CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 8: Transport in Plants
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Function of Xylem in transport
To transport water and soluble mineral ions
Function of Phloem in transport
To transport nutrients such as sucrose, amino acids and hormones
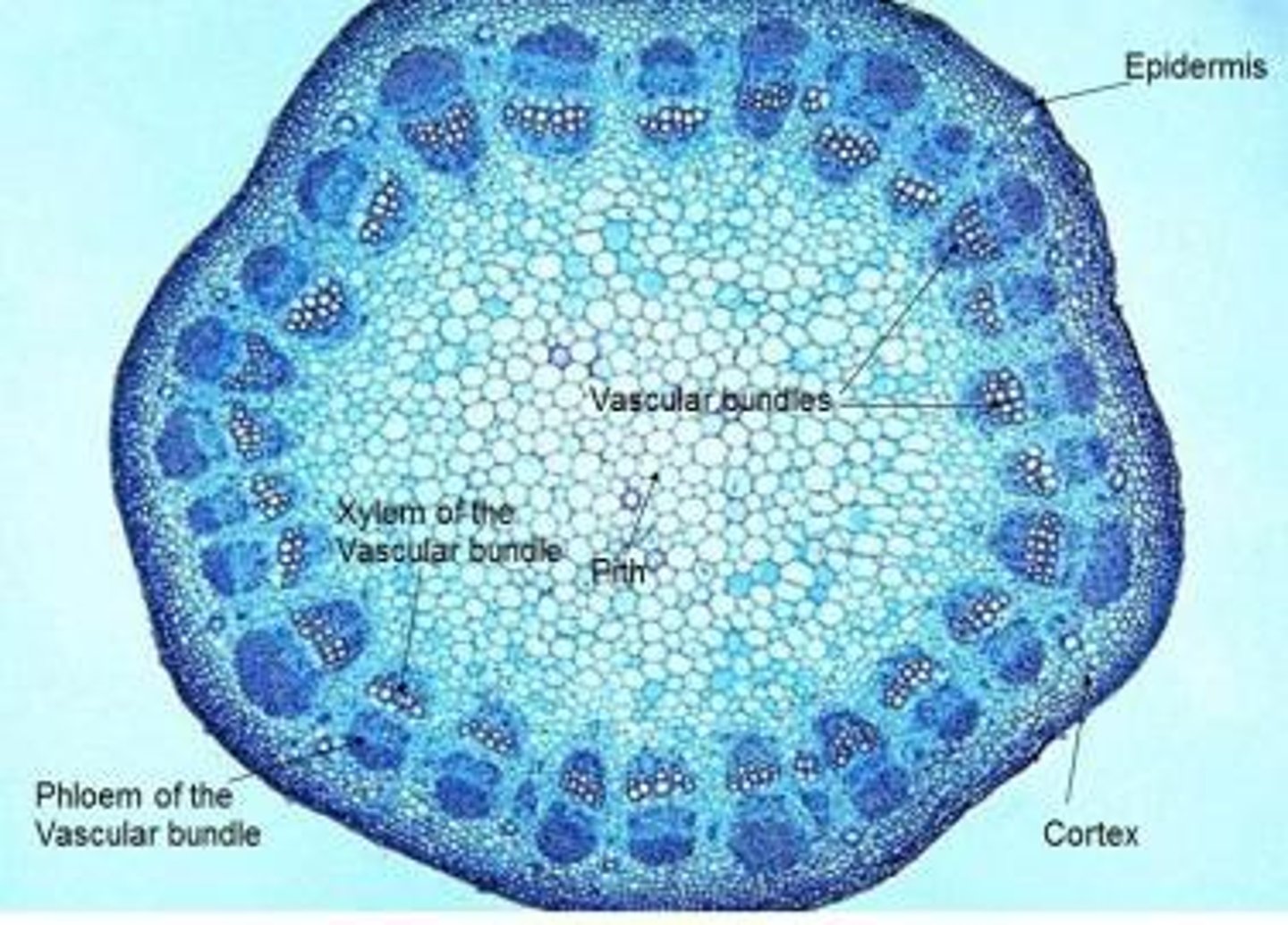
