UWORLD Hematology & Oncology Step 2 CK
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
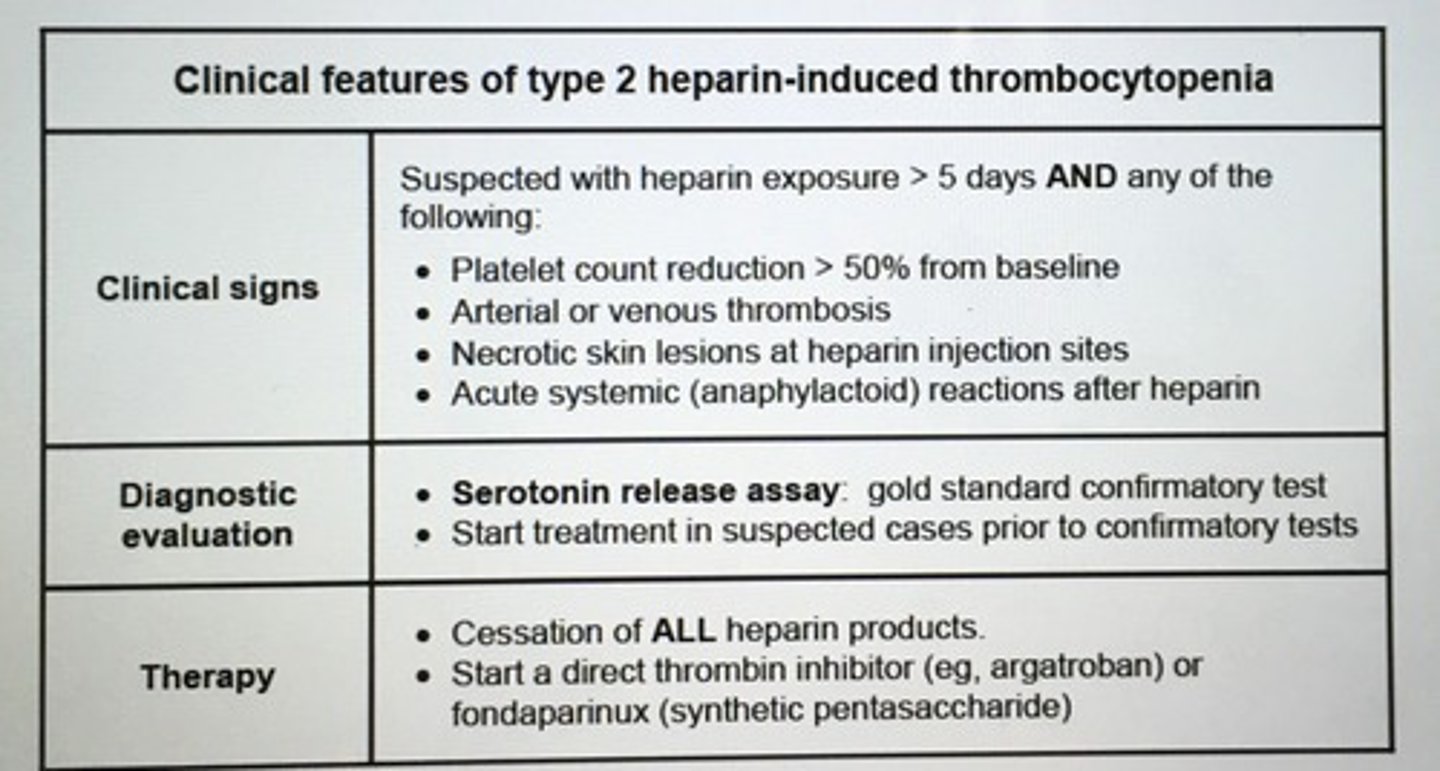
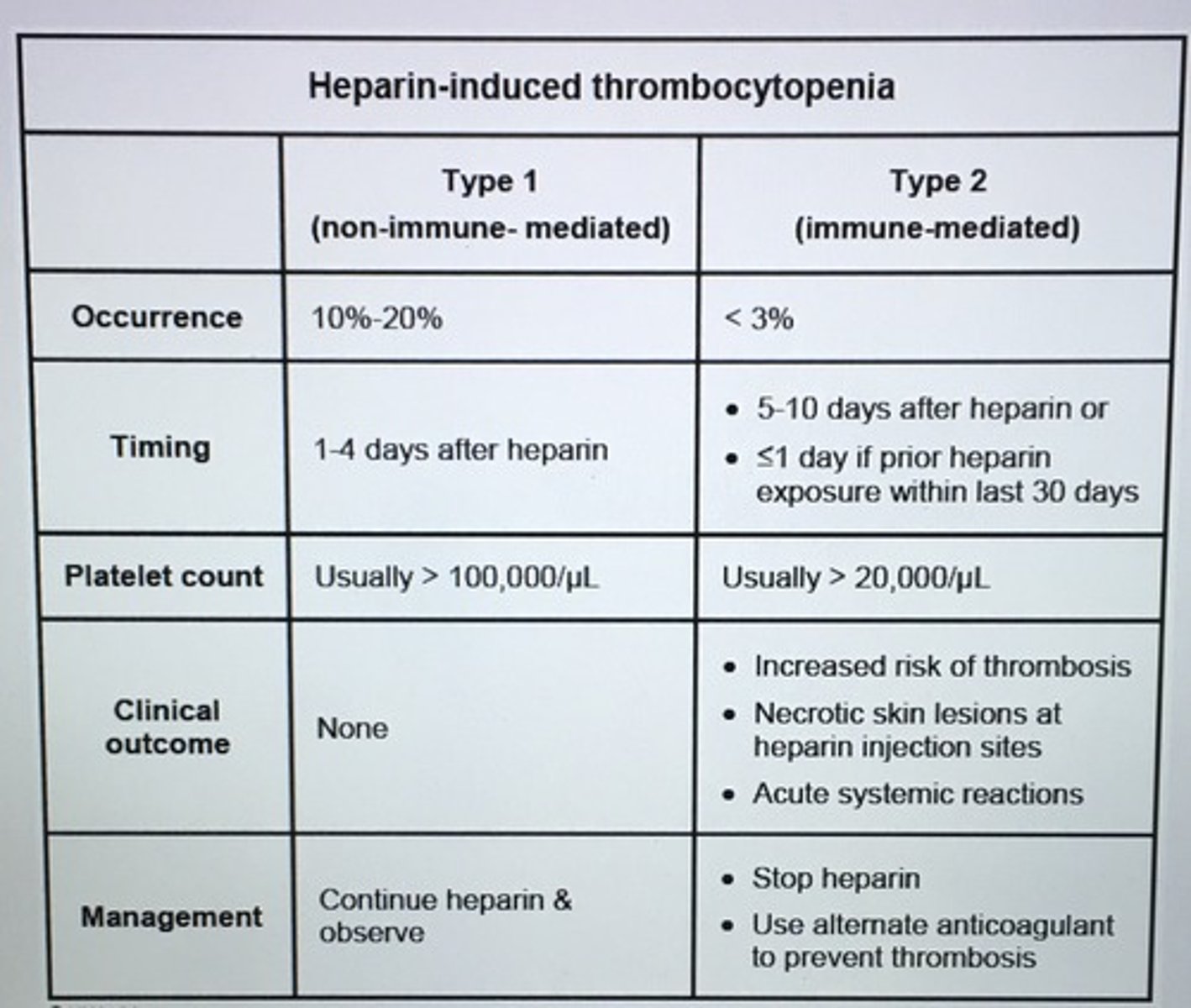
Clinical features of type 2 heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Tx first-line for chemo induced nausea.
