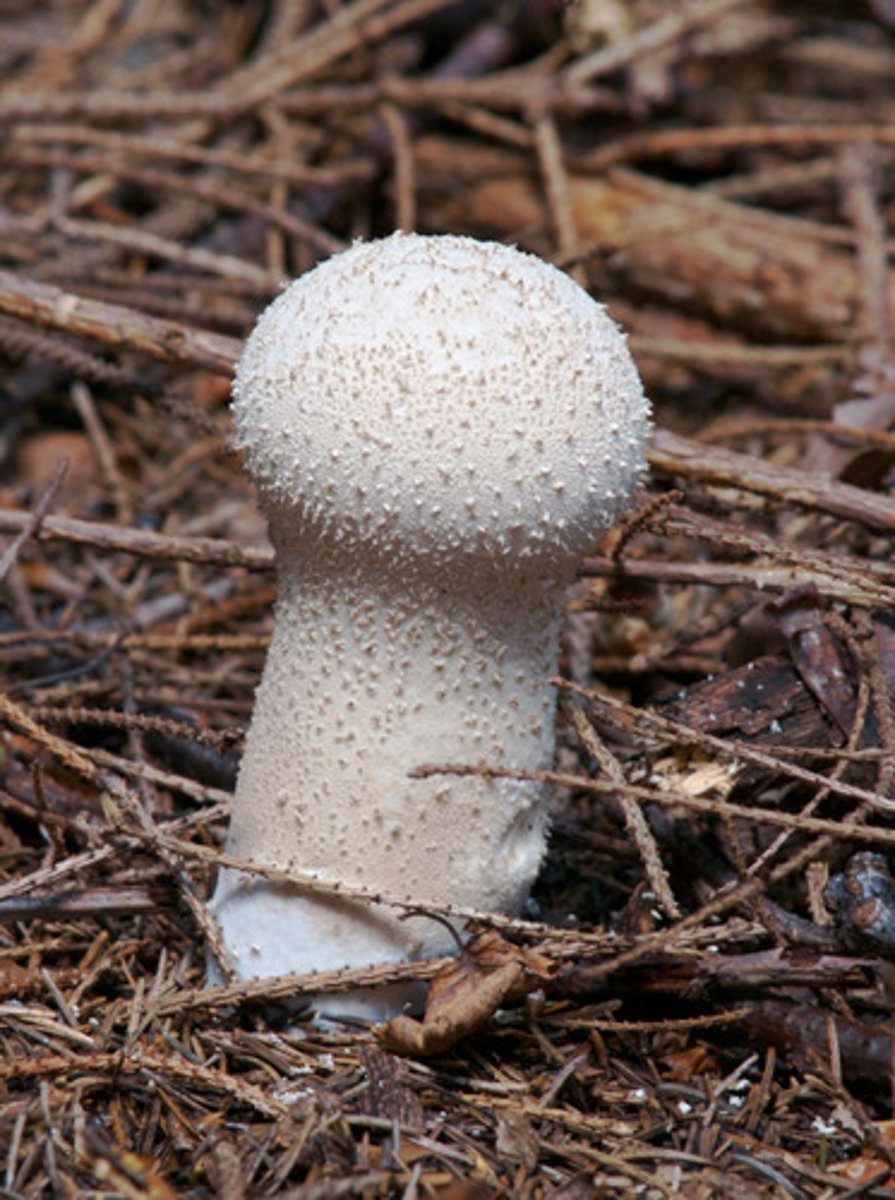
puffball
a macroscopic club fungus that bursts when mature, releasing a cloud of up to 7 trillion spores

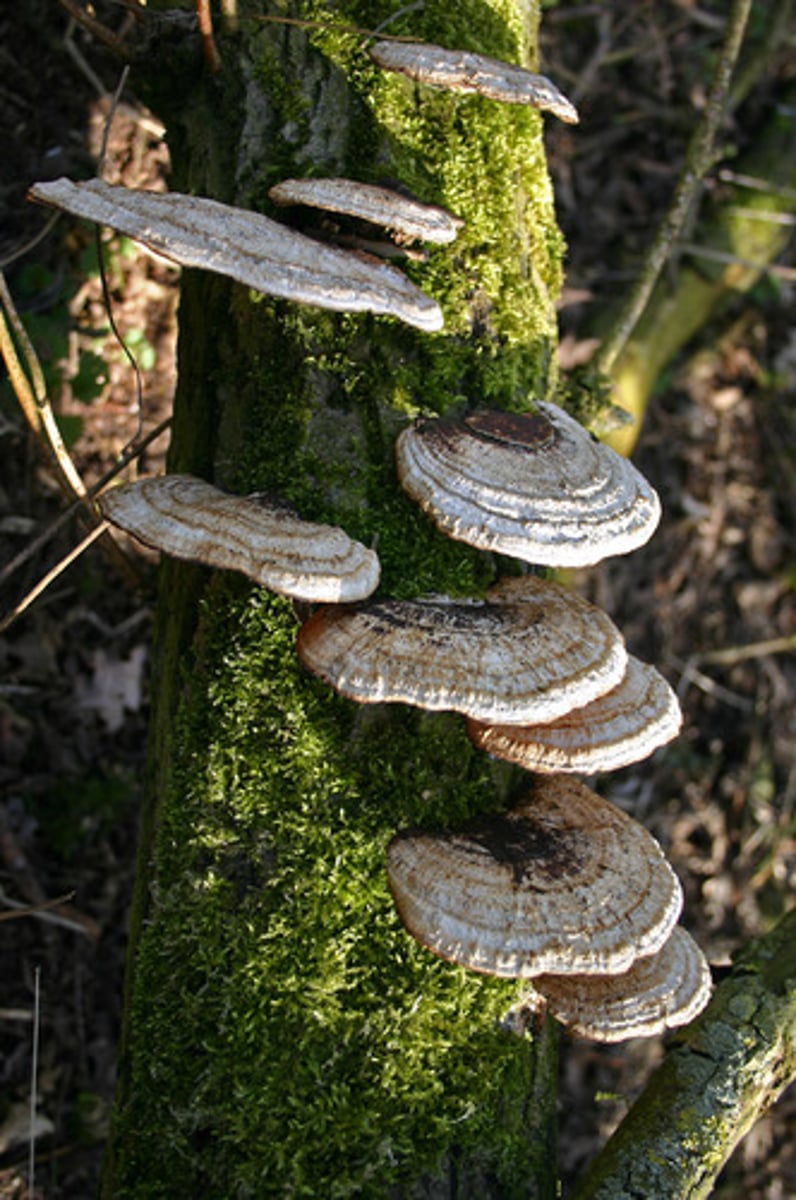
shell/bracket fungus

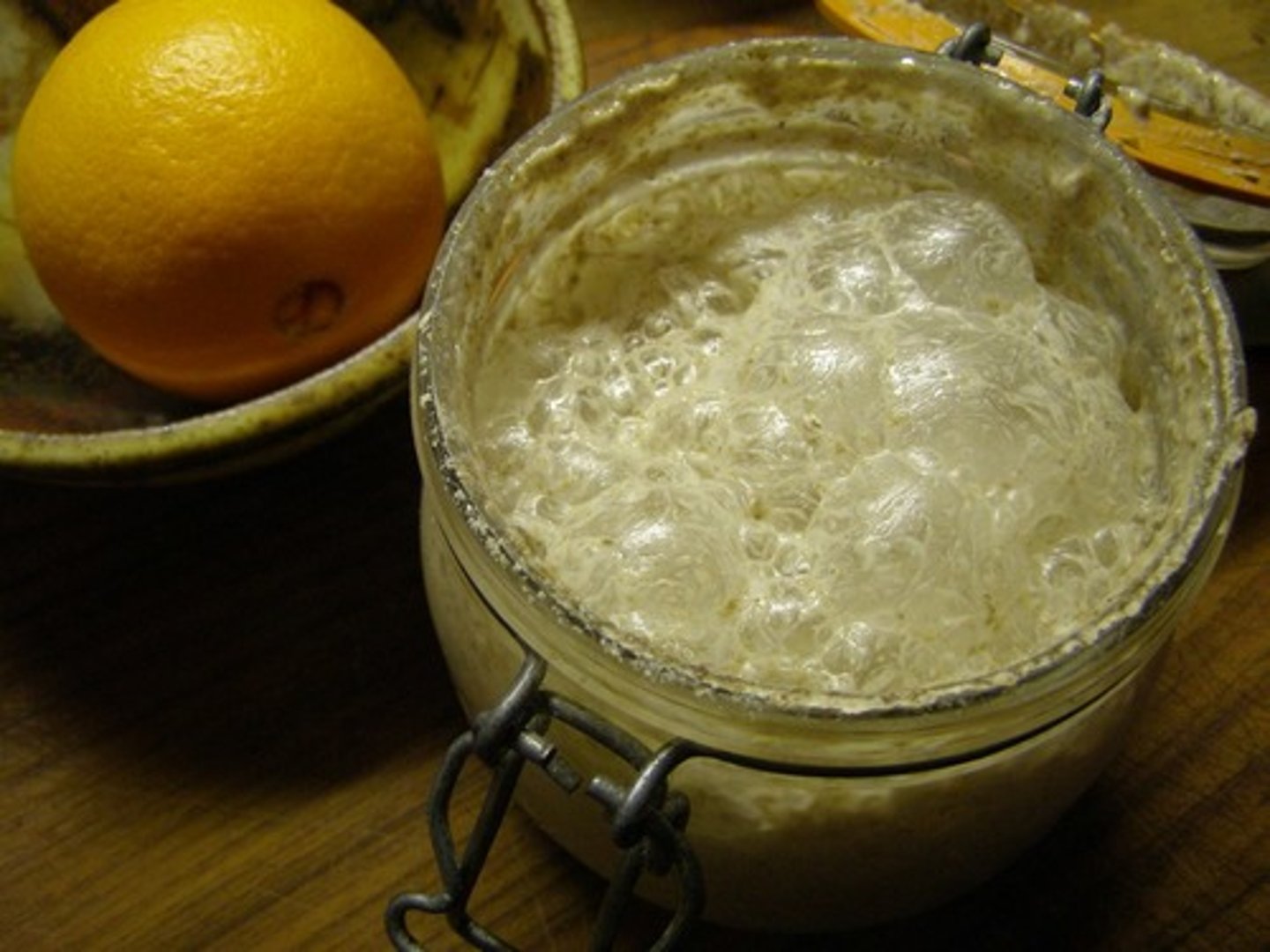
yeast
unicellular fungi

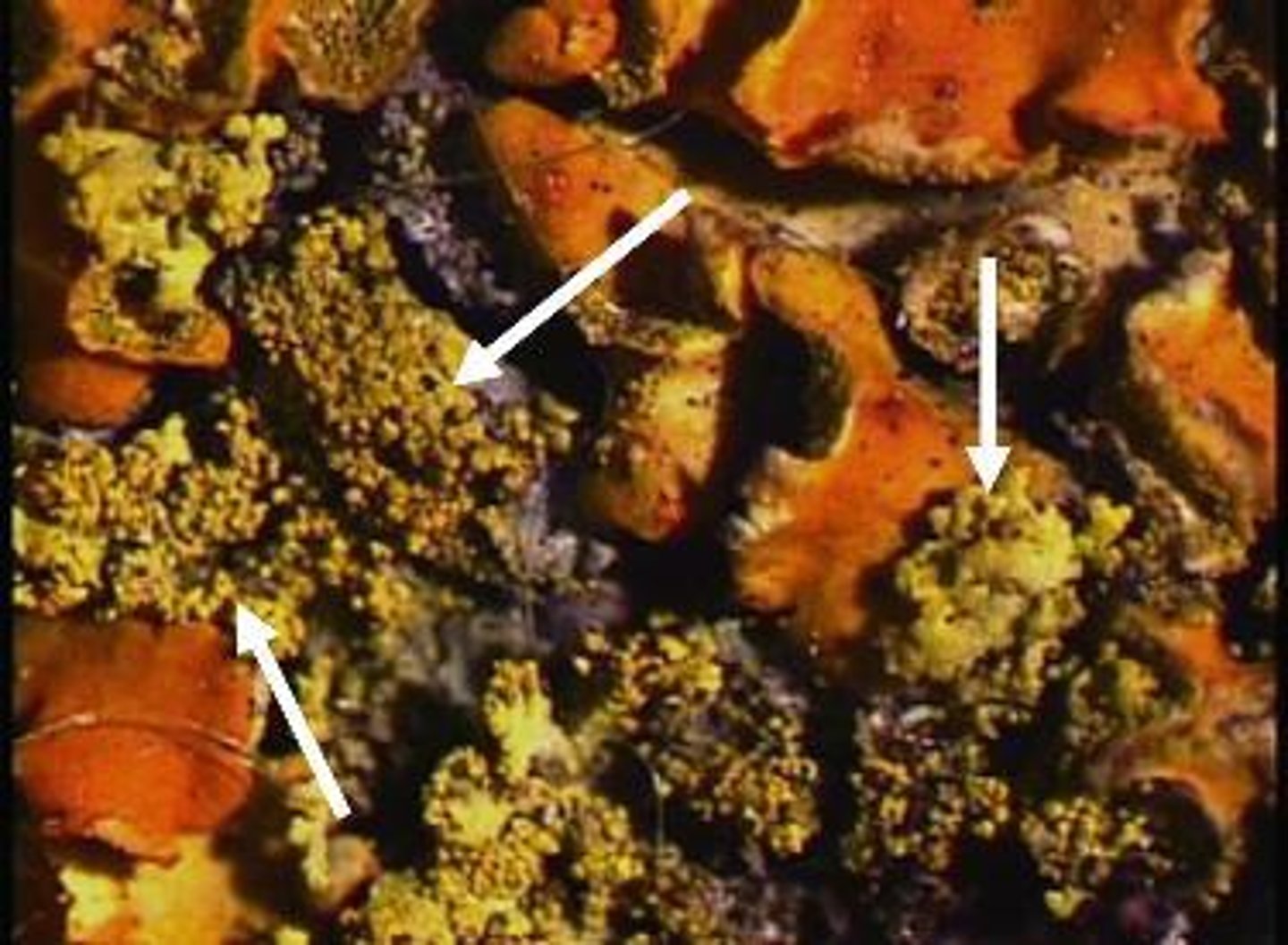
soredia
small clusters of hyphae with embedded algae

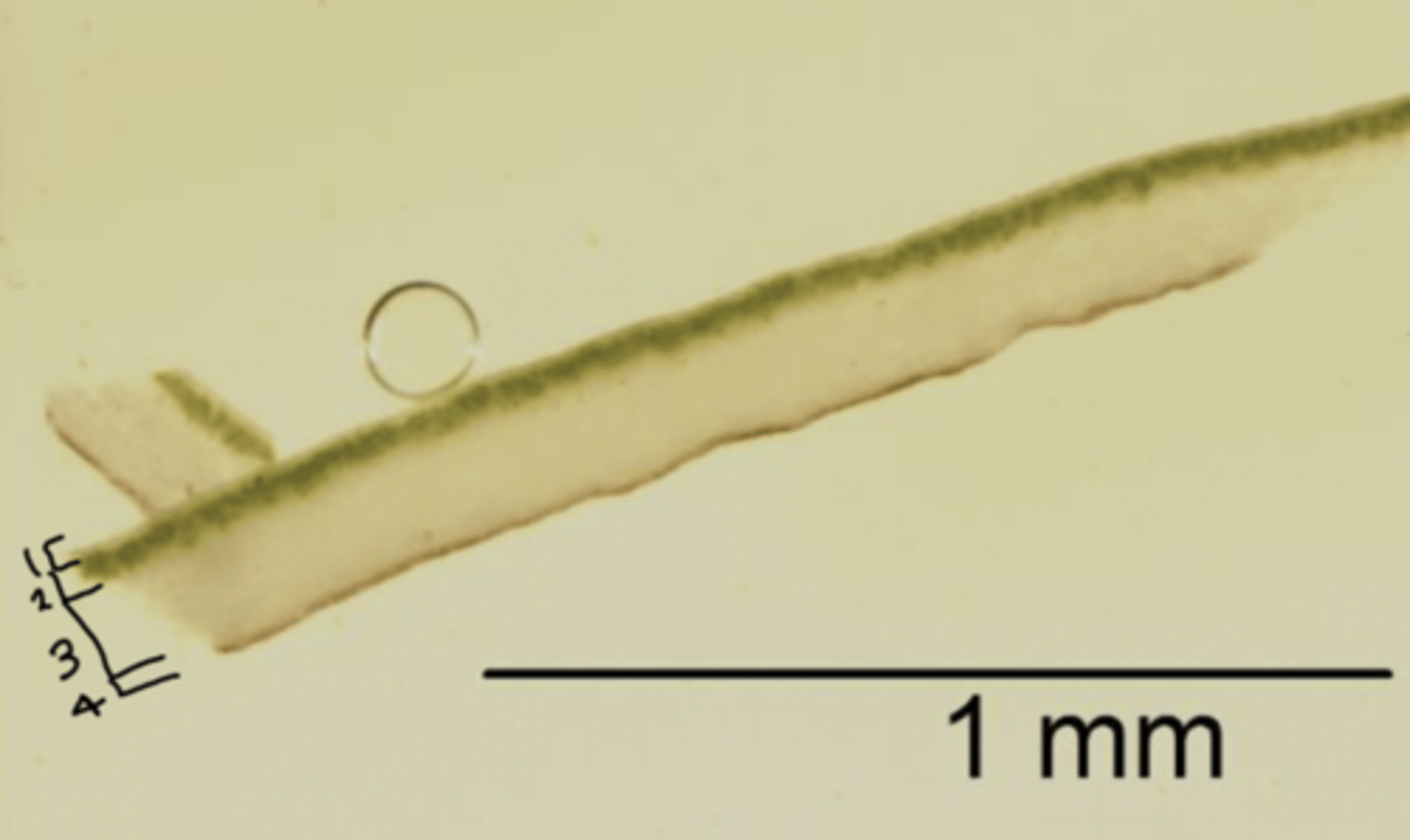
photobiont layer