Vascular bundles
Bundle of phloem and xylem with phloem on the outside and xylem on the inside of the bundle
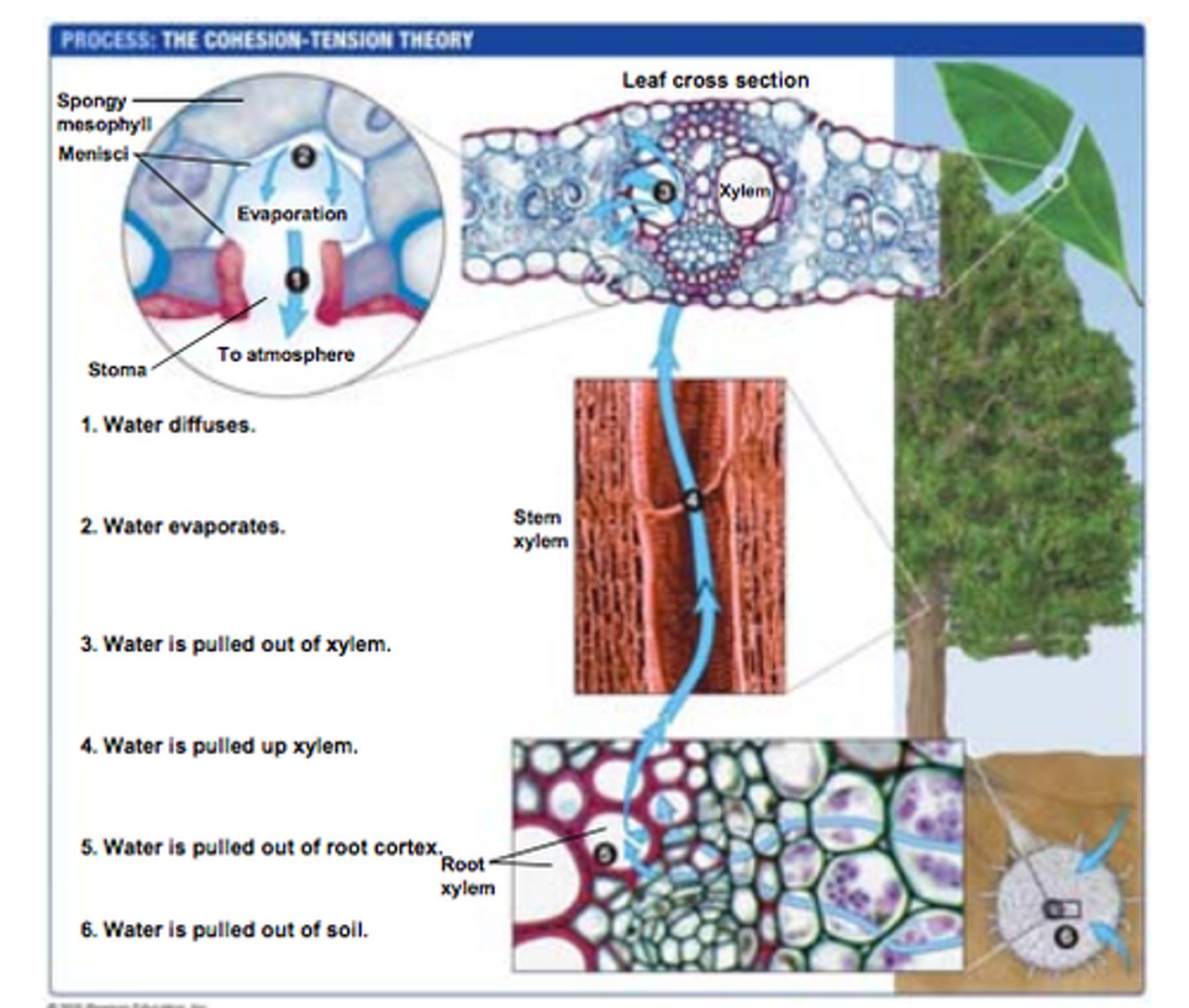
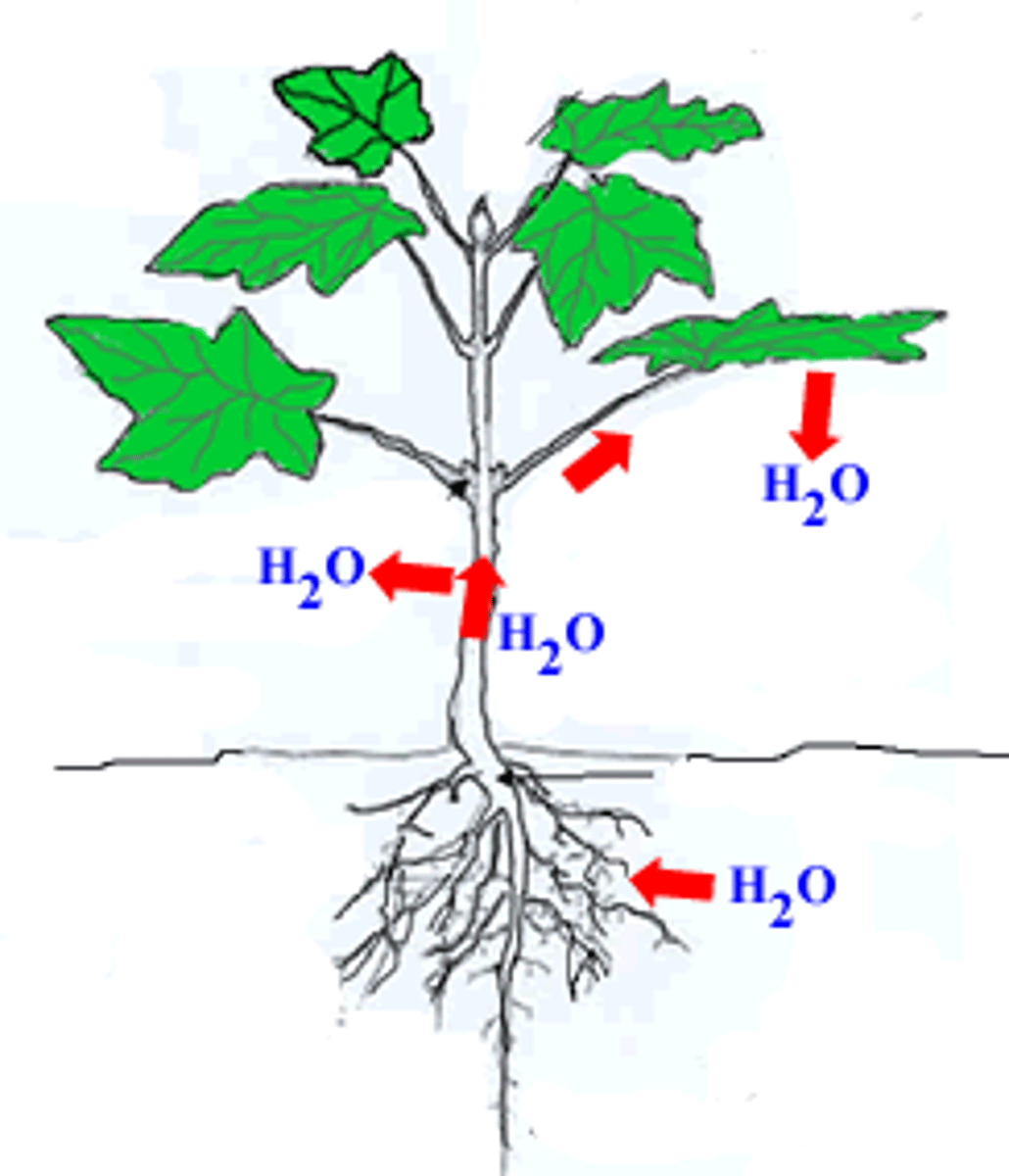
Water uptake by roots
Water enters root hair by osmosis,
passes through root cortex cells by osmosis then pass into xylem up the stem,