Serotonin antagonists 5HT3 receptors
- Ondansetron
Smudge cells and INC lymphocytosis.
CLL
- lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly
- anemia and thrombocytopenia
- elderly
___ is common in pts with sickle cell anemia and sickle cell trait impaired ability kidney concentrate urine.
Hyposthenuria
- result from RBC sickling in the vasa rectae of the inner medulla, impairs countercurrent exchange and free water reabsorption
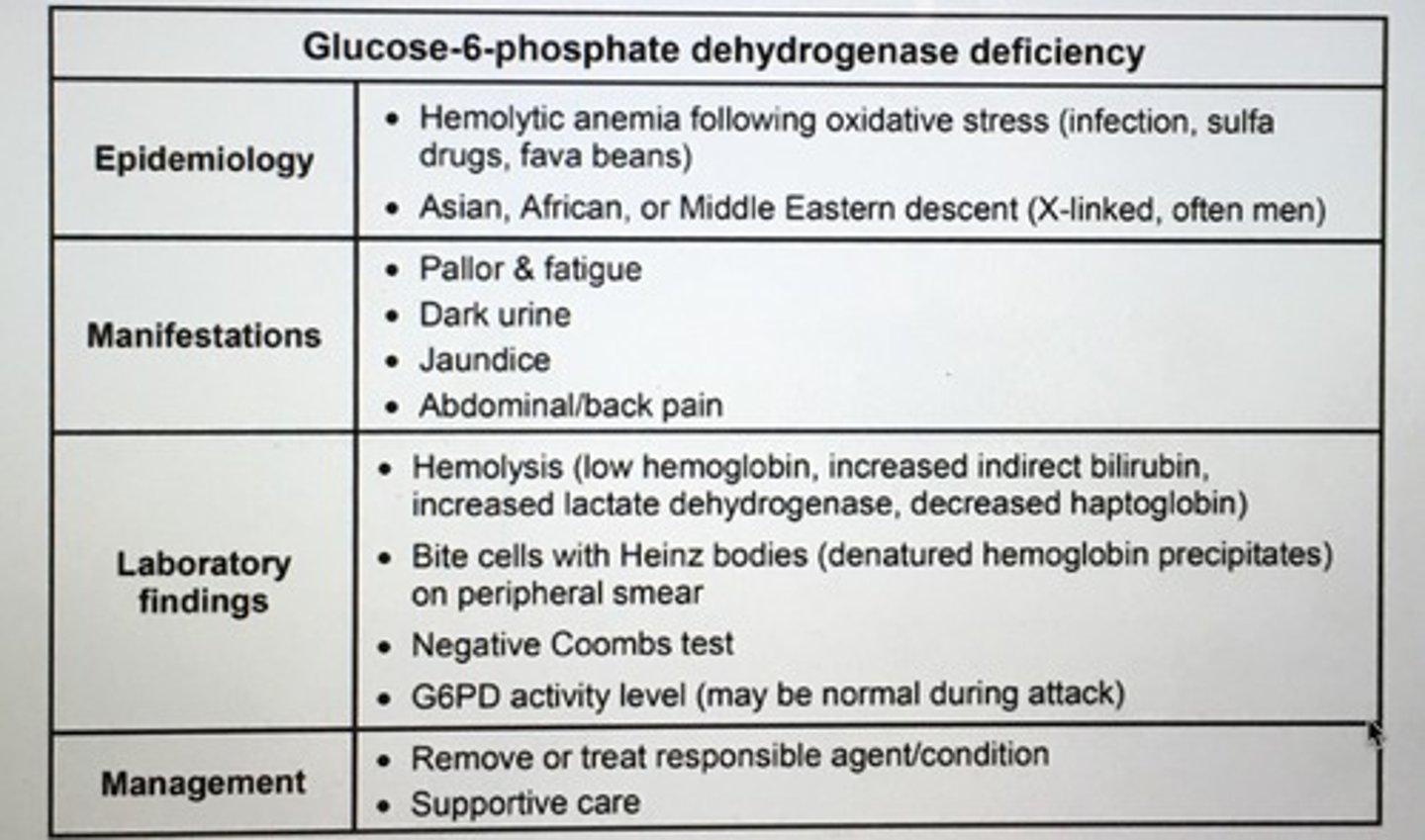
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency epidemiology, manifestations, labs findings, management.
Management of back pain in patient with malignancy.
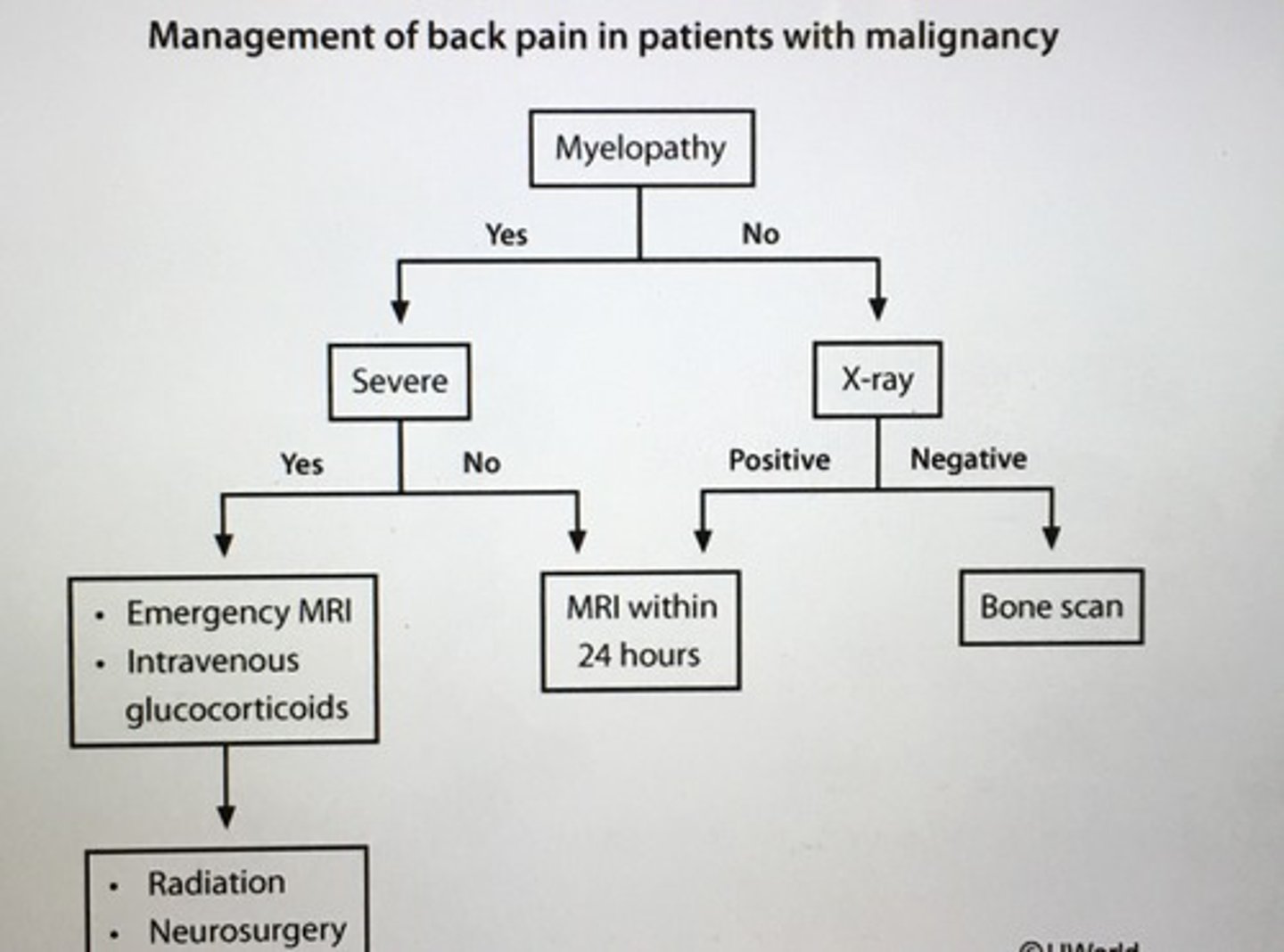
Management of spinal cord compression.
