Animal reproduction
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
asexual reproduction budding, fission, parthenogenesis
asexual: budding new organism developing from a bud or outgrowth of the parent,
fission involves the splitting of the parent into two or more daughter organisms.
parthenogenesis (production of an embryo from a female gamete without any genetic contribution from a male gamete)
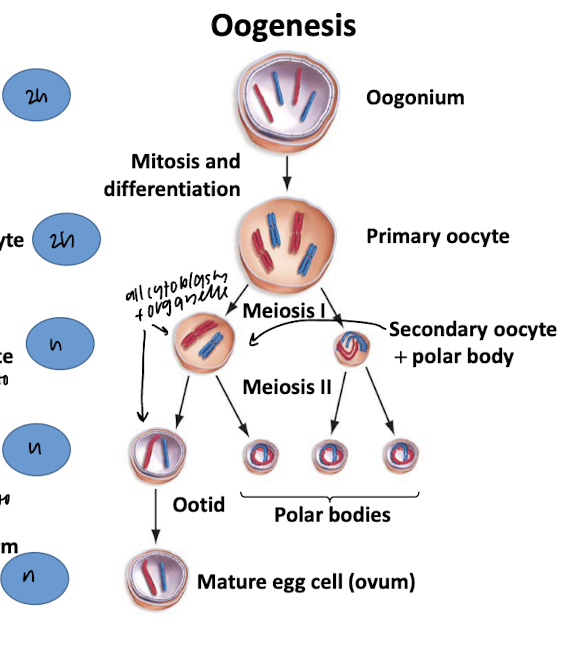
spermatogenesis
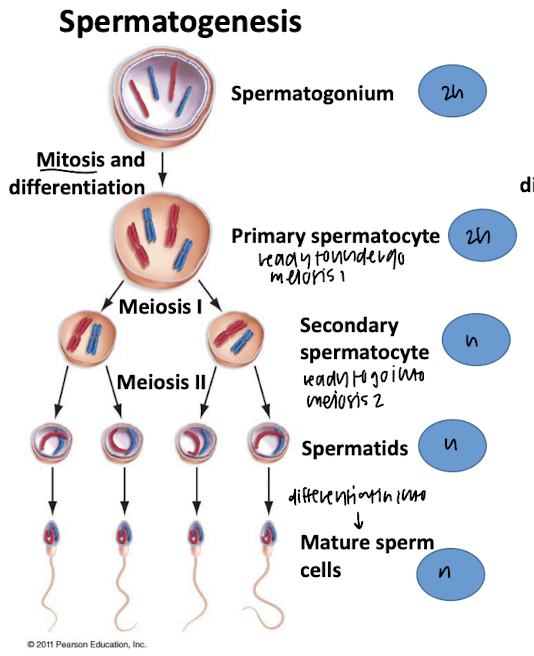
oogenesis
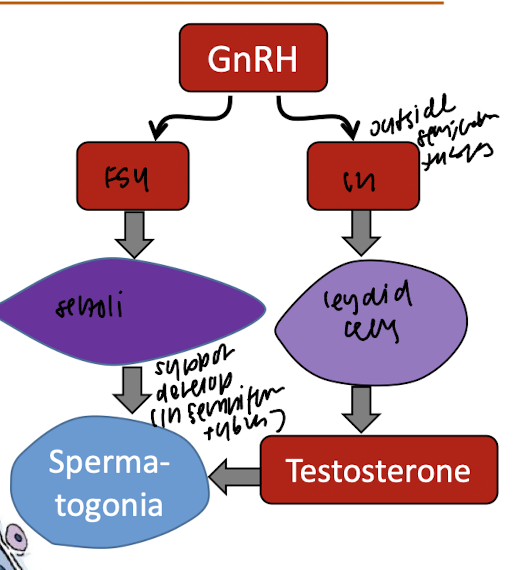
