Macroeconomics- week 1
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
The wage setting curve
Represents the relationship between the real wage rate and the level of employment that firms are willing to provide. It shows how changes in the real wage rate impact the quantity of labor demanded by firms.
The price-setting curve
Gives the real wage value consistent with the mark-up over costs, when all firms profit maximizes.
Nominal wage
The wage rate measured in current dollars without adjusting for inflation. It represents the actual amount of money paid to an employee for their work.
Employment rent
The economic rent a worker receives when the net value of her job exceeds the net value of her next best alternative (that is, being unemployed). Also known as: cost of job loss
Real wage
The wage rate adjusted for inflation, which reflects the purchasing power of wages. It is calculated by dividing the nominal wage by the price level index
Population of working age
Refers to individuals typically between 15 and 64 years old who are considered to be part of the labor force.
Labor force
Refers to the total number of people who are employed or actively seeking employment in a country or region. .
Participation rate
Labor force/ population of working age
Unemployment rate
unemployed/ labor force
employment rate
employed/ population of working age
Best response function
A best response function in game theory represents the optimal strategy for a player given the strategies of other players. It shows the player's best response to the strategies chosen by others. here: shows how much/little a worker is willing to put in effort compared to their wage and reservation wage
Reservation wage
A reservation wage is the lowest wage rate at which a worker is willing to accept a job. It represents the worker's minimum acceptable compensation.
Labor productivity
A measure of the efficiency of a worker or group of workers in producing goods or services. It is calculated by dividing total output by total input.
MRT= 1+r (interest rate)
The marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) equals 1+ the interest rate (r) in economics. It represents the rate at which one good must be sacrificed to produce one more unit of another good. = the slope of the feasible set
MRS= 1+ p (discount rate)
MRS stands for Marginal Rate of Substitution, which represents the rate at which a consumer can give up some amount of one good in exchange for another while maintaining the same level of utility.
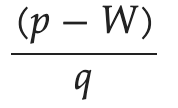
Markup
Markup refers to the difference between the cost of a good or service and its selling price. It is usually expressed as a percentage and is used to calculate profit margins.
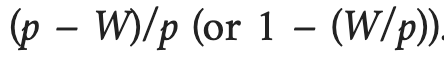
What determines the price-setting curve?
Competition and labor productivity
Cyclical unemployment
Cyclical unemployment is the type of unemployment that occurs due to fluctuations in the business cycle, where job opportunities decrease during economic downturns and increase during economic upswings.
Business cycle
Fluctuations in economic activity characterized by periods of expansion, peak, contraction etc.
Monetary policy
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to control the money supply and achieve macroeconomic goals such as controlling inflation, stabilizing currency exchange rates, and promoting economic growth. It involves setting interest rates, regulating the money supply, and influencing borrowing and spending in an economy.
The labor market
Population→Population of working age→Labor force & out of labor force→Employed & unemployed

Fiscal policy
Fiscal policy refers to the government's use of taxation and spending to influence the economy. It aims to achieve economic goals such as controlling inflation, reducing unemployment, and promoting economic growth.
Demand-deficient unemployment
Demand-deficient unemployment occurs when there is insufficient demand for goods and services, leading to a decrease in production and a rise in unemployment.
Aggregate demand
Aggregate demand is the total demand for goods and services within an economy at a given price level and period of time.
What is the Labor market equilibrium and how can you find it?
Labor market equilibrium is the point where the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded, resulting in stable wages and employment levels.- it is where the wage-setting curve and the price-setting curve intersect
How do firms set their wages?
Firms and employers set wages sufficiently high to make job loss costly, in order to motivate employees to work hard in the absence of complete contracts
How do firms set their prices?
Firms set a mark-up above the cost of production, to maximize their profits subject to demand.
What is the firm’s optimal price?
Where the demand curve is tangent to the isoprofit curve.