Emergency MRI
IV glucocorticoids
Radiation-oncology & Nsx consult
Both folic acid and cobalamin deficiency will involve in INC ___ levels.
Homocysteine
- cobalamin deficiency INC methylmalonic acid
Pt has recurrent nose bleeds, diffuse telangiectasis, and widespread AV malformations.
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome
- hereditary telangiectasia (AD)
- AVMS in mucosal membranes, skin and GI -> liver, brain and lung
- Lung can shunt blood from the R to L side of the heart causing chronic hypoxemia and reactive polycythemia
Patients with MM are in INC risk for infection due to both a DEC in functional ___ and ___ that develops as the bone marrow is filled with malignant plasma cells.
DEC functional antibodies
Leukopenia
CRAB: calcium (hypercalcemia), renal impairment, anemia, and bones (bone pain, lytic lesions, fractures)
Pt presents with antecedent viral infection, asx petechiae & ecchymosis, mucocutaneous bleeding (epistaxis, hematuria, GI bleed). Isolated thrombocytopenia < 100,000. Peripheral smear with megakaryocytic and no other abnormalities.
Immune thrombocytopenia
- test for HIV, hep C virus testing (if risk factor present)
tx: systemic glucocorticoids for pts w/ severe thrombocytopenia (platelets < 30,000)
Discovery of iron-deficiency anemia in adult male or post-menopausal woman should prompt the physician to look for GI causes of blood loss via?
Tests for occult blood in the stool should be done first
- R sided colon cancer can manifest as iron deficiency anemia
- GI causes: PUD, angiodysplasia, colonic diverticula
Tx of Anemia of chronic disease.
Tx the underlying disease first will often improve the anemia
Hereditary spherocytosis
AD inheritance, INC mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
Abnormal eosin-5-maleimide binding test
INC risk: bilirubin gallstones and parvovirus B19 causing aplastic crisis
Tx: folic acid supplementation, blood transfusions, splenectomy

___ and __ have been shown to INC appetite and wt gain in patients with cancer-related anorexia/cachexia syndrome.
Progesterone analogs (megestrol acetate and medroxyprogesterone acetate) and corticosteroids
Progesterone analogs are preferred over corticosteroids due to fewer SE
Hypercalcemia manifestations.
> 12 mg/dL
Constipation (due to altered intestinal smooth m. tone)
Anorexia
Vomiting
Weakness
Polyuria
Neuro abnormalities (confusion/lethargy)
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is characterized by?
1. Venous thromboembolism and recurrent early miscarriages
2. Presence of antiphospholipid antibody such as lupus anticoagulant (LA), anticardiolipin antibody, or beta 2 glycoprotein 1 antibody
Prolonged PTT
- specific test Russell viper venom test and the kaolin clotting time
What is the cause of the polycythemia observed in obstructive sleep apnea?
Hypoxemia-induced INC EPO production
- tx of OSA causes polycythemia to improve
Major toxicity of azathioprine.
Diarrhea
Leukopenia
Hepatotoxicity
*purine analog converted to 6-MP
Major SE cyclosphorine
Nephrotoxicity
Hyperkalemia
HTN
Gum hypertrophy
Hirsutism
Tremor
SCC skin
* Tacrolimus similar toxicity minus the gum hypertrophy or hirsutism, but has higher incidence neurotoxicity, diarrhea, and glucose intolerance
SE Mycophenolate
bone marrow suppression
inhibitor of IMPDH in de novo purine synthesis
__ is the most common vaccine-preventable disease among travelers.
Hep A
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
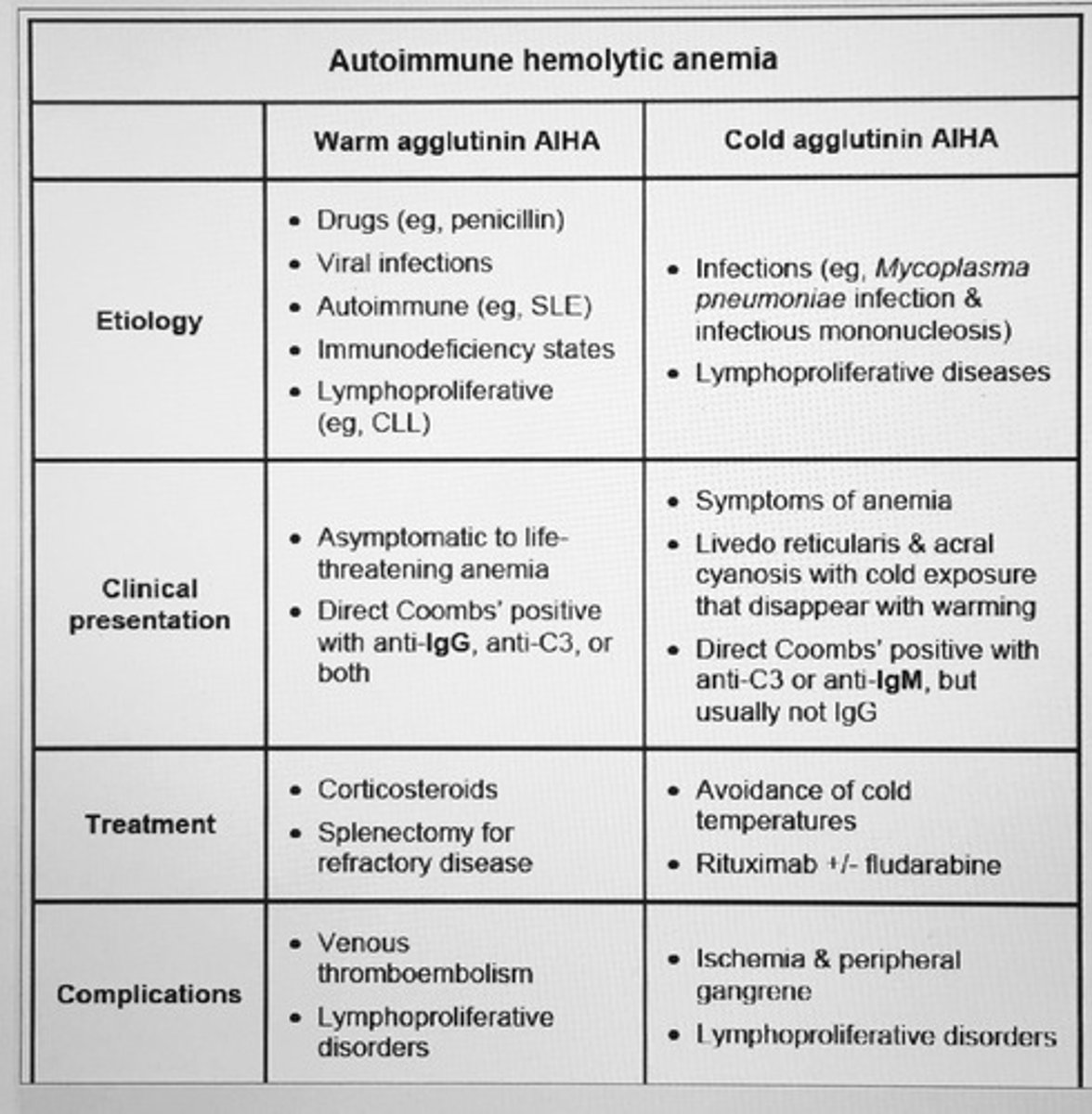
Dyspnea
Venous congestion
Swelling of the head, neck, and arms
Hx smoking
Superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome
- malignancy most common cause obstruction (lung cancer small cell, nonHodgkin lymphoma)
- x-ray chest, followup with chest CT and histo
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase stain and CD11c marker in ___.
