MRI in Dental Imaging: Beyond the Bones
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Learning objectives
Explain the basic principles of MRI and how it differs from other imaging modalities
Identify the key dental and maxillofacial structures best visualized by MRI
Describe clinical indications for MRI in dental practice
Recognize the role of dental hygienists in supporting MRI based diagnostic
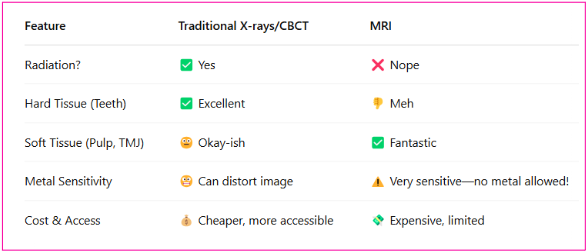
Compare MRI to traditional dental imaging methods in terms of safety, resolution, and applications
What’s hiding in the soft tissue?
Dentistry has long relied on x-rays and CBCT scans for hard tissues exams
What about muscles, nerves, discs, and glands?
MRI
X-rays and CBCTs are like a blueprint of the house (hard walls), MRI is like seeing where the plumbing and wires (soft tissues) are
What is MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging
uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images
no ionizing radiation- safe for repeated use
best for soft tissue contrast
common in medicine for brain, joints, hearts…and now teeth!
MRI vs Traditional Dental Imaging
MRI isn’t replacing dental x-rays, it’s complementing them, especially for soft tissue diagnostic
Uses in Dentistry
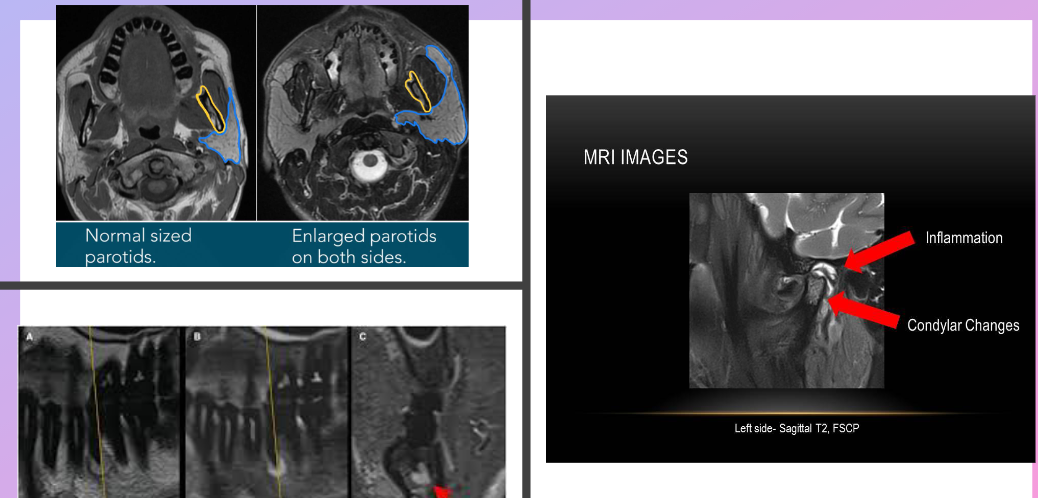
TMJ Disorders
shows disc position, joint fluid, inflammation
no other imaging does this as clearly
important for distinguishing muscle pain vs joint dysfunction
Salivary Glands
detects tumors, blockages, or sialoliths
Pulp Tissue and Nerves (Experimental Use)
can visualize inflamed or necrotic pulp
still being studied but looks promising
Oral pathology
evaluation of soft tissue massess
differentiates between inflammatory and neoplastic lesions
Specific case examples
Patient with jaw pain when chewing, jaw locks, no visible swelling, and no significant findings on PANO
MRI can reveal disc replacement and/or joint inflammation that is not visible on a PANO
Patient with recurrent swelling on left cheek, no pain but discomfort, reduced salivary flow from parotid, negative PA and PANO findings
MR sialography to view ductal system of gland
Trauma to central incisor, gray color, no mobility, asymptomatic, no fracture on CBCT
MRI of the pulp chamber can detect changes in blood flow or inflammation in pulp
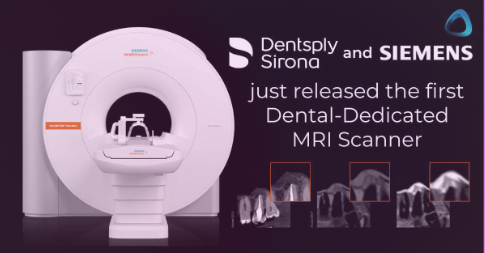
Dental MRI Technology
Most MRI machines used are medical grade, full body
New tech is emerging
Nano MRI, ORAL-MR, Fraunhofer MRI scanner
Shorter scan times, small and focused FOV size, high-resolution for small oral structures
Scan time and experience
Takes 15-45 min
depends on region scanned, image resolution needed, patient motion
Comfortable, non-invasive, often done without contrast
Limitations and Challenges
Physical Limits
metal artifacts-metal restorations, braces, or implants distorts MRI images
motion sensitivity-blurry images if movement (kids, anxiety)
claustrophobia-enclosed space and loud sounds
cost and time-MRIs are expensive and can take 20-45 min or more
NOT ideal
routine cavity checks
detailed images of enamel or restorations
patients with inability to sit still for 20-40 min
Most dental clinics won’t have MRI, but may refer patient to a medical imaging center
Ethical and safety considerations
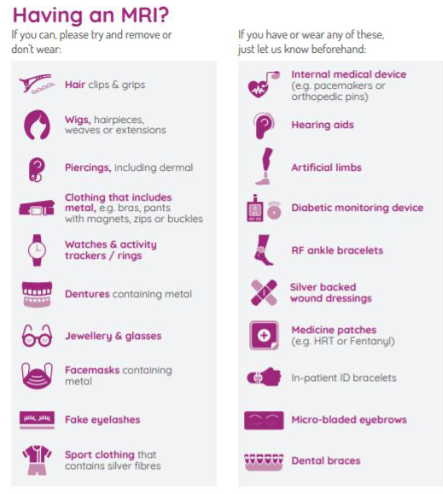
Always screen contraindications
pacemakers, cochlear implants, certain metallic restorations
MRI-safe environments are highly controlled
MRI has no radiation, but strict safety protocols apply
Role of the DH
Know when MRI might be indicated
Take a thorough history (pacemakers, metal implants, etc)
Educate patients on need and process
no metal, may take 30+ min, completely painless
Record referrals and findings
Research and future of MRI in dentistry
Explore the uses for
caries detection (especially early stage lesions)
high resolution dental MRI for root canal anatomy
AI-enhanced MRI interpretation for diagnosis and treatment
Final thoughts
MRI opens new windows into dental diagnostics
It complements, no replaces, traditional imaging
As technology improves, MRI may become standard in complex dental cases
Stay informed- you’re part of the future of dental imaging