Small Animal Head and Neck
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
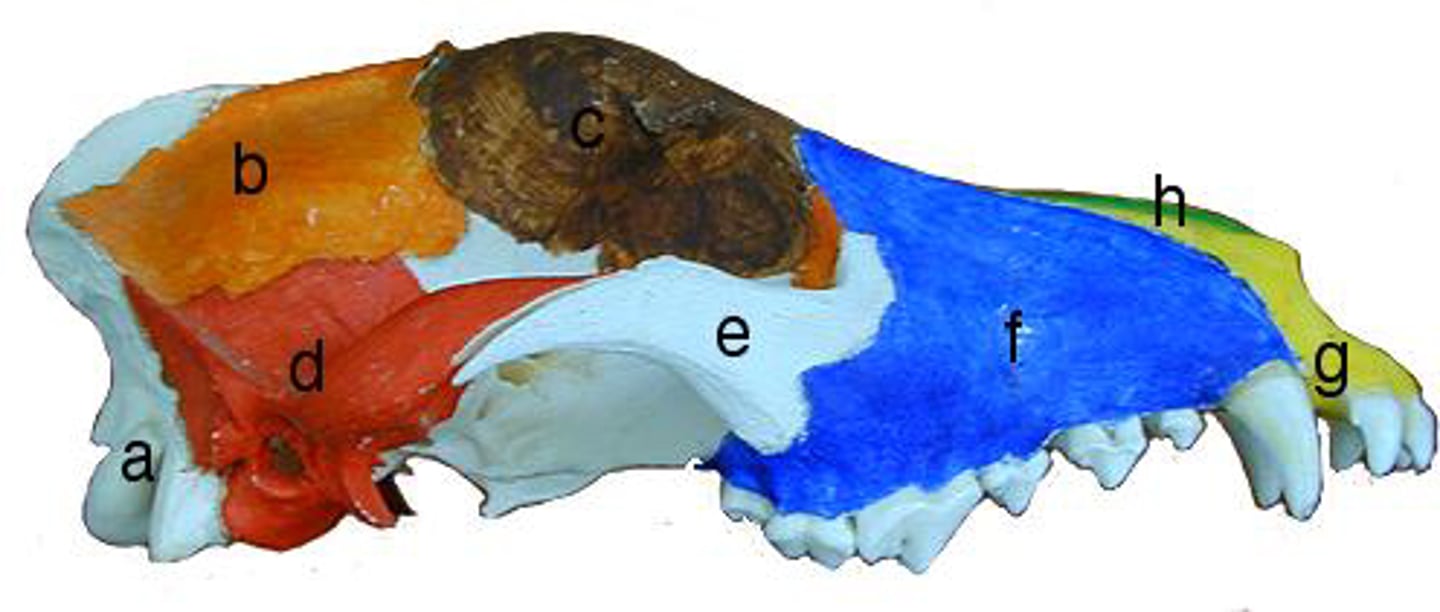
A. Occipital
B. Parietal
C. Frontal
E. Zygomatic
F. Maxillary
Label A, B, C, E, F
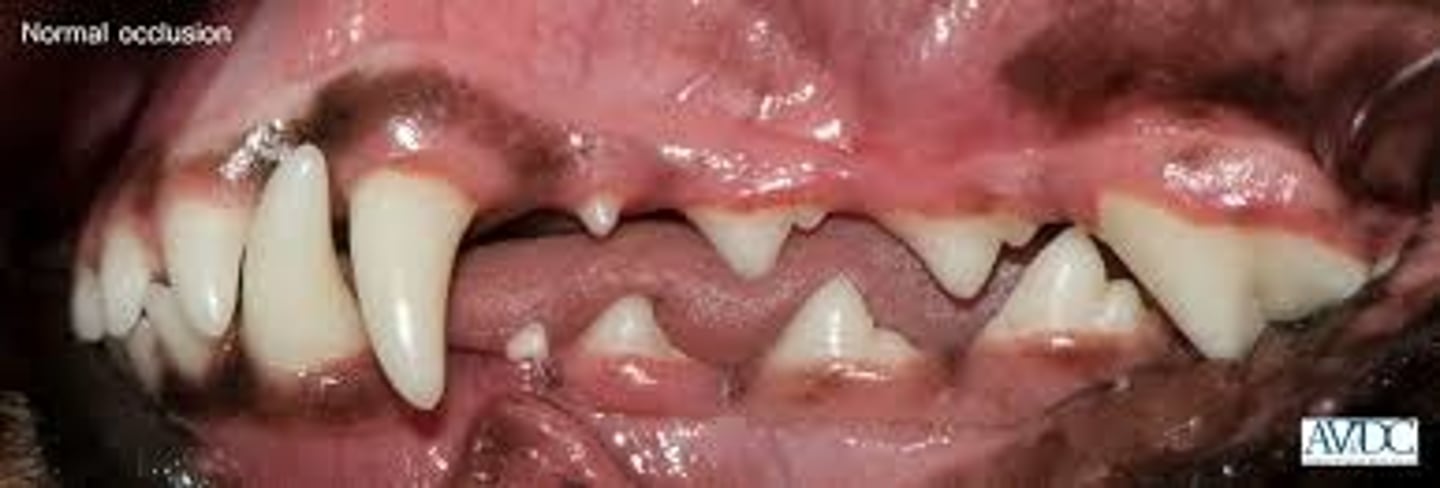
Normal canine occlusions
What is this an example of?