Hairy cell leukemia
___ mutation is present > 95% of PV patients.
JAK2 V617F mutation
- low EPO
___ deficiency is common after total or partial gastrectomy.
B12
- defect DNA synthesis in purine
___ hyperviscosity of blood 2/2 excess production of IgM. IgM spike on electrophoresis.
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
__ is the therapeutic agent of choice for the coagulopathy in patients with liver failure.
fresh frozen plasma
___ are the drug of choice for stabilizing bony metastatic lesions to prevent hypercalcemia of malignancy and pathologic fractures.
Bisphosphonates
- Zoledronic acid
- Pamidronate
RBC show dimorphic hypochromic and normochromic patient has been on anti-TB meds. Tx.
Pyridoxine
- dx is acquired sideroblastic anemia
- defective heme synthesis
- INC iron concentration and decrease TIBC
__ should be suspected in patient with hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia. Altered mental status, renal failure, and/or fever.
TTP
- ADAMTS13
- schistocytes on peripheral smear
- plasmapheresis tx
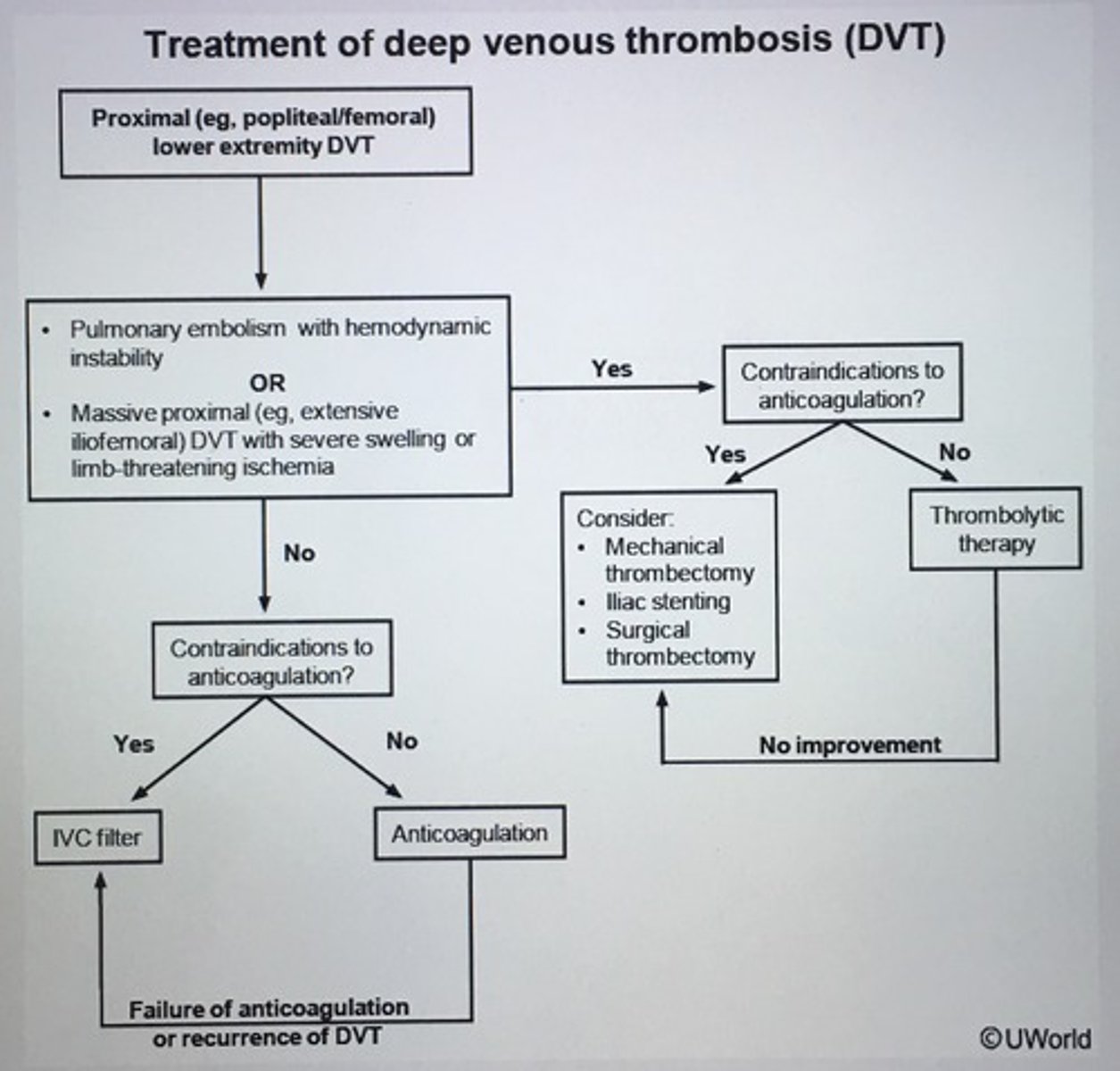
Treatment of DVT
Tx polycythemia vera.
