OIA1011 DISTRIBUTION OF SOLUTE BETWEEN INMMISCIBLE SOLVENTS
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Q:What is partitioning in chemistry?
A:The distribution of a solute between two immiscible solvents at equilibrium.
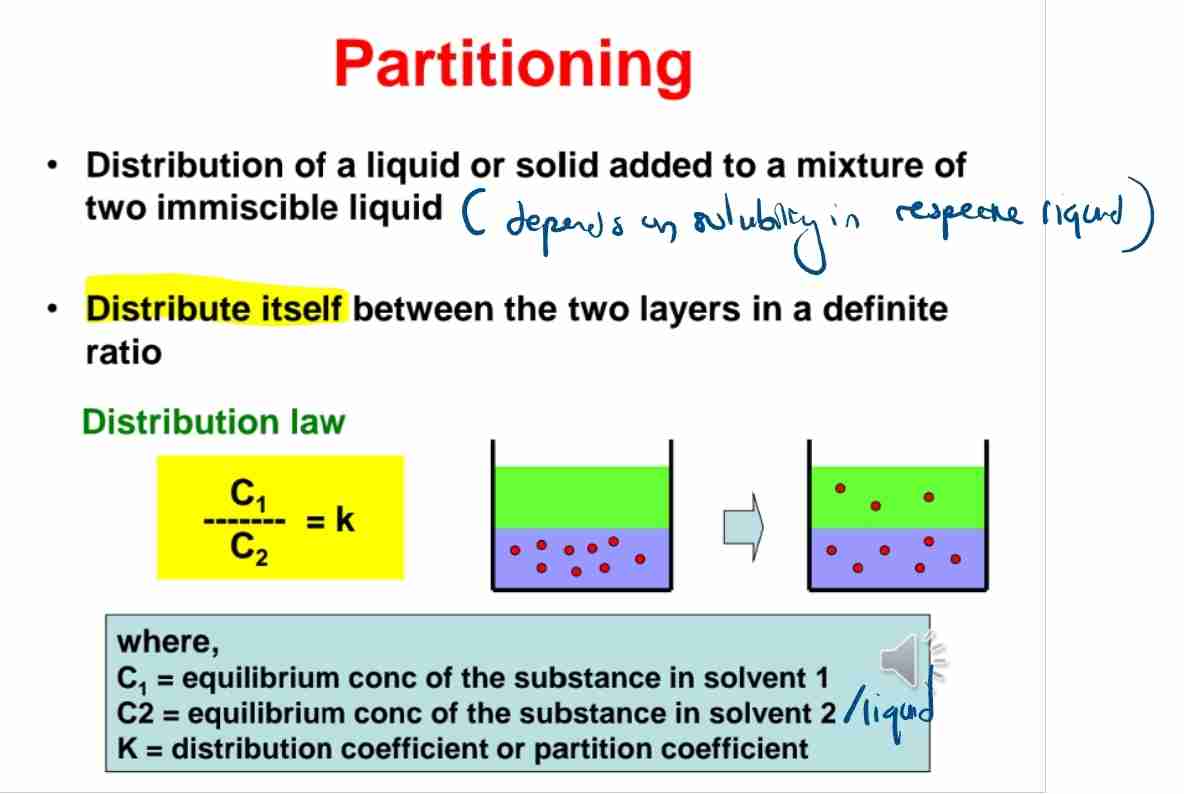
Q:State the partition law.
A:C1/C2=K, where C1 and C2 are solute concentrations in two solvents, and K is the partition coefficient.
Q:What is the partition coefficient?
A:A ratio that describes the equilibrium distribution of a solute between two immiscible phases.
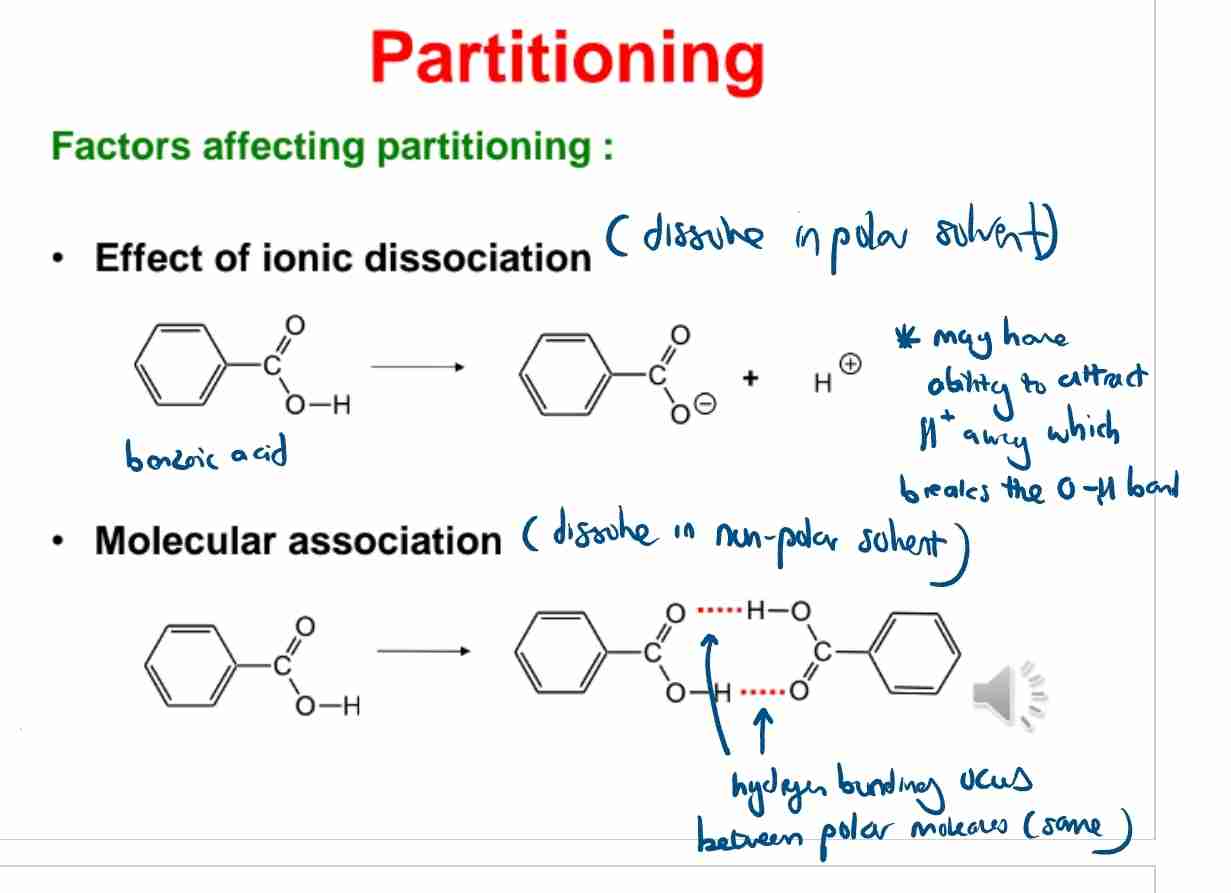
Q:Name two factors affecting partitioning.
