Fungal Diseases (PEARLS) - Candidiasis, Pneumocystis, Histoplasmosis, Cryptococcosis (Smarty PANCE)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
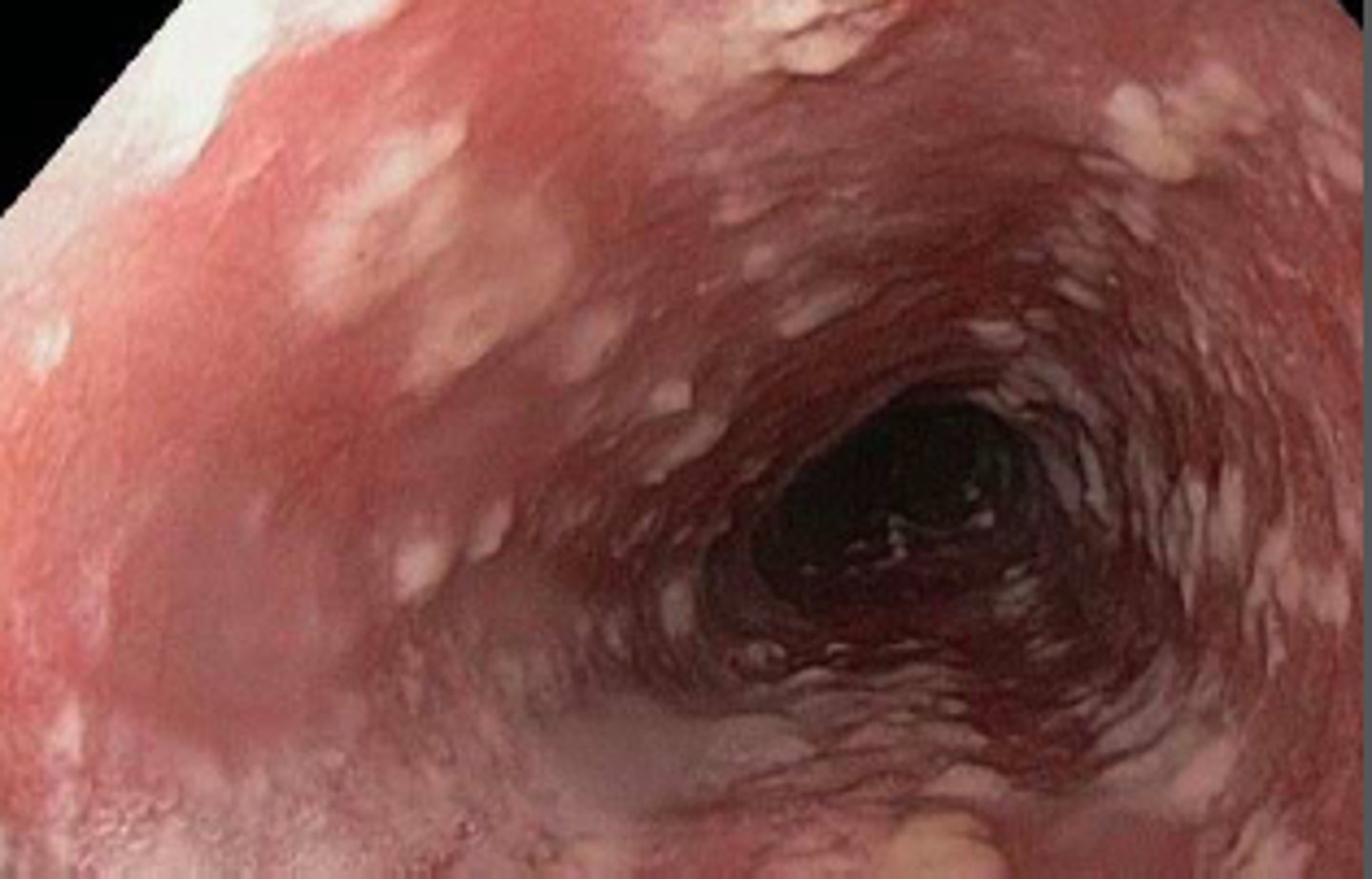
Esophageal Candidiasis diagnosis?