Phlebotomy to keep HCT < 45%
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an immune-mediated process that can also lead to ___.
thrombosis (venous or arterial)
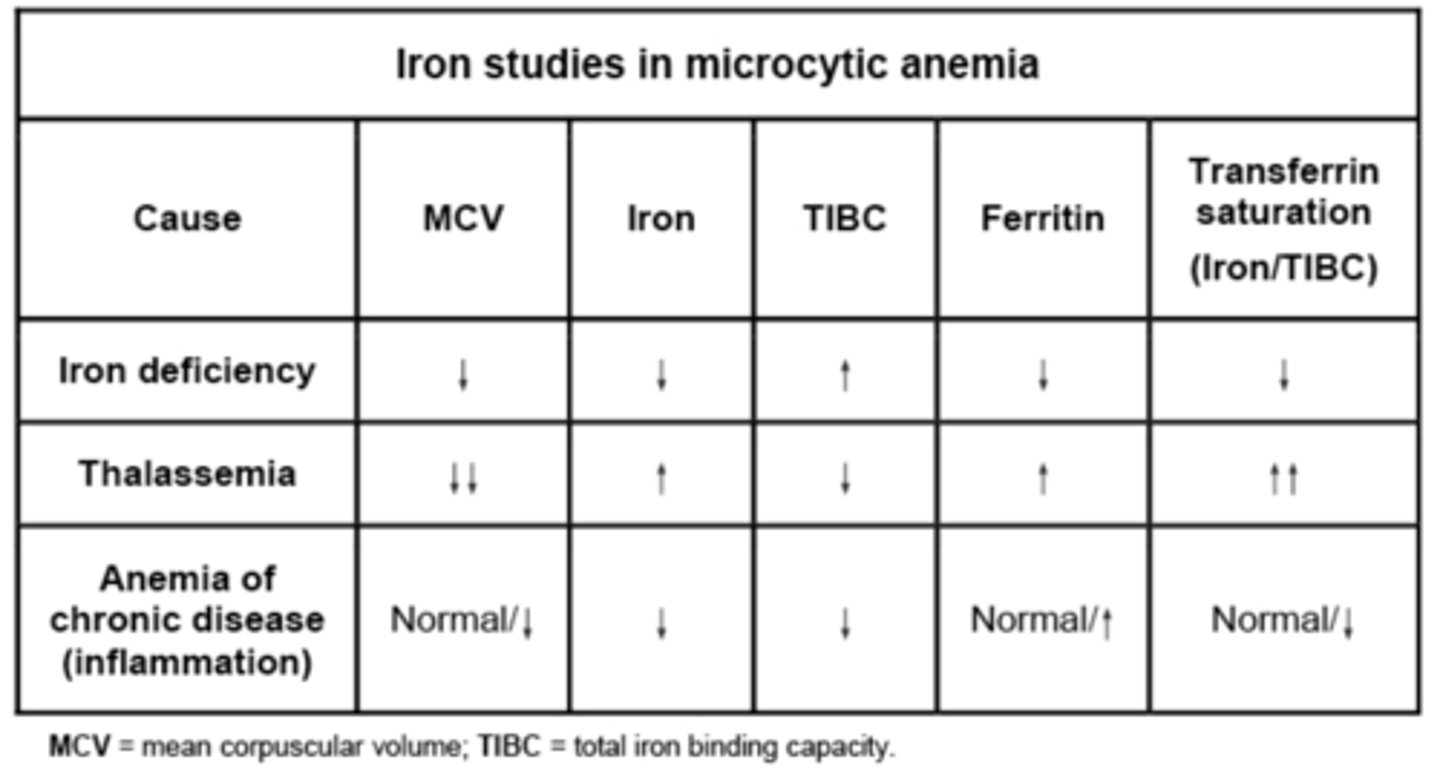
Iron studies in microcytic anemia
___ syndrome is hypercoagulability disorder presenting with recurrent and migratory superficial thrombophlebitis at unusual sites (arm, chest).
Trousseau's
- associated with occult visceral malignancy such as pancreatic (MC), stomach, lung, prostate
- the tumor likely releases mucins that react with platelets to form platelet-rich microthrombi
Pt has polycythemia, nausea, dizziness, and HA works enclosed space in underground rail. Dx.
CO poisoning
- carboxyhemoglobinemia
- INC RBC production high hematocrit
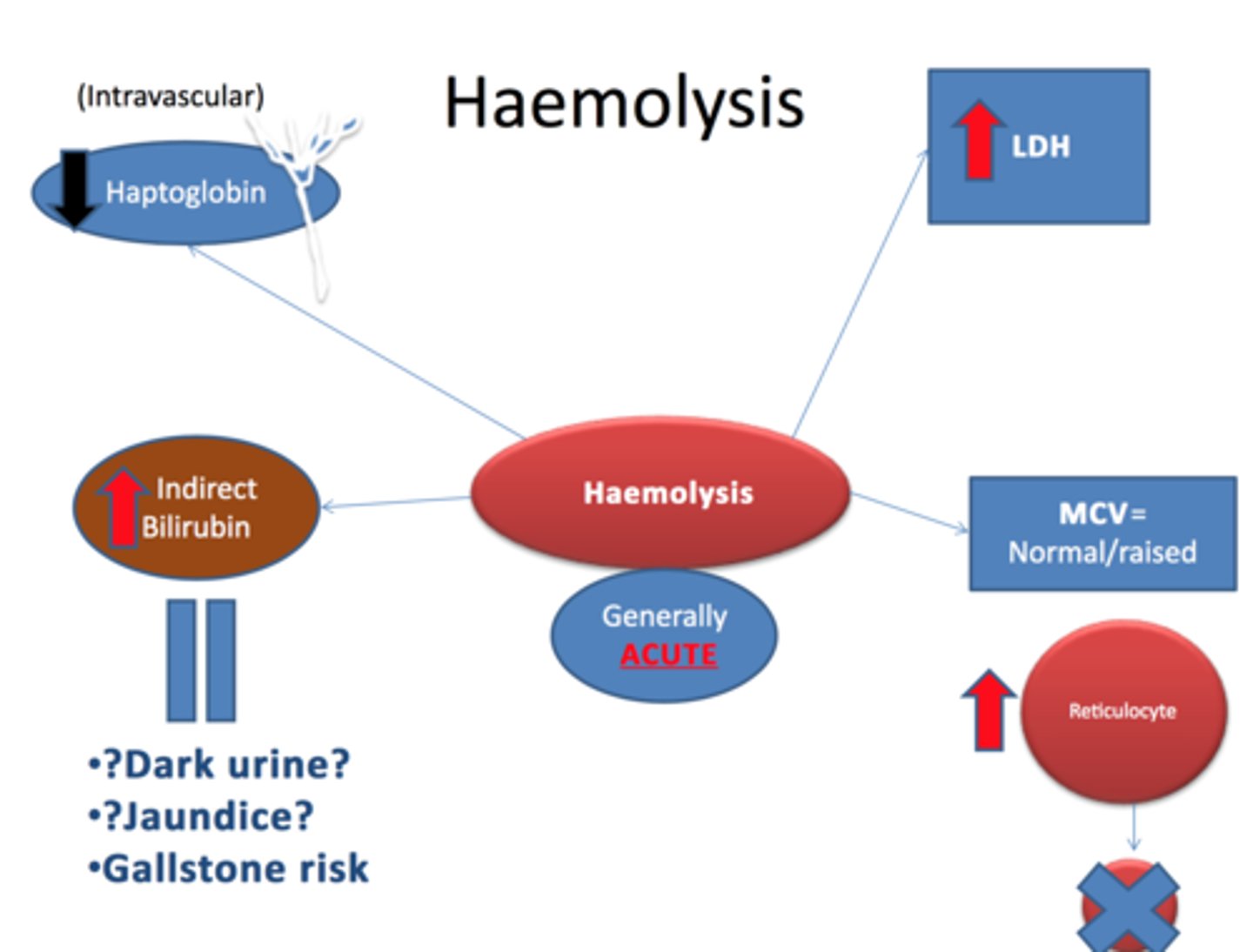
Elevated reticulocyte count, INC LDH, DEC haptoglobin are indicative of __ anemia.