A:Ionic dissociation and molecular association.
Q:Why is partitioning important in pharmaceuticals?
A:It influences drug absorption, distribution, and formulation in oil-water systems.
Q:How does pH affect the partitioning of benzoic acid in oil-water systems?
A:pH changes the degree of ionization, affecting its solubility in each phase.
Q:What is the partition coefficient formula for ionizing substances like benzoic acid?
A:K= Co/Cw = [HA]o/[HA]w+[A−]w.
![<p>A:K= Co/Cw = [HA]o/[HA]w+[A−]w.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d0a28354-99a1-4ec2-abad-03ad1de758dc.jpg)
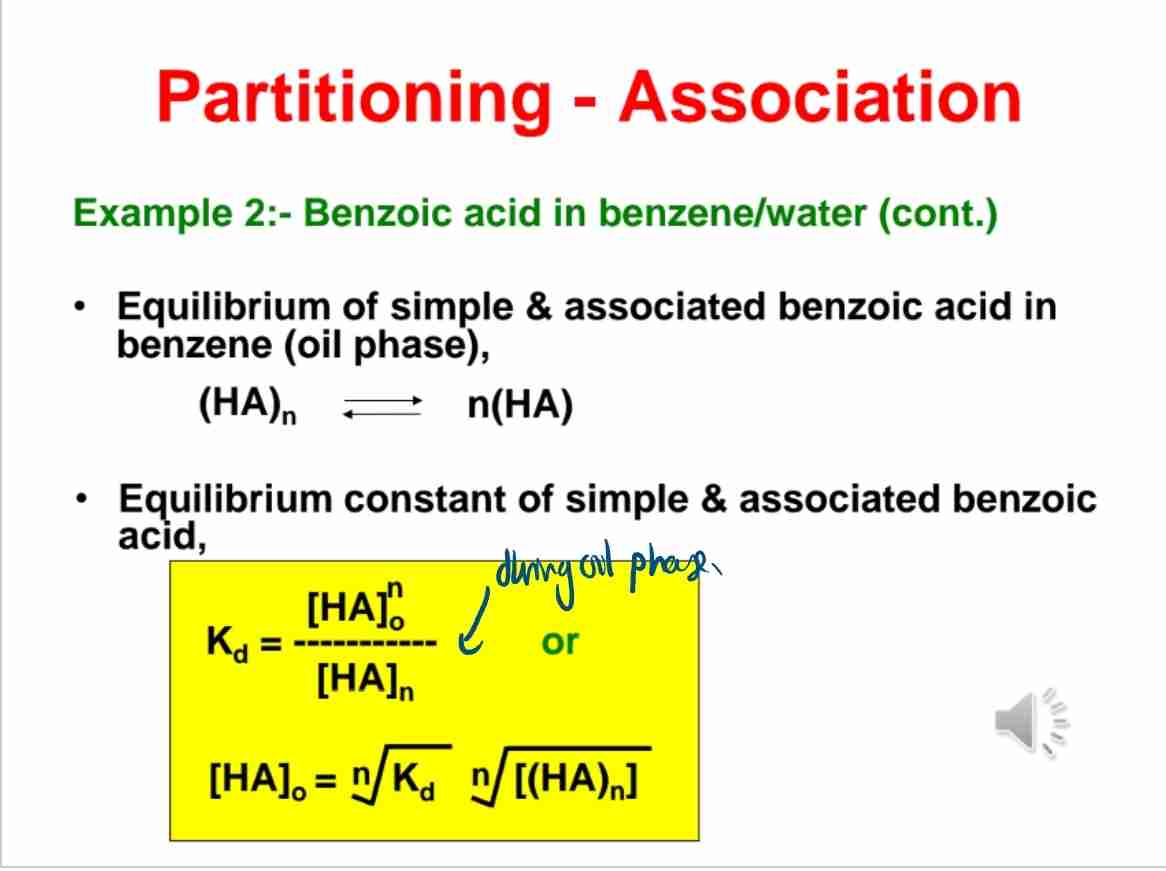
Q:How does molecular association in benzene affect the partitioning of benzoic acid?