has photosynthesizing green algae

mycotoxin
a toxin produced by a fungus
aflatoxin
carcinogenic toxin produced by Aspergillus
ergotism
poisoning produced by eating food affected by ergot, typically resulting in headache, vomiting, diarrhea, and gangrene of the fingers and toes.
penicillin
antibiotic
conidia
Asexual fungi spores of Ascomycetes
zygosporangium
thick-walled sexual structure that characterizes members of the phylum Zygomycota
zygospore
resting spore that contains zygotes formed during the sexual phase of a mold's life cycle
ascoma
a multicellular fruiting body of the cup fungi
ascocarp
in sac fungi, the reproductive structure in which haploid nuclei fuse to form a zygote
ascus
the reproductive structure where spores develop on sac fungi
ascospore
haploid spore produced within the ascus of ascomycetes
basidioma
a multicellular fruiting body of the club fungi
basidia
Reproductive structures that produce sexual spores
basidiospore
spore in basidiomycetes that germinates to produce haploid primary mycelia
gill fungi
any of the radiating leaflike spore-producing structures on the underside of the cap of a mushroom or similar fungus
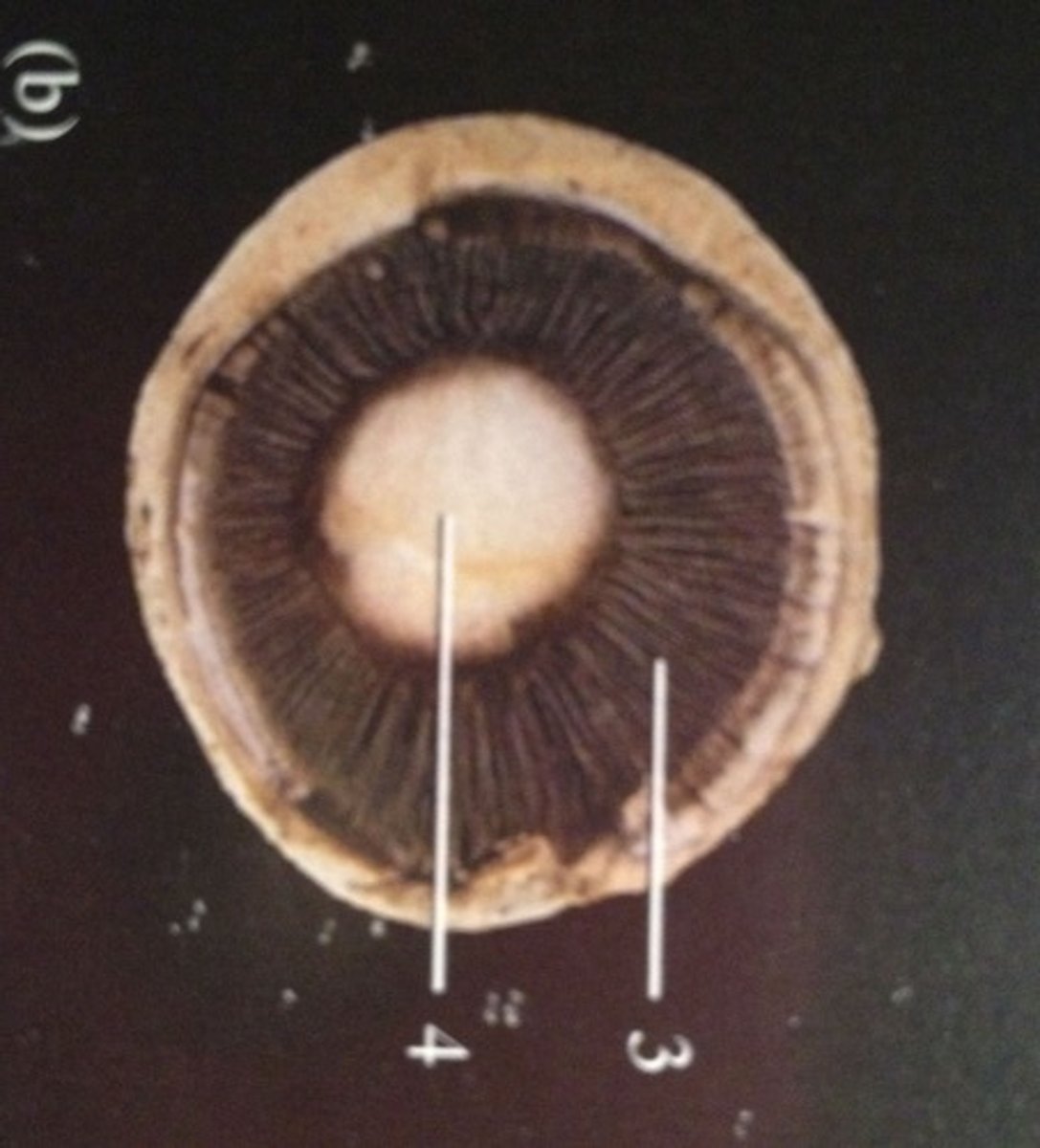
stalk fungi
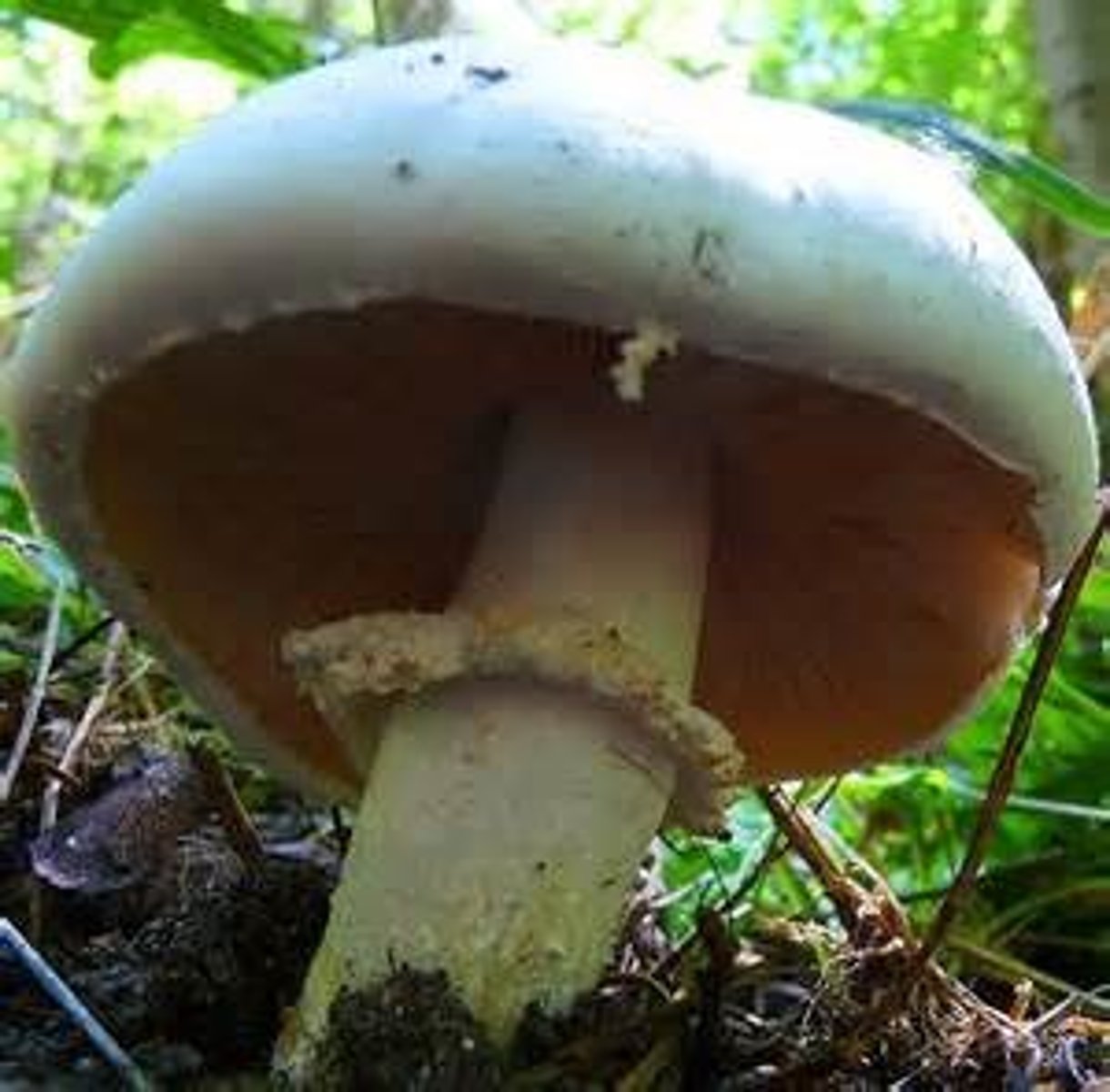

cap fungi
head

dikaryotic
Referring to a fungal mycelium with two haploid nuclei per cell, one from each parent.
eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
isomorphic
Referring to alternating generations in plants and certain algae in which the sporophytes and gametophytes look alike, although they differ in chromosome number.
heteromorphic
Referring to a condition in the life cycle of plants and certain algae in which the sporophyte and gametophyte generations differ in morphology.