and to the leaves
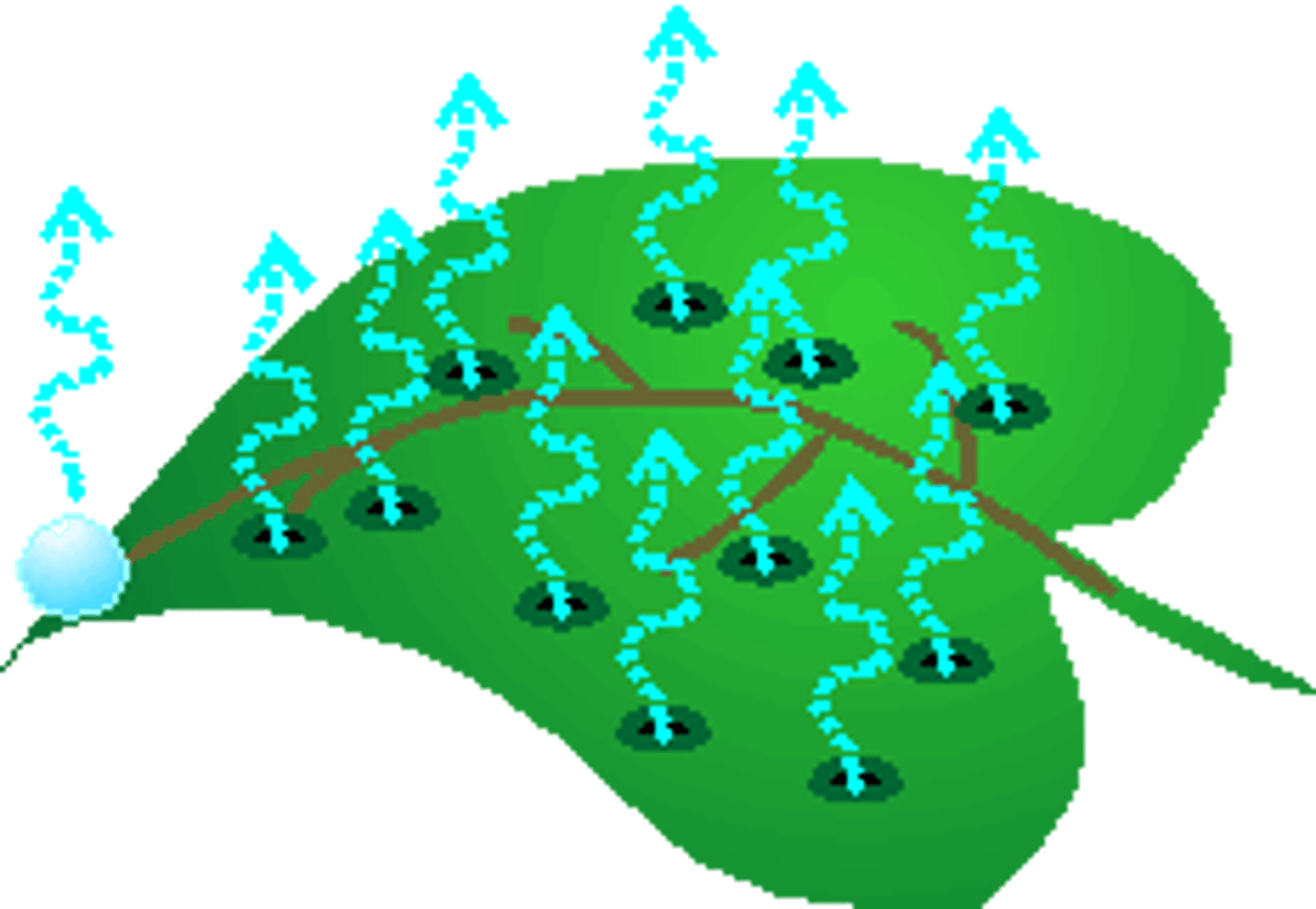
Cause of water vapor lost
High surrounding temperature, low humidity, causes water to evaporate at higher rate
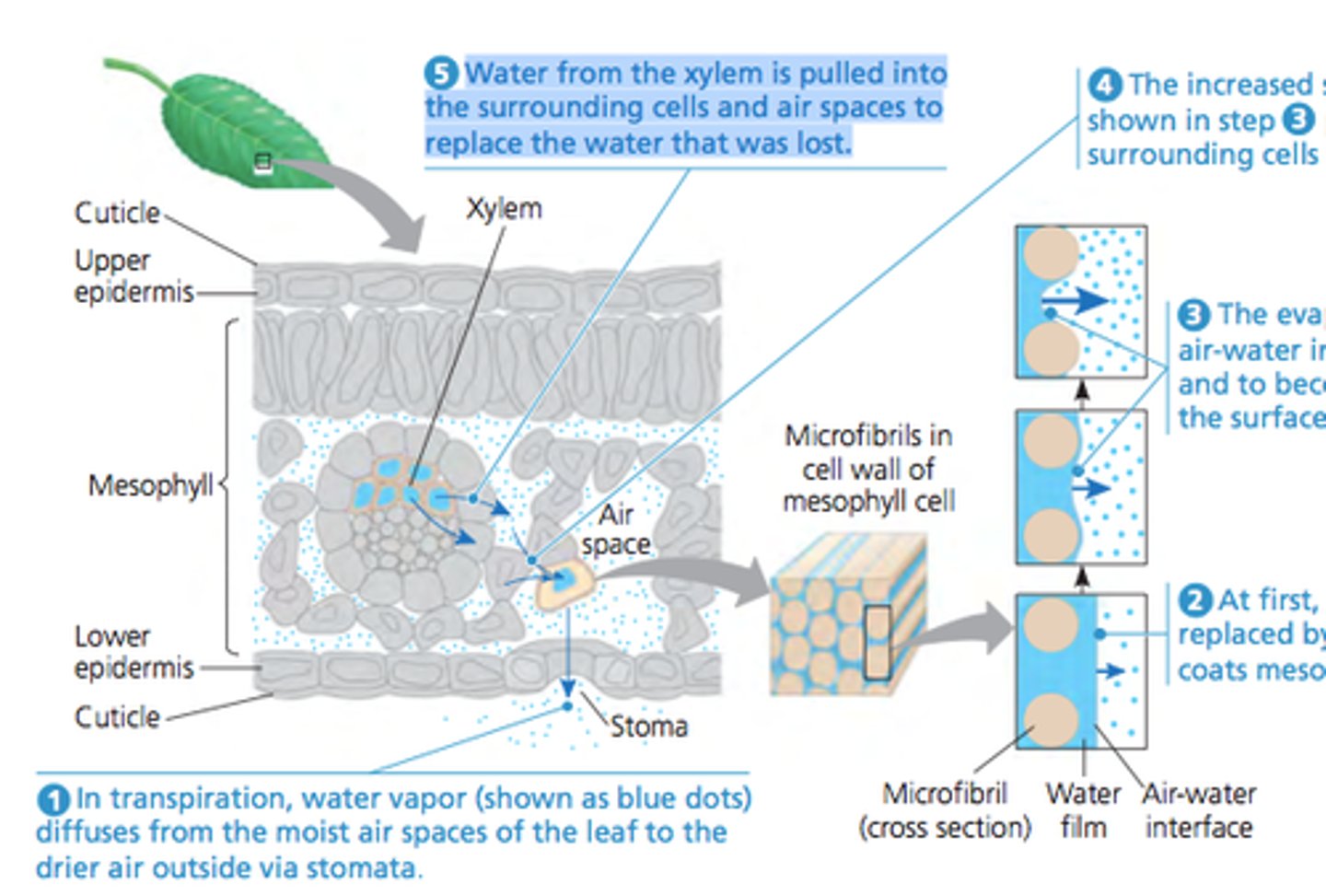
Transpiration
loss of water vapour from plant leaves by evaporation of water at the surfaces of the mesophyll