A:Benzoic acid forms dimers in benzene, altering its effective concentration.
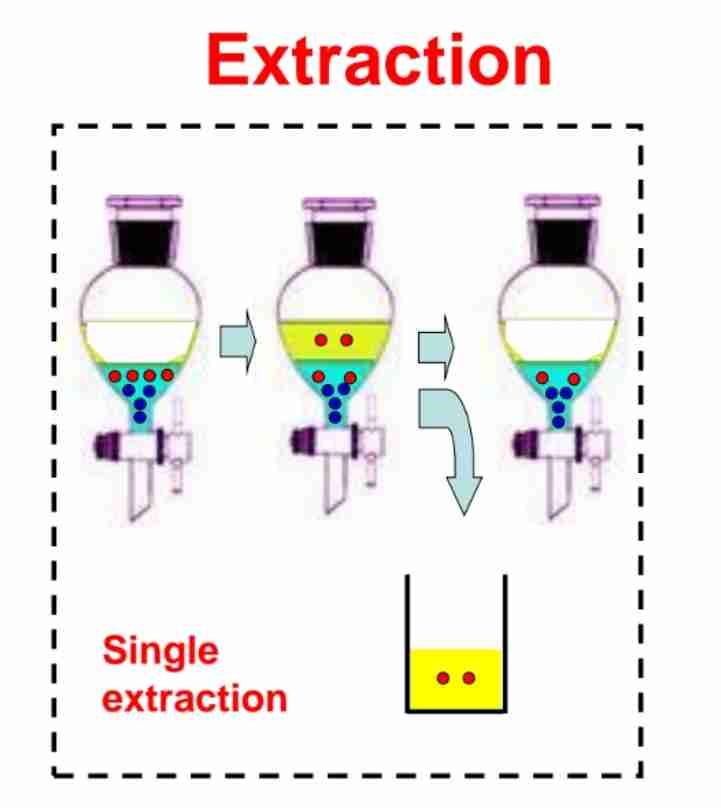
Q:What is extraction in chemistry?
A:A technique to separate components of a mixture using two immiscible solvents.
