Chapter 8 Mcgraw hill questions
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
The structural (not functional) classification of a freely movable joint enclosed in a joint capsule is a(n) ___ joint.
synovial
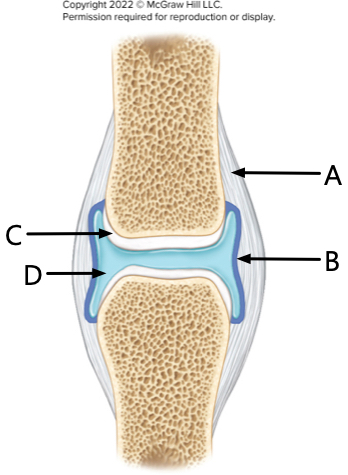
What is label A?
Fibrous Layer
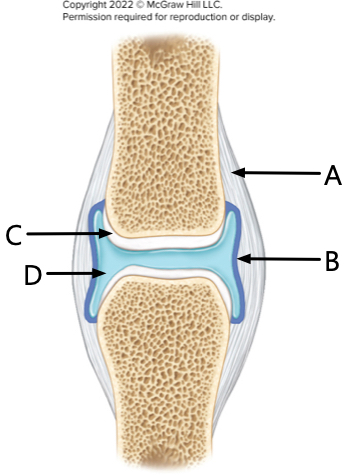
What is label B?
synovial membrane

What is label C?
articular cartilage
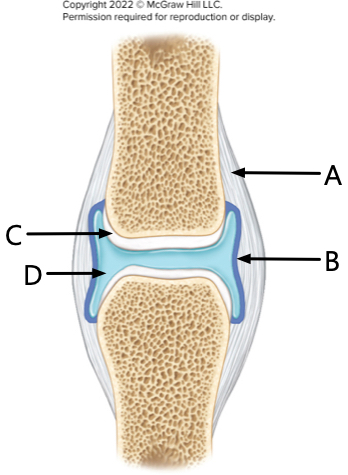
What is label D?
synovial fluid
The ______ of a synovial joint encloses the joint and ensures that bone ends cannot be pulled apart.
joint capsule
In general, wherever two bones come together, a junction called a(n) ___ is formed.
articulation, joint, articulations, or joints
Where is articular cartilage located?
Covering the bone ends in a synovial joint
At synovial joints, the joint capsule is reinforced by relatively inelastic ____ that help stabilize the joint and bind together the bone ends.
ligament
Which of the following can be found connecting two bones in a cartilaginous joint?
hyaline cartilage
Choose the three components of a typical synovial joint.
Synovial membrane, Joint capsule, Articular cartilage
The synovial ____ lines most of the area within the joint capsule of a synovial joint.
membrane
The joint ____ of a synovial joint encloses the joint and prevents bone ends from being pulled apart.
capsule
A functional junction between bones is called a(n) _____
articualtion
The synovial membrane synthesizes ______.
synovial fluid
What connects two bones together in a synovial joint?
ligaments
what are the features of the synovial membrane?
It secretes and reabsorbs synovial fluid, It may have villi, folds, and projections, It is only a few cells thick, It can store adipose tissue.
describe the location of the synovial membrane.
They cover all the surfaces of a synovial joint, except the parts covered by articular cartilage.
The ______ of a synovial joint encloses the joint and ensures that bone ends cannot be pulled apart.
joint capsule
Which structure functions to lubricate the joint and nourish the structures in the joint? It also contains stem cells for tissue repair.
synovial fluid
Where does the fluid found within the synovial cavity come from?
It is secreted by the synovial membrane.
The menisci found in some synovial joints are attached to the ______ at the periphery of the joint cavity.
joint capsule
What functions are served by the menisci found in some synovial joints?
They help distribute body weight.
Identify three types of synovial joints.
Condylar, Ball-and-socket, Plane
Indicate three functions of the synovial fluid.
It provides nutrients to the articular cartilage, It moistens and lubricates the cartilaginous surfaces in the joint, It contains stem cells.
A globular head articulating with a deep cup. is what type of joint?
Ball and socket joint
Some synovial joints contain fibrocartilage discs called ______.
menisci
Structures called ____ that are found in some synovial joints cushion the articulating surfaces and help distribute body weight at joints such as the knee.
menisci
There are six major types of synovial joints based on their shapes and the movements they permit: ball-and-socket joints, ____ joints, plane joints, ____joints, pivot joints, and saddle joints.
hinge; condylar
A synovial joint consisting of a bone with an egg-shaped head that articulates with the cup-shaped cavity of another bone is called a ______ joint.
ball-socket joint
A type of synovial joint called a(n) ____ joint consists of articulating surfaces that are nearly flat and are slightly curved.
plane
The menisci found in some synovial joints are attached to the ______ at the periphery of the joint cavity.
joint capsule
What joint only allows for movement in one plane (uniaxial) that is described as a bending and straightening motion?
hinge joint
A(n) ____ joint consists of the cylindrical surface of one bone rotating in a ring formed by another bone and a ligament.
pivot
What best describes the surface of the articulating bones in a condylar joint?
