Unit 2: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
Heredity and the Environment both…
interact to influence an individual's traits and behaviors, shaping their development and personality.
Heredity
internal factors like genetic or predisposed characteristics that influence physical, behavioral, mental traits and processes
Environmental Factors
external influences such as family, culture, and experiences that shape an individual's development and behavior.
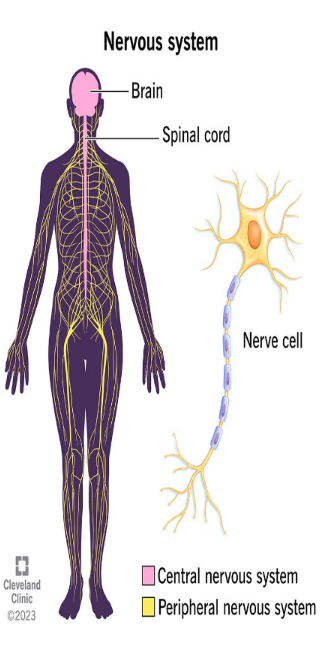
Central Nervous System
comprises the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing sensory information and coordinating responses.
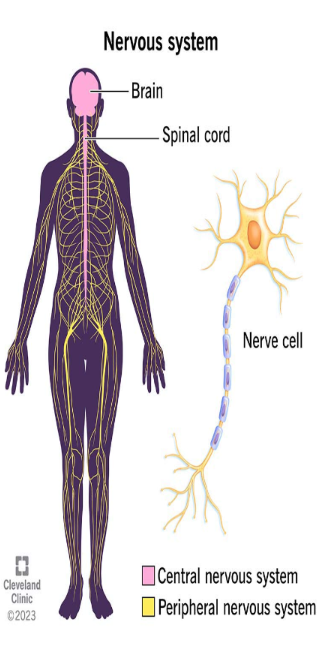
Peripheral Nervous System
consists of all nerves outside the central nervous system, connecting the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Somatic Nervous System
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary muscle movements and transmits sensory information to the central nervous system.
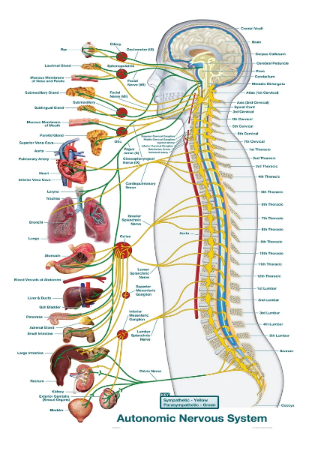
Autonomic Nervous System
the part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
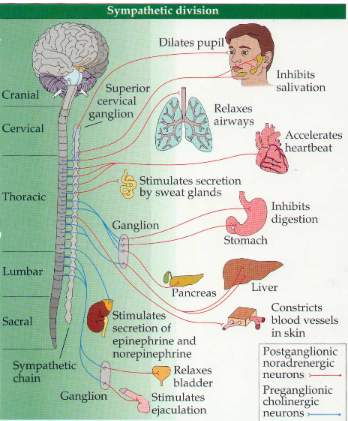
Sympathetic System
a division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations, often referred to as the "fight or flight" response.
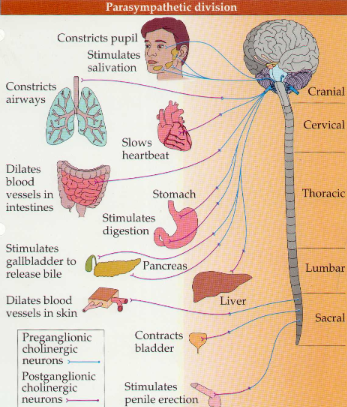
Parasympathetic System
a division of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy and promotes rest and digestion, often referred to as the "rest and digest" response.
Neurons
the basic building blocks of the nervous system that transmit information throughout the body via electrical and chemical signals.

Dendrites
branch-like structures of neurons that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them toward the cell body.
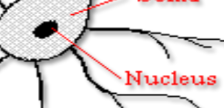
Nucleus
the control center of a cell that contains its genetic material and regulates cellular activities.
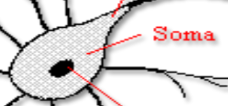
Soma
the cell body of a neuron that contains the nucleus and integrates incoming signals from the dendrites.