Diagnosis is by EGD with biopsy will demonstrate linear erosions on endoscopy
Vaginal Candidiasis treatment?
Treat with miconazole cream x 1-7 days or fluconazole 150 mg PO single dose
- Clotrimazole
- Terconazole
- Butoconazole
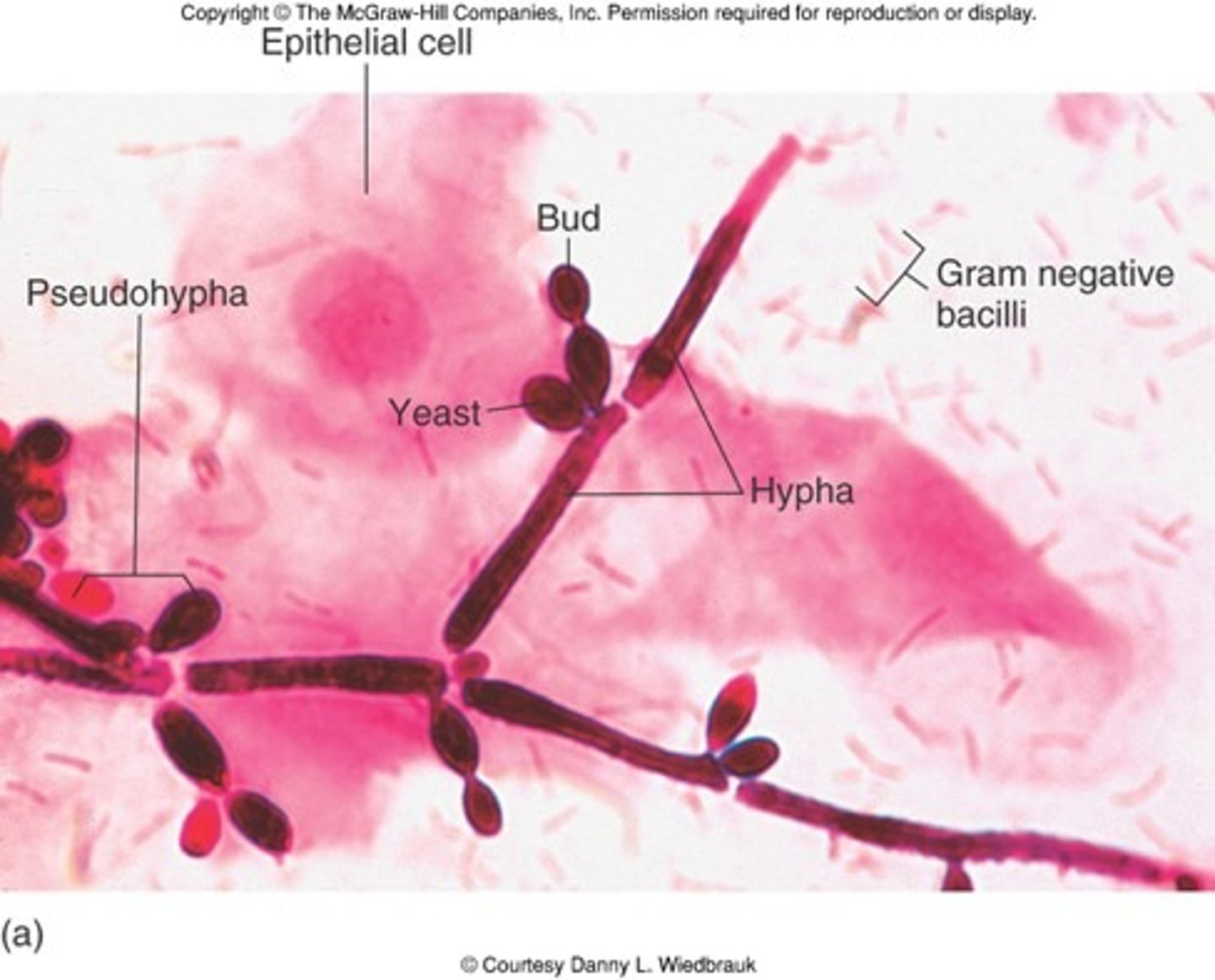
KOH vaginal candidiasis?