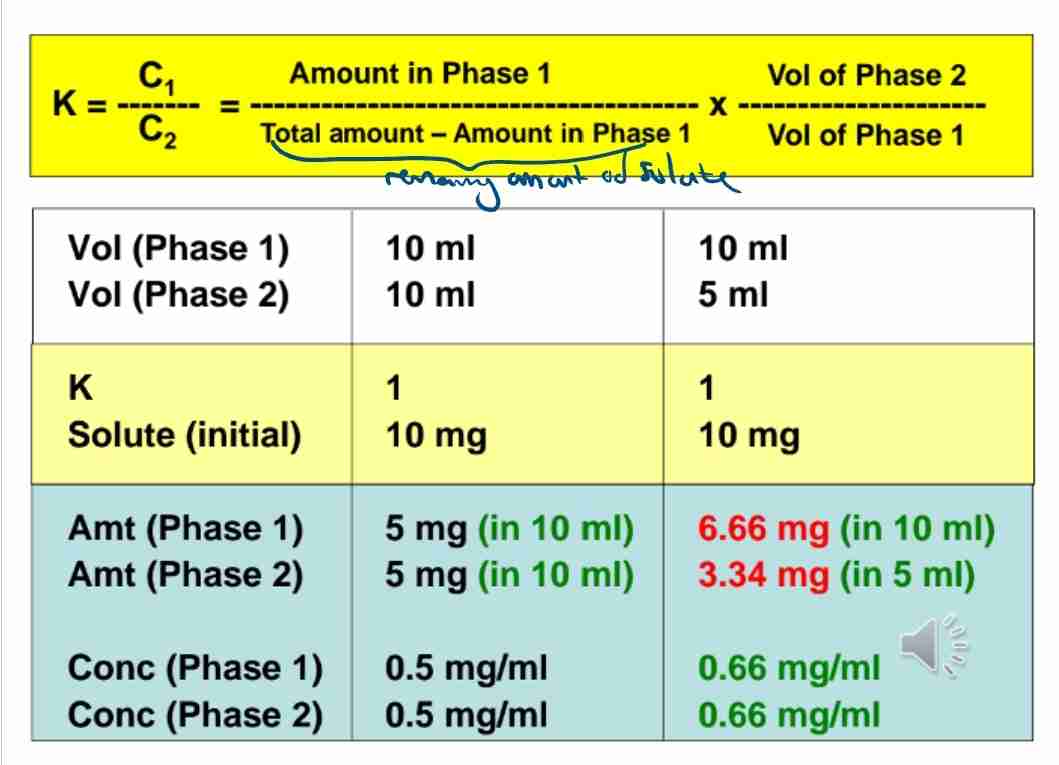
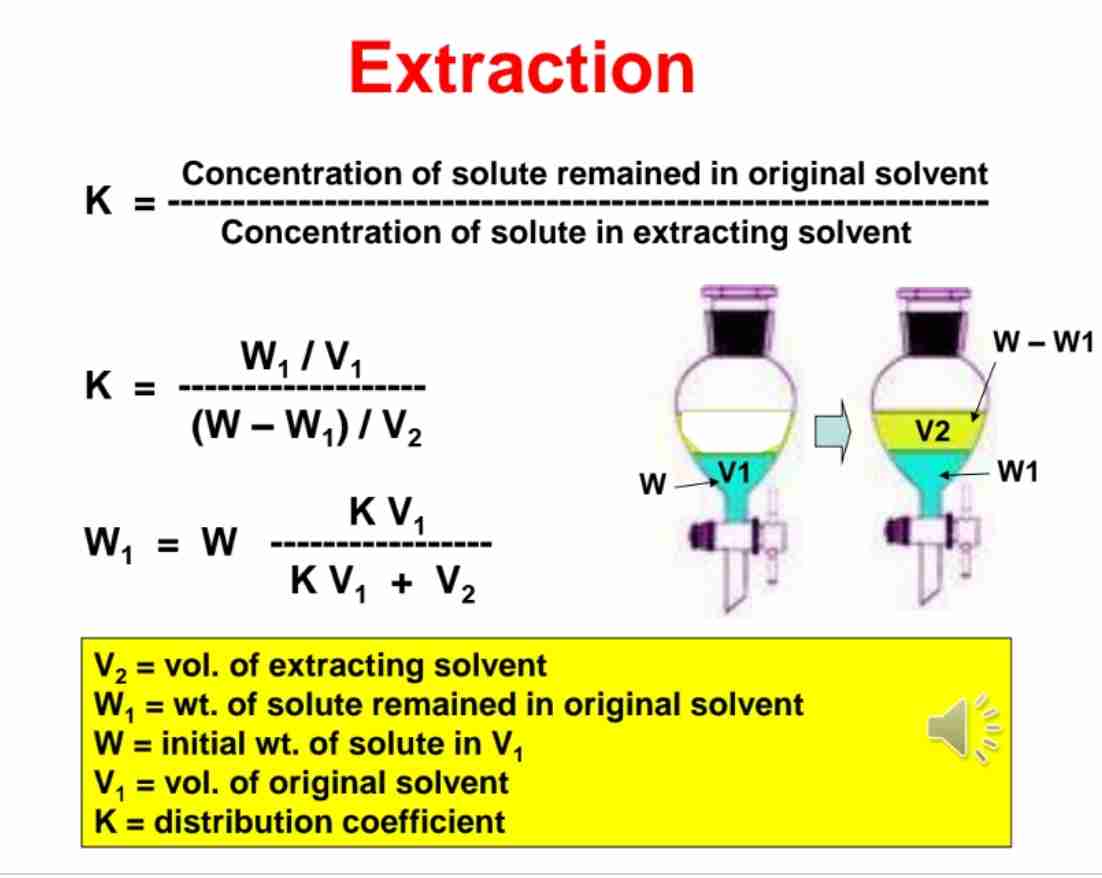
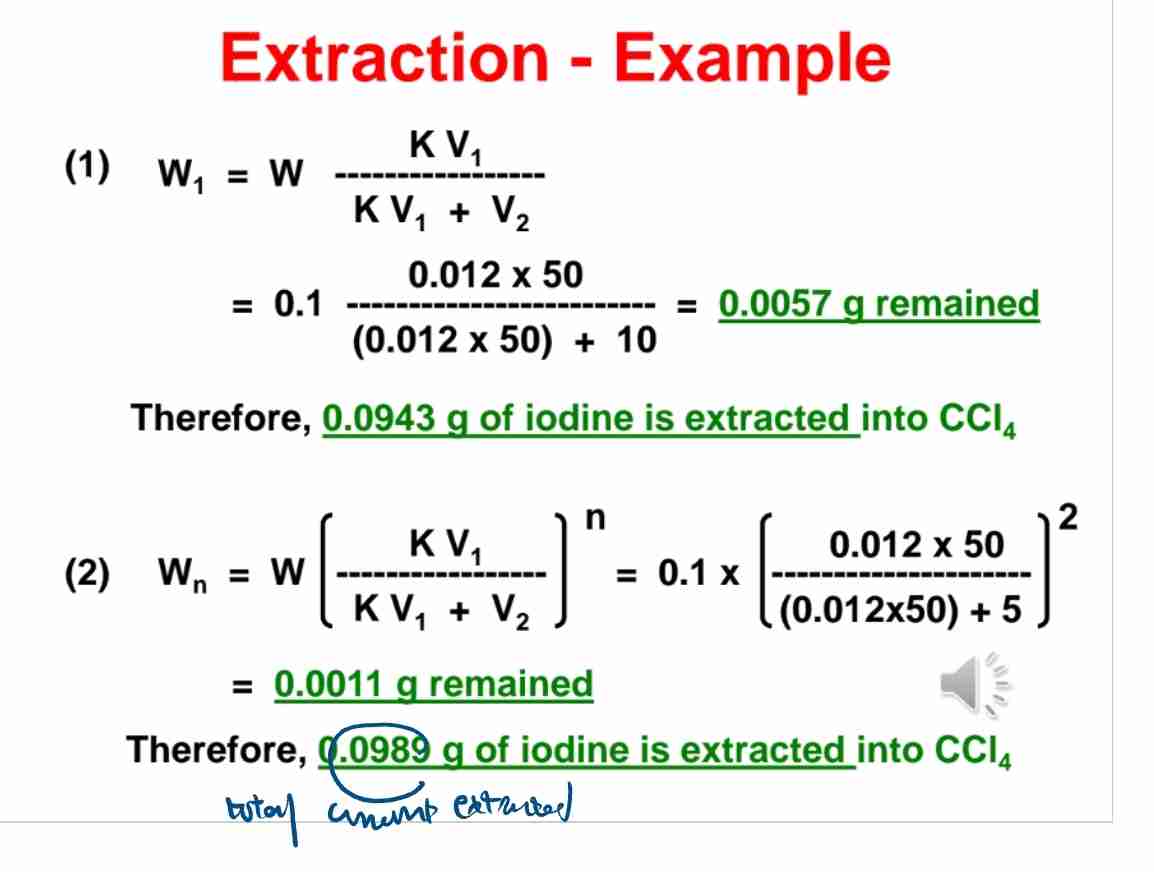
Q:Write the formula for the weight of solute remaining in the original solvent after single extraction.