cells followed by diffusion of water vapour through the stomata
Function of Transpiration
- transporting mineral ions
- providing water to keep cells turgid in order to support the plant
- providing water to leaf cells for photosynthesis
- keeping the leaves cool by evaporation
Transpiration pull
draws up a column of water molecules through the xylem, held together by cohesion caused by the loss of water through the leaf (water moves up by cohesion and adhesion)
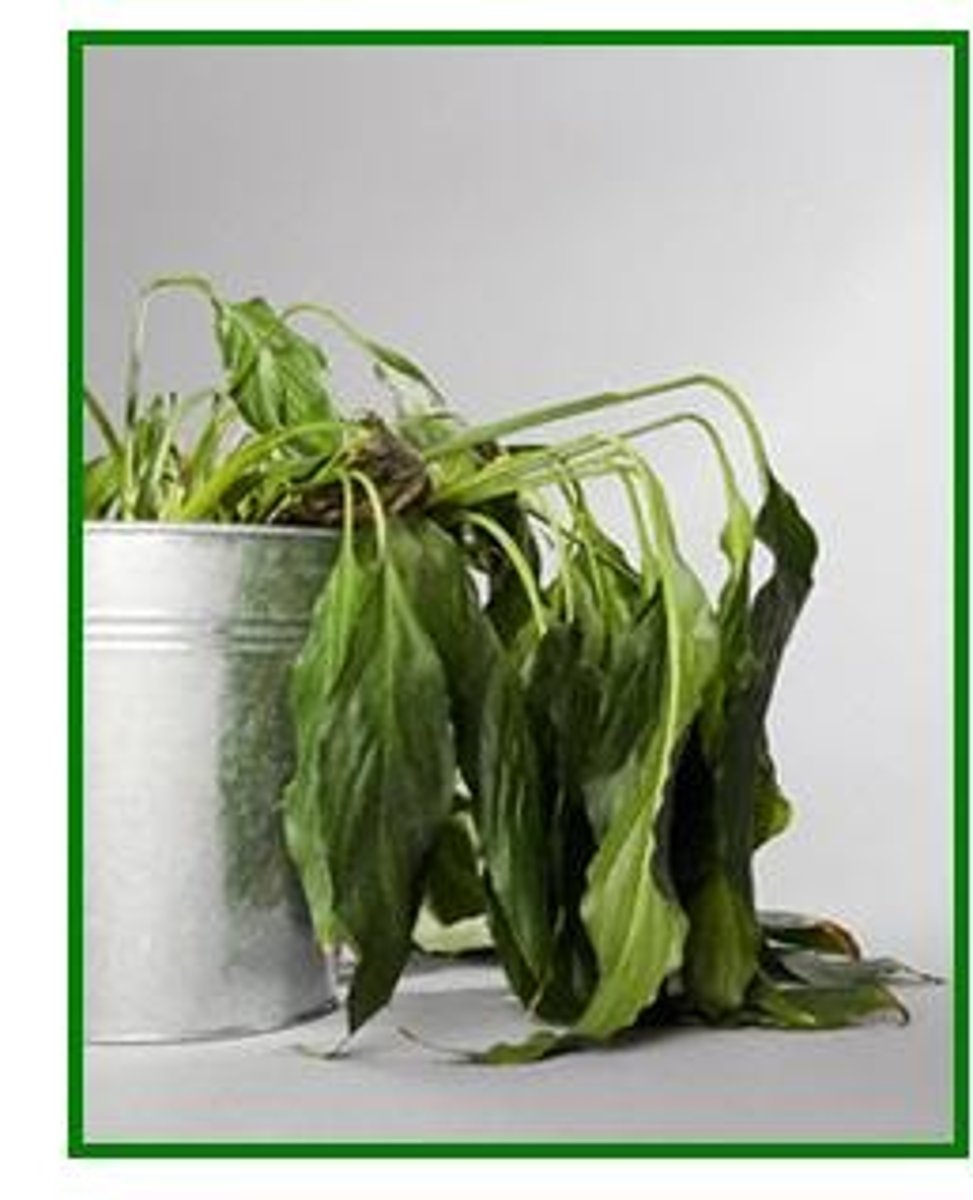
Wilting
Plant cells lose water becoming flaccid, mechanical support fails and plant no longer can support itself

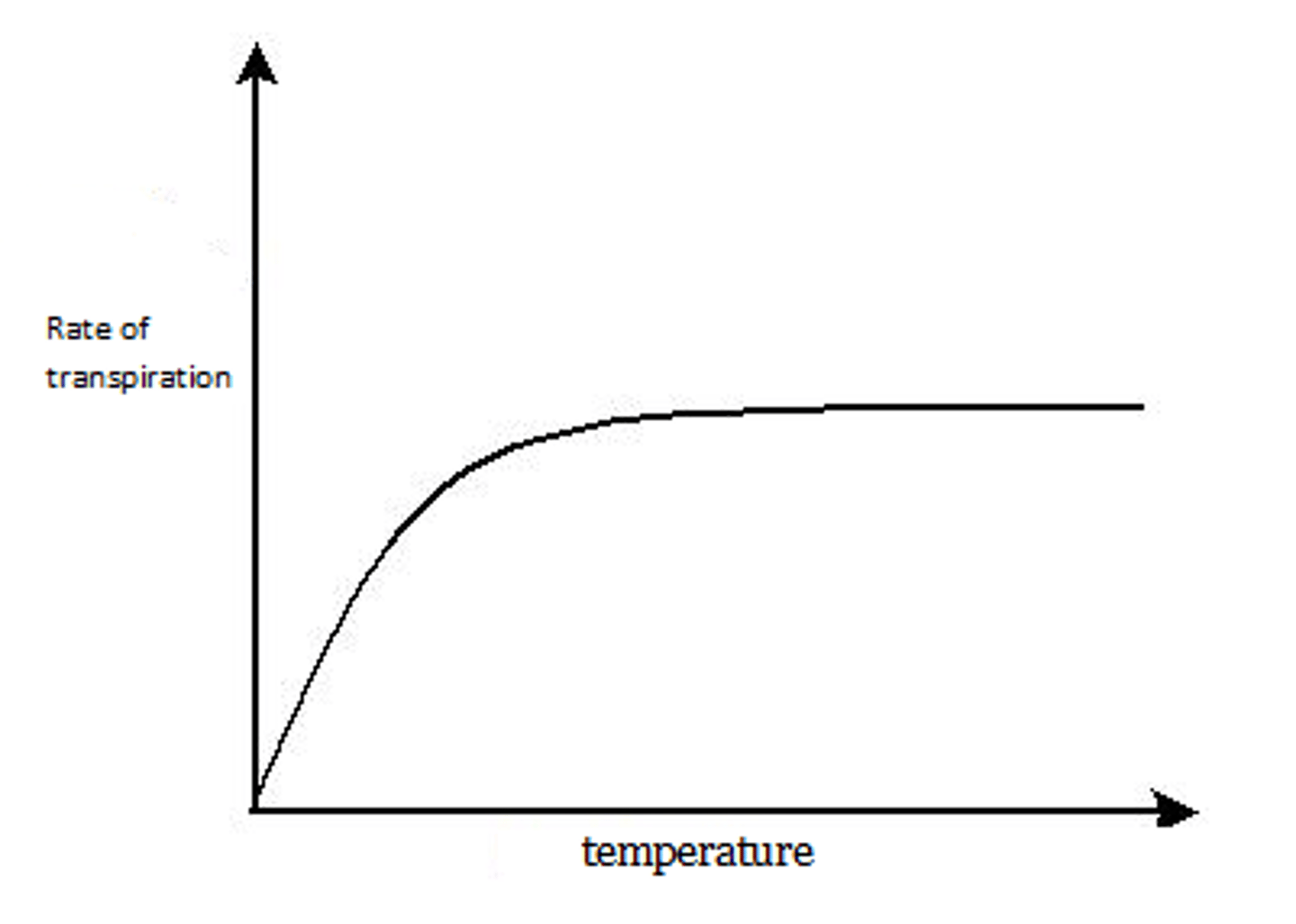