Will demonstrate budding yeast and hyphae
Intertrigo treatment?
Ketoconazole and Hydrocortisone 2.5% cream bid
- Ketoconazole and Desonide cream bid
- Zeasorb AF powder or Nystatin powder for prevention
- ZNP bar soap
Oral thrush treatment?
Nystatin (Mycostatin) oral suspension for oral thrush (swish and swallow) QID
Friable oral lesions white plaques that bleed if scraped?
Oral thrush
Moist macerated areas, pruritic rash BEEFY RED ERYTHEMA with distinct scalloped borders and satellite lesions. What's the dx?
Intertrigo
Risk factors for candidiasis?
HIV infection, recent antibiotic use, pregnancy, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, malnutrition, inhaled steroid use
An HIV patient presents with a nonproductive
cough and a CXR showing diffuse interstitial
infiltrates. What diagnosis should you be thinking
of?
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCJ) formerly known as Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
What is the newer and more appropriate species for a pneumocystis infection in humans?
Pneumocystis jirovecii. Pneumocystis carinii infects only rats and not humans.
What is the classic triad of Pneumocystis?
Dyspnea on exertion + fever + nonproductive cough
Besides the classic triad, what other symptom do patients with pneumocystis show?
Oxygen desaturation with ambulation
What is the definitive diagnostic test for pneumocystis infection?
Obtaining a respiratory tract specimen, either by tissue sample or by aspiration of secretions.
What test is run once they have a sample of the sputum?
Direct fluorescent antibody staining to see trophic and cyst forms of the fungus
T/F: Pneumocystis jirovecii is the most common opportunistic infection seen in HIV/AIDS.
True
How do you treat pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
(PCJ)?
Treat with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