A:W1=W(KV1+V2) , where K is the partition coefficient, V1 and V2 are solvent volumes.
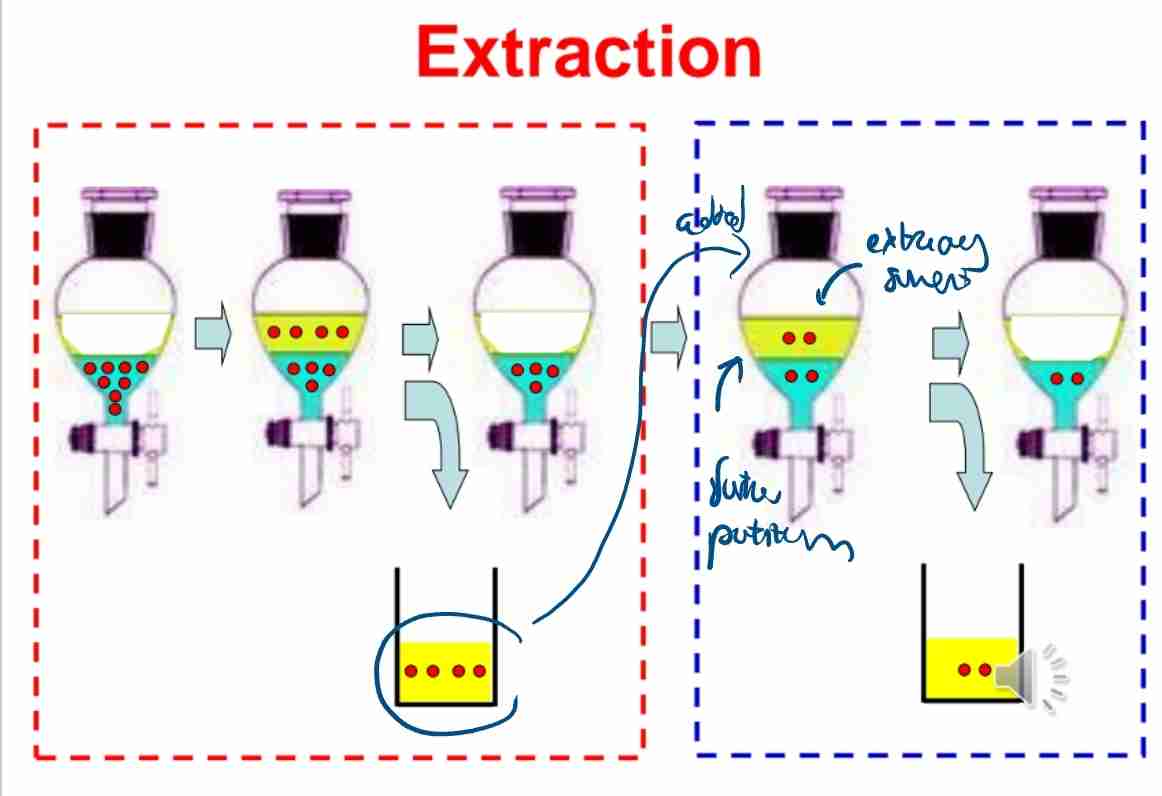
Q:What is the principle behind multiple extractions?
A:Repeating extractions with smaller solvent volumes increases overall efficiency.
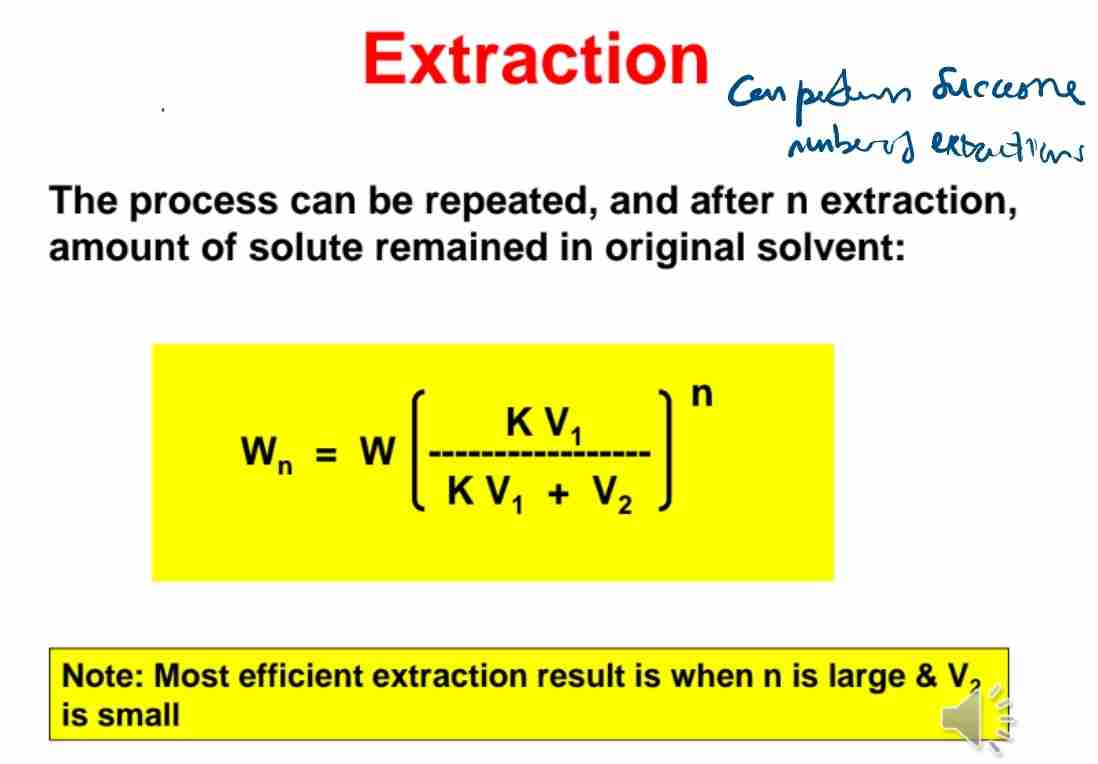
Q:State the formula for solute remaining after n extractions.