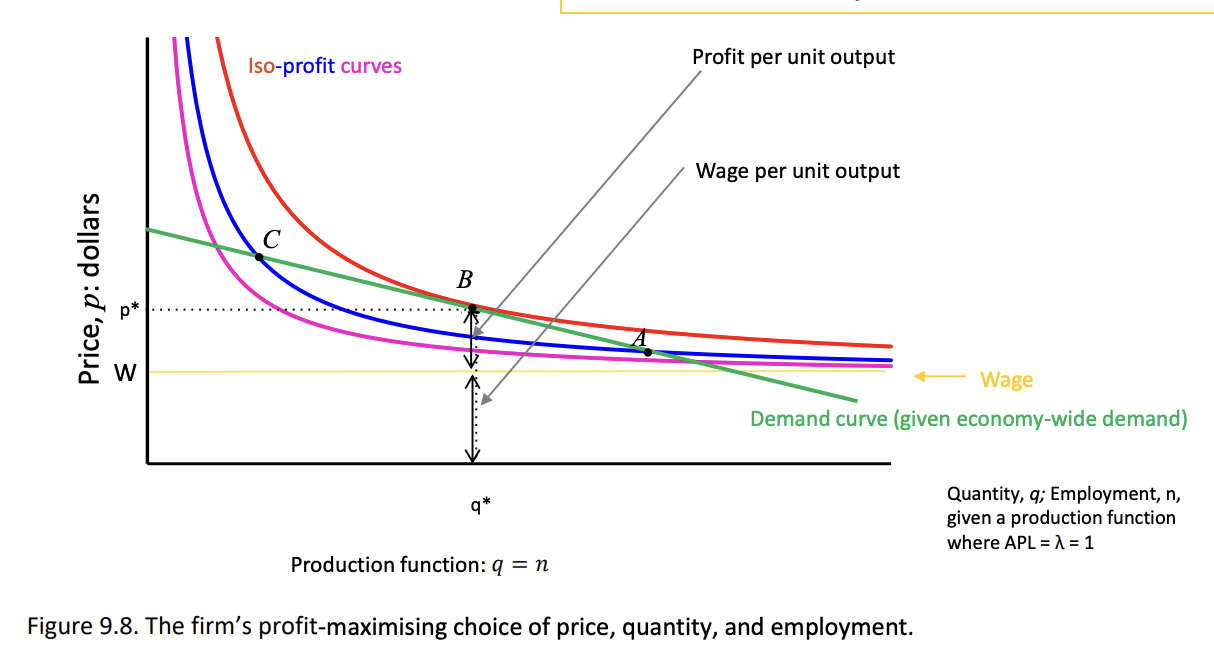
How is output distributed between the firm-owners and the workers?
This is because the choice of profit-maximizing price also determines the firms’s optimal markup above the marginal cost of production: price= profit/output+nominal wage/output
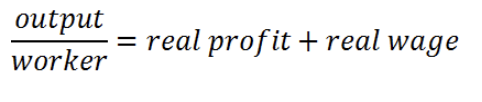
What happens to the price-setting curve if there is an increase in competition?
Price decreases, so there will be a lower markup and the price-setting curve moves up
Why wouldn’t demand-deficient unemployment automatically adjust itself? (ddu→ decrease in production→ decrease in wages→ cut prices→increase in demand→firms hire more)
Because in the real world workers tend to look at their nominal wage and not the real wage. Lowering the nominal wage leads to less effort and maybe strikes. Lower wages also mean that people spend less → AD falls
Labor union
An organization formed by workers to protect their rights and improve working conditions through collective bargaining with employers.
Wage bargaining
Negotiation process between employers and employees to determine the terms and conditions of employment, including wages and benefits.
Bargaining curve
Indicates the wage that the union-employer bargaining process will produce for every level of employment. Its position above the wage-setting curve depends on the relative bargaining power of the union and the employer.
The union voice effect
Providing employees with a voice in how decisions are made may induce them to provide more effort for the same wage.
The bargained wage curve shifts downward.
The overall effect of labour unions on employment is ambiguous.
Shifts in the price-setting curve:
education and training: labor productivity increases →shifts up
Wage subsidy: Production costs and prices decreases → shifts down
Shifts in the wage-setting curve:
Reservation wages decreases = downward shift in the wage-setting curve
Shifts in labor supply curve
Immigration policies: labor supply increases
Childcare provision: female labor participation increases