21 days of Abx:
a) TMP-SMX (IV or PO); OR dapsone-trimethoprim OR
b) Pentamidine (IV); OR
c) Primaquine (PO) + Clinda (IV/PO) if sulfa allergy
Patients with pneumocystis pneumonia who have an arterial oxygen partial pressure (PaO2) less than 70 mmHg or alveolar-arterial gradient greater than 35 mmHg on room air should receive corticosteroids
What is the PCP prophylaxis in HIV?
Prophylaxis with daily Bactrim for high-risk patients with a CD4 < 200 or with a history of PJP infection
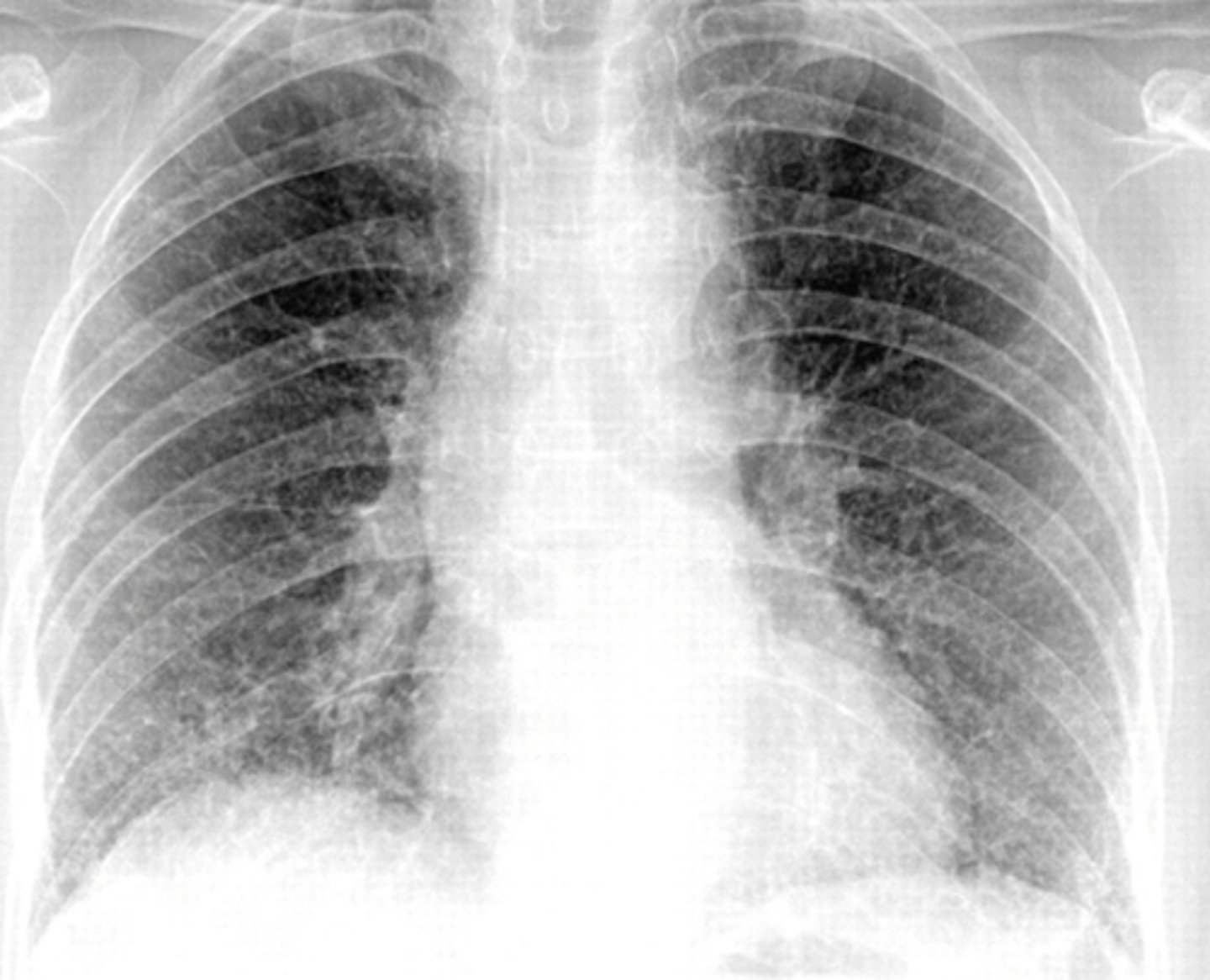
What does PCP look like on a radiograph?
Classic is bilateral diffuse symmetric finely granular opacities/reticular-interstitial airspace disease
What are the risk factors for PCP pneumonia?
Risk factors include not receiving ART, a CD4 cell count < 200, a CD4 cell percentage of less than 14 percent, previous episodes of PCP, oral thrush, recurrent bacterial pneumonia, unintentional weight loss, and higher plasma HIV RNA levels.
Labs of PCP pneumonia would show what?
Elevated LDH
If a patient has mild PCP with a G6PD deficiency and sulfa intolerance, how should they be treated?
Atovaquine in sulfa-intolerant patients
If a patient has moderate PCP with G6PD deficiency and sulfa intolerance, how should they be treated?
IV pentamidine (*avoid dapsone or primaquine)
What is Histoplasma capsulatum?
Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungi and an opportunistic fungus that is known to cause systemic disease in HIV patients that involves low-grade fevers, cough, hepatosplenomegaly and tongue ulceration.
Soil containing *birds and bat droppings* in the *Mississippi and Ohio River Valleys*
Histoplasmosis
Name three things that should make you think of Histoplasmosis?
1. Bats
2. Bat caves
3. Mississippi and Ohio River Valleys
What other communicable disease may Histoplasmosis mimic in presentation?
