Vocab - Neuromuscular
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Frontal Lobe
thinking, memory, behavior and movement
intellect, personality, reasoning, behavior, self-awareness, executive functions
Parietal Lobe
language and touch
touch, kinesthesia, vibration, meaning for objects, language, words
Temporal Lobe
hearing, learning and feeling
auditory and olfaction, speck, memory
Occipital Lobe
vision/sight
visual info, light, color, shapes, 3D, cortical blindness with bilateral lobe involvement = blind
Cerebellum
balance and coordination
Brain Stem
breathing, HR, temp
ASIA Impairment scale:
A
= complete
no motor/sensory function at S4 - S5
ASIA Impairment Scale:
B
= sensory incomplete
sensory intact, no motor
sacral sensory sparing
ASIA Impairment scale:
C
= motor incomplete
some sparing of motor function 3 levels below
MMT 3 and below
sacral motor sparing
ASIA Impairment scale:
D
= motor incomplete
50%+ of key muscle functions 1 level below
More muscle function, most key muscles below injury are stronger (MMT ≥3/5).
ASIA Impairment scale:
E
= normal
Spinal Shock Syndrome
build up of edema and inflammatory response
Edema builds 3- 6 days s/p SCI
Immediate, temporary loss of power, sensation, and reflexes below the lesion
Autonomic Dysreflexia
A dangerous, sudden spike in blood pressure caused by an irritating stimulus below the level of a spinal cord injury (usually at or above T6)
AD S&S
Severe, pounding headache
Dangerously high BP
Flushed face / sweating above injury
Goosebumps below injury
Bradycardia
Nasal congestion
Anxiety
Cold, pale skin below injury
If head goes red…
raise the head (AD)
If head goes pale…
raise the tail (OH)
agnosia