Axon Hillock
the specialized part of a neuron where the axon begins and where the action potential is initiated. connects soma to the axon
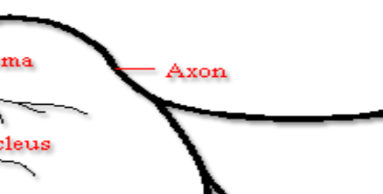
Axon
a long, slender projection of a neuron that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
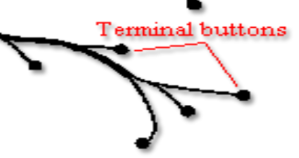
Axon Terminal Button
the endpoints of an axon where neurotransmitters are released to communicate with other neurons or muscles.
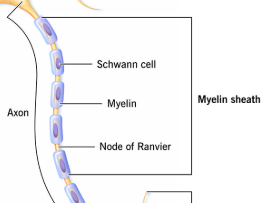
Myelin Sheath
a fatty layer that surrounds the axon of some neurons, increasing the speed of electrical impulses. insulates and protects the axon
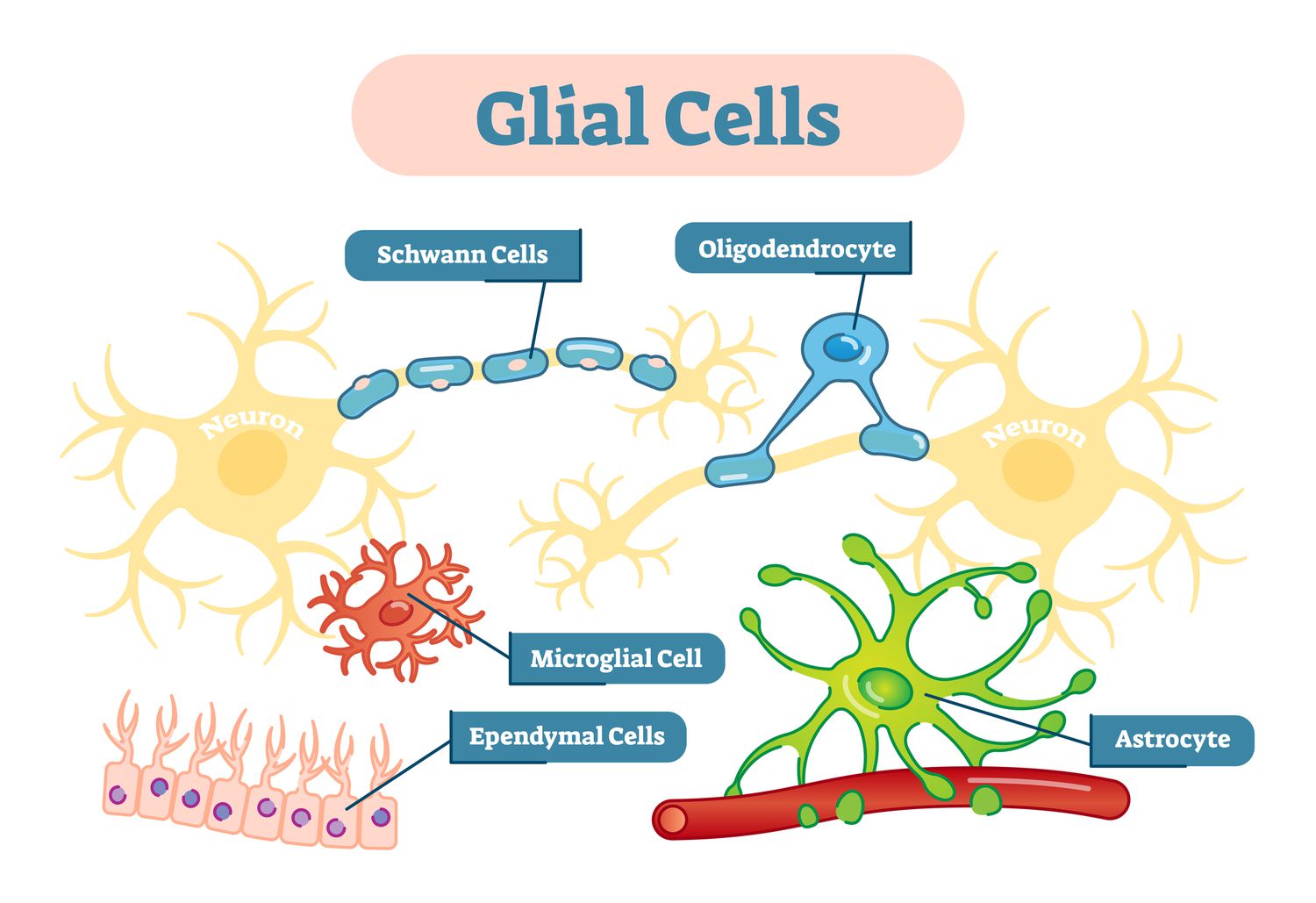
Glial Cells
supporting cells in the nervous system that provide support, nourishment, and protection to neurons.