Histoplasmosis (fungus) may mimic tuberculosis in presentation and should always be borne in mind in spelunkers presenting with tuberculosis-like symptoms
What CD4+ cell count is associated with opportunistic Histoplasma capsulatum infections in HIV patients?
The CD4+ cell count of < 150 cells/mm3 is associated with opportunistic Histoplasma capsulatum infections in HIV patients.
Histoplasmosis is associated with what skin disease?
Histoplasmosis can cause erythema nodosum, a skin disease presenting with painful inflammatory lesions on the anterior shins
What is the method of spread for Histoplasma fungi?
Inhalation of fungal spores is the method of spread for Histoplasma fungi
Is histoplasmosis spread through person-to-person transmission?
Histoplasma does not show person-to-person transmission
Where can calcifications be seen on the chest x-ray of a patient with histoplasmosis?
Calcifications can be seen in the hilar region on the chest x-ray of a patient with histoplasmosis.
What is used to treat local or mild Histoplasma infections?
Local or mild Histoplasma infections are treated with the azole class of antifungals. Itraconazole orally for weeks to months is usually recommended.
What is used to treat disseminated histoplasmosis infection?
Amphotericin B is recommended for patients who cannot tolerate or fail itraconazole therapy or in patients with disseminated disease
Should you administer antifungal prophylaxis to prevent primary infection in HIV infected patients with CD4 counts below 150?
In general, do not administer antifungal prophylaxis with itraconazole to prevent primary infection with histoplasmosis since there are limited data to suggest the efficacy of prophylaxis, and most patients will have immune recovery (ie, increased CD4 count) on antiretroviral therapy. However, in areas where histoplasmosis is hyperendemic (>10 cases/100 patient-years), such as certain parts of South America and French Guiana, some providers administer itraconazole (200 mg daily) to patients with CD4 counts ≤150
A 43-y/o HIV+ patient develops confusion, nausea, staggering gait, and headache. Lumbar puncture shows organisms seen on India ink stain.
Cryptococcosis
Soil contaminated with pigeon/bird droppings?
Cryptococcosis - If soil contaminated with pigeon/bird droppings are mentioned you should be thinking Cryptococcosis.
NOTE: Soil containing birds and bat droppings in the Mississippi and Ohio River Valleys you should be thinking histoplasmosis
Involves the brain and meninges, lungs, and skin. Caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans, common in AIDS and immunocompromised states, is considered an AIDS-defining illness.
Cryptococcosis
How is Cryptococcus transmitted?
It is transmitted through inhalation (soil, bird and pigeon feces) and causes illness in patients with cellular immune deficiency, such as HIV, cancer, or long-term corticosteroid therapy.
How does Cryptococcus present?
In immunocompetent patients, infection is typically asymptomatic and self-limited. In immunocompromised patients, Cryptococcus may disseminate to many sites, commonly to the brain and meninges, and to the skin. Manifestations of cryptococcosis depend on the affected area. In patients with AIDS, cryptococcal meningitis may cause minimal or no symptoms, but headache frequently occurs and sometimes slowly progressively altered mental status. Those with pneumonia usually have cough and other nonspecific respiratory symptoms. Dermatologic spread can manifest as pustular, papular, nodular, or ulcerated lesions, which sometimes resemble acne , molluscum contagiosum , or basal cell carcinoma .
Cryptococcus diagnosis
Diagnose using culture, staining, and/or serum and cerebrospinal fluid testing for cryptococcal antigen.