An ovoid condyle on one bone end and an elliptical cavity on the other
Flexion is a movement where the two bones or parts of the body are moved ______ each other.
closer to
What best describes the surface of the articulating bones in a plane joint?
Two articulating flat surfaces slide over one another.
What best describes the surface of the articulating bones in a hinge joint?
A convex surface of one bone fits into the concave surface of another.
Bending your knee is an example of what type of movement?
Flexion
What types of movement is characteristic of a hinge joint?
It allows for a bending and straightening movement.
What best describes the surface of the articulating bones in a pivot joint?
A cylindrical surface on one bone rotates in a ring formed by the other bone and a ligament.
A movement that increases the angle between bones at a joint, moving them farther apart, is called ______ of the joint.
extension
A movement that decreases the angle of a joint, bringing the bones closer together, is called .
flexion
The movement that results in straightening a bent elbow is an example of
extension
Hyperextension is ______.
extension beyond anatomical position
Bending your elbow is an example of ______ a joint.
flexing
Movement at the ankle that brings the foot closer to the shin is called
dorsiflexion
What type of articulation forms between the head of the radius and the capitulum of the humerus in the elbow joint?
A plane articulation
Abduction is defined as a movement of a limb______ the midline of the body.
away from
Bending the trunk to the side, is what type of flexion?
lateral flexion
The two articulating surfaces of the hip joint are the _____ of the femur and the _____ of the hip bone
head; acetabulum
When you spread your fingers apart, you are ______ them.
abducting
The rounded head of the _____ articulates with the shallow glenoid cavity of the ____ to form the shoulder joint.
humerus; scapula
The elbow joint contains two articulations. The articulation between the trochlea and trochlear notch is a ______ joint.
hinge
Moving a part away from the midline of the body or the axial line of a limb is called
abduction
The hip joint consists of the head of the ___ and the acetabulum of the pelvis.
femur
Lifting your arm horizontally to form a right angle with the side of the body involves a movement called ____ of the arm.
abduction
What two bony structures articulate to make the shoulder joint?
Glenoid cavity of the scapula, Head of the humerus
Articulation between humerus and ulna involves which bone surfaces?
Trochlea of the humerus, Trochlear notch of the ulna
Articulation between humerus and radius involves which two bone surfaces?
Capitulum of the humerus, Fovea of the radius
Abduction is defined as a movement of a limb ______ the midline of the body.
away from
The knee joint includes several articulations. Indicate the articulations that are part of the knee joint.
Articulation between the tibia and the femur, Articulation between the femur and the patella
The hip joint is an articulation between what two bony structures?
Head of the femur, Acetabulum of pelvis
When you spread your fingers apart, you are ______ them.
abducting
When considering the classification of joints based on the shape of the articulating bone ends, the knee functions as a type of synovial joint called a modified____ joint.
hinge
What type of articulation forms between the head of the radius and the capitulum of the humerus in the elbow joint?
A plane articulation
Joint between the femur and patella is what type of joint?
plane joint
The femur articulates anteriorly with the patella in ______ joint.
knee
The joint capsule of the knee is______ and ______ reinforced by muscles and ligaments.
thin; is
Which movements are allowed at the knee?
Extension, Flexion
Two of the ligaments that stabilize the knee joint are the _____collateral ligament and the ____ collateral ligament.
fibular: tibial
The tibiofemoral joint is a ______ joint.
hinge (modified)
The joint between the patella and the femur is a ______ joint.
plane
Even though it is relatively thin, the joint capsule of the knee is greatly strengthened by many ____ and the _____ of several muscles.
ligaments; tendons
In addition to flexion and extension, the modified hinge articulation at the knee joint also allows a certain degree of ____ when the knee is flexed.
rotation
The patellar, arcuate popliteal, and oblique popliteal ligaments are ligaments that stabilize the ______ joint.
knee joint
Which joint functions as a modified hinge joint?
knee joint
Joint between the femur and patella is what type of joint?
plane
The tibiofemoral joint is a ______ joint.
hinge
The joint between the patella and the femur is a ______ joint.
plane
What structures of the knee joint function to separate and align the articular surfaces within the joint capsule?
Menisci
What are the primary movements that occur at the knee joint?
Flexion and extension
The lateral and medial menisci of the knee form depressions upon the condyles of the tibia that fit the corresponding ______ of the femur.
condyles
The two _____ ligaments (anterior and posterior) serve to prevent displacement of the articulating surfaces of the knee joint.
cruciate