phytoplankton
Microscopic, free-floating, autotrophic organisms that function as producers in aquatic ecosystems
red tide
An algal bloom that occurs in salt water
bioluminescence
the production of light by means of a chemical reaction in an organism
zooxanthellae
a yellowish-brown symbiotic dinoflagellate present in large numbers in the cytoplasm of many marine invertebrates.
fucoxanthin
The yellow to golden brown photosynthetic pigment of brown algae
phycoerythrin
red pigment in red algae
phycocyanin
A blue-green phycobiliprotein found in cyanobacteria, glaucophytes, cryptomonads and red algae.
carrageenan
a sticky polysaccharide that coats the cell walls of certain species of red algae and that is used in the food industry to control the texture of many food products
agar
a gel-like polysaccharide compound used for culturing microbes; extracted from certain red algae
alginates
consist of calcium salt of alganic acid that is extracted from seaweed. highly permeable and non-occlusive. requires a secondary dressing. based on the interaction of calcium ions in the dressing and the sodium ions in the wound exudate.
alternation of generations
the alternation between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte in a plant's life cycle
embryophyte
Another name for land plants, recognizing that land plants share the common derived trait of multicellular, dependent embryos.
megagametophyte
female gametophyte
microgametophyte
the male gametophyte produced by a microspore
archegonium
female reproductive structure in some plants, including mosses and liverworts