towards the midline
Mesial means?
towards the lips
Labial means?
pertaining to the cheek
Buccal means?
towards the tongue
Lingual means?
pertaining to the palate or roof of the mouth
Palatal means?
28, No molars.
How many deciduous teeth do dogs have?
42
How many permanent teeth do dogs have?
2
3
Dogs have ___ maxillary molars and ____ mandibular molars?
6 w
When should deciduous teeth be finished?
3-5m
When should the permanent canine incisors erupt
4-6m
When should the permanent canine canines erupt?
4-5M
When should the permanent canine premolars erupt?
5-7m
When should permanent canine molars erupt?
Maxillary 4th PM
Mandibular 1st M
What are the carnassial teeth?
26 (3 Maxillary PM 2 mandibular pm)
Cats will have how many deciduous teeth?
30, (small maxillary molar, large mandibular molar)
How many permanent teeth will cats have?
3.5-5.5 M
When are permanent incisors of a cat going to erupt?
5.5-6.5 M
When are permanent canines of a cat going to erupt?
4-5 M
When are permanent premolar of a cat going to erupt?
5-6M
When are permanent molars of a cat going to erupt?
Infraorbital canal, blocks feeling from incisors - P3 to the midline of the maxilla
Where do we insert a rostral maxillary block what does its numb?
Behind the last molar numbing ipsilateral side to the maxillary midline
Where is a caudal maxillary block given?
Safer, protects the eyes, may be better to actually reach the nerves
Why might we use a modified caudal maxillary block using the infraorbital canal?
Mental foramen
Blocks 2nd (maybe 3rd) to the incisors
Where we give a rostral mandibular block?
Interior alveolar entier side of the mandibule
Where do we give the caudal mandibular block? What does it numb?
Mandibular notch
Lateral campus of the eye
What are the landmarks for a caudal mandibular block?
condylar process of mandible and mandibular fossa of temporal bone
What makes up the TMJ?
In hospital never send home w/ O
A nasogastric tube should only be done?
common passageway for food and air
What is the pharynx?