Temperature effect on Transpiration
Temperature increase rate of transpiration increase, as water evaporate faster from leaves due to high temperature
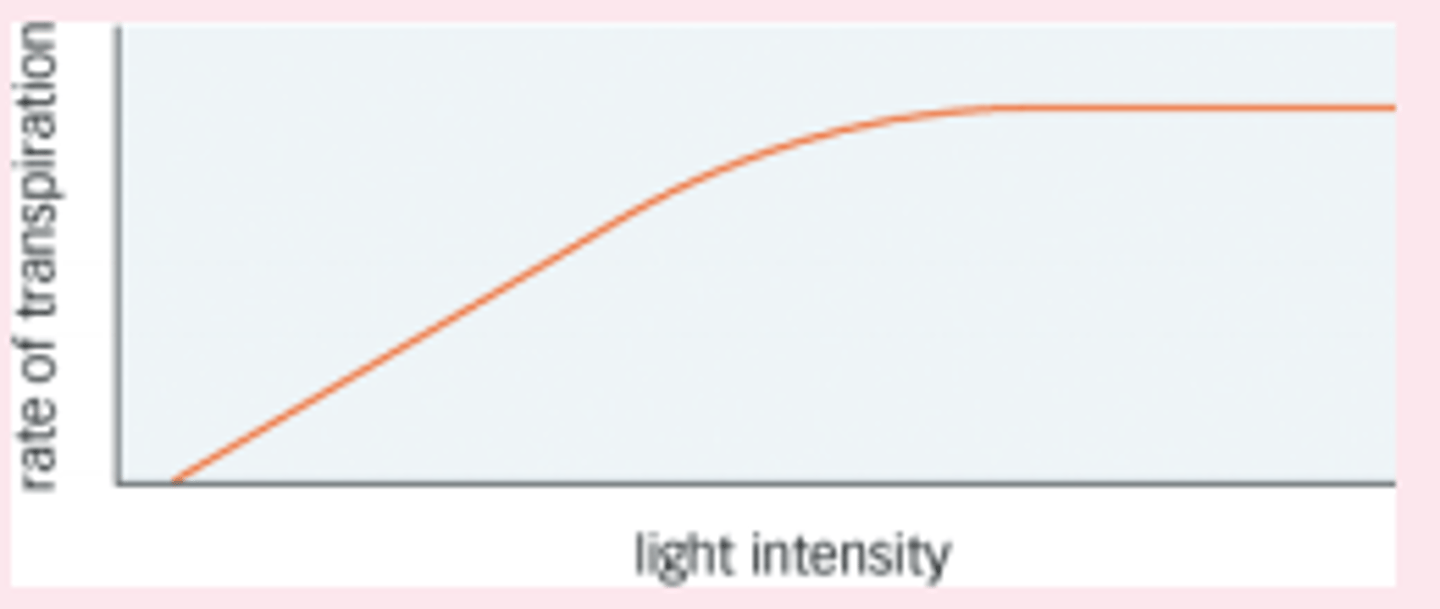
Light intensity effect on Transpiration
Light intensity increase rate of transpiration increase as stomata open wider allowing larger area for water vapour to escape