A:Wn = W(KV1/KV1+V2)^n.
Q:How much iodine is extracted from water into CCl44 if K=0.012,W=0.1g, V1=50ml, and V2=10ml?
A:0.0943 g of iodine is extracted.
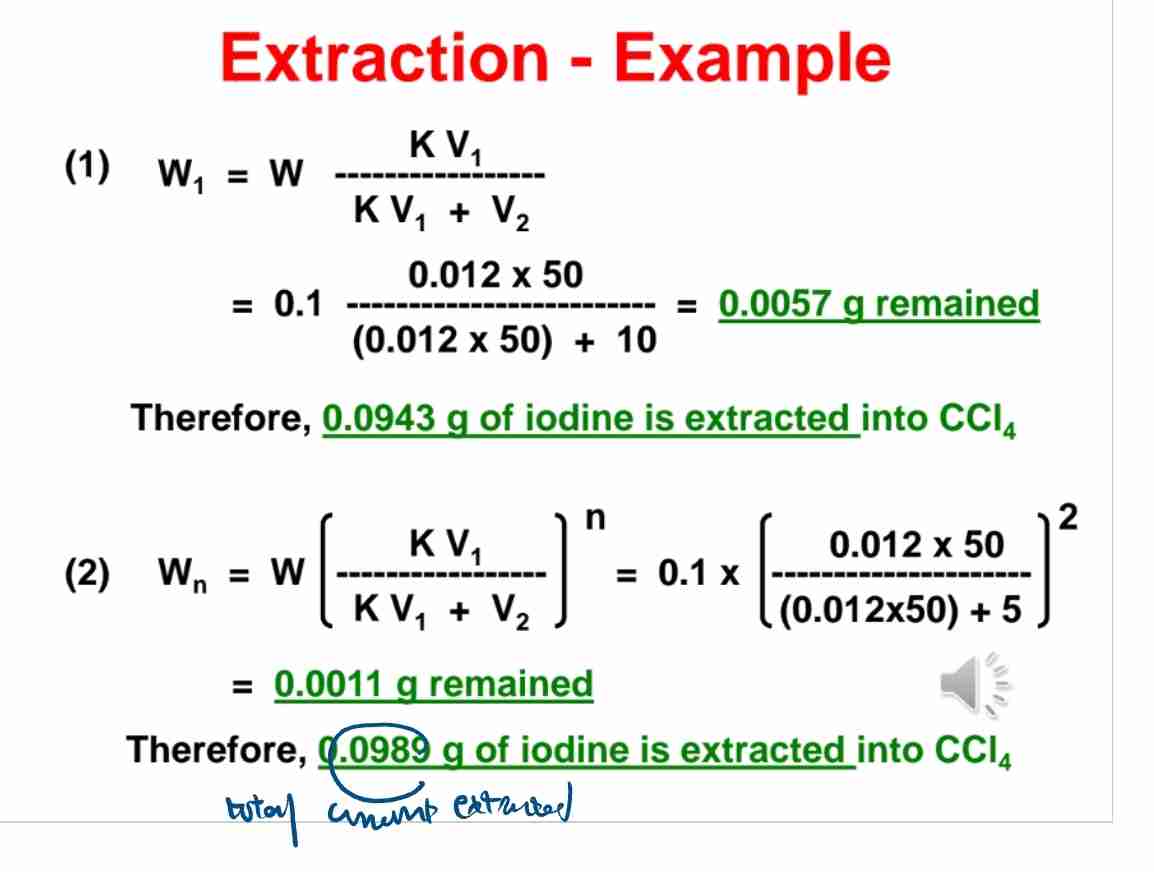
Q:What is the iodine remaining in water after two 5 ml extractions with CCl44?
A:0.0011 g.
Q:Why is small solvent volume preferred for multiple extractions?
A:To maximize the extraction efficiency.
Q:How is the partition coefficient K calculated for a drug in octanol and water?
A:K=Co/Cw, where Co and Cw are the drug concentrations in octanol and water, respectively.
Q:How does partition coefficient affect drug absorption?
A:Drugs with moderate K values (−0.4 to +5.6) can cross cell membranes efficiently.
Q:Define Lipinski’s Rule of Five in drug design.
A:
molecular weight: mw < 500 daltons
octanol-water partition (log P)
-log P « 5 (measure lipophilicity)
- decrease in log P → hinder solubility in aqueous phase
H-bond donors
-no more than 5 H-bond donors (sum of -OH & -NH groups)
H-bond acceptors
-no more than 10 H-bond acceptors (sum of N & O atoms)
Rotatable bonds
-highly Rotatable bond increases conformation flexibility → complete absorption & distribution.