describe the hormonal pathway for testosterone
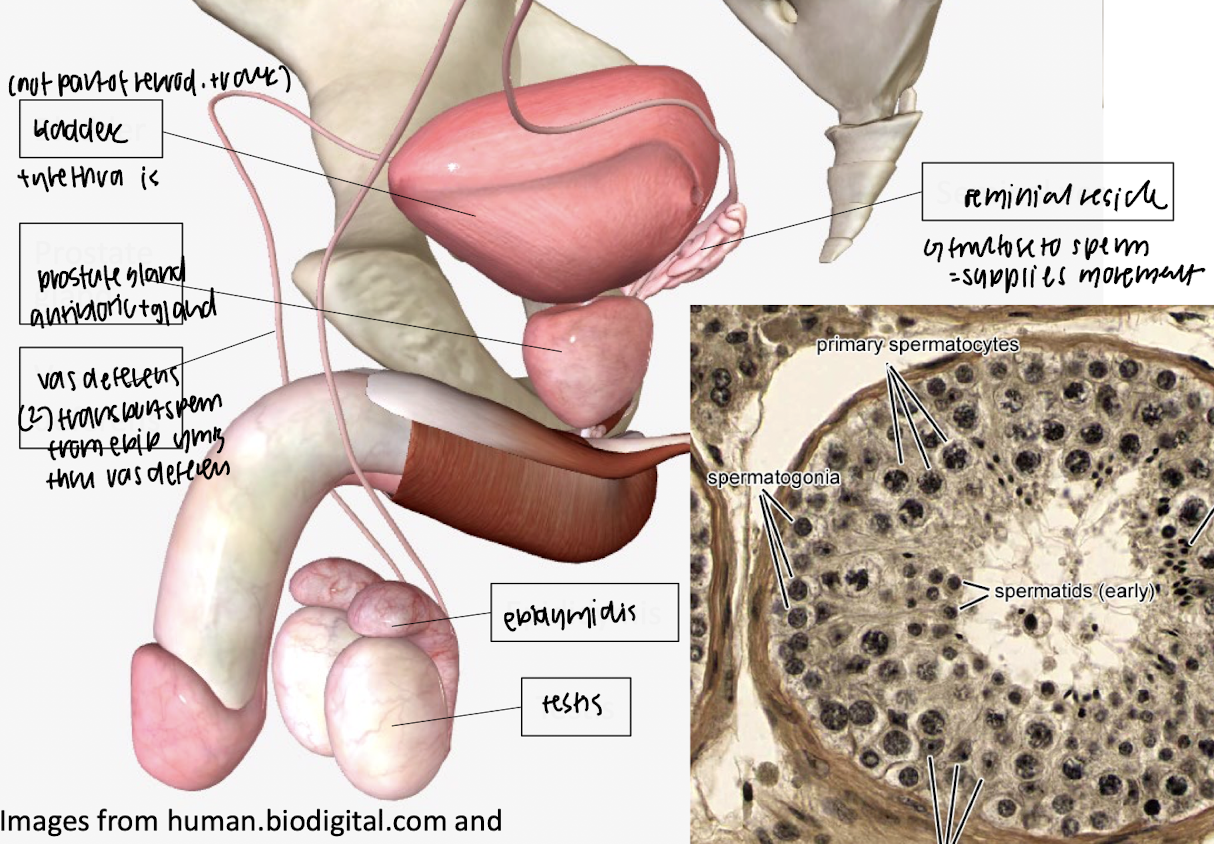
male reproductive system
seminial vesicle: supply furtose to sperm, supply movement
prostate gland: nourish and protect sperm
vas deferenes: transports sperm from epidymidis
epidymidis: sperm undergo maturation
testis: produce testosterone
ovarian cycle
follicular phase: follical develops in prep for ovualtion
primary oocyte
support cells grow around
secondary oocyte ready to go through meiosis 2, ready for ovulation
ovulation: secondary oocyte released from ovary