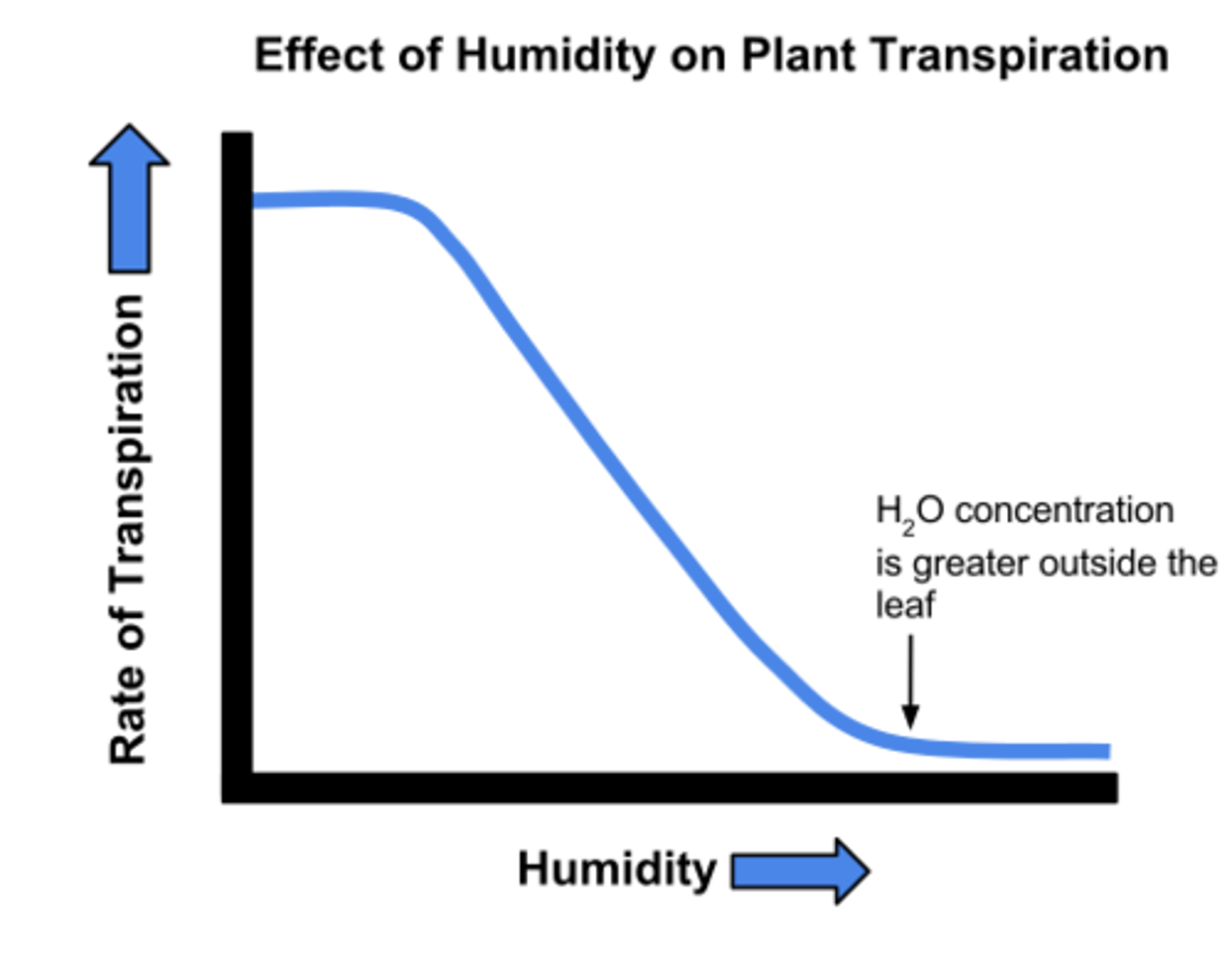
Humidity effect on Transpiration
Rate of transpiration decrease as humidity increase, water outside of leaf collide with water vapour inside leaf reducing rate of transpiration
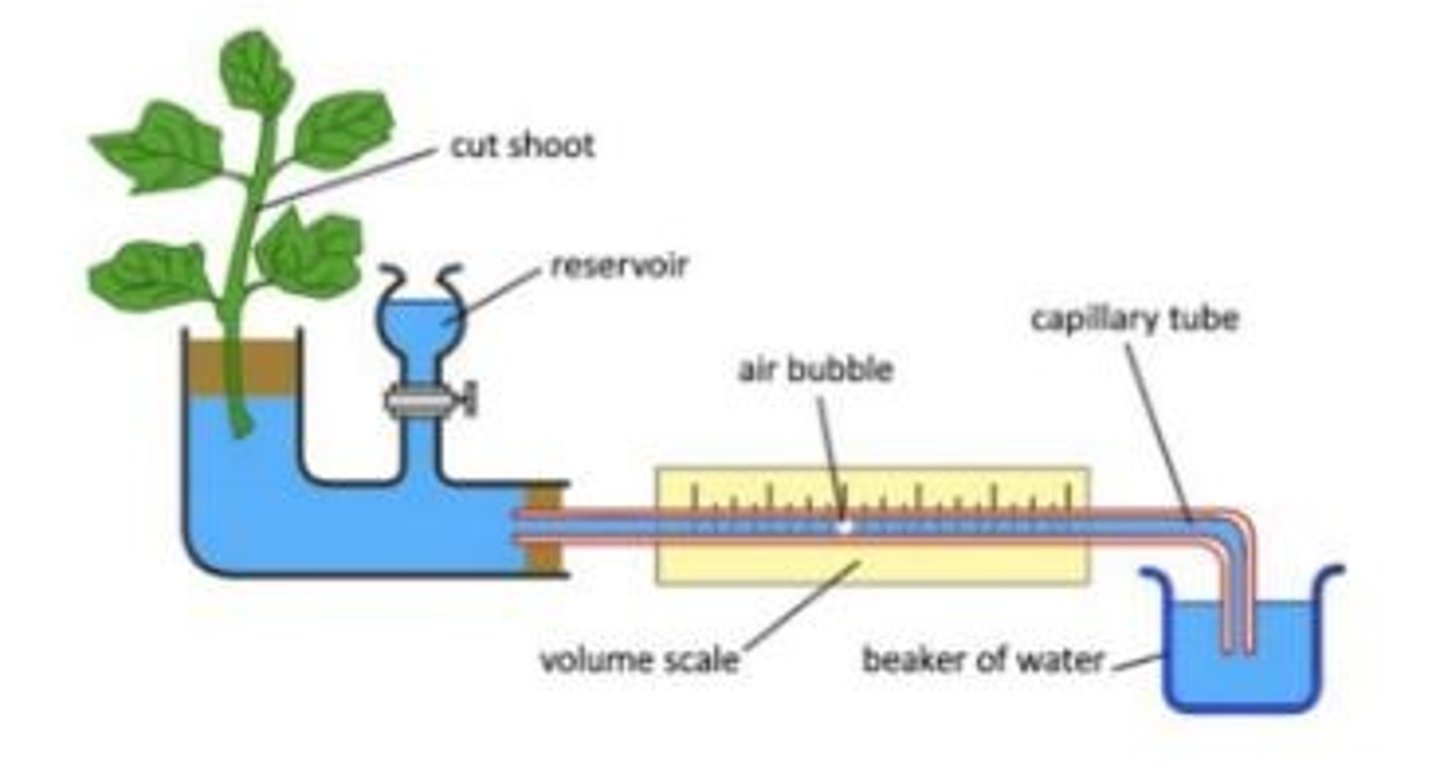
Measure transpiration (potometer)