the inability to recognize faces, voices, object, or places
apraxia
impairment of voluntary skilled learned movement
Dix-Hallpike Test
measures the presence of posterior canal BPPV
do the Epley’s maneuver for tx
To make a wheelie easier, shift the axle…
FORWARD
Median N lesion
Attempting to make a fist, 1-3 fingers do not flex
d/t weakness of flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus on the radial side (innervated by median n.)
ulnar N lesion
Loss of 3 - 4 lumbricals
Hand at rest - 4th and 5th fingers appear flexed
UMN Signs
Spasticity, clonus, hypertonia, hyper reflexive, positive Babinski sign
LMN signs
Muscle wasting, flaccidity, hypotonia, hypo reflexive
“Lazy Motor Neurons”
Deep Tendon Grading:
0
absent, no reflex
Deep Tendon Grading:
1+
diminished, race, or seen only with reinforcement
Deep Tendon Grading:
2+
active normal response
Deep Tendon Grading:
3+
brisk, exaggerated response; often with spread to other muscle groups
Deep Tendon Grading:
4+
clonus, very brisk, hyperactive with clonus
Grades 0 - 1 (Deep Tendon Grading) indicates…
indicates a LMN lesion
Grades 3 - 4 (Deep Tendon Grading) indicates…
indicates a UMN
Broca’s Area
knows what to say, but cannot say it
they understand but cannot speak
affecting the frontal lobe
“Expressive / Non-fluent aphasia”
Wernicke’s Area
talks but words don’t make much sense
They DON’T understand but CAN speak
affecting the temporal lobe
“Receptive / Fluent Aphasia”
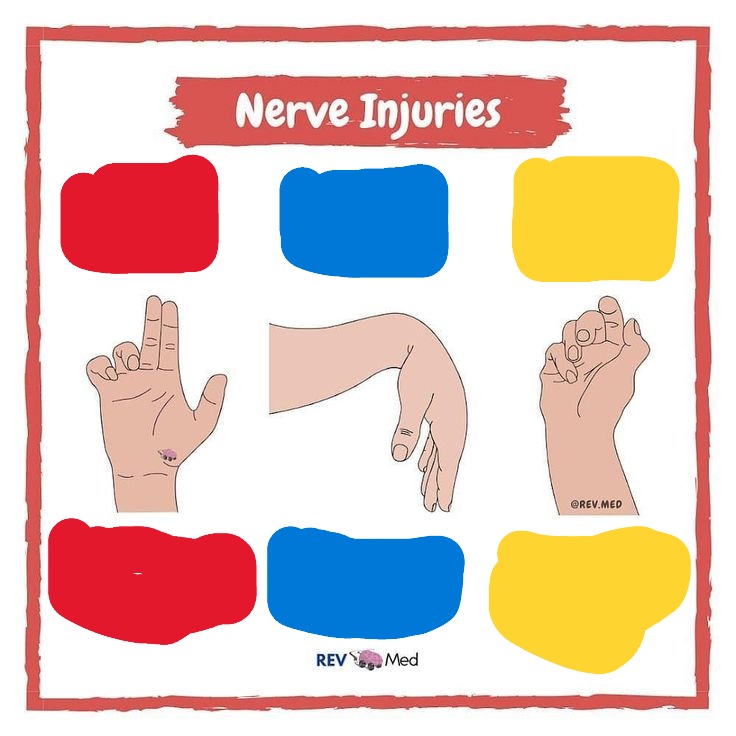
Red
Median N
Ape Hand
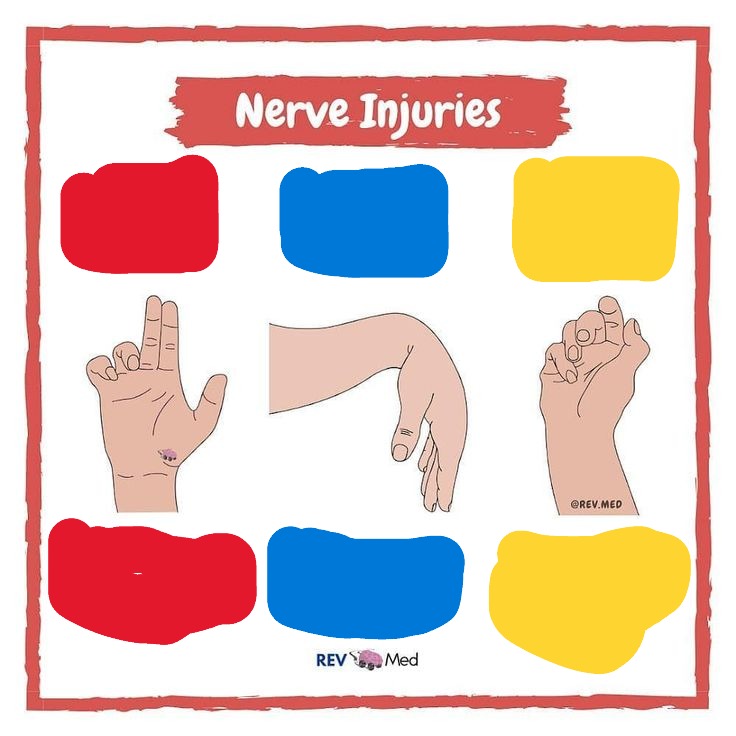
Blue
Radial N
Wrist Drop
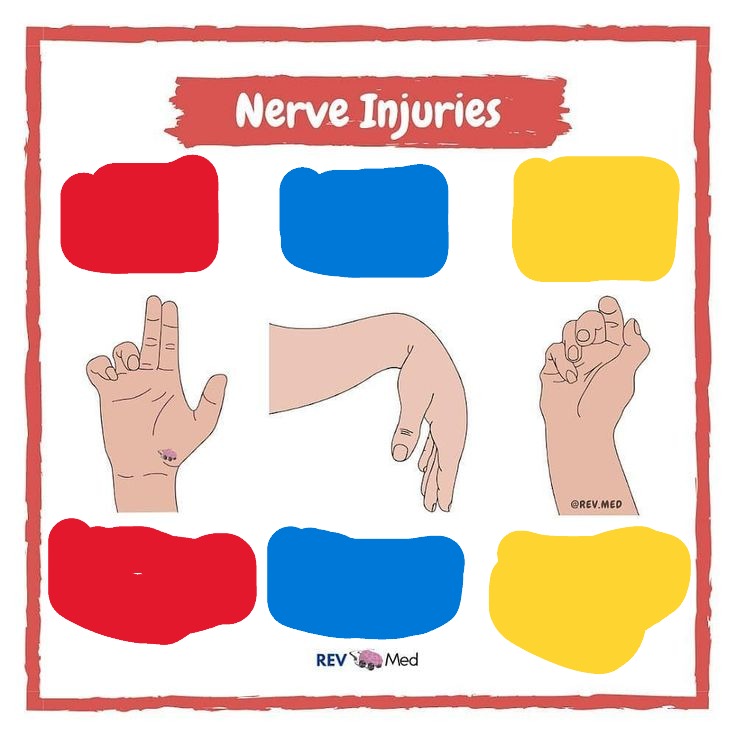
Yellow
Ulnar N
Claw Hand
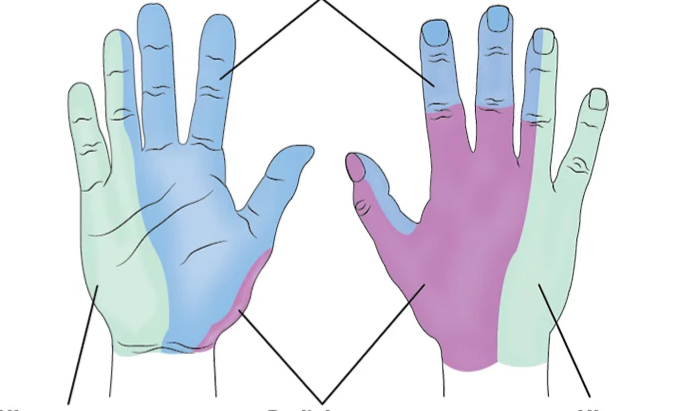
What nerve is with Green?