Intravascular hemolytic anemia
- mechanical trauma from calcified aortic valves (microvascular traumatic hemolysis)
- helmet cells, fragmented RBC
Tx hairy cell leukemia.
Cladribine
- toxic to bone marrow
- SE: neurologic and kidney damage
CHOP regiment used treatment ___.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Chlorambucil and prednisone used tx of ___.
CLL
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia Type 1 versus Type 2
When is blood transfusion indicated?
Previously healthy pt Hb < 7-8
CAD, CHF pt Hb < 10
Pts with pernicious anemia need to be monitored for the development of ___ cancer.
Gastric cancer (periodic stool testing for blood)
- chronic atrophic gastritis leads to DEC intrinsic factor by gastric parietal cells INC gastric cancer and gastric carcinoid tumors 2-3x
Tumor lysis syndrome electrolyte abnormalities.
Hyperkalemia
Hypocalcemia
Hyperphosphatemia
Hyperuricemia
Tumors high cell turnover (poorly differentiated lymphomas Burkitt's, ALL, AML)
Allopurinol reduce possibility of acute urate nephropathy
What is the next step find 1 cm lymph node non-tender, rubbery?
Observation
nodes < 1 cm always benign
nodes > 2 cm, fever, chills, weight loss, evaluate
Acquired RF for VTE include?
Immobilization
Surgery
Pregnancy
OCP use
Connective tissue disease (SLE)
Malignancy
Trauma
Patient after transfusion has hypocalcemia what is the cause?
Pt who receive more than 1 blood volume of blood transfusion or PRBC over 24 may have elevated plasma levels of citrate (substance stored in blood)
- citrate chelates calcium and magnesium and may reduce plasma levels causing paresthesias
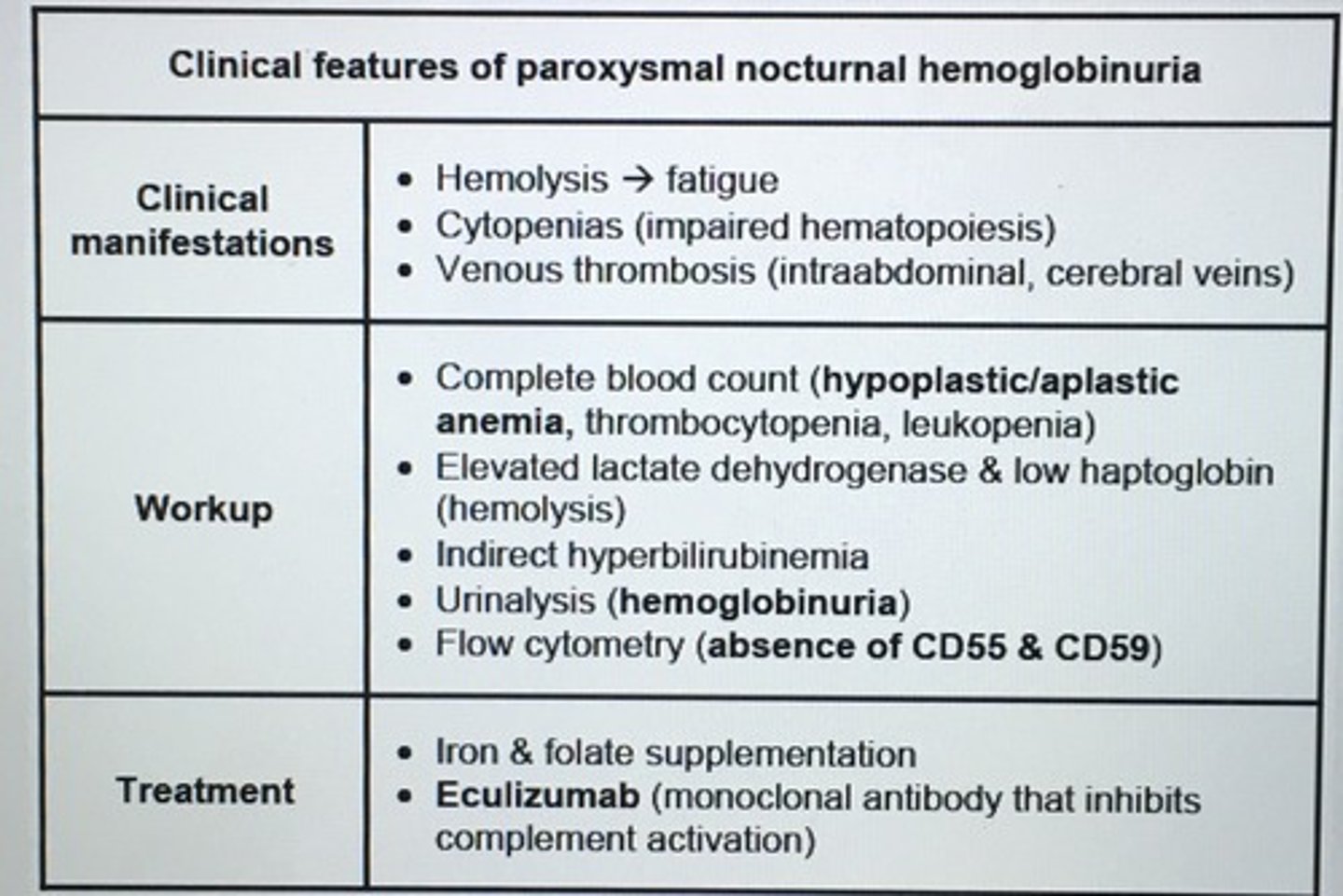
Clinical features of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
1. Hemolysis leading to hemoglobinuria
2. Cytopenias - fatigue and dyspnea from anemia
3. Hypercoagulable state (portal venous thrombosis) - acute abdominal pain that may be due to severe hemolysis or portal venous thrombosis
Post-splenectomy patients are at INC risk for sepsis from encapsulated organisms due to ___.
Impaired antibody-mediate opsonization in phagocytosis.