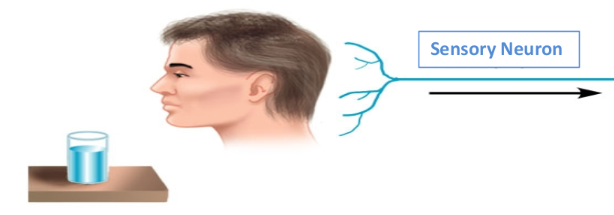
Sensory Neurons
nerve cells that transmit sensory information from the body to the brain and spinal cord. They carry signals from external stimuli such as touch, sight, and sound.
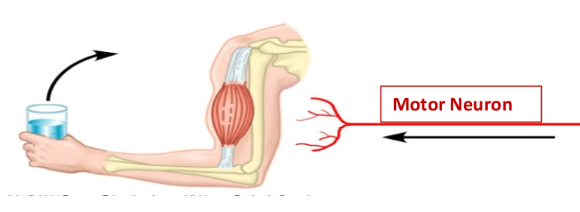
Motor Neurons
nerve cells that transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands, facilitating movement and activity.
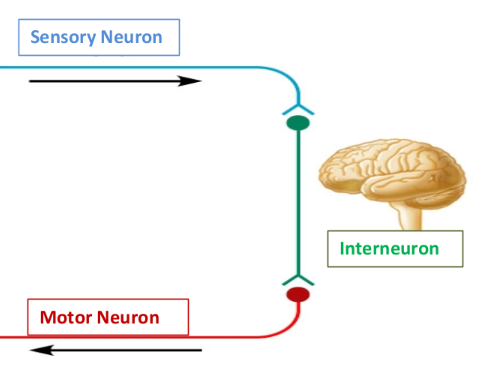
Interneurons
nerve cells that connect sensory and motor neurons, processing information within the central nervous system.
Reflex Arc
A neural pathway that controls a reflex action. It typically involves sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons to produce an immediate response to a stimulus.
Resting Potential
the electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron in its inactive state, typically around -70 mV, creating the conditions necessary for the generation of action potentials.
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger an action potential in a neuron, typically around -55 mV, marking the point at which a neuron becomes activated.
Action Potential
A rapid change in electrical charge that travels along the axon of a neuron, initiated when the threshold is reached, resulting in neurotransmitter release.
Depolarization
The process by which the membrane potential of a neuron becomes less negative (more positive) than the resting potential, often leading to the initiation of an action potential.
All-or-Nothing Response
The principle that a neuron either fires completely when the threshold is reached or does not fire at all, without partial responses.
Refractory Period
A brief phase following an action potential during which a neuron is less responsive to stimuli and cannot fire another action potential until it returns to its resting state.

Synapse
The junction between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released, allowing communication between the two.
Vesicles
Membrane-bound sacs in neurons that store neurotransmitters and release them into the synapse during neurotransmission.
Reuptake
The process by which neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron after transmitting a signal across the synapse, thereby terminating the signal.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another, influencing various physiological and psychological functions.
Neurotransmitters communicate to increase or decrease __________.
neurons firing

Excitatory Neurotransmitters
neuron firing, promoting the transmission of signals. stimulate the brain

Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
decrease neuron firing, dampening the transmission of signals. slows down the brain
Acetylcholine
a neurotransmitter involved in muscle activation, memory, and learning. too MUCH can lead to depression, and too LITTLE can lead to dementia & alzheimer’s
Dopamine
a neurotransmitter that plays a role in reward, motivation, and motor control. Its imbalances are linked to disorders such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and depression tremors
Endorphins
neurotransmitters that act as the body's natural painkillers, promoting feelings of pleasure and well-being. They are involved in the regulation of mood and pain perception.
GABA
a neurotransmitter that primarily inhibits neuronal activity in the brain, helping to regulate anxiety and promote relaxation. Its dysfunction is associated with anxiety disorders and epilepsy
Glutamate
a major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, playing a key role in learning and memory. Its excessive activity is linked to neurotoxicity and conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, migraines and seizures, and psychosis or coma
Norepinephrine
a neurotransmitter involved in the body's 'fight or flight' response, regulating arousal, attention, and stress. It contributes to mood regulation and is implicated in conditions like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia
Serotonin
a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, appetite, and sleep. It is often linked to feelings of well-being and happiness, and its imbalance is associated with depression, anxiety disorders, and heart issues confusion
Substance P
a neuropeptide involved in pain perception and inflammatory responses. It transmits pain signals and contributes to the sensation of pain and the body's stress response.