Ulnar N
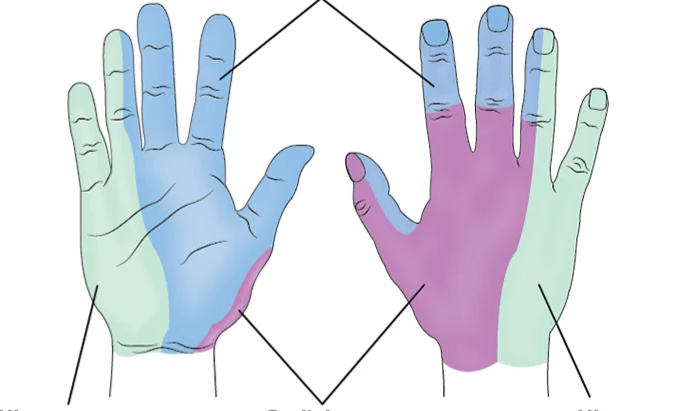
What nerve is with Blue?
Median N
What nerve is with Purple?
Radial N
spasticity
velocity-dependent increase in muscle tone
Meniere’s Disease
A disorder of the inner ear caused by excess fluid (endolymph), leading to episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and ear fullness/pressure.
Blocked Practice
practice of a single motor skill repeatedly
Variable Practice
practice of varied motor skills in which the performer is required to make rapid modifications of the skill in order to match the demands of the task
Random Practice
practice of a group or class of motor skills in random order
Serial Practice
practice of a group or class of motor skills in serial or predictable order
Mobility
The ability to initiate movement through a functional range of motion
Stability
The ability to maintain a position or posture through contraction and tonic holding around a joint. Unsupported sitting w/ midline control is an example of stability through contraction and tonic holding
controlled mobility
The ability to move w/in a weight bearing position or rotate around a long axis. Activities in prone on elbows or weight shifting in quadruped are examples of controlled mobility.
Inhibition Techniques define
decrease tone or calm spastic muscles
used when a muscle is tight, overactive or spastic
Facilitation Techniques define
increase muscle activation
used when a muscle is weak, low tone, or needs to fire
Facilitation Techniques - how to
Tapping
Quick stretch
Approximation
Weight-bearing
High-frequency vibration
Fast movements
Inhibition Techniques - how to
Prolonged stretch
Deep pressure
Slow rocking / rhythmic movement
Neutral warmth / heat
Joint traction
Low-frequency vibration
stupor
general unresponsiveness with arousal from repeated stimuli
obtunded
state of unconsciousness that is a state of sleep, decreased alertness to arousal, delated response to stimuli
delirum
state on consciousness with disorientation, confusion, agitation, loudness
UE Flexion Synergy Pattern
Scapula: Retraction
Shoulder: Abduction, ER
Elbow: Flexion
Forearm: Supination
Wrist/Finger: Flexion
UE Extension Synergy Pattern
Scapula: Protraction
Shoulder: Adduction, IR
Elbow: Extension
Forearm: Pronation
Wrist/Finger: Flexion
LE Flexion Synergy Pattern
Hip: Flexion, Abduction, ER
Knee: Flexion
Ankle: DF, inversion
LE Extension Synergy Pattern
Hip: Extension, Adduction, IR
Knee: Extension
Ankle: PF, inversion
Median N glide
Shoulder depression + slight abduction
Elbow extension
Wrist/finger extension
Forearm supination
Neck side bend away
Radial N glide
Shoulder depression + abduction
Elbow extension
Forearm pronation
Wrist/finger flexion
Shoulder internal rotation
Neck side bend away
Ulnar N glide
Shoulder depression + abduction
Elbow flexion
Forearm pronation
Wrist/finger extension
Shoulder external rotation
Neck side bend away
Max score on Berg Balance is …
56 = normal
Berg Balance score of 45 or below = …
high fall risk
Berg Balance score of 40 or below = …
severe fall risk
Who is more prone to get autonomic dysreflexia?
SCI levels T6 and above