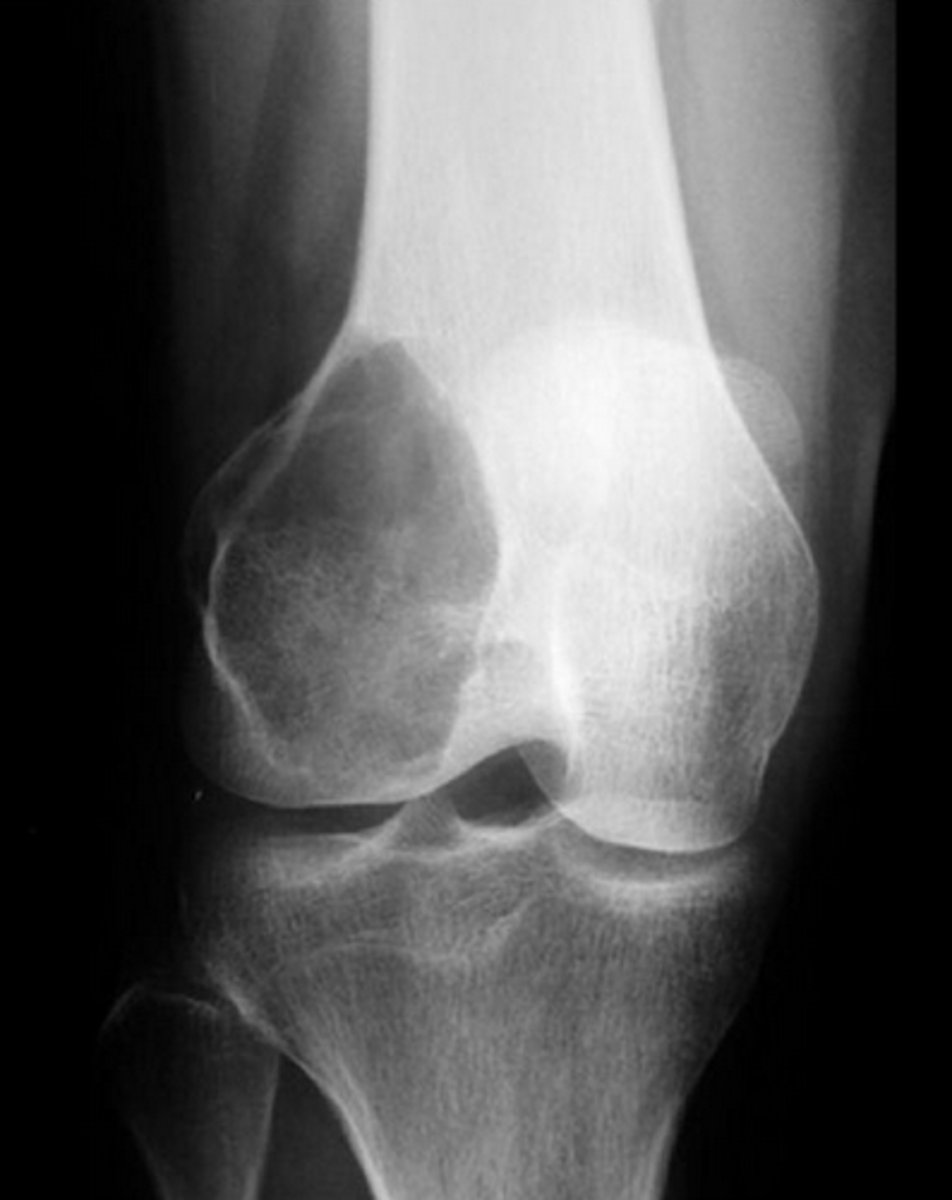
___ shows x-ray expansile and eccentric lytic area, pain, swelling in epiphysis of femur.
Giant cell tumor of bone
"soap bubble"
- benign, locally aggressive
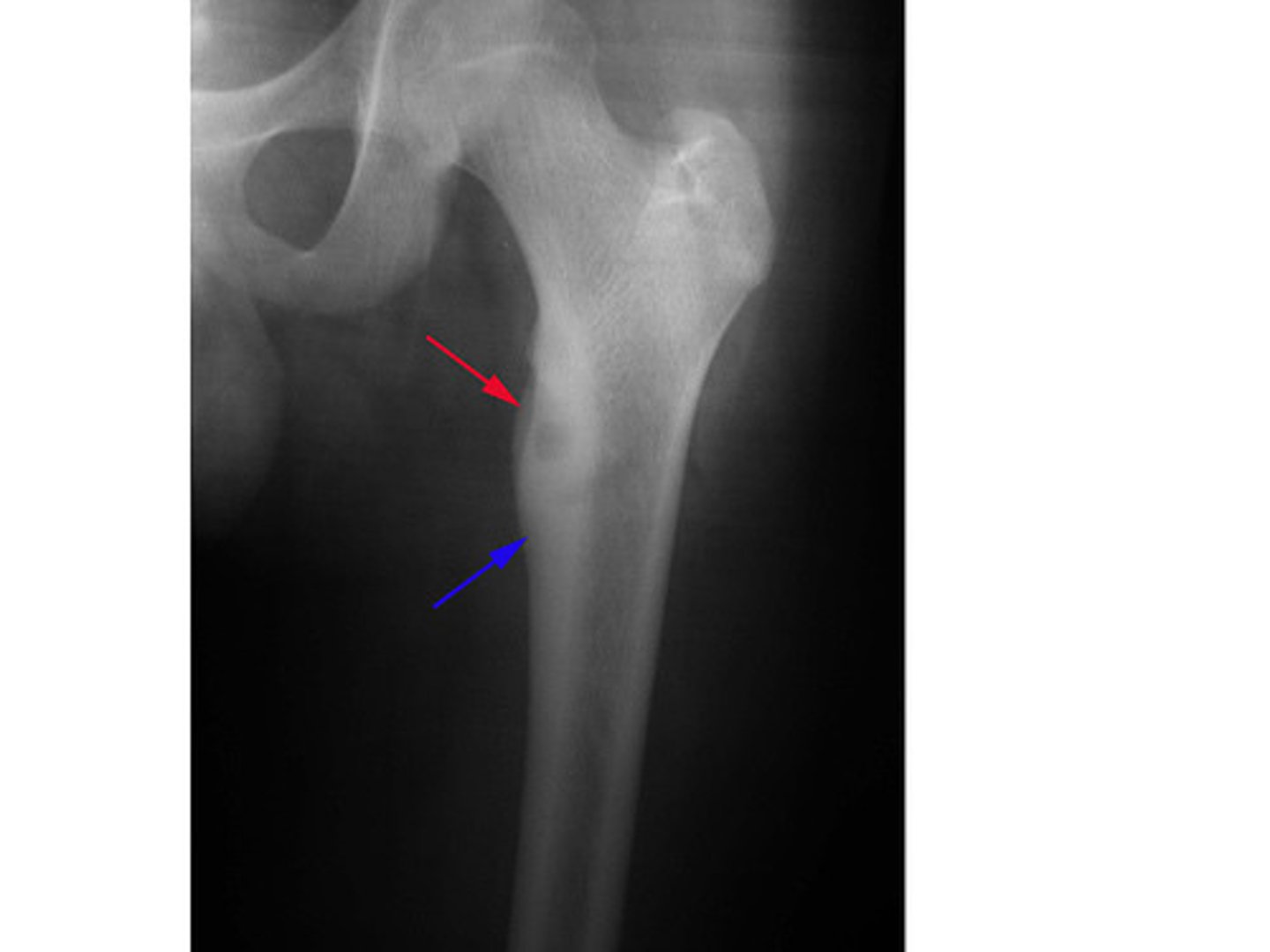
__ sclerotic, cortical lesion on imaging with central nidus of lucency on X-ray. Pain worse at night, unrelated to activity. Pain quickly relieved by NSAIDs.
Osteoid osteoma
___ is driven by a reciprocal translocation of chromosome 9 and 22 the BCR-ABL fusion gene.
CML
- tyrosine kinase active
- imatinib tx inhibitor of tyrosine kinase
Confirm dx of CLL.
Flow cytometry
- lymphocyte clonality
Patient is unable to be compliant with warfarin what is an alternative medication?