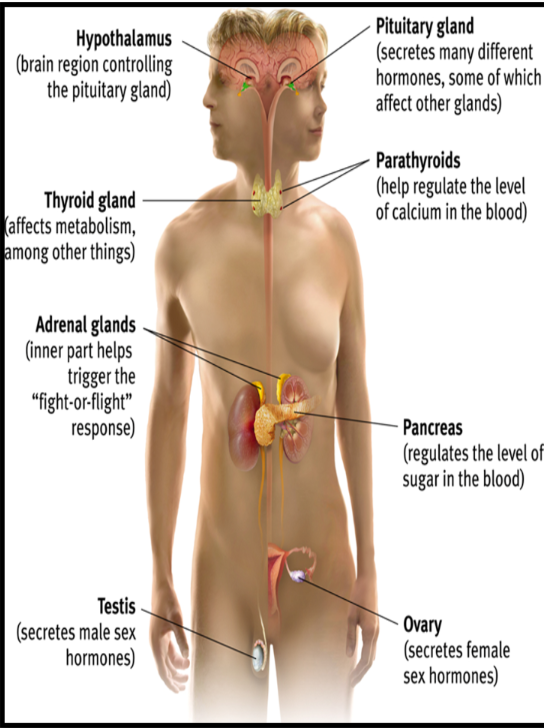
Endocrine System
a network of glands that produce and release hormones into the bloodstream, regulating various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis.
Hormones
are chemical messengers produced by the endocrine system that regulate physiological processes and influence behavior.
Adrenaline
a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses. It increases heart rate, blood flow, and energy availability during stressful situations.
Cortisol
a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex that helps regulate metabolism, immune response, and stress adaptation. It plays a vital role in the body's response to stress and maintains homeostasis.
Melatonin
a hormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms in the body.
Ghrelin
a hormone produced mainly by the stomach that stimulates appetite, increases food intake, and promotes fat storage.
Leptin
a hormone produced by adipose tissue that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger, thus aiding in weight control.
Oxytocin
a hormone produced by the hypothalamus that plays a role in social bonding, sexual reproduction, and childbirth.
Psychoactive Drug
a chemical substance that alters brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, and behavior. A
Agonists
substances that bind to receptors and activate them, mimicking the effect of natural neurotransmitters.
Antagonists
substances that bind to receptors but do not activate them, blocking or dampening the effects of agonists.
Stimulants
a class of psychoactive drugs that increase brain activity, leading to enhanced alertness, attention, and energy.
Depressants
a class of psychoactive drugs that reduce brain activity, leading to decreased alertness, relaxation, and sedation.
Hallucinogens
substances that cause perceptual distortions, altered states of consciousness, and sensory experiences that are not based in reality.
Opioids
a class of drugs that act on the brain's opioid receptors to produce pain relief, sedation, and feelings of euphoria.
Tolerance
a physiological state where a person's reaction to a drug decreases, necessitating a higher dose to achieve the same effect.
Addiction
a chronic condition characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior and loss of control over substance use, often leading to negative consequences.
Physical Dependence
a condition in which a person's body becomes reliant on a substance, leading to withdrawal symptoms when the substance is not available.
Psychological Dependence
a condition where an individual feels a strong desire or reliance on a substance due to emotional or mental factors, often leading to cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Withdrawal
the physical and mental symptoms that occur after stopping or reducing intake of a substance on which a person has become dependent.
Brain Stem
the lower extension of the brain that connects to the spinal cord, responsible for regulating vital functions such as heart rate and breathing.
Medulla
the part of the brain stem that controls autonomic functions such as heartbeat and respiration.
Pons
the part of the brain stem located above the medulla that relays signals between the cerebellum and other parts of the brain and is involved in regulating sleep and arousal.
Cerebellum
a brain structure located at the back of the head, responsible for coordination, balance, and fine motor skills.
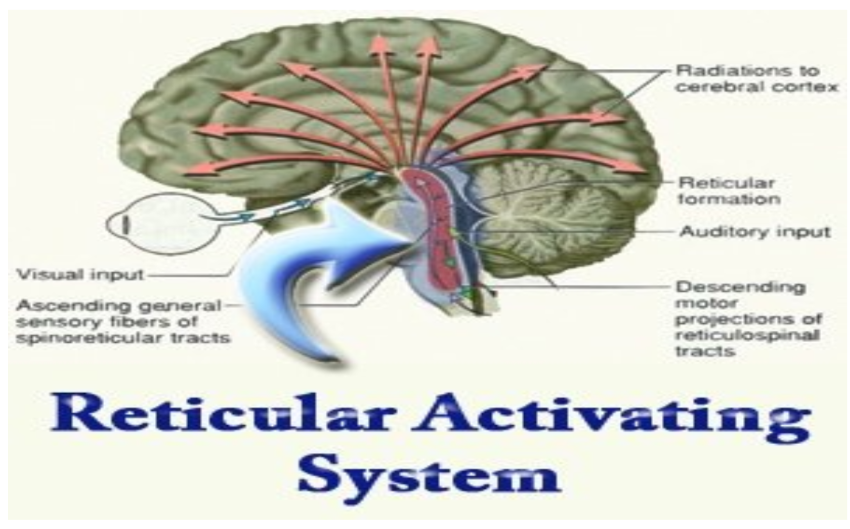
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
a network of neurons in the brainstem that are involved in regulating wakefulness, arousal, and attention.