antheridium
Male reproductive structure in some algae and plants
zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
sphagnum peat
types of mosses with excellent air- and water-holding qualities
fiddle head
new fern frond
prothallus
small, green, heart-shaped gametophyte plant form of a fern that can make its own food and absorb water and nutrients from the soil
acrocarpous
having the reproductive organ at the end of the primary axis
pleurocarpous
in mosses, bearing the sporophyte on reduced lateral branches, correlated with lateral or creeping growth
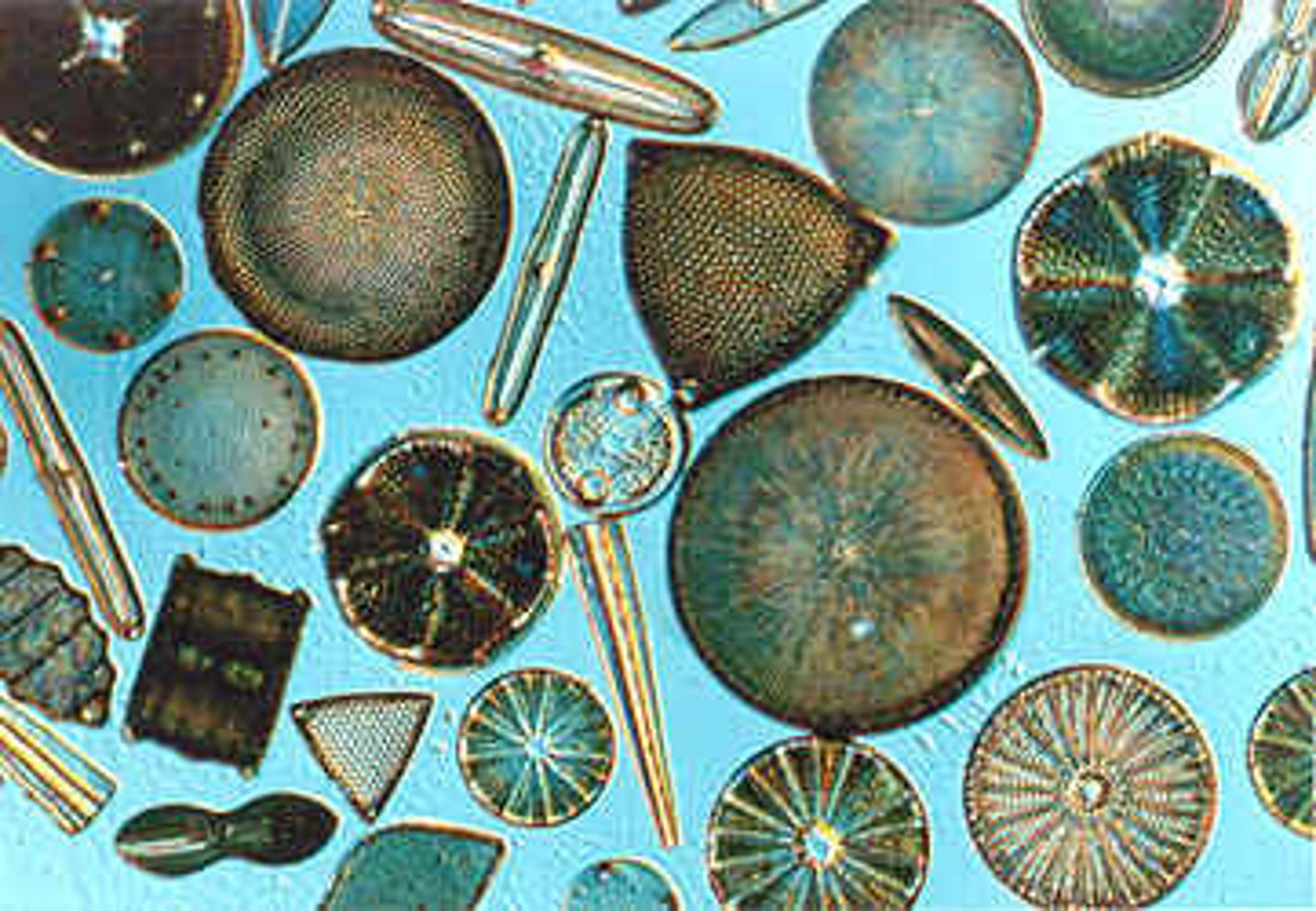
diatoms

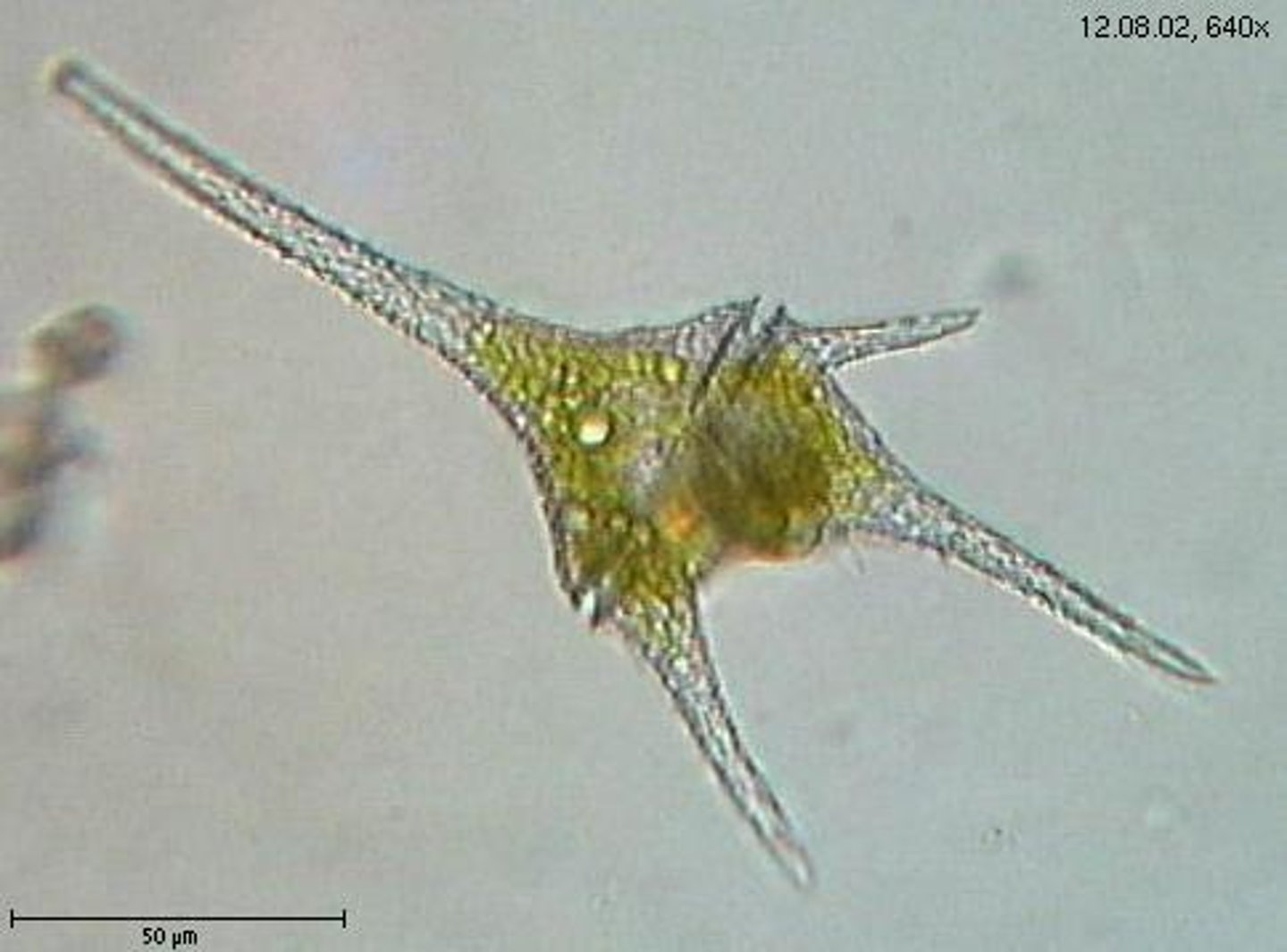
dinoflagellates

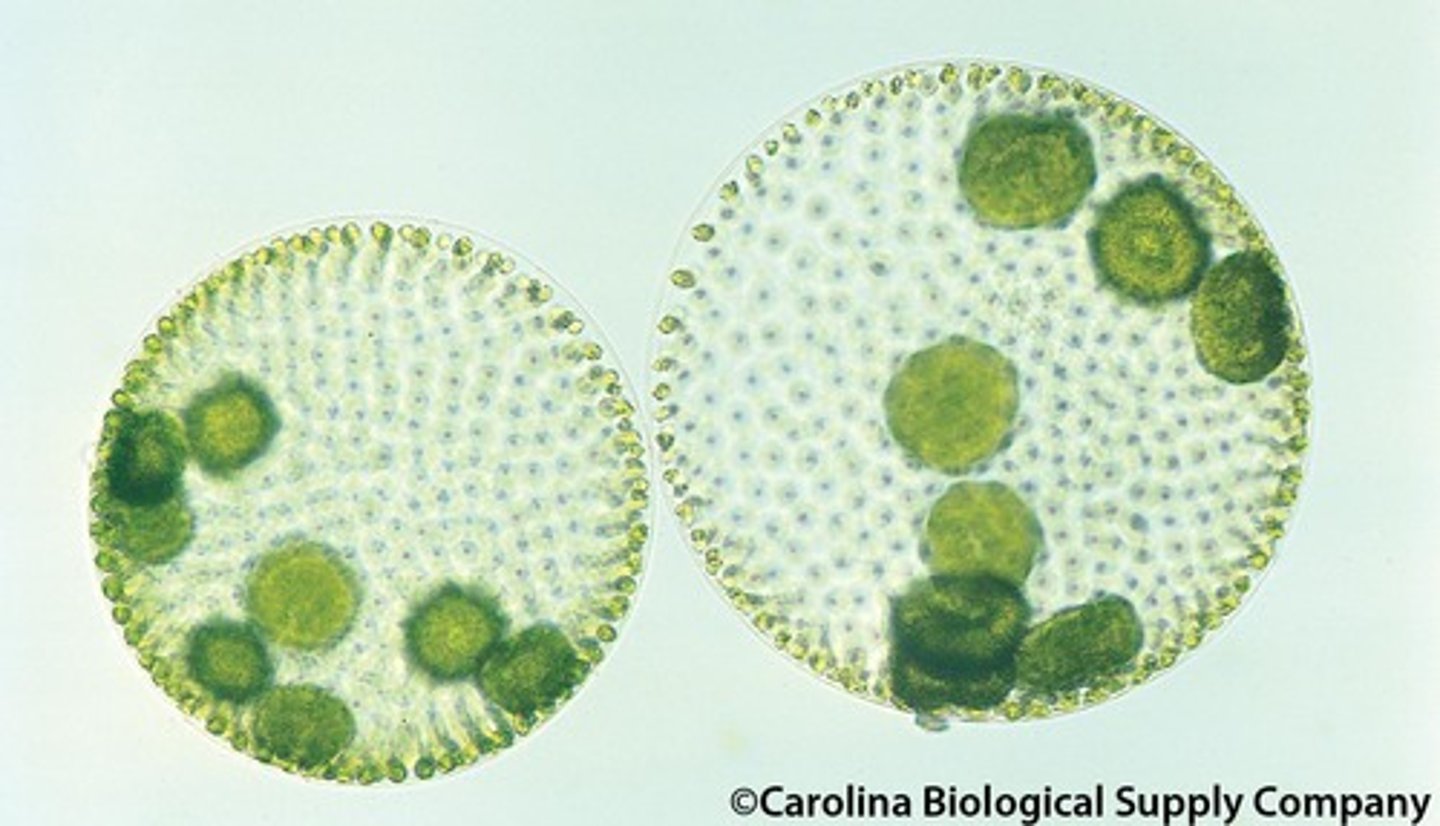
volvox
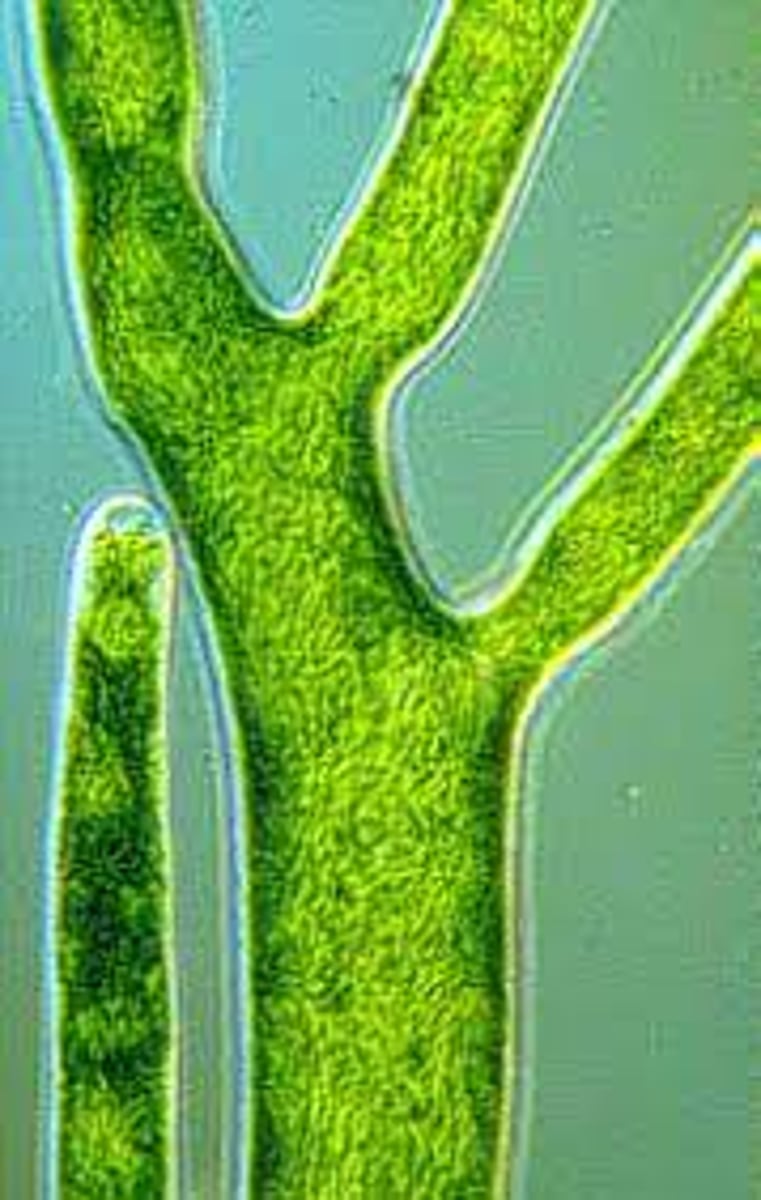
coenocytic alga
cyanobacteria