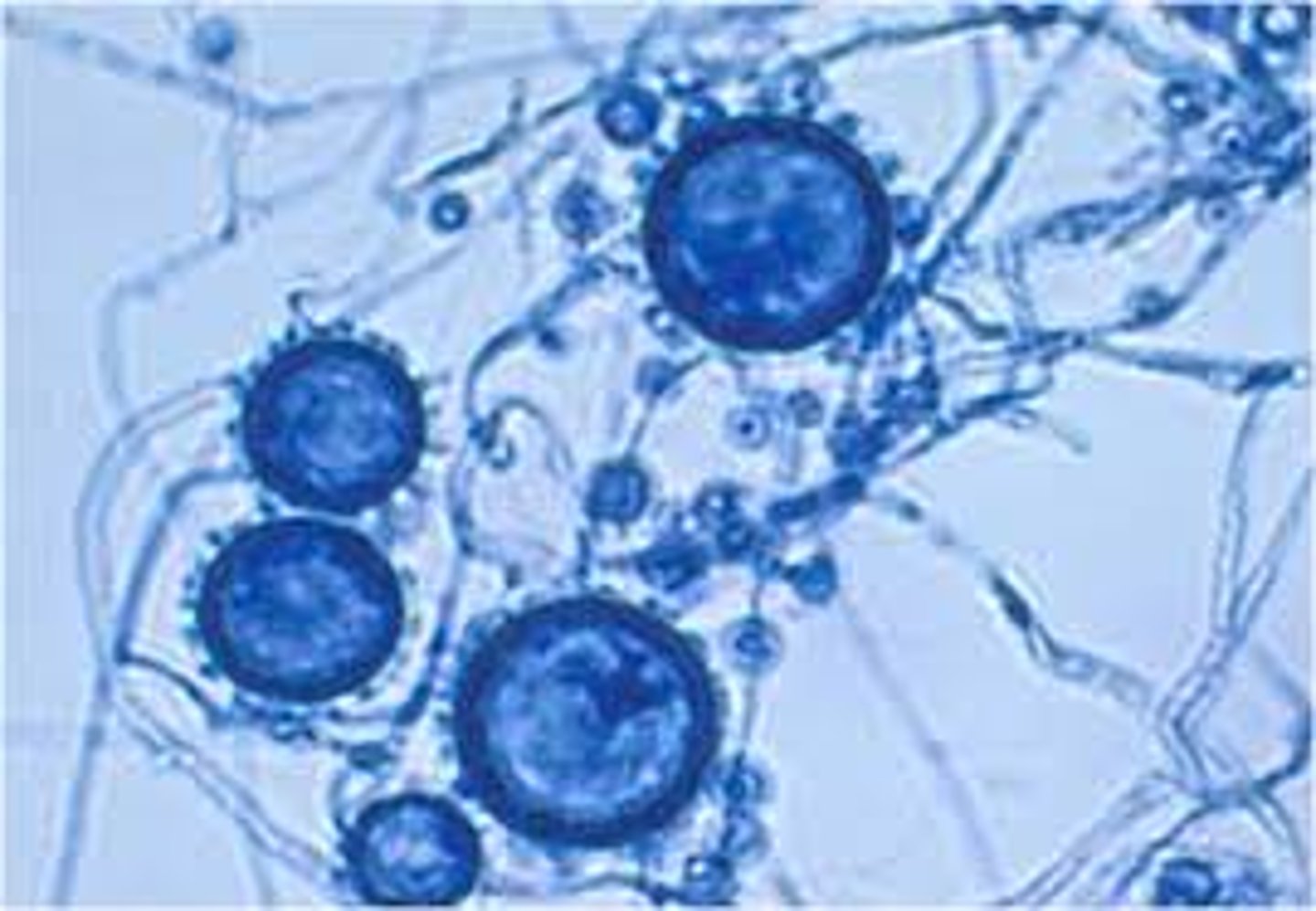
What diagnostic finding should make you think of Cryptococcus?