Set up potometer to measure water loss by transpiration
Translocation
the movement of sucrose and amino acids from the leaves to regions of respiration, growth, and storage through the phloem
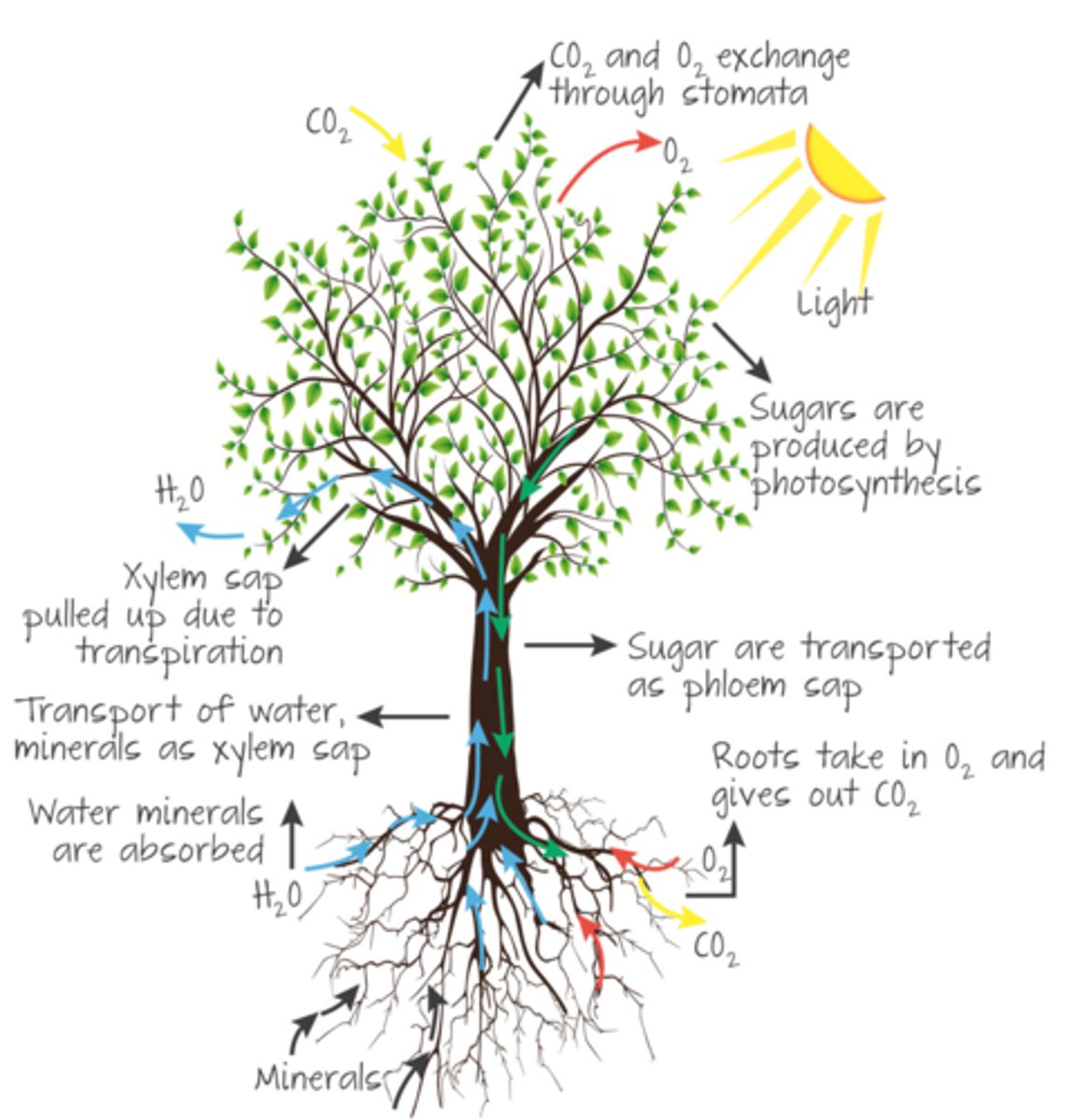
Sources
Regions of productions in plants

Sinks
Regions of respiration, growth, and storage