Rivaroxiban (direct factor Xa inhibitor) similar efficacy compared to LMWH and warfarin in tx of acute DVT or PE
HIGH YIELD: Studies have shown that the risk for sepsis is present for up to __ years and probably longer after splenectomy. Current recommendations state that patients receive anti-pneumococcal, Haemophilus, and meningococcal vaccines ___ weeks before the operation, and daily oral PCN prophylaxis for ___ following splenectomy.
30 years
several weeks
3-5 years PCN prophylaxis
___ is the most common adverse reaction that occurs within 1-6 hours of transfusion. Pt develop fever/chills, malaise w/o hemolysis. ___ of donor blood can prevent this and reduce the risk of HLA alloimmunization and CMV transmission.
Febrile non hemolytic transfusion
Leukoreduction
Transfusion reaction timeline
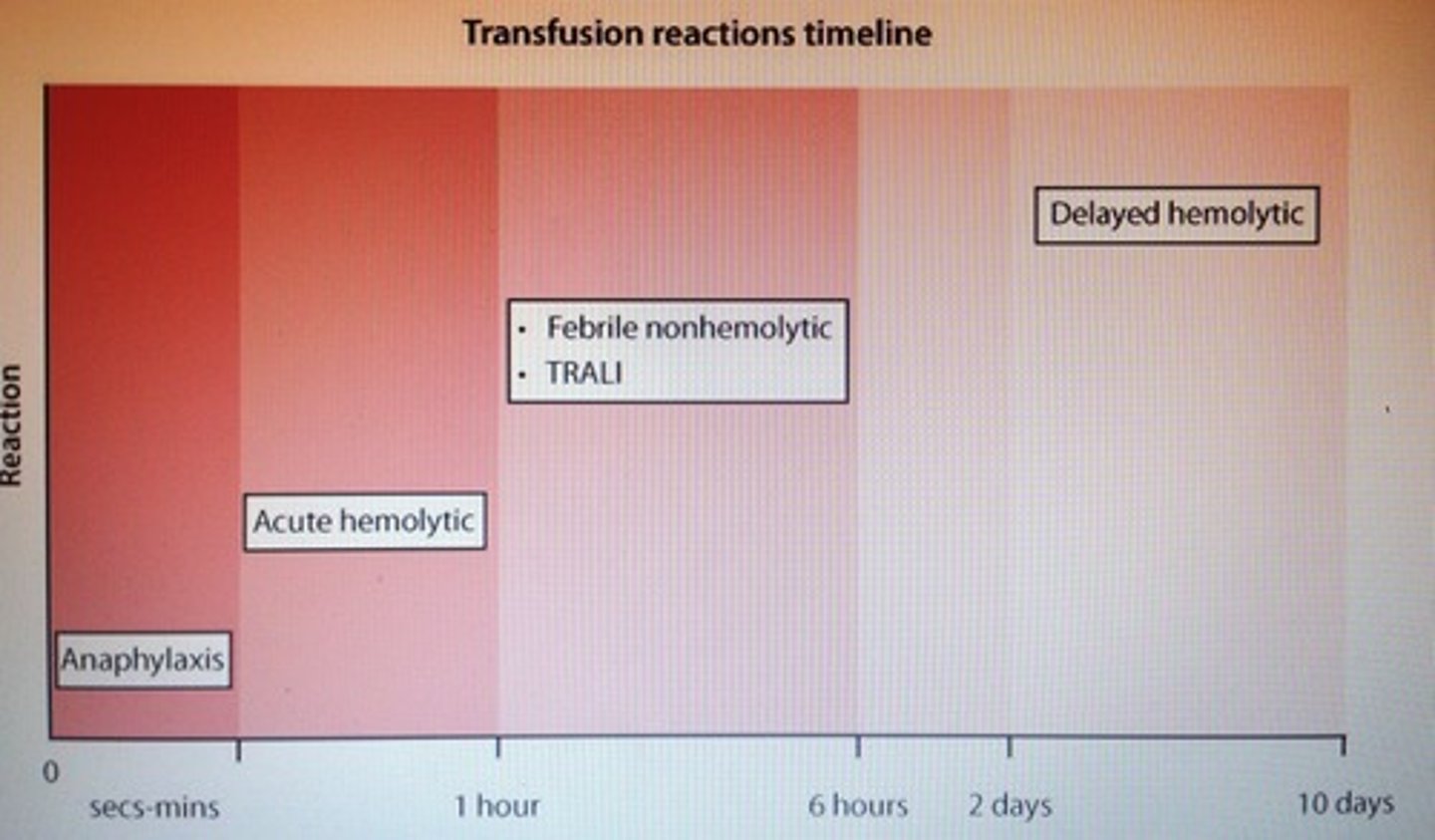
Pt has angioedema, hypotension, and respiratory distress post-transfusion with rapid loss of consciousness, shock, and respiratory failure. Cause and prevention.
IgA-deficiency
- red cells should be washed to remove as much of plasma as possible
___ is the most common cause of B12 deficiency in whites of northern European ancestry. It should be suspected in patients with megaloblastic anemia, atrophic glossitis (shiny tongue), vitiligo, thyroid disease, and neuro abnormalities.
Pernicious anemia
Bone marrow bx of MM.
> 10% clonal plasma cells
HIGH YIELD: Which drugs can lead to folate deficiency?
Impair absorption of folic acid:
Phenytoin
Primidone
Phenobarbital
1. Trimethoprim: inhibits dihydrofolate reductase and high doses can cause megaloblastic anemia
2. Methotrexate: inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Folinic acid (leucovorin) is indicated to reverse the chemo anti-folate effect
*Most common cause of folate deficiency is poor diet and/or alcoholism
Low leukocyte alkaline phosphatase score in [Leukamoid reaction/CML].
CML
- neutrophils are cytochemically and functionally abnormal, LAP (leukocyte alkaline phosphatase) score is low
Hemolytic anemia, jaundice, and splenomegaly in a person of Northern European ancestry. Acute cholecystitis from pigmented stones common complication. Dark urine and calcium bilirubinate gallstones.
Hereditary spherocytosis
Warfarin inhibits the synthesis of vitamin K-depenednet factors ___.
II, VII, IX, X, protein C and protein S
Sickle cell disease (SCD) which vitamin deficiency.
Folate
- INC RBC turnover and INC consumption of folate in the bone marrow
___ reaction is life-threatening reaction from transfusion of mismatched blood. Patients have fever, flank pain, hemolysis, oliguric renal failure, and DIC w/in an hour of transfusion.
Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction
- ABO mismatch
HIGH YIELD: SE of EPO therapy.
1. Worsening HTN: > 10 mmHg rise diastolic BP
2. HA
3. Flu-like syndrome
4. Red cell aplasia
All patients with hematocrit < 30% are candidates for recombinant EPO therapy after iron def has been r/o
The major cause of anemia in patient with ESRD is deficiency of ___.
EPO
__ is defined as treatment for a disease when standard therapy fails, such as radiation therapy for PSA recurrence after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer.
Salvage
___ is an initial dose of treatment to rapidly kill tumor cells and send patient into remission.
Induction
- Consolidation therapy is therapy after induction therapy
__ defined as treatment given before the standard therapy. Pt gets radiation therapy before radical prostatectomy.
Neoadjuvant