luteal phase: corpus lutuem produces hormones then decays, helps keep uterun linign of implantation of eggs (shedding)
describe what happens in the follicular phase- oviarian hormone cycle, pituitary hormone cycle, menstrual cycle
follicle phase increases estradiol , switches to positive feedback stimulating LH (has slight - feedback), progesterone stays same,
FSH and LH stimulate follicle to develop
estradiol stimulate development of uterine lining, estradiol keeps FHS and LH low (negative feedback inhibition)
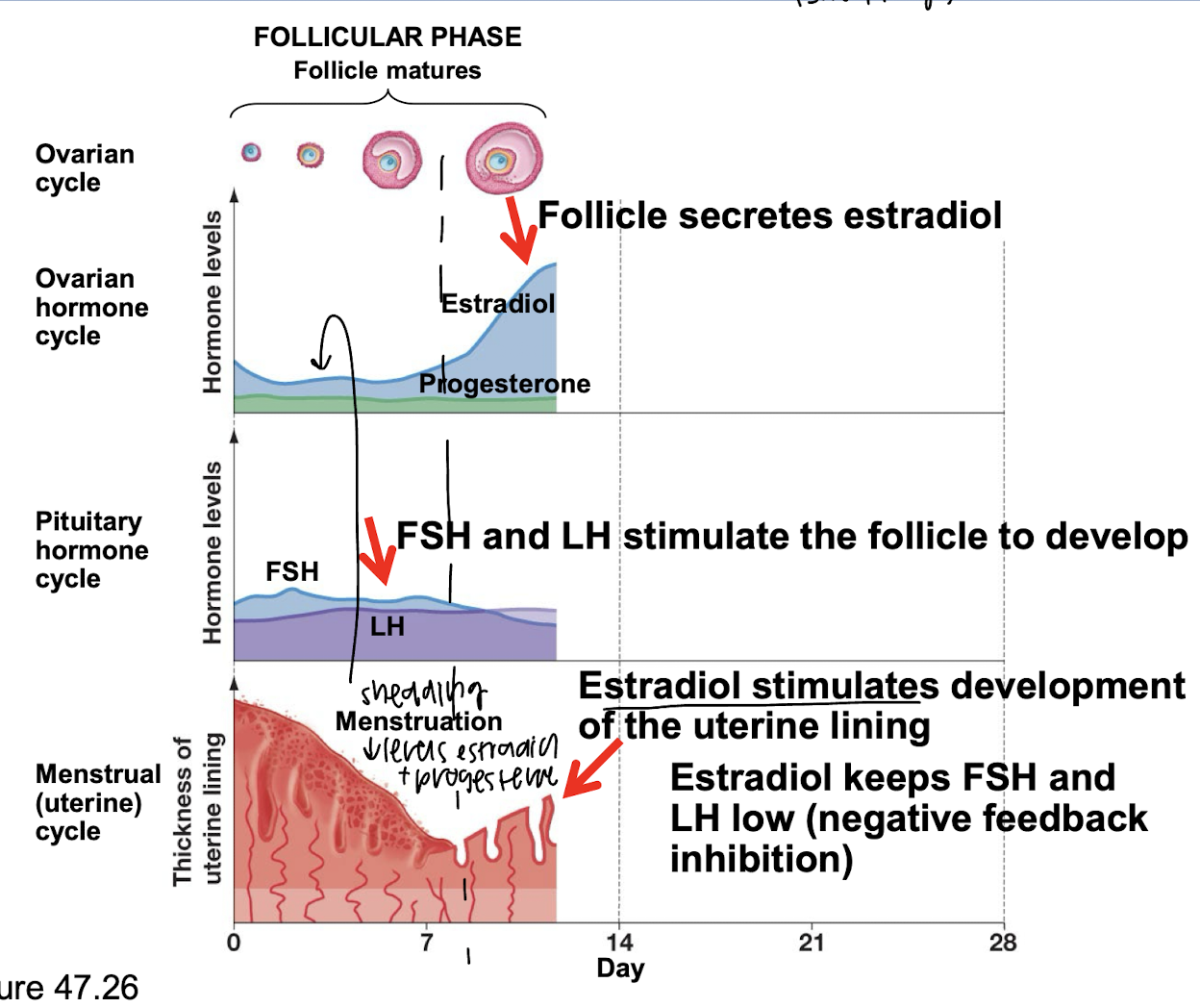
what happens during ovulation