Q:Give an example of a drug with high partition coefficient.
A:DNIB, with logP=2.87.
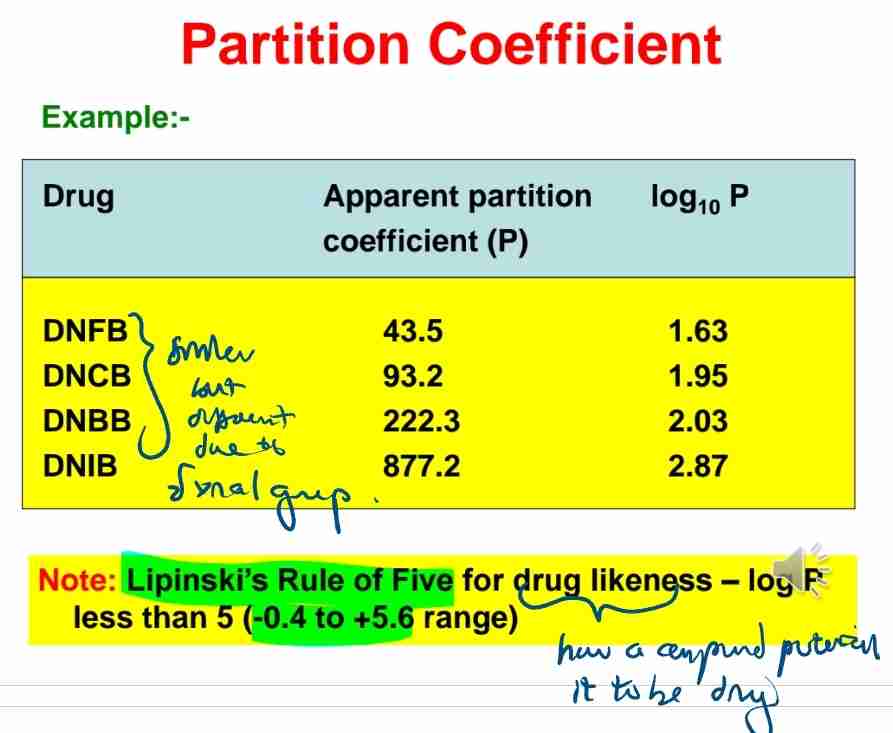
Q:Why is partitioning studied for drug delivery?
A:To understand drug behavior in biological systems like absorption and distribution.
Q:What does a high logP value indicate about a drug's solubility?
A:It is more lipid-soluble and likely to remain in lipid layers.
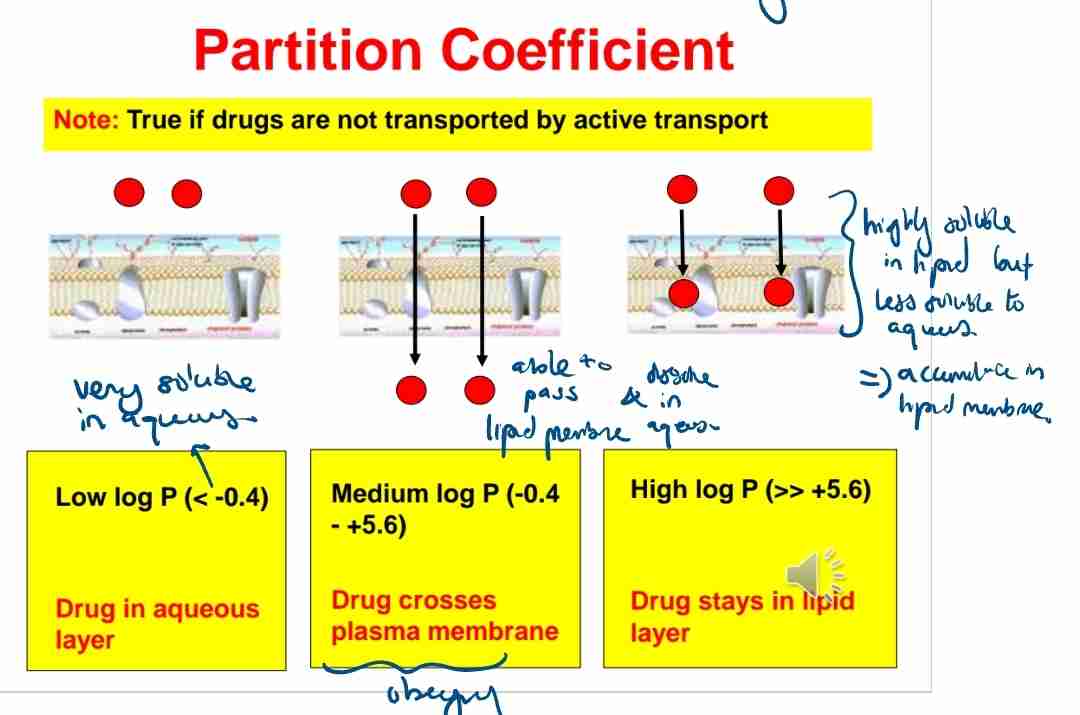
Q:What happens to drugs with logP< -0.4?
A:They remain in the aqueous layer and have poor membrane permeability.