An India ink stain showing cysts
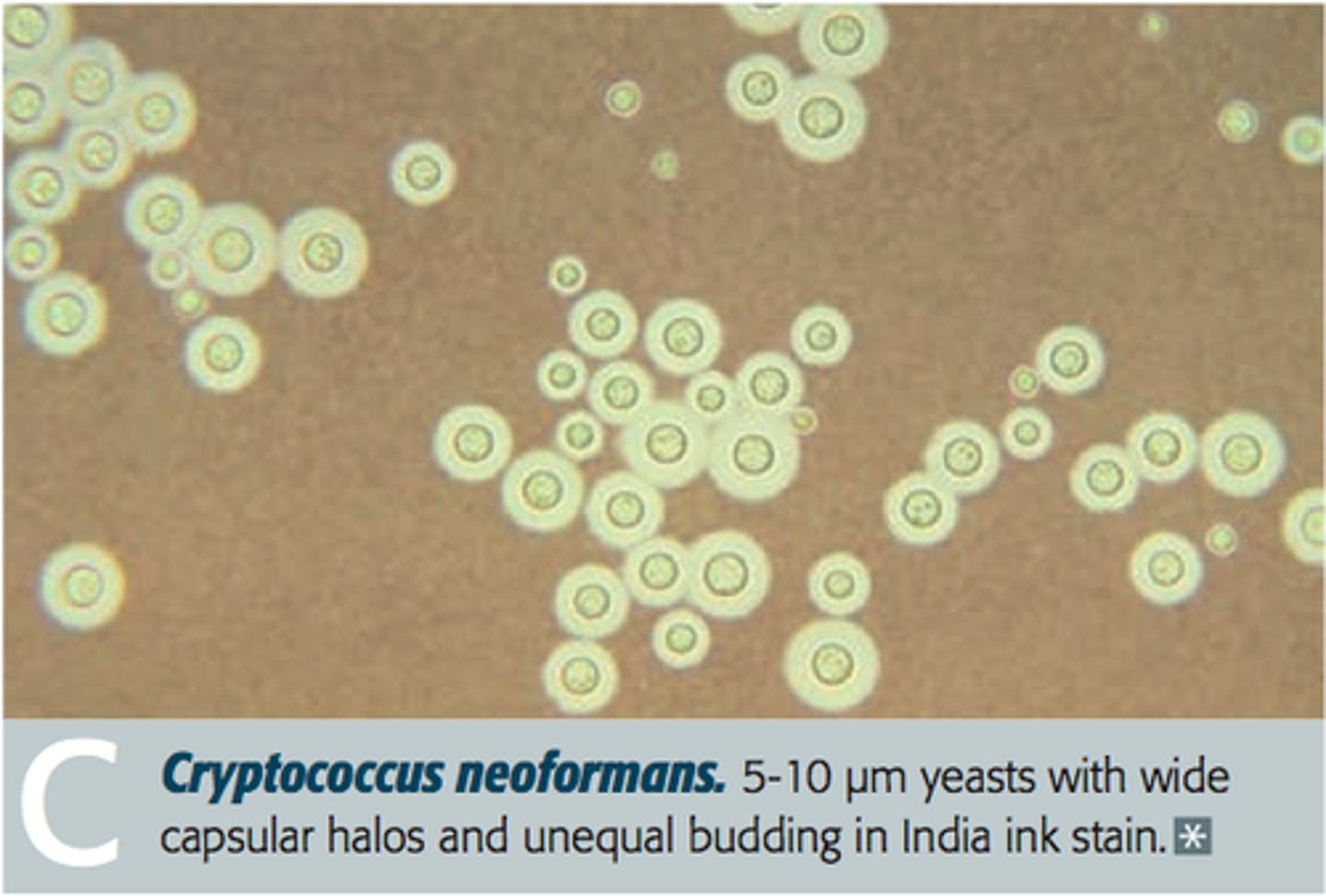
Treatment of Cryptococcus?
Treat with Amphotericin B + Flucytosine for 2 weeks followed by Fluconazole for 10 weeks.
Cryptococcosis prophylaxis?
Fluconazole if CD4 < 100
Amphotericin B side effects?
Anti-fungal. HIGHLY TOXIC
- infusion reactions (fever and chills)
- nephrotoxicity
- hypokalemia
- hepatoxicity
- gynecomastia
- C/I with aminoglycosides (just like PCN)