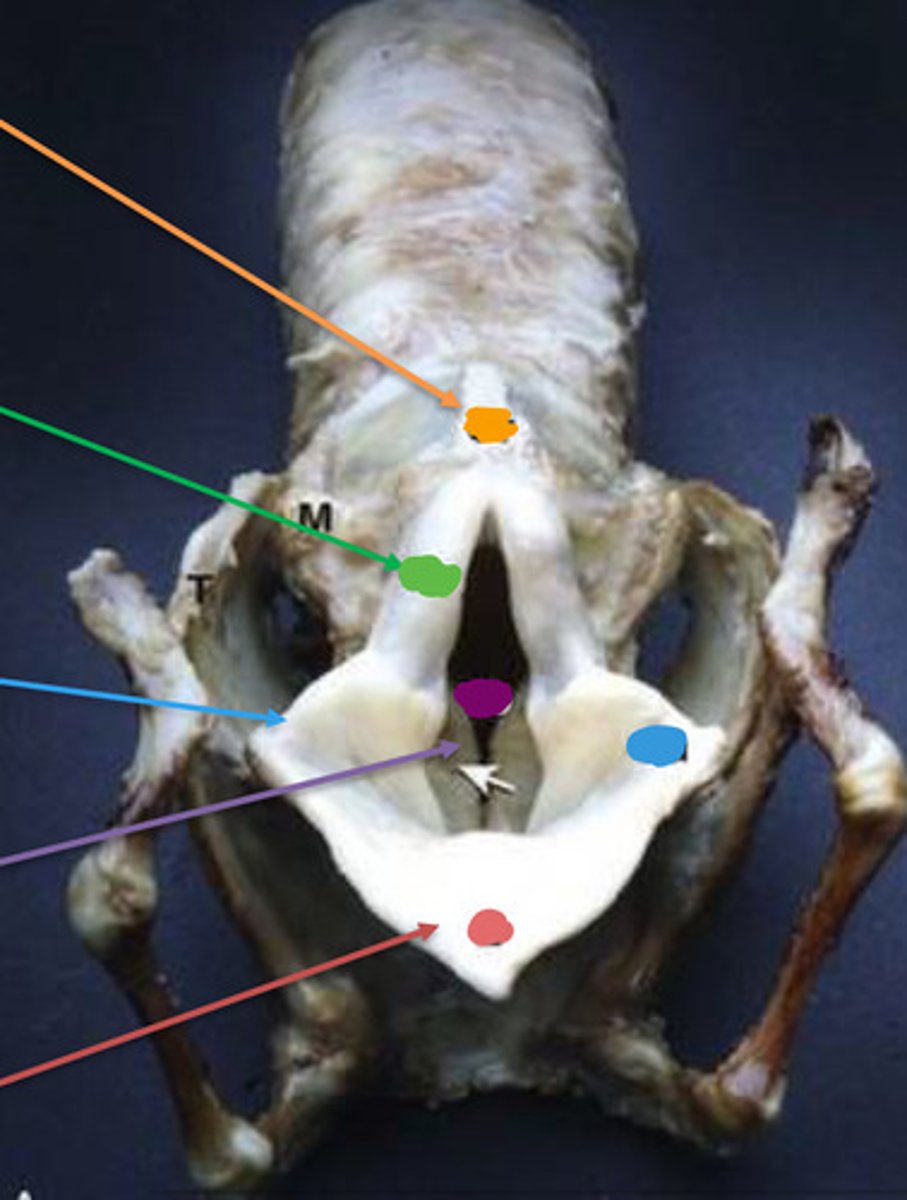
Orange: Cricoid arch
Green: Corniculate process
Blue: Cuneiform process
Purple: Vocal folds
Pink: Epiglottis
Label the image?
Recurrent laryngeal n. from the vagus n.
What nerve is affected w/ laryngeal paralysis?
Most laryngeal muscles are affected gut Cricoarytenoideus dorsals is most affected.
What muscle is affected most w/ laryngeal paralysis?
one side of the cricoarytenoid is sutured leaving the airway open an increases risk of regurgitation and aspiration pneumonia
What are risks of cricoarytenoid lateralization?
Stenotic nares
Elongated soft palate
Hypoplastic trachea
Everted laryngeal saccules
What are things that can cause Brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome?
Alar fold
What is the movable portion of the canine nares?