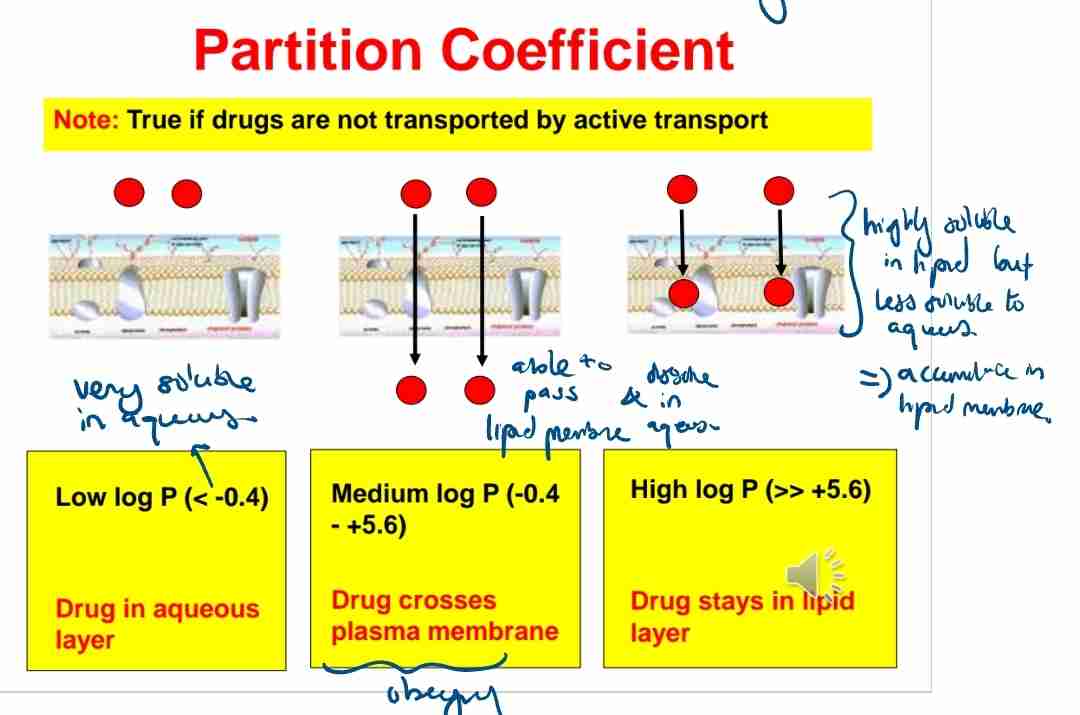
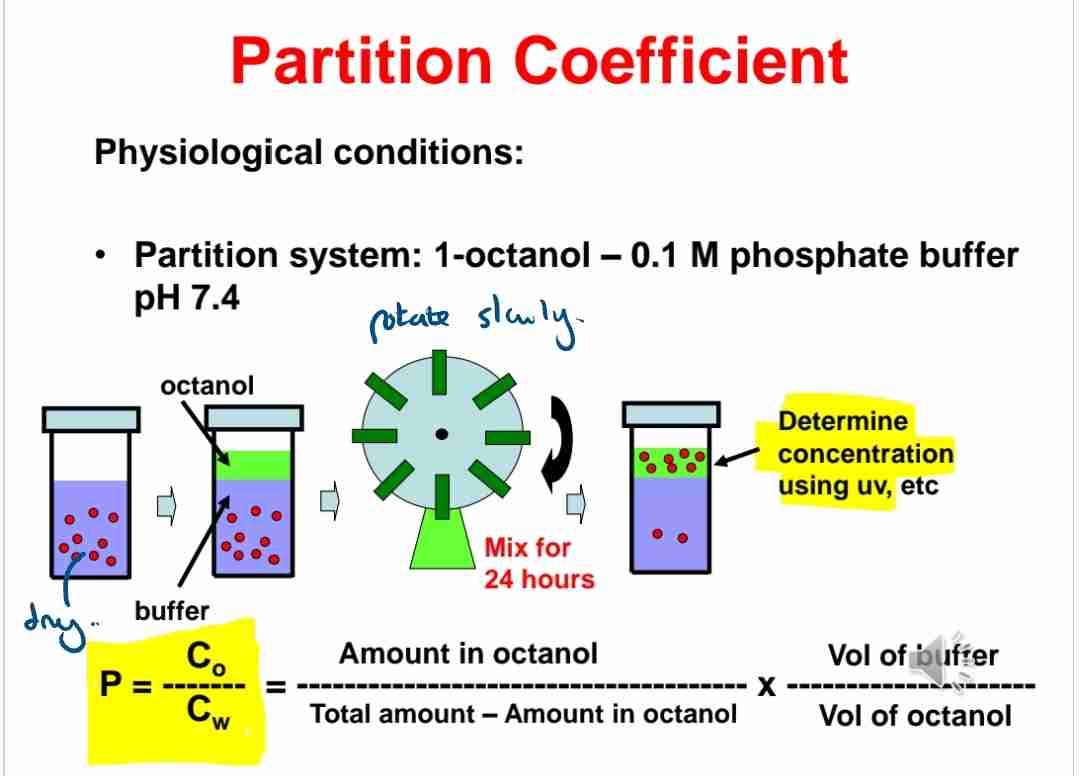
Q:What is the physiological partition system used for testing?
A:Octanol and 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 7.4.
Q:How does temperature affect partitioning?
A:It can change solute solubility, altering the partition coefficient.
Q:Why is UV spectroscopy used in partition studies?
A:To determine solute concentrations in different phases.
Q:What is the role of partition coefficient in excretion?
A:It predicts drug removal via lipid or aqueous pathways.
Q:How can dimerization affect partition coefficients?
A:It reduces the apparent solute concentration in one phase, altering KK.
Q:Why are immiscible solvents used in partitioning studies?
A:To separate phases clearly for accurate measurements.
Q:What is the significance of partition coefficient in toxicity studies?
A:It helps predict accumulation in biological tissues.