Thalamus
the brain's relay station that transmits sensory information to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for processing.
Limbic System
a complex set of structures in the brain that deals with emotions, memory, and motivation.
Amygdala
a component of the limbic system that plays a key role in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure.
Hypothalamus
a region of the brain that regulates vital bodily functions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, and temperature control, as well as emotional responses.
Hippocampus
a structure in the limbic system primarily involved in memory formation and spatial navigation.
Pituitary Gland
often referred to as the "master gland"; it regulates various hormones and controls other endocrine glands. It plays a crucial role in growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes.
Split Brain Phenomenon
A condition resulting from the surgical severing of the corpus callosum, which connects the two hemispheres of the brain. This leads to a range of cognitive and behavioral changes, highlighting the lateralization of brain function.
Corpus Callosum
a large bundle of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
Cerebral Cortex
the outer layer of the brain responsible for complex functions such as perception, thought, and decision-making. It is divided into four lobes, each associated with different functions.
Frontal Lobe
the part of the cerebral cortex located at the front of the brain, involved in executive functions, impulse control, and decision-making.
Primary Motor Cortex
the region of the cerebral cortex located in the frontal lobe that is responsible for the planning and execution of voluntary movements.
Broca’s Area
a region in the frontal lobe associated with speech production and language processing.
Parietal Lobe
the part of the cerebral cortex located behind the frontal lobe, involved in sensory perception and spatial awareness.
Primary Sensory Cortex
the area of the cerebral cortex that processes sensory information from the body, including touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception.
Temporal Lobe
the part of the cerebral cortex located beneath the lateral fissure, associated with processing auditory information and memory.
Primary Auditory Cortex
the region of the cerebral cortex that receives and processes auditory information, playing a key role in the perception of sound.
Primary Olfactory Cortex
the region of the brain responsible for processing smell information received from the olfactory bulb.
Wernicke’s Area
a language comprehension center located in the left temporal lobe, crucial for understanding spoken and written language.
Occipital Lobe
the region of the cerebral cortex located at the back of the brain, primarily responsible for processing visual information.
Primary Visual Cortex
the part of the occipital lobe that processes visual information received from the eyes, essential for vision.
Plasticity
the brain's ability to change and adapt in response to experience, injury, or learning. It allows for the reorganization of neural pathways throughout life.
Functional Lateralization
refers to the specialization of the left and right hemispheres of the brain for different functions, such as language in the left hemisphere and spatial abilities in the right hemisphere.
Roger Sperry
A neuropsychologist known for his pioneering work on functional lateralization and split-brain research, demonstrating how each hemisphere of the brain has distinct functions.
Left Brain
Typically associated with logical reasoning, language processing, and analytical thinking.
Right Brain
Usually associated with creativity, intuition, and spatial abilities.
Michael Gazzangia
A prominent neuroscientist known for his contributions to the study of split-brain patients and collaboration with Roger Sperry, focusing on how brain hemispheres communicate and function.
Surgical Procedure
used to sever the corpus callosum to reduce seizures in patients with epilepsy.
EEG
shows brain waves in various states such as sleeping, dreaming, or awake in order to measure brain activity. helps to diagnose or monitor epilepsy, brain tumors, sleep disorders, head injuries, and alzheimer’s
CT Scan
A medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed images of the brain and other internal structures, often used to detect tumors, bleeding, or brain injuries.
PET Scan
A medical imaging technique that uses radioactive substances to visualize the functioning of the brain, often used to assess blood flow, glucose metabolism, and to identify abnormalities like tumors or brain disorders. SEE BRAIN DURING TASKS
MRI Scan
A medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, commonly used to detect abnormalities such as tumors, neurological diseases, or injuries.
fMRI Scan
A functional MRI technique that measures and maps brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels, often used in research and clinical settings to study brain functions. BRAIN ACTIVITY AND FUNCTIONS DURING COGNITIVE TASKS