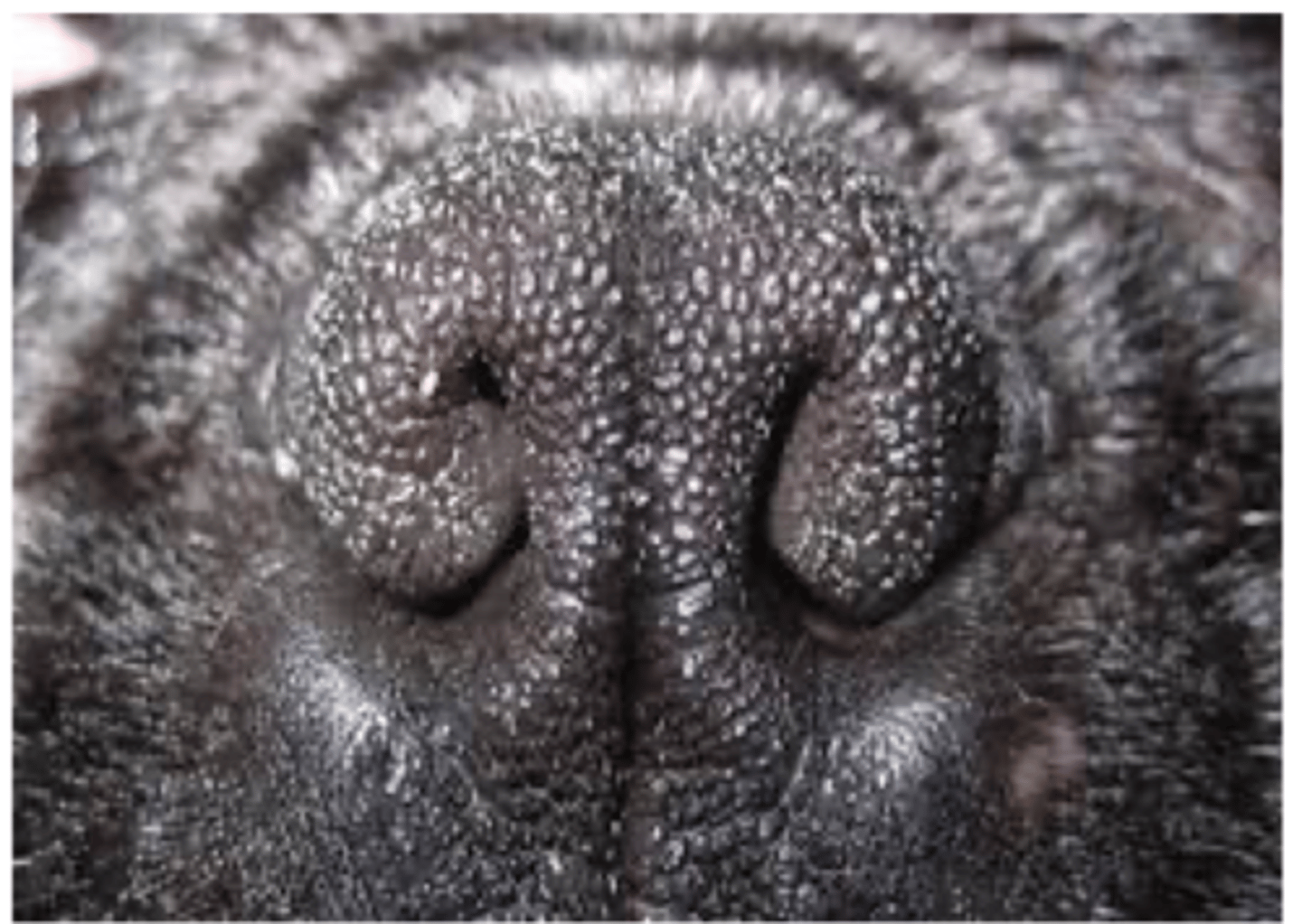
Stenotic nares
What is this?
Everted laryngeal saccules
What is this image depicting?
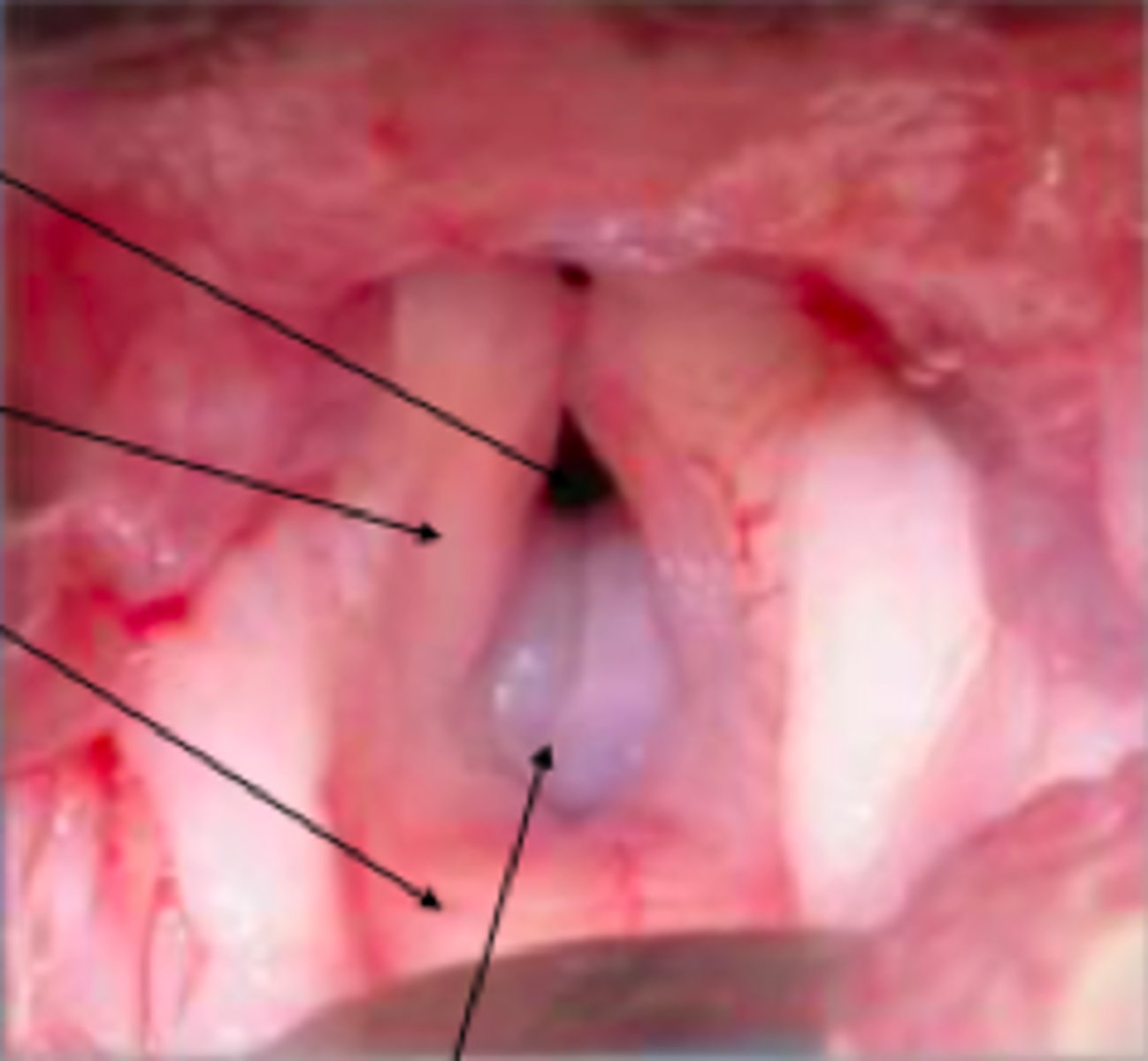
Chronic increased resp effort resulting in soft tissues between vocal folds protruding
What causes everted laryngeal saccules
Can indicate a hyperthyroid cat due to increased size of thyroid
What is a thyroid slip test going to tell us?
Carcinomas/ malignant
Dogs tend to have what kind of thyroid masses if they are enlarged?
2, 2
An animal will have _ external and __ internal parathyroid glands?
Maintain Ca levels in the blood
What is PTH going to do?
Vagosympathetic trunk, carotid artery
What is found in the carotid sheath?
Sublingual and mandibular glands
What are the two mandibular salivary glands?
Parotid and zygomatic
What are the two salivary glands of the maxilla?
Upper neck,
Pharynx
Cervical mucocele will have swelling in the ____?
Pharangeal mucocele will have swelling in the ___?
Ranula
What can a sublingual mucocele be called?
Lingofacial
Maxillary
What two major veins go through the parotid and mandibular salivary glands?
L shaped
Gentle sloped that is more sensitive
Dogs will have ____ shaped ear canal and cats will have a ____ shaped ear canal that is more ____?
Ototoxicity
Cats ears are at a higher risk of what?
median and intermediate and lateral articular branch
What are the two arteries in the ear we must be careful not to ligate when doing a aural hematoma repair?
Benign inflammatory growth that comes out of the middle ear either into the oropharynx or the tympanic membrane
What is a nasopharyngeal polyps?
third eyelid
What is the nictitating membrane?
Lacrimal gland (dorsalateral)
Nasolacrimal duct (medial)
What produces tears, what drains them?
No blink in menace response
Doesn't follow cotton ball
Bumps into objects
What sign might we see if CN II was not working?
Atrophy of the temporalis, mass ester muscles,
Decreased jaw tension/ dropped jaw unable to close mouth
Struggles to eat/ chew
What might we see if CN V is damaged?
Facial drooping on one side, drooling and unable to blink
What might we see w/ CN VII damage?
Deafness,
Head tilt
Nystagmus
What might we see if we have damage to CN VIII?