U.1 (Genetics🧬): Cell Division & Reproduction vocab
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Genetics
scientific study of heredity and variation
Somatic cell
the cells in the body other than sperm and egg cells
Centromere
holds two chromatids together in a pair of chromosomes
Mitosis (PMAT)
when cells divide into two identical ones
Centriole
protein bodies in the cytoplasm that form & organize spindle fibers
Spindle fibres
attaches to centromere to pull sister chromatids apart
Chromosome
structure that contains DNA
→ counted by # of centromeres
Sister chromatid
identical copy of a chromosome, remains attached to it until anaphase
Sex chromosome
type of chromosome that determines sex
→ x + x = female → x + y = male
Autosome
any chromosome other than sex chromosomes
Genome
a complete set of DNA in an organism
Gene
segment of DNA, the basic unit of heredity
Allele
a specific form of gene
→ dominant or recessive
Karyotype
a visual representation of homologus pairs
Asexual reproduction
the production of offspring from a single parent; the genetic makeup of the offspring is identical to that of a parent
Sexual reproduction
the production of an offspring when a male gamete (sperm) fertalizes female gamete (egg)
Cancer
uncontrolled cell growth
Apoptosis
state in which a cell self-destructs (kills itself)
Gamete
a sex cell, female (ovum)/ male (sperm)
Haploid
single set of unpaired chromosomes
Diploid
two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
Fertilization
the formation of a zygote by the joining together or formation of two gametes
Zygote
a fertilized egg cell when a male gamete (sperm) enters the female (ovum/egg)
Meisois
a two-stage cell division
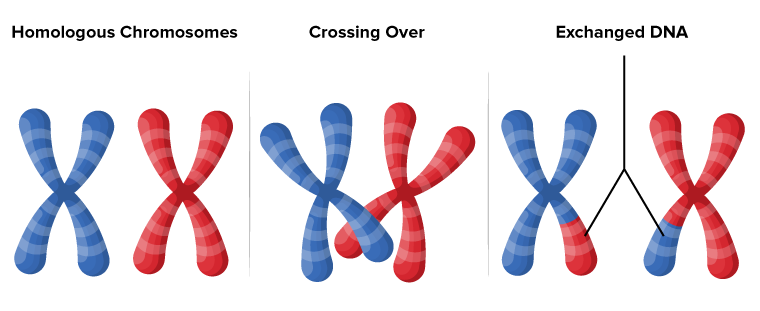
Crossing over
the exchange of chromosome segments between homologous pairs during synapsis
Homologous chromsome
matching pair of chromosomes, similar in size and carrying information for the same genes
Synapsis
the fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis
Spermatogenesis
the production of mature sperm cells
Oogenesis
the production of mature egg cells
Non-disjunction
the failure of homologous chromosomes to move to opposite poles of the cell during meiosis; results in abnormal # of chromosomes in meiosis
Monosomy
absence of one member of a pair of chromosomes
Trisomy
extra chromosome in a homologous pair
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
the joining of a woman’s egg and a man’s sperm in a petri dish
Stem cell
cells that can develop into many different cell types