LH surge causes ovulation
FSH also peaks a little
estradiol decreases
progesterone starts to rise
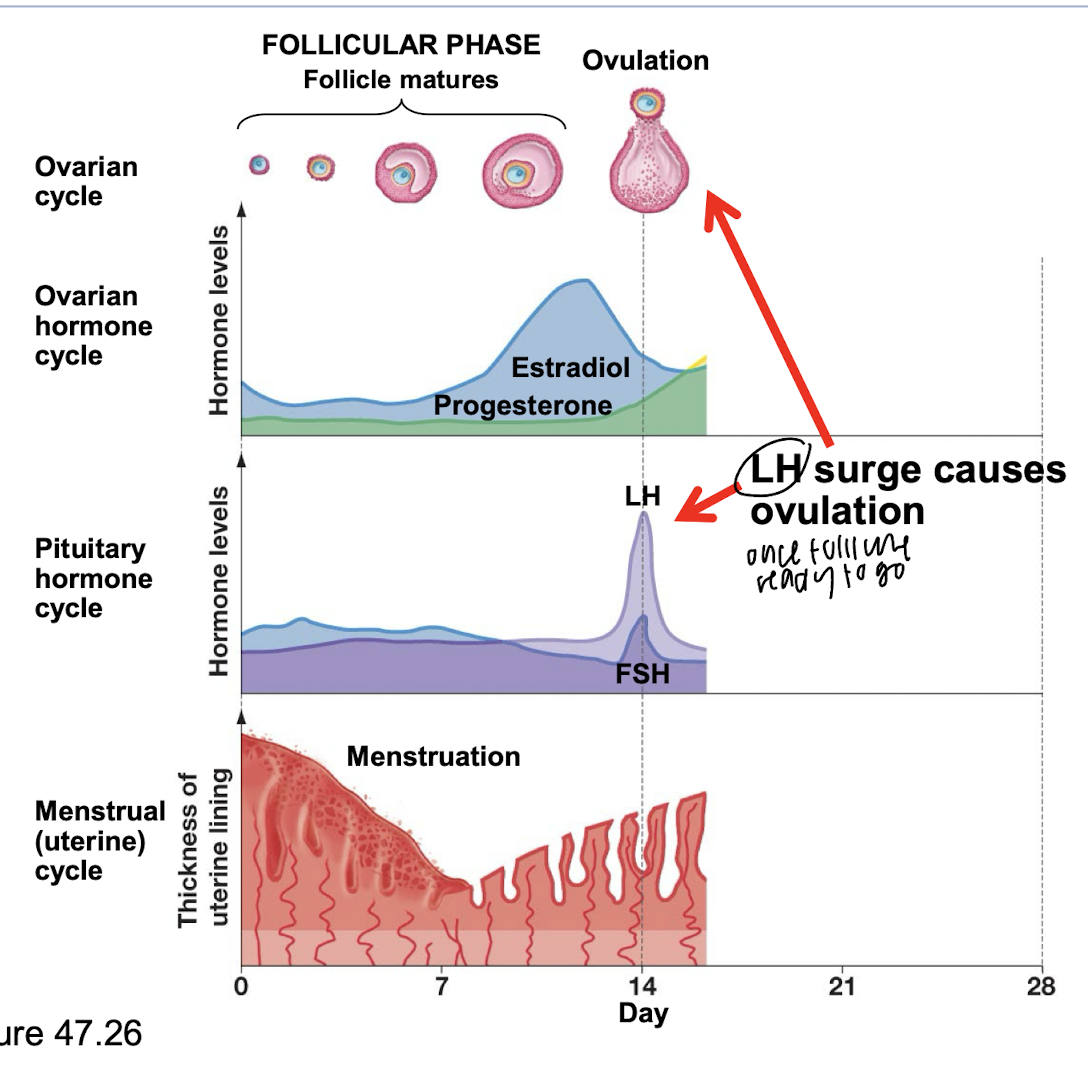
luteal phase and how the cycle restarts again
corpus luteum, LH stimulates corpus luteum to make progesterone
corpus luteum makes progesterone and keeps lining around
progesterone inhibits LH and FSH and protects uterine lining in case egg gets ovulated
drop in progestrone causes next menstruation cycle
if implantation
corpus luteum does not degenerate, no drop in progesterone, so no menstruation
what happens in the luteal phase
LH stimulates corpus luteum to make progesterone, estradoil starts to decrease, progesterone inhibits LH and FHS, progesterone protects uterine lining
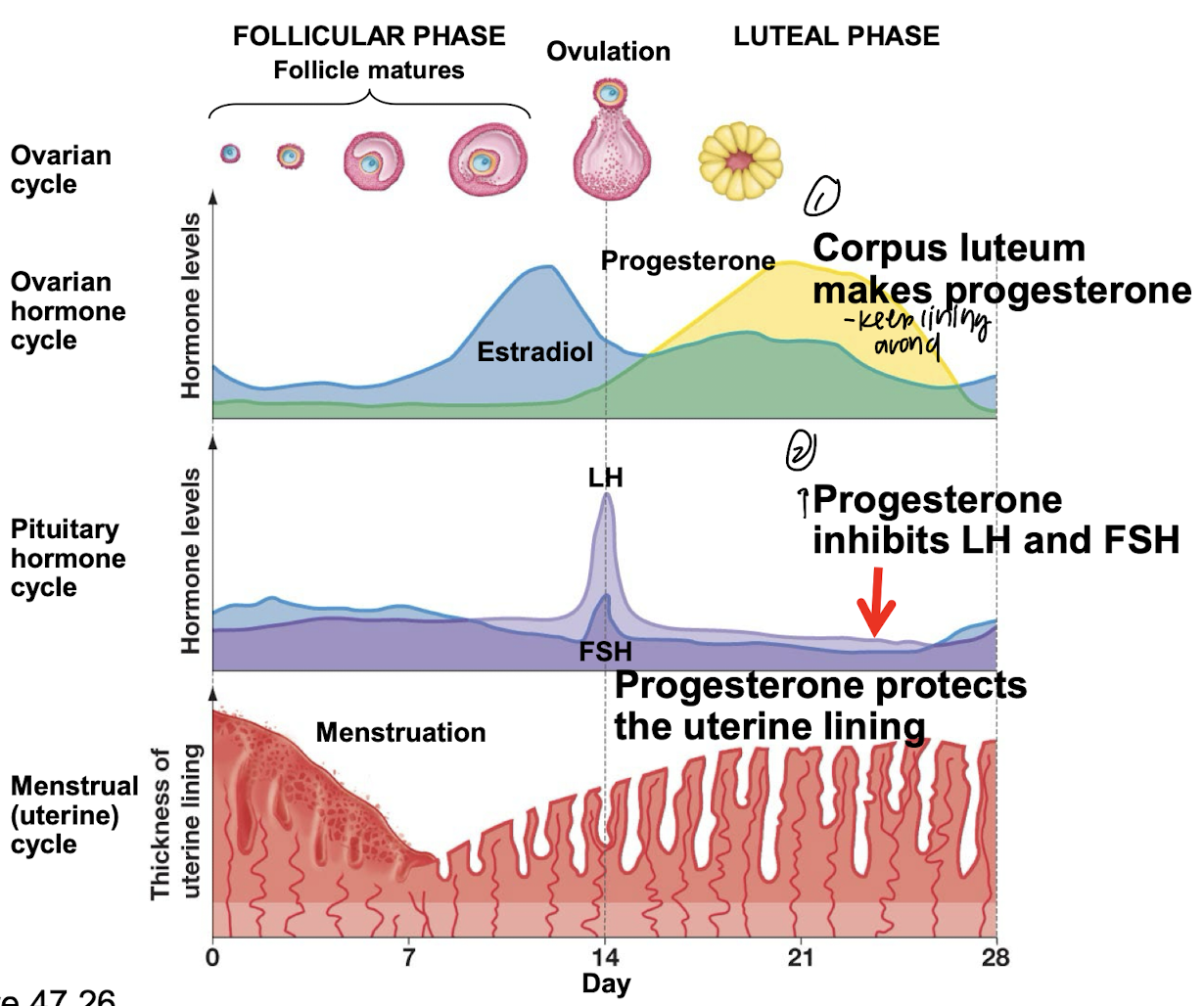
when progesterone drops, what happens?
menstruation starts
birth control
prevents ovulation, - feedback LH and FSH
if miss a day keeping estrogen and progestin levels high enough to inhibit the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) needed to release an egg.
Thickening cervical mucus: making it harder for sperm to reach the uterus.
Thinning the uterine lining: reducing the chance of implantation.
emergency contraception
- feedback prevents ovulation, if embyo already implanted, cannot do anything
abortion pill
blocks progesterone receptors to cause shedding of uterine lining including embryo
how spermatozoon fertilizes sea urchin egg,
sperm attracted to egg via chemical signals
sperm make contact w jelly layer
acrosome (tip of head of sperm) reaction enzymes break down jelly layer and viteline envelope, penetrates
bindin binds to bindin receptors
fusion of cell membranes
sperm nuclues enters egg
meiosis 2 of egg cell complete
how polysperm is prevented
Ca+2 released= depolarization
release of ions and solutes from cortical granules into space around plasma membrane
viltiline envelope swells outward and becomes rigid
what is difference between sea urchin egg and human egg
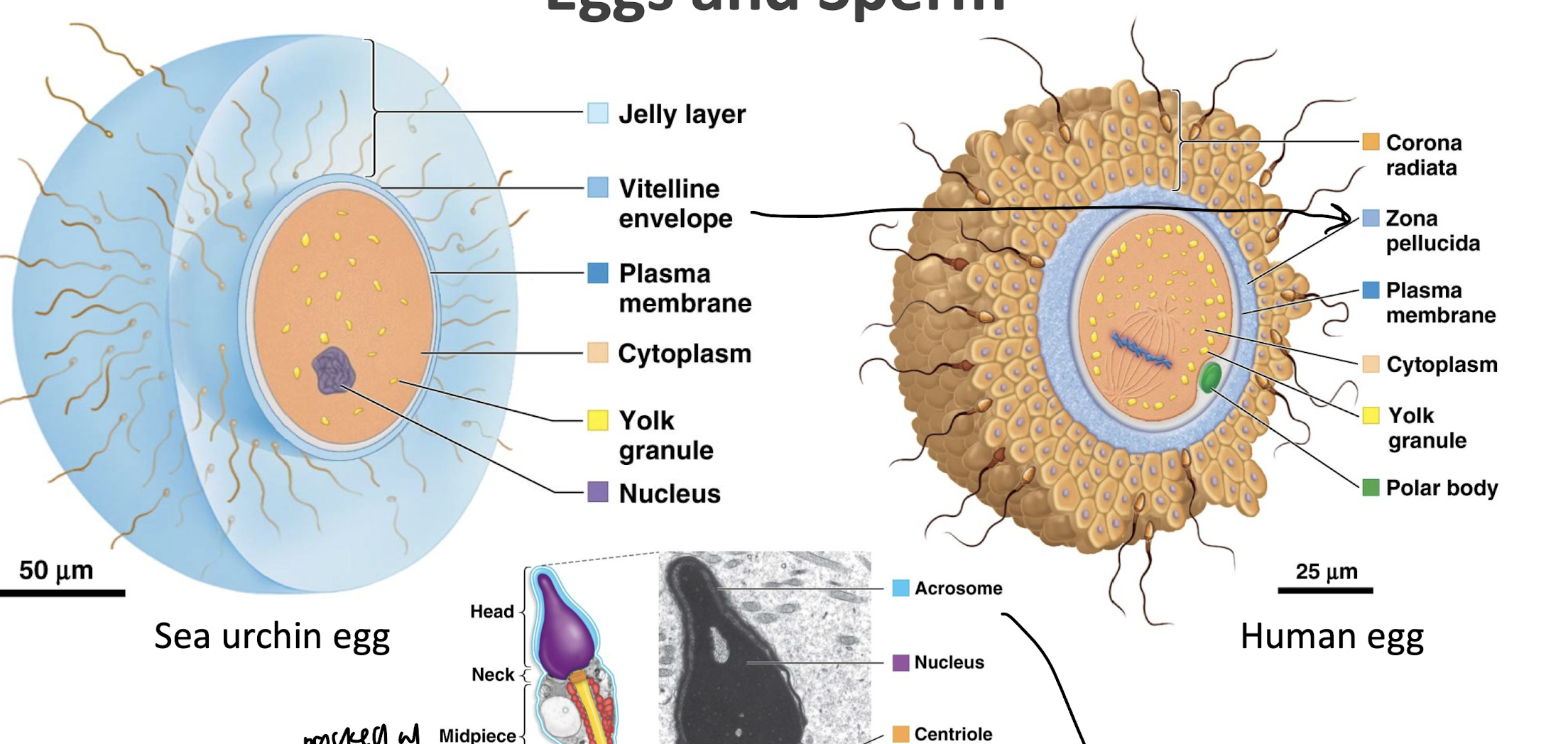
human egg: corona radiata (crown), zone of pellucida, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, yolk granule, polar body
jelly egg: jelly layer, vitelline envelope, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, yolk granule, nucleus
internal fertilization
animals: mammals, reptiles, birds
parental investment often higher, fewer offspringex
external fertlization
animals: amphibians, fish, aquatic invertebrates
sperm released into environment, lower success rate, parental investment lower
oviparity
eggs laid and development occurs outside moms body (birds)vi
viviparity
embryo develops in mom, direct nourishment from placenta- present in cold climates because temperature regulation
what happens during cleavage
converting the single-celled zygote into a multicellular embryo. This process involves dividing the zygote's cytoplasm into called blastomeres.
gastrulation
formation of ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm, makes future gut
what does ectoderm differeintate into
nervous system, epidermis of skin, epithelial lining of mouth and rectum
what does mesoderm make
skeletal, circulatoary, lympahtic, msuclar system, linging of body cavities, dermis of skin
endoderm makes
epithelial lining of digestive respiratory, reproduct, urininary, liver pancreas, htyroid, thymus
compare gestation and development in marsupial mammals and placental mammal
m: shorter gestation period, embryo underdeveloped at birth, goes into pouch to cont development, simpler placenta
e: longer gestation, fetus develops fully in uterus. highly specialized placenta
male reproductive system
Testis (Testes)
Produces sperm.
Secretes testosterone.
Epididymis
Stores and matures sperm after production.
Vas Deferens
Transports mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
Seminal Vesicle
Produces fluid rich in fructose to nourish sperm.
Contributes to semen volume.
Prostate Gland
Secretes an alkaline fluid that protects sperm in the female reproductive tract.
Penis
Delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract.
Also functions in urination.
Urethra
Conducts urine and semen out of the body
spermatozoon
mature male gamete
ovum
haploid female gamete
intersitial cells of leydid
cells that synthesize testostrone in testes
spermatid
immature spermatozoon that have not developed flagellumg
granulosa cells
cells form corona radiate surrounding egg
sertoli cells
cells that release cytokines that promote spermatogenesis
what happens during each major stage of embryonic development
cleavage, gastrulation, neuraliation, organogenesis
cleavage
Shortly after fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of mitotic divisions. These early divisions are called cleavages.
The resulting smaller cells are called blastomeres.
Blastula Formation: After several cleavages, a hollow sphere of cells called the blastula forms. The internal fluid-filled cavity is called the blastocoel.
Key Features:
Establishes the early multicellular structure of the embryo.
Cell size decreases with each division.
gastrulation
Cells of the blastula begin to move inward through a structure called the blastopore.
Formation of Germ Layers:
Ectoderm (outer layer): will form the skin, nervous system.
Mesoderm (middle layer): will form muscles, bones, blood, and other internal organs, systems
Endoderm (inner layer): will form the lining of the gut and other internal organs.
cell differentiation
basltopore becomes what
mouth or anus
neuraluation
formation of neural tube
mesoderm forms notochord- forms neural plate
neural tube: nneural plate folds inwards becoming neural tube (brian and spinal)
neural crest cells form other structures
organogenesis
cells differentiate based on germ layer (ecto, endo, meso)
somite and trophobalst
somite: mesoderm forms msucle and body tissue
trophoblast forms placenta
womens reproductive system
clit
cervix
fallopian tube
urethra
vagina
ovary
labia majora
clit: Erectile tissue containing numerous nerve endings
cervix: muscular sphincter between the vagina and uterus
fallopian tube: Tube in which the egg may be fertilized following ovulation
urethra: Common tube through which sperm or urine can be released
vagina: Tube in which sperm is deposited during mating in a mammal
ovary: produces ova, estrogen, and progesterone
labia majora: Hairy folds of skin that cover the